General information
Wasps are insects that can be found in different places - both in villages and cities.
There are several varieties of these insects. However, the reaction to their bite is the same: it is very painful and unpleasant, since the venom of all types of wasps acts in a similar way. The ICD-10 code is W57 (bite or stinging by non-venomous insects and other non-venomous arthropods). But in some cases, a wasp or hornet is a particularly dangerous insect. After all, when talking about how dangerous a wasp sting is for a person, it should be taken into account that it can provoke a very acute allergic reaction . Therefore, it is most dangerous for those who are prone to allergies .
Multiple bites are especially dangerous. Therefore, it is very important to know how to act correctly if a person is bitten by an insect, and what to do if an allergic reaction occurs. This will be discussed in the article.
1.General information
Insect bites
- a phenomenon familiar to everyone. This is especially true in the summer, when most representatives of the order of arthropods can be found literally everywhere where there is land and sunlight.
Many insects (wasps, bees and others) when bitten, secrete a toxic liquid, which, when it enters the body of a hypersensitive person, causes allergic reactions. Despite the fact that they are rarely serious, causing only minor swelling and redness, the basic symptoms of allergies should be known to every person. This information will help you identify an allergy to insect bites in order to cope with it yourself or with medical help.
A must read! Help with treatment and hospitalization!
Pathogenesis
The venom of Hymenoptera insects contains non-allergenic amines and peptides. They determine the appearance of local reactions to the bite, provoking the inflammatory process and affecting the blood vessels. In addition, the venom contains allergenic proteins (in particular antigen-5), under the influence of which antibodies . If we talk about wasp venom in more detail, it contains the following components:
- Histamine – provokes the development of an allergic reaction (redness, itching, swelling of the skin).
- Phospholipases - destroy blood cells and tissues, stimulating the manifestations of allergies.
- Acetylcholine – conducts nerve impulses.
- Hyaluronidases - destroy cell membranes, leading to an inflammatory process.
- Hyperglycemic factor – increases blood sugar levels.
If an insect stings a person on a peripheral nerve, this leads to disruption of its function.
With increased sensitivity to allergens, a strong local reaction can develop even after one episode. As a rule, an allergy to a wasp sting develops almost immediately - within a few minutes. But sometimes a so-called delayed allergy can develop. Its symptoms appear 10-14 days after the bite.
With multiple bites (10 or more), a toxic reaction occurs.
You can often come across the question of whether a wasp dies after a bite and whether the wasp leaves a sting in the human body. Due to the structural features of the sting of this insect, it can sting many times. The sting is slightly jagged and therefore does not remain in the skin.
Another interesting question concerns how the benefit or harm of a wasp sting manifests itself. As you know, bee stings are used for treatment purposes. There is also some benefit from wasp stings, but only if the person has no allergic reaction to the poison. After all, wasp venom is a stronger allergen than bee venom.
After wasp bites hemoglobin and blood vessels dilate. However, the harm outweighs the benefit, since there is a high risk of developing allergies . Moreover, with each subsequent bite this risk increases.
If you are bitten...
In the warm season, the number of victims of animal and insect bites, burns caused by plants and some animals increases. Moreover, not somewhere in the distant Amazon, but here in St. Petersburg and the Leningrad region and in traditional vacation spots - in Crimea, Bulgaria, and the Mediterranean.
Snakes
The common viper is widespread in Russia, as well as in Northern and Central Europe and Northern Asia. The poison causes pain, swelling at the site of the bite, a rise in temperature, heart function may sharply deteriorate, and in severe cases, loss of consciousness is possible. Cases of death from a viper bite are quite rare. However, allergy sufferers may have a very severe reaction. Therefore, the first thing to do is take an antihistamine and go to the doctor. You need to remain calm, drink more fluids (but not alcohol). Sometimes it is recommended to suck out the poison if there are no damaged teeth or abrasions in the mouth.
The steppe viper lives in the Crimea, the Caucasus, Europe, Kazakhstan and China. Its bites are less poisonous than those of the common viper. There are no known cases of death from steppe viper bites. But the bites of large species of vipers are dangerous to humans. For example, the bite of a viper, which injects about 50 mg of poison. This snake lives in Transcaucasia, Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan, Kazakhstan, northern Africa, the countries of the Eastern Mediterranean, etc.
