Otolaryngologist for adults and children
Son of the gods
Stanislav Vladimirovich
25 years of experience
Otorhinolaryngologist of the highest category, Candidate of Medical Sciences, member of the European Rhinological Society (European Rhinologic Society)
Make an appointment
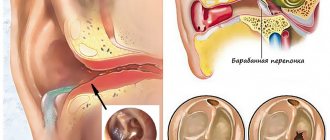
A wax plug is a collection of earwax in the ear canal. Over time, this formation becomes dense and completely blocks the outer canal of the ear. The patient notices a blockage after a significant decrease in hearing acuity without an objective reason such as injury, infection or neoplasms in adjacent tissues.
Typical signs of cerumen impaction include tinnitus, a feeling of fullness, dizziness, cough, nausea, and pain of variable intensity. The method of removing obstruction depends on the consistency of the cork mass. Common options are rinsing the external auditory canal or dry removal of the plug using instruments. Otolaryngologists do not advise patients to make independent attempts to remove wax plugs from the ear by rinsing the canal with hydrogen peroxide or using cotton swabs, disks and sticks.
General information about pathology
The composition of the wax plug in the ear is formed from the secretion of the skin glands of the external auditory canal. The basis of sulfur is sebum and secretions of the corresponding glandular tissues. Over time, particles of keratinized epithelium and secretion products of apocrine sweat glands are added to them. The color of the substance may vary depending on the dominant element, the age of the patient, the characteristics of metabolic processes in the body, the intensity of physical activity, and the presence of chronic or systemic pathologies.
The main function of the secretion of the glands located in the external auditory canal is to protect the tissue from damage, excessive drying or softening when exposed to water. The acidic environment of sulfur secretions provides an antiseptic effect upon contact with bacteria and fungi, which prevents the development of external otitis. During chewing, speaking and during bouts of yawning, sulfur moves to the outer opening of the ear canal, providing mechanical cleaning of the canal from dirt, dust particles, and small foreign bodies. The formation of wax plugs in adults and children disrupts the functioning of the protective mechanisms of the ear.
How to choose drops for ear plugs
To dissolve an ear plug, drops must be selected in accordance with several characteristics - the purpose of the liquid solution, age indications from the manufacturer, as well as effectiveness and reviews. Let's take a closer look at each point.
Purpose
When choosing any medicine, it is important to consider the purpose. In the instructions, this item is prescribed with indications for use depending on the causes of congestion. Conventionally, the nominees can be divided into several groups - capable of dissolving, cleaning, removing sulfur, anti-inflammatory, analgesic, antiseptic compounds.
Age
Before you buy a medication, make sure that it is suitable for your age. Most of the presented nominees are effective for congestion not only in adults, but also in children, but there are still solutions with strict contraindications.
Efficiency and reviews
You can verify the effectiveness of ear drops for removing wax plugs not only by the indicated pharmacological properties, but also by customer reviews. Their real experience in carrying out procedures will help you choose the best option.
The best nasal drops
Types of cork formations
During the examination of the patient, the otolaryngologist diagnoses the type of cerumen plug formed. The consistency of the secretion of the glands allows us to distinguish the following types of formations in the ear canal:
- pasty - have a light or dark yellow color, plastic;
- plasticine-like – characterized by viscosity and rich brown color;
- hard – dark-colored, have a hard texture, and do not contain moisture.
Removal of ear wax plugs should be performed at the initial stage of their development. The soft formation becomes dense over time, and in advanced cases, rocky. Audiologists and otolaryngologists consider epidermal layers, which are formed from desquamated cells of the stratum corneum of the epidermis, to be a special type of plugs. This type of formation is characterized by high density, white or gray color. A characteristic feature is a tight junction with the walls of the auditory canal, which can lead to the development of bedsores of the bone region.
The location of the plugs makes it possible to distinguish parietal and obstructive forms. In the first case, the accumulation of gland secretions fills part of the external auditory canal, in the second, they completely block it.
