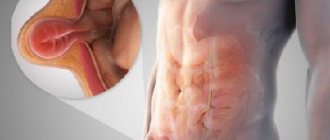
Infographic: gastroenteritis
Each season has its own disease. In winter and autumn we are faced with the traditional cold season, in the spring people suffer from hay fever, and in the summer, especially in August, there is a peak in cases of gastroenteritis.
Gastroenteritis is inflammation of the mucous membranes of the intestines and stomach. It develops under the influence of toxins from viruses and bacteria that enter the body. Everyone has suffered from gastroenteritis at least once in their life. It occurs especially often in children under 5 years of age. The immune system of children is usually weaker than that of adults, which means that it is much easier for bacteria and viruses to penetrate a child’s body.
How does gastroenteritis occur?
The main causative agents of intestinal infections are viruses; they are responsible for approximately 70% of cases of gastroenteritis. Most often, the culprit is rotavirus, and in general almost two dozen different viruses can cause unpleasant symptoms.
Viruses spread through contact: you can become infected by touching objects or products that an infected person has touched. That is why you should not try unwashed peaches at the market or taste watermelon cut by the seller right on the counter.
About a third of cases of gastroenteritis are caused by bacteria. The most common causes of gastroenteritis are Salmonella, Campylobacter, Yersinia and Shigella. They enter the body when eating unwashed or spoiled foods. This happens much more often in the summer, because warm weather promotes the growth and spread of bacteria.
Bacteria that come into contact with a suitable nutrient medium - dairy products, meat, seafood - begin to actively multiply. Each cell divides once every 20 minutes. This means that every thousand bacterial cells turn into more than 30 million bacteria in 5 hours. The barbecue meat that you spent half a day defrosting in the sink, or the milk in the mug that you forgot on the veranda in the morning is literally teeming with germs.
Symptoms mild to severe
Diagnostics
Photo: beautymedicaltouch-usa.com
Most often in practice, infectious gastroenteritis occurs, the symptoms and diagnosis of which depend on the type of pathogen. However, the reason may also be the damaging effects of drugs and chemicals that are aggressive to the mucosa. Gastroenteritis is not an independent nosological entity and usually represents a symptom complex of manifestations of other diseases.
Diagnostic methods
Diagnosis of gastroenteritis consists of examining the patient, collecting an anamnesis of his disease, differential diagnosis with similar pathologies, and the use of laboratory and instrumental research methods.
As a rule, diagnosis of gastroenteritis can be made based on examination and complaints of the patient. Signs of gastroenteritis can vary in severity. It all depends on the nature of the disease, its etiology, severity, age of the patient, and concomitant pathologies.
The disease manifests itself suddenly.
Patient's complaints
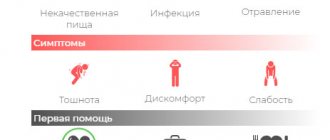
The main complaints are as follows:
- lack of appetite;
- weight loss;
- nausea, vomiting;
- rumbling in the abdomen;
- pain of varying intensity of a spastic nature;
- diarrhea of various types;
- muscle pain;
- general severe weakness;
- feeling of bloating;
- temperature increase.
Diarrhea may be absent, but this does not exclude the presence of rumbling in the abdominal cavity, which is one of the specific features of this disease, which facilitates the diagnosis of gastroenteritis.
Vomiting and diarrhea can be so significant that they sometimes provoke dehydration with corresponding manifestations: decreased blood pressure, increased heart rate, and renal failure.
Increased temperature: it can vary from low-grade to high, depending on the pathogen.
Features of the disease depending on the pathogen
With viral etiology, the main manifestation of gastroenteritis is loose to watery stools. Rarely there are mucus or blood impurities.
Rotavirus causes significant intoxication. The temperature is often low-grade, but can sometimes rise to high levels. Vomiting is typical. The acute period lasts about a week.
Caliciviruses are characterized by an acute onset of the disease with severe vomiting and spasmodic pain of significant intensity. Vomiting is more pronounced in children, and diarrhea in adults. Often all this is accompanied by headache and muscle pain. This period does not last long - 1-2 days.
Under the influence of adenoviruses, the disease lasts a long time - 2-3 weeks. Vomiting is not expressed. Begins 1-2 days after diarrhea. In half of the cases, an increase in temperature is observed, but rarely to high levels.
Bacterial gastroenteritis is accompanied by severe intoxication symptoms: high fever, severe general weakness. Severe diarrhea, accompanied by bleeding. Some bacteria synthesize large amounts of enterotoxin, which causes profuse, watery stools.
Parasites do not cause acute symptoms. As a rule, gastroenteritis caused by them develops with mild diarrhea. Blood in the stool is rare. Only for amoebic dysentery. Characterized by severe general malaise and weakness.
Differential diagnosis
Differential diagnosis is carried out by analogy with acute diseases of the abdominal organs (appendicitis, ulcerative colitis, cholecystitis).
Gastroenteritis is supported by watery diarrhea, consumption of potentially contaminated food, and the presence of the disease in others.
Stool examination
The attending physician determines what tests should be taken if gastroenteritis is suspected. A rectal examination is performed. Feces with gastroenteritis are indicative. If blood and watery diarrhea persist for more than a couple of days, a test is carried out for occult blood, for the content of parasites and their eggs in the feces, and a bacterial culture is carried out.
An enzyme-linked immunosorbent method can be used to determine the presence of lamblia and some viruses. However, such studies are carried out only in the event of a disease outbreak.