Bees, wasps, bumblebees
The bite causes short-term pain and burning, followed by redness and swelling. In most cases, the pain and itching goes away within one to two days. It is dangerous if a person is stung by tens or hundreds of bees at the same time (the lethal dose is 100-500 stings). If an insect bite occurs on the inside of the mouth or throat, or in the eyeball, in these cases you should immediately consult a doctor. There are people with increased sensitivity to Hymenoptera bites. They can have a severe reaction even if they are stung by one or two insects.
For a country walk, it is better to wear clothes made of light fabric that cover your neck, arms and legs as much as possible. Bright and dark colors attract insects more. If a wasp or bee is flying near you, do not make sudden, fussy movements.
If you are stung by a bee, you need to carefully remove the sting. It is not recommended to squeeze out the sting with your fingers, as this may spread the poison. Place a cotton swab moistened with a weak solution of potassium permanganate or water and soda on the bite site. You can apply ice. Allergy sufferers should always have with them antihistamines recommended by their doctor.
Scolopendra
The ringed scolopendra is found in large quantities in the Crimea, the Mediterranean and Transcaucasia. The bite is dangerous to humans, but not fatal.
Scolopendras often crawl into tents and houses. You can step on it on the beach or accidentally touch it with your hand while assembling a tent or turning over a stone.
The sting of a scolopendra is quite difficult for many people. The bite site swells greatly, and the swelling gradually spreads to a large area of the body. The temperature often rises to 38-39°, chills and aches often occur. Symptoms usually disappear within 24-48 hours. However, in any case, victims should urgently consult a doctor. Bites are especially difficult for children, allergy sufferers, or people suffering from heart disease.
Australia and South America are home to larger species of scolopendra that are purple, red, and yellow in color. In total, about 600 species of scolopendra are known.
Scorpions and spiders
Scorpion venom has a toxic effect on the central nervous and cardiovascular systems. The most dangerous in the territory of the former USSR is the karakurt (“black widow”). Karakurt is found in the desert and steppe zones of Central Asia, Crimea, the Caucasus, southern Europe and northern Africa. The bites of the female can be fatal to humans and animals such as a camel or horse - the karakurt venom is 15 times stronger than the venom of a rattlesnake. The spider does not attack a person unless he is disturbed.
After a karakurt bite, a small red spot appears on the skin, which quickly fades. After 10-15 minutes, acute pain occurs in the abdomen, lower back, chest, severe anxiety, agitation, and fear of death. The victim's legs go numb, breathing becomes difficult, vomiting and headache appear. The face takes on a bluish tint. The heart rate drops, the pulse is arrhythmic. It is necessary to administer anti-karakurt serum, so the patient must be taken to a medical facility.
Dogs, cats, foxes, rats
Animal bites can cause infection with rabies and tetanus. Rabies is an infectious disease of the nervous system with a 100% fatal outcome. The victim is prescribed a course of vaccination against rabies. If the dog can be monitored, then after a 10-day period, in the absence of rabies in the dog, vaccinations can be stopped; in all other cases, vaccinations are continued until the course is completed.
Tetanus is another dangerous disease transmitted by animals. It is recommended to get a tetanus shot every 10 years. If more than five years have passed since the last vaccination, and the wound is deep and dangerous, it is necessary to re-vaccinate within 48 hours from the moment of the bite. Less dangerous, but much more common complications of animal bites are wound infection and the development of an abscess.
Avoid contact with unknown animals. Even animals that seem friendly can bite. Do not feed or try to catch or play with wild animals - squirrels, raccoons, rats. Do not disturb the animal while it is eating or feeding its offspring. And don't stick your fingers into the cages at the zoo.
Sea urchins and jellyfish
Many people suffer from sea urchin stings. They are found at the bottom off the coast of Turkey, Cyprus, Montenegro, etc. The injections are very painful and take a long time to heal. Small fragments of sea urchin spines very often remain in the wound. Removing them is not always easy - they are very fragile. It is better not to swim where there are hedgehogs, or to go into the water in rubber slippers. If the injection could not be avoided, you will have to consult a doctor.
You shouldn't joke with jellyfish either. When you touch a jellyfish, a burn occurs, sometimes quite severe. You should wash the damaged area with salt water, not fresh water, which can worsen the burn. Apply ice well. Allergy sufferers may experience a severe reaction, and in such cases they should urgently consult a doctor, and before that take an antihistamine. There are known cases of anaphylactic reactions to the burn of ordinary jellyfish, which ended tragically.