Rating of drops from ear plugs
When compiling a list of the best drugs, we consulted with leading otolaryngologists and audiologists. Their medical experience and practice determined the main characteristics by which the nominees were selected:
- Composition of the product;
- Principle of operation;
- Purpose;
- Age indications;
- Rules of application;
- Efficiency;
- Price, manufacturer company.
In total, VyborExpert considered more than 5 dozen new generation drugs, time-tested products. The result of a comprehensive analysis and study was a top list of 6 names of ear drops for earwax. Review monitoring showed the strengths and weaknesses of each nominee.
Why does wax plug appear?
Long-term clinical observations of patients have allowed otolaryngologists to accumulate significant knowledge about the causes of cork obstruction of the ear canal. One of the most common reasons for blockage is increased secretory activity of the sulfur glands. Excess secretion does not have time to be removed from the ear canal. Its intensive accumulation provokes the formation of a plug. Hypersecretion becomes a consequence of various pathologies - dermatitis, eczema, chronic otitis. A significant role in stimulating the sulfur glands is played by the level of cholesterol in the blood and the patient’s failure to comply with personal hygiene rules when cleaning the ears.
Difficulty evacuating wax from the ear canal is an equally common cause of obstruction. Impaired outflow of sulfur masses can occur due to anatomical narrowness or excessive lengthening of the ear canal of a child or adult. Pathological changes in tissue due to inflammation, swelling, injury or exposure to foreign objects stimulate blockage of the opening of the outer ear.
A similar effect occurs when patients regularly use in-ear headphones or hearing aids. Elderly people experience problems with the outflow of wax due to active hair growth in the external auditory canal. At risk are people who work in industries with large amounts of dust in the air (mines, tobacco factories, bakeries). Divers and swimmers experience chronic narrowing of the ear canal due to constant skin contact with moisture.
Improper cleaning of the hearing organs remains a significant risk factor for the accumulation of sulfur masses. The production of earwax occurs in the membranous cartilaginous part of the ear, but the patient’s manipulations during hygiene procedures can lead to its entry into the bony part of the ear canal. The narrow isthmus between these sections will not allow the sulfur to return back for successful mechanical evacuation.
Oil-based preparations
The previous drops were water based. But, they were basically able to break down earwax into individual components, only if it was of a soft consistency or of recent origin. Oil-based preparations are fat-soluble, and therefore are better able to emulsify earwax lipids, they lubricate and soften it. And although they also may not cope with hard and old wax, they produce approximately the same effect as water-soluble preparations. Paraffin has long been used for these purposes, and even more ancient is the use of almond, rose or olive oil. Nowadays, there are some preparations, for example, Klin-Irs based on paraffin, or Vaxol based on olive oil. But here we will talk about one drug in drops - Remo-Vax.
Remo-Wax
Rating: 4.9
Remo-Vax was originally created as a drug specifically for the care of the skin of the auricle and external auditory canal. This product contains allantoin, phenylethanol, benzethonium chloride, and other compounds. The solvent is liquid lanolin, which is obtained from the rinsing waters of sheep wool, as well as mink oil. A well-chosen combination made it possible to create a hypoallergenic solution used for ear hygiene and removal of excess earwax. This drug is also instilled warm, lying on the side so that the required ear canal faces upward. In order to straighten a crooked external auditory canal, you need to take your ear by the lobe and pull it down and back. Then, trying to get to the back wall of the ear canal, you need to drip 15-20 drops, but not less than 10, to cover all the walls of the ear canal evenly.
You should not try to drip into the center of the hole; you may end up with an air lock and the drug will not penetrate the required amount into the ear canal. Then you need to wait 5 to 10 minutes, turn on your side, let the solution flow out quietly, and then wipe the ear with a towel or napkin. For hygienic purposes, it is enough to use it once every 2 weeks, but in order to remove the wax plug, you need to lie with the drops in the ear longer, up to 30 minutes. If the cork is extremely hard and durable, then in some cases the procedure will have to be repeated up to 5 times in a row. As a result, the exposure time can reach 2 hours; during this period of time, any plug will soften and can be safely removed. Remo-Vax is produced by the French company Orion; a 10 ml spray will cost from 370 to 460 rubles. Drops of the same volume (10 ml) will cost a little more: from 380 to 480 rubles.