All patients who have bloody diarrhea must be tested for the presence of E. coli.
If bloody diarrhea occurs in adult patients, sigmoidoscopy is performed. In this case, a biopsy is taken and culture of the contents is taken to test the blood for gastroenteritis.
General tests for acute gastroenteritis
General blood tests for this pathology are not very specific. A general blood test for gastroenteritis can reveal inflammatory manifestations and an increase in the level of eosinophils. In severe cases, the number of electrolytes may change, which requires their correction.
Diagnosis, as well as treatment, should only be carried out by a specialist. Self-diagnosis can lead to erroneous diagnoses and, consequently, complications.
Prevention of relapse
The basis for the prevention of gastroenteritis is proper nutrition and a healthy lifestyle. The development of the disease can be avoided through simple measures:
- washing hands thoroughly before eating and after visiting the toilet;
- daily change of underwear;
- consumption of heat-treated products.
You need to drink purified water, wash well and pour boiling water over fresh fruits, berries, and vegetables. It is not recommended to visit food establishments with insufficient sanitation.
If one of the family members falls ill with gastroenteritis, it is necessary to provide him with individual dishes and a towel. Young children should be vaccinated against rotavirus infection, which causes intestinal flu.
If you suspect gastroenteritis, contact the doctors of the First Family Clinic of St. Petersburg in the Primorsky and Petrogradsky districts to receive highly qualified care and timely treatment.
Don't let yourself dry out
| Symptoms of viral gastroenteritis: | |
| severe runny nose; cough; sore throat; increased body temperature; headache; vomit; diarrhea; dry mouth. | |
The most dangerous consequence of gastroenteritis is dehydration. Due to incessant vomiting and diarrhea, the body quickly loses water, and with it useful microelements. As a result, this can lead to low blood pressure, fainting, and, if medical attention is not provided in time, kidney failure. Therefore, if you suspect an infection, it is important to consult a doctor without wasting time.
Drinking plenty of water will only help cope with thirst, but will not restore the water-salt balance. Therefore, patients must be hospitalized in the infectious diseases department. Here, based on the results of a scatological examination, the pathogen is identified and appropriate therapy is prescribed.
Symptoms of gastroenteritis in children
In childhood, bacterial and viral gastroenteritis is very severe. The disease is especially dangerous for infants, since in the presence of dehydration, irreversible processes occur in the baby’s body.
The first symptoms of acute gastroenteritis occur a few hours after infection. The clinic depends on the age of the child, the state of immunity and the type of pathogen. Symptoms of the initial stage:
- stomach pain, flatulence;
- general weakness;
- nausea, vomiting;
- headache;
- diarrhea.
As the disease develops, the initial manifestations intensify with increased temperature, decreased blood pressure and bradycardia.
How to treat childhood gastroenteritis? Broad-spectrum antibiotics and antimicrobial agents are used. In addition, the use of antiemetics, enterosorbents, antispasmodics, and enzymes is indicated.
Classification
Acute gastroenteritis is distinguished:
- Nutritional (caused by overeating with the intake of large amounts of spicy or too rough food, seasonings that irritate the mucous membrane, strong alcoholic drinks).
- Infectious and viral origin (cholera, typhoid fever, salmonellosis, sometimes influenza, etc. occur with the clinical picture of severe gastroenteritis).
- Allergic (with idiosyncrasy to certain foods - strawberries, eggs, crabs, etc. or with an allergic reaction to medications - iodine, bromine preparations, some sulfonamides, antibiotics, etc.).
- Toxic (in case of poisoning with arsenic compounds, sublimate and other poisons; poisoning with mushrooms - toadstool, fly agarics, false honey mushrooms, other toxic substances of a non-bacterial nature that may be contained in food products - stone fruits, some fish products - burbot liver, pike, mackerel caviar etc.).
Diet and proper nutrition
As part of the treatment of gastroenteritis, dietary nutrition is necessarily prescribed - the duration of treatment depends on how accurately the patient adheres to the recommended diet.
- The acute form of gastroenteritis implies restriction in food intake - white bread crackers, bananas and rice porridge (viscous) are allowed on the menu.
- Meals should be frequent, but in small doses, the patient should refuse too hot or very cold foods.
- It is necessary to completely exclude from the menu carbonated drinks (even ordinary mineral water), coffee, dairy products, cakes and pastries, marinades, fast foods, fried and smoked foods, and too fatty foods.
- If the first symptoms have subsided, then the patient can introduce into the daily diet porridge with water, boiled potatoes, fruits, boiled vegetables, low-fat meat and fish and in very limited quantities (no more than 200 g per day), compotes, jelly and tea with sugar - thus the menu begins to expand.
After the symptoms of gastroenteritis subside, such a regimen and diet should be followed for at least a month, and people suffering from a chronic form of the disease must adhere to such a diet constantly.
All in your hands
Gastroenteritis is one of those diseases that can be easily prevented. For specific prevention of rotavirus infection, there are two vaccines that have undergone clinical trials. Both contain a weakened live virus and are taken orally.
You can also avoid infection by following basic hygiene rules:
- wash your hands before eating;
- pay attention to the expiration date of food products and monitor their storage temperature;
- drink only filtered or bottled water, exclude all drinks with ice;
- prepare cuts on clean cutting boards;
- wash vegetables, fruits and herbs thoroughly;
- do not eat raw eggs;
- buy food and drinking water only in supermarkets;
- Carry alcohol or wet wipes with you to disinfect your hands.