In the Black Sea, aurelia and corneros are the most common species; they are not very dangerous. More aggressive jellyfish live in the Mediterranean - cyanea ("hairy jellyfish"), pelagia ("small lilac sting"), chrysaora ("sea nettle"), etc. Their burns are stronger than those of the Black Sea, and allergic reactions are more common. The most dangerous jellyfish are in Australian waters.
Dangerous plants
Some plants can cause severe burns that take a long time to heal.
Ash tree, or burning bush, is a plant with very beautiful flowers. They smell them, bring them to the face, pick them off... At the moment of touching, a person does not feel anything, but after 10-12 hours the skin at the site of contact turns red, becomes blistered and burns form (up to the second degree). Skin lesions over a large surface are life-threatening. Grows in Europe, Turkey. It can be found in Crimea and the Caucasus.
Hogweed is distributed throughout the European part of Russia and in Estonia. A short period of sun exposure to an area of skin stained with plant juice is enough to cause a second-degree burn. They are treated in the same way as regular burns. You need to remember what these plants look like and not touch them or inhale their aroma.
Bloodsucker healer and other useful creatures
It turns out that some bites and venoms not only cause pain, but also bring benefits.
Doctors actively use leeches, bees and snakes to treat many diseases. Bee venom is used to treat pain of various origins, chronic bronchitis and bronchial asthma, the consequences of stroke, etc. Medicinal preparations that have an analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect are made from snake venom.
Hirudotherapy – treatment with leeches – is also widely used in medicine. 82 different substances were found in the saliva of leeches. An insignificant amount of this “medicine” enters the patient’s blood and does its good work there. Leeches help in the treatment of arthrosis and arthritis, gastric and duodenal ulcers, myopathy, neurodermatitis, and bronchial asthma.
Treatment with leeches also has contraindications: hemophilia, congenital incoagulability, severe anemia, hemorrhagic diathesis, pregnancy. In addition, leeches are not recommended for people with persistently low blood pressure, as well as those who have an individual intolerance to any component contained in the secretion of the salivary glands of these beneficial annelids.
The “bite” itself is no more painful than a mosquito: by piercing the skin, the leech injects a special substance, which relieves swelling and pain. The famous surgeon Nikolai Pirogov, even during the Russian-Turkish War, applied a hundred or more leeches to extensive lacerations. And this saved hundreds of wounded people from painful shock and infections!
There are about 400 types of leeches on the globe, but only medical and pharmaceutical ones can work wonders. The first information about their healing properties dates back to Ancient Egypt. These are wall paintings that were discovered in the tomb of the pharaohs of the 18th dynasty (1567–1308 BC). They say that the secret of Nefertiti’s extraordinary beauty is that she added... dried leeches to her cosmetic potions.
Our clinic is often visited by patients who have received wounds or damage from animal or insect bites - dogs, cats, bees, ticks and even foxes, iguanas, parrots and jellyfish...
Often there are difficult cases, the wounds from bites are lacerated, extensive, multiple, and often infected. Jellyfish burns take a long time to heal. Animals and insects can be carriers of various dangerous infections. Allergy sufferers, asthmatics, children, and the elderly especially suffer from insect venom from bites. They need to be especially careful and protect themselves, and if the bite cannot be avoided, then immediately consult a doctor. When going even for a short walk in the forest, you need to carefully cover your body in any weather, even hot. You need to use products that repel insects and ticks - now there is a large selection in pharmacies and stores. Be careful when interacting with pets and especially with wild animals. Be sure to have at home and take with you outside the city and to the resort a small first aid kit in which to put a bandage, iodine, a plaster, a small bottle of hydrogen peroxide, and soda powder. You need to dilute soda with water and apply a bandage to the bite - this is one of the simple and effective first aid methods. People with allergies must have with them antihistamines recommended by their doctor.
To prevent tick-borne encephalitis, you need to take a course of vaccination. If you are planning to travel to epidemiological areas, you also need to get the necessary vaccinations in advance. All vaccinations, except for rabies vaccination, can be done in our clinic. Rabies vaccination in St. Petersburg is given only at the City Anti-Rabies Center on Kavalergardskaya Street, 26.
Causes
There are several varieties of hymenoptera that sting people most often: wasps, bees, bumblebees, hornets. Wasps and bees sting most often. In this case, the bites themselves do not have an adverse effect on the body, but only cause some discomfort and pain. The cause of negative symptoms is an allergic reaction to the venom of such insects.