Advantages and disadvantages
The drug is balanced, allows you to partially dissolve even the strongest plugs, does not cause skin irritation and is safe even with long-term use, including in children with allergies and skin diseases. Drops can be used both for prevention and for dissolving sulfur plugs. Contraindications include only perforation of the eardrum, leakage of fluid from the external auditory canal, and ear pain. After administering the drops, there may sometimes be discomfort for a few minutes, which then goes away.
A-cerumen (surfactant)
Rating: 4.8
Finally, there are drops based on a fundamentally different action: not on the influence of a solvent, but on surfactants. These are special molecules that reduce the density of sulfur, reduce adhesion, or sticking to the walls of the external auditory canal. Surfactants then increase the moisture content of the cork and cause it to dissolve.
One of the most popular and active means for dissolving traffic jams is drops or spray, A-Cerumen, produced by the French company Laboratory Gilbert. In the fall of 2021, the cost of this drug will be approximately 440 rubles. for a spray, volume 40 ml, and 420 rubles. for drops packaged in plastic ampoules of 2 ml (5 pcs).
This is a triple action medicine, and consists of three surfactants that have the ability to reduce surface tension at the media interface. It is an amphoteric, anionic and nonionic surfactant. They dissolve the plug, and most importantly, they break the connection between it and the wall of the external auditory canal, reducing its adhesion, or ability to stick to the walls.
The drug is very convenient for both treatment and prevention; it is enough to drip these drops twice a week. If there is a formed sulfur plug, then A-Cerumen drops can be dripped once or twice a day for 3 to 5 days. With this tactic of treatment with drops, the plug gradually dissolves, sulfur secretion is restored, and there is no risk of complaints, auditory or vestibular disorders.
In order to use the drops, you need to turn your head to the left while lying down, if we are talking about the right ear, and vice versa. By pressing the plastic ampoule bottle once, half of the ampoule is poured into the ear. It is necessary to lie with your head turned for 1 minute. After this, the head tilts in the opposite direction, and the remains of the sulfur plug and the remaining drops flow freely. Then you need to wipe your ear with a cotton swab, and under no circumstances use cotton swabs.
To completely clean the external auditory canal, you can rinse it with plain water, or 0.9% table salt; you can also use sea water for this, which was mentioned above. To simply prevent the formation of wax plugs, you should use these drops 2 times a week.
A-Cerumen should not be used in case of perforation of the eardrum, hypersensitivity to the components of the drug, in case of exacerbation of otitis media, and in children under 3 years of age. Also a contraindication is an eardrum shunt and the time that has passed since its removal is at least 6 months to 1 year.
Advantages and disadvantages
A-Cerumen is well tolerated, patient adherence to treatment is high, since the drops are simple to use and do not require any other drugs. In addition, this remedy can be used for prevention, for example, if a person often uses hearing aids or internal headphones.
Symptoms
Sometimes patients suffering from wax impaction experience ear pain. This is caused by a gradual increase in the size and weight of the sulfur formation. But most adults and children do not experience any discomfort until the ear canal is completely blocked. The consistency of the cork does not play a significant role - the set of characteristics will be the same.
The plugs appear suddenly when water gets into the ear. Contact with liquid provokes a rapid increase in the volume of the sulfur lump. Obstruction of the lumen of the auditory canal develops. The process is accompanied by typical symptoms:
- congestion and noise in the ears;
- decreased hearing acuity;
- an attack of dizziness or headache;
- sensation of a foreign body in the ear canal;
- local pain syndrome.
A common symptom of blockage is autophony - the echo of the patient's own voice in the affected ear while speaking. The pressure of the plug on the eardrum can provoke an attack of nausea, coughing, and migraines. Prolonged compression of the membrane can lead to inflammation - myringitis - and otitis media.
Are you experiencing symptoms of wax plug?
Only a doctor can accurately diagnose the disease. Don't delay your consultation - call
Dissolving plugs with ear drops
Finally, let's move on to the pharmacological part. Let's look at what medications can soften and dissolve earwax, and what drops are used. We will assume that the drops will work simply by dripping into the ear. And then calmly, by turning your head, everything flows out on its own. We will not consider liquids and solutions that need to be injected into the ear under pressure, for example, using the same syringe.
In outpatient settings, at home, there are drops, and there are sprays that penetrate the ear under pressure. But the pressure in the spray can is incomparable to the pressure in the Janet syringe; the spray is produced solely for convenience. No mechanical energy is created from the spray canister; the effect depends solely on the chemical composition and temperature of the medicine.
There are several such effective drugs on the modern market, in the form of drops that allow you to dissolve and remove ear plugs. As a rule, they are contraindicated for children under 2.5 years of age. It should be remembered that complete dissolution of sulfur plugs does not occur in 100% of cases: according to some sources, the effectiveness of using drops alone does not exceed 70%. Therefore, it is advisable to still see an otolaryngologist after using them at home in order to finally remove the plug.
This review presents drugs that are sold in pharmacies without a prescription. The inclusion of any drug in the list, or absence from the list, does not constitute advertising or anti-advertising. All drops are taken from national and international recommendations, instructions and protocols for removing wax plugs. The information is for informational purposes only; the source of information is the official instructions for drops and sprays for removing ear plugs, which are freely available. For each drug, the name, characteristics, and price range are given, relevant for November 2021 for pharmacies of all forms of ownership in the Russian Federation.
Diagnosis of blockage
The decision on how to remove the wax plug is made by the otolaryngologist after otoscopy or microscopy. A probe directed into the patient's ear allows the consistency of the wax to be determined. An examination of the eardrum is performed to exclude damage from the diagnosis - perforations or ruptures caused by previous diseases.
The condition of the resonating membrane becomes the basis for choosing a method for eliminating obstruction. Otoscopy allows the otolaryngologist to conduct a differentiated diagnosis, excluding the presence of foreign bodies, malignant or benign neoplasms and cholesteatoma in the patient’s ear canal.
Diagnostics
An otolaryngologist can diagnose a wax plug; for this he needs, at a minimum, a regular ear specula and a forehead reflector for otoscopy. In some cases, a special microscope is required to perform an otomicroscopy and examine the eardrum in detail. Finding out whether the eardrum is intact is very important. For example, if due to chronic otitis media there is perforation, then some methods of treating and removing the ear plug will become inapplicable.
If there is a plug, the ENT doctor must pay attention to its size, location, and when trying to touch it with a microspatula or loop, it is very important to evaluate its consistency in order to understand how it can be most easily removed.
Corks can be either soft or dry:
- soft cork can have a rather viscous consistency (pasty, plasticine), similar to dense honey, and have a color dominated by yellow shades: light yellow, dark yellow, or honey yellow. Such plugs are flexible, and usually there are no problems with them. Also, a soft cork may resemble plasticine rather than paste, but still be viscous and pliable;
- Finally, the doctor will have the most work in the presence of dry plugs. They are always dark brown or completely black, unyielding, and their consistency is hard and dense.
Removing wax plug
Attempts by patients to independently remove wax plugs by dissolving with drops or removing with tweezers can lead to injury to the skin of the external auditory canal, damage to the eardrum, the development of infections, and the progression of otitis media or otomycosis. Any manipulations related to wax lumps in the ears should be entrusted to an otolaryngologist.
Soft plugs are removed by washing. This method is not used if the integrity of the eardrum is damaged - the fluid will enter the middle ear cavity, causing an acute inflammatory process. Paste-like and plasticine-like plugs are removed immediately after diagnosis when the integrity of the resonating membrane is confirmed.
The washing process involves the use of a Janet syringe, into which a sterile saline solution or furatsilin solution is drawn. The temperature of the liquid is 37 degrees Celsius. Heating of solutions is mandatory, since low temperatures will have an irritating effect on the skin of the ear canal and will ensure the manifestation of increasing reflex reactions - dizziness, nausea, headache.