It is important to remember that wasps sting people for self-defense or to protect their own offspring. It often happens that a person brushes away an insect circling nearby with his hands. This gesture is perceived as aggression, and the wasp stings the person. There is a risk of being attacked by insects even if you are near their nest.
What to do if stung by a wasp in nature
If a wasp attacked during a rest period, and you don’t have a first aid kit with you, what is used as an aid for bee and wasp stings? The wound and surrounding skin are not washed with water. Do not immerse the bitten area in the nearest body of water. The bee sting is doused with vodka. There is no need to take alcohol internally; your health will worsen.
Plantain is also used, which has a wound-healing and tonic effect. The leaves are fixed on the wound as a lotion and bandaged.
Onions will also help in eliminating puffiness. In addition to being bactericidal, it has a sorbing property, neutralizing the toxin. The patient is advised to move less and drink more fluids.
Symptoms of a wasp sting
The symptoms that appear after a bite largely depend on what kind of insect stung, as well as on how the body reacts to its venom.
The main features are as follows:
- A sharp pain appears.
- Swelling develops. Moreover, the more fat or fiber there is at the site of the bite, the more significant the swelling.
- There is redness near the bite site.
Most people experience exactly these symptoms, which then go away after a few hours. Sometimes people also notice that the bite itches a little later. But even if there is a red spot left and the bite area itches, there is nothing to worry about. If one or more insects have stung, the wasp's venom does not pose a threat to life. However, the body may react more violently if a person is stung by a large number of wasps.
About 1% of people develop an allergic reaction to wasp venom. Symptoms of a wasp sting allergy may include the following:
- Very severe swelling appears, the tumor quickly increases.
- Itching and rash develop throughout the body.
- Nausea and vomiting are observed.
- It becomes difficult for the victim to breathe.
- Severe dizziness .
- The pulse becomes either too fast or slow.
- The person may lose consciousness.
Bites to the lips, tongue, and palate are very dangerous. When swelling develops, it can block the airway, and the victim risks suffocation. It is also important to consider that in people allergic to venom, the first bite can lead to sensitization, that is, a disruption of the immune response. But in the second such case, a number of pathological reactions occur, as a result of which an allergy is noted.
After a wasp sting, various types of allergic reactions may occur:
- Localized urticaria - a few minutes after the bite, the skin begins to itch, and a rash appears on some parts of the body. Slight weakness may develop. The swelling is small.
- Generalized urticaria is a rash that spreads throughout the body, but this condition is not yet life-threatening.
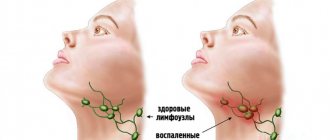
- Quincke's edema is a very serious condition in which the soft tissues of the face swell. If the process spreads to the neck, there is a danger of developing laryngeal edema. This is a dangerous condition in which the upper respiratory tract becomes blocked and a person dies from suffocation.
- Anaphylactic shock is a dangerous condition in which, over the course of several minutes, blood pressure , the pulse increases, and the entire body is covered in a rash. In anaphylactic shock, a person dies from acute cardiovascular failure if help is not provided to him in a timely manner.
Wasp or bee sting: what to do at home
If you are stung by a bee, the first step is to remove the sting. For this purpose, use tweezers or a sterile needle (you can calcinate a regular sewing needle over a fire). The bite site is treated with any antiseptic, and ice is applied to reduce the absorption of the poison into the narrowed blood vessels. Some mothers are interested in how to relieve swelling in a child after a wasp sting. Ice will help reduce its severity.
It is advisable to apply any hormonal ointment locally - hydrocortisone, prednisolone. If the victim is prone to allergies or the sting occurs in a dangerous place (oral cavity, neck, face), he needs to take a tablet of one of the antihistamines - Tavegil, Suprastin. Loratadine and cetirizine are not very suitable due to their rather slow onset effect.
Severe allergies require administration of medications in the form of injections. Most often, this is available only to specialists who administer adrenaline, prednisolone and suprastin intramuscularly, and in critical cases, intravenously. In case of anaphylactic shock, drip infusions of various solutions may be required, without which it is impossible to raise the decreased blood pressure. In addition, the victim is placed on his back, with his legs raised above head level. In case of vomiting and loss of consciousness, the patient is placed on his side.
For angioedema, accompanied by swelling of the larynx, a mini-surgery may be required, which can only be performed by a qualified doctor. In this case, the soft tissues of the neck are cut in a certain place so as to open the lumen of the larynx. A tube is inserted into it through which the victim will breathe. This operation is called cricoconicotomy and sometimes it is the only way to save a person’s life.