Before removal, hard plugs are softened with a solution of hydrogen peroxide instilled into the patient's ear by an otolaryngologist. The solution is preheated. The duration of the softening process depends on the type of plug formation. The preparatory stage can last several days - instillations are carried out three times for every full day. A side effect of hydrogen peroxide entering the ear canal is increased hearing loss. The reason for this phenomenon is the swelling of the cerumen plug under the influence of liquid and increased obstruction of the ear canal.
If there are contraindications to washing the ears, dry instrumental removal of the wax is performed. The manipulation is carried out using otolaryngological instruments: an ear hook, forceps and a spoon. The process of removing the plug is carried out under visual control using a microscope. Successful removal of the lump by the otolaryngologist is completed by introducing a turunda soaked in boric acid into the patient’s ear canals. After 2-3 hours, the tampon is removed. A child or adult can do their usual activities without any restrictions.
Composition and functions of earwax
The main components of earwax are fats, cholesterol, unsaturated fatty acids and wax esters. Therefore, it does not dissolve in water, providing natural lubrication to the skin of the external auditory canal, as well as preventing it from drying out and protecting it from dust particles.
In addition, earwax contains sulfonamides (suppress the growth of pathogens), lysozyme (an enzyme that destroys the cell walls of bacteria) and immunoglobulins (cells of the immune system). Thanks to these components and the acidic reaction (pH = 4-6), earwax protects the external auditory canal from bacteria and fungi.
That is, the formation of earwax is a physiological process that is necessary for the protection and normal functioning of the hearing organ.
What is the self-cleaning mechanism of earwax?
The external auditory canal contacts the inside of the temporomandibular joint. And thanks to his movements during talking or chewing, earwax moves outward from the eardrum.
In addition, the skin of the external auditory canal grows at a rate equal to the growth of nails. As it grows, it moves outward from the eardrum, pushing earwax toward the exit. That is, for example, wax attached to the eardrum will move outward on its own within 3-4 months.
Also in the skin of the external auditory canal there are cilia, which, making oscillatory movements, promote earwax from the inside out.
However, unfortunately, often when exposed to certain factors, the work of the sulfur and sebaceous glands, as well as the self-cleaning mechanism, is disrupted.
Causes of wax plug formation Improper hygienic care of the external auditory canal Excessively frequent and rough use of cotton swabs or cleaning the external auditory canal with improvised means (for example, pins or knitting needles) is the most common cause of wax plug formation.
As a result, the skin of the external auditory canal is injured, and the production of secretion by the sulfur glands is enhanced. Next, the earwax is pushed deeper into the eardrum, where it becomes compacted. Therefore, the process of its self-cleaning is disrupted.
In addition, during intensive cleaning, the cilia of the skin of the external auditory canal are damaged. Therefore, they cease to perform their function: moving the formed sulfur outward. It is noteworthy that often methods of improper hygienic care of the external auditory canal come from childhood. Because children, watching adults, adopt their methods of removing earwax. Anatomical features There is tortuosity or narrowness of the external auditory canal, therefore the process of self-cleaning of earwax is disrupted. Moreover, the anatomical features of the structure can be either congenital or acquired (for example, appear after an injury).