A wasp or bee sting is usually not dangerous, however, it always requires attention. No one knows how the human body will react to this type of injury. Therefore, at the slightest sign of trouble in the body, you should immediately call an ambulance and follow all the recommendations of doctors.
Treatment with folk remedies
It happens that insects sting in a field or forest, and there are no pharmaceutical products at hand for treatment. In this case, you can use some folk remedies:
- Parsley juice - you need to pick several stems of the plant, rub them and apply the juice that has been released to the affected area.
- Lemon juice – it is recommended to lubricate the skin to neutralize the effect of wasp poison.
- Berries – if you have any sour berries nearby, you can make a compress from them. The berries need to be crushed and placed on the bite site. Vinegar can also be used as a compress.
- Dandelion milk – applying fresh dandelion juice to the area can relieve pain. Using fresh calendula juice is also effective.
- Garlic and onion juice help relieve swelling and pain.
First aid
Speaking about what to do if a wasp stings at home, it should be noted that assistance must be competent and provided in a timely manner. Treatment of a wasp sting, if it stung outside the home, can begin with the use of folk remedies.
First aid for a wasp sting at home should begin with confirming the diagnosis. Before treating the bite with anything, you need to make sure that it is not another insect that stung the person, and that there is no sting in the wound.
If possible, you can try to suck out the poison from the wound. Also, first aid for a wasp sting involves treating the bite site with antiseptic solutions - alcohol or hydrogen peroxide. This helps numb the affected area and reduce swelling.
To reduce the severity of intoxication in a child or adult, he must be given clean water to drink. You should also drink as much as possible throughout the day. The liquid helps remove toxins from the body faster.
Cold helps relieve swelling after a wasp sting. If you have been stung by a wasp and you need to remove the tumor, then before applying any medication to the bite site, you should apply ice from the freezer or a cold compress. A compress with a soda solution also helps relieve swelling.
Treatment for this condition involves taking antihistamines. If an insect stings a child or adult, you should take a tablet of this drug. However, it is better to discuss its use with your doctor.
If your arm or leg is swollen, you should try not to make sudden movements. The bite site can be wrapped with a sterile bandage. This will help relieve pain and stop the spread of poison.
After a wasp bite on an adult or child, you can also smear the area where there is redness and itching of the bite with any ointment that contains hormonal components. It is advisable to treat the bite site after the antiseptic has been used. A specialist can tell you in more detail how to treat a wasp sting.
If vomiting begins or the person loses consciousness, he should be placed on his side.
In case of an allergic reaction, which can occur with multiple insect bites, a hornet bite to the head, etc., a feeling of heat and lack of air appears. In this case, you should remove all tight clothing, lay the person horizontally, and provide him with an influx of fresh air.
At the first manifestation of an allergic reaction, you should immediately call an ambulance. If there are indications, the patient is given injections of dexamethasone or adrenaline .
As for what to do, if after a wasp sting your arm or leg is swollen, and there are no medications at hand, then in this case it is worth using folk remedies. You can lubricate the affected area with any means that helps relieve swelling: juice of sour berries, garlic, onions, etc.
How to relieve swelling from a wasp sting on the second day
In a localized reaction, the next day after the bite, the swelling begins to subside, but pain and burning persist. To more quickly eliminate these symptoms, the bite site can be lubricated with a gel or ointment that contains antihistamines (Fenistil gel, Moskitol, Psilo-balm).
If tissue swelling persists after 48 hours, then alcohol compresses can be used to resolve the tumor. To do this, you need to moisten a small cotton napkin with vodka and apply it to the bite site. The top of the napkin is covered with wax paper or a piece of cellophane and secured with a warm bandage. How long to keep the compress? The answer to this question depends on the individual’s tolerance to the procedure. It should be removed immediately if a strong burning sensation occurs.
In case of severe swelling, which is usually observed in systemic reactions to wasp stings, treatment should be carried out as prescribed by a doctor. The patient may be prescribed antihistamines, anti-inflammatory and diuretic drugs. In some cases, corticosteroid therapy is given for a short course.
Severe swelling requires medical attention
Prevention
To prevent insect bites, you must adhere to the following rules:
- If a wasp flies nearby, do not wave your arms or panic. It is important not to make sudden movements so as not to provoke an attack.
- You should not walk barefoot on the grass while in nature.
- It is important to be careful when consuming food outdoors. Sweet foods, as well as fruits and soda, can attract wasps.
- In places where there are a lot of insects, it is better not to wear very loose clothes and loose hair, so that wasps do not get entangled in them.
- Picnics should not be held in areas where there are many wasps swarming.
- If a bite does occur, do not scratch the affected area.
Wasps don't just attack
According to the leading researcher at the Laboratory of Terrestrial Invertebrate Animals of the Scientific and Practical Center of the National Academy of Sciences of Belarus for Bioresources, Anatoly Kulak, stinging insects that live on the territory of the republic do not just attack humans. “They either protect their lives or protect the family - the nest. Therefore, the first and most important rule of behavior around them is caution. You should not unnecessarily approach places where stinging insects accumulate, especially the nest,” he said.
Nests of wasps (a hornet is also a wasp) can be found anywhere by chance: in Poles they are located on the stems of low-growing plants, the red wasp settles in cavities underground, German and common wasps, hornets willingly populate the attics of buildings, verandas, bathhouses, sheds, climb into brickwork, under slate roofs. A small, easily accessible wasp house can be removed by yourself if you have the knowledge. To eliminate a huge colony in a hard-to-reach place, it is better to seek the help of specialists. Rescuers free preschool institutions, homes for the elderly and disabled, hospitals and some other social facilities from dangerous neighborhoods with insects. In other cases, this service is provided on a paid basis.
“The second rule is not to be afraid of wasps. Wasps, which now mostly fly under fruit trees and eat apples and pears, do not pose any danger unless you step on them barefoot or accidentally bite the apple along with the insect. Usually, when they pester people, it means that we attract them with some pleasant smell associated with food, for example, a drop of jam accidentally fell on our clothes. That is, the wasp has no desire to sting,” the entomologist emphasized.
Another group of stinging hymenoptera insects are honey bees. “Their reaction to a person is very diverse. It depends on what breed of bee. There are apiaries where they raise very aggressive bees that are able to protect their home from uninvited guests - both from bears and from hornets (the latter greatly harm them). It is these bees that are capable of attacking a person, sometimes even sensing his scent from afar or noticing his silhouette. And there are honey bees that let them get close to the hives and don’t touch them. In general, it’s worth making a rule: when you come to a village to relax in the summer, do not use deodorants or body eau de toilette - these synthetic fragrances, pleasant for us, can cause anger in the bees,” noted Anatoly Kulak.
The most peaceful of the large stinging insects are bumblebees. They can be called safe creatures, although they sting just as painfully.
Consequences and complications
The consequences of a wasp sting, like the consequences of a hornet sting, are dangerous for those who are prone to allergies.
Swelling may develop in the affected area, which quickly increases. If your hand is swollen, this condition does not pose any particular danger. But when such a reaction develops, airway obstruction may occur in the larynx or oral cavity.
An allergic reaction can manifest itself in the form of anaphylactic shock, which is likely to result in death.
Other consequences and complications depend on where exactly the person was stung by the insect. glaucoma , iris atrophy, etc. may later develop
Torso and limbs
No less dangerous are wasp bites on the arms, legs and other parts of the body. If your hand is swollen, in addition to first applying cold, treat the bite site with iodine or alcohol. You shouldn’t use brilliant green; it will immediately dry out and close the wound, and the poison that gets there needs to be “pulled out.”
Prepare a saline solution, a teaspoon of salt per glass of water, and make lotions. A napkin soaked in the solution should be kept at the site of the bite for at least an hour, periodically wetting it. The saline solution can be replaced with a soda solution.
If the swelling at the site of the bite, despite everything, increases, it means that the wasp venom has entered a place saturated with blood vessels. You can apply a tight bandage and try to stop the further spread of the toxin in the circulatory system. But, as a rule, this does not always give the desired result, since the poison spreads very quickly.
For a tumor on the leg, the best remedy is a napkin soaked in an ice-cold saline solution and secured with an adhesive plaster or bandage. The skin on a person’s legs is quite dense, the blood vessels are located somewhat deeper from the surface of the skin, therefore, if the fixed bandage does not interfere with walking, wear it for as long as you like until the swelling is completely eliminated.
If your foot is swollen in the foot area or between the toes, wash the area as thoroughly as possible with soap. Then place your foot in a bowl of cool salt or soda solution. Perhaps the procedure is not very pleasant, but in any case useful.