Tendency to increased secretion of earwax Occurs when there are disturbances in the metabolism of fats in the body, which lead to increased formation of cholesterol, which is part of earwax. As a result, it becomes more viscous, and therefore the process of self-cleaning from the external auditory canal is disrupted. Inflammatory and infectious diseases of the external auditory canal (for example, otitis ) Lead to increased secretion production by the sebaceous and sulfur glands, but it does not have time to be removed, so it accumulates. In addition, the lumen of the external auditory canal decreases due to inflammatory swelling of the skin. As a result, a mechanical obstacle is created in the path of self-cleaning of earwax. The qualitative composition of earwax also changes: the number of protective factors in it decreases (lysozyme, immunoglobulins and others). Therefore, the ear glands are secondarily affected by pathogens, and the course of the infectious-inflammatory disease is aggravated. Using hearing aids or regularly using headphones leads to injury to the skin of the external auditory canal (for example, abrasions), so the production of earwax increases. Subsequently, it is pushed inside the external auditory canal and compacted. In addition, conditions are created for the addition of a secondary infection and the development of inflammatory diseases in the outer ear. Excessive hair growth inside the external auditory canal leads to disruption of the process of self-cleaning of earwax. This cause most often occurs in elderly patients. Working in a dusty environment (for example, in a mill or in mines) Dust settles in the external auditory canal. As a result, the secretion production of the ear glands increases, and the functioning of the skin's cilia is disrupted. A foreign body in the lumen of the external auditory canal leads to increased secretion production by the ear glands (a natural protective reaction of the body), which does not have time to be removed. In addition, a mechanical obstacle is created in the way of self-purification of sulfur. Prolonged stay in a room with dry air (humidity up to 40%) leads to the drying out of the secretion of the external auditory canal, so a sulfur plug of solid consistency is formed. The older a person is, the higher his risk of developing wax plugs. Because with age, the self-cleaning mechanisms of earwax weaken, and its production by the glands increases. In addition, in older patients, the number of hairs in the external auditory canal tends to increase. Therefore, an additional obstacle is created in the way of self-purification of sulfur.
Symptoms of wax plug
As a rule, sulfur plugs do not manifest themselves for a long time. Only when the lumen of the external auditory canal is almost completely blocked (70% or more) do signs of cerumen plug appear. Moreover, they can occur on either one or both sides, if wax plugs have formed in both ears. Ear congestion and , hearing loss Symptoms develop slowly due to the gradual accumulation of wax in the external auditory canal. Therefore, the patient usually does not pay any attention to the fact that he gradually becomes deaf and noise appears in the ears. Dry and irritating cough , nausea and dizziness, moderate pain and the echo of your own voice in the ear. Signs appear if the wax plug presses on the eardrum, irritating its nerve endings. With prolonged pressure from wax plugs, inflammation of the eardrum (myringitis) or the middle ear cavity (otitis media) sometimes develops. As a result, mild pain in the ear appears (with otitis media it intensifies during chewing or talking), body temperature may rise moderately, and small discharge (most often purulent) appears from the external auditory canal. On a note! Most often, the first signs of wax impaction appear upon contact with water (for example, after diving in a pool or taking a shower). Because it swells and partially pushes inward closer to the eardrum, blocking the lumen of the external auditory canal.
How to remove wax plug
There are several ways: using pharmaceutical drugs at home, as well as using hardware methods in a medical institution.
How to remove wax plug at home
Trying to remove large wax plugs at home yourself and in the presence of severe symptoms is useless, and not always harmless. Since you can accidentally get an infection, damage the eardrum or the skin of the external auditory canal. However, small wax plugs can be removed at home, using caution. Moreover, it is necessary to use pharmaceutical products (ear drops), and not hygienic cotton swabs.
Why can't you use cotton ear swabs?
Because with their help, earwax is compacted and pushed closer to the eardrum. That is, the sulfur plug, on the contrary, increases in size. In addition, such deep cleaning may cause injury to the skin of the external auditory canal and/or eardrum (perforation - loss of integrity). Drops for removing wax plugs - pharmaceutical products
They are used for the safe and painless removal of wax plugs at home, as well as to prevent its formation. In addition, ear drops are used as a preparatory step before an ENT doctor removes wax plugs. The most commonly used agents for cerumenolysis
| A drug | Release form | Mode of application |
| A-Cerumen | In 2 ml dropper bottles | To remove wax plug , 1 ml of solution (half of a dropper bottle) is instilled into the external auditory canal, and after one minute it is cleaned. The procedure is carried out twice a day for 3-4 days. To prevent the formation of wax plugs (for example, in patients using hearing aids), a solution of 1 ml is instilled into each ear canal twice a month. |
| Remo-Wax | In 10 ml bottles with a plastic dispenser | To remove wax plug, 10 to 20 drops of solution are instilled into the external auditory canal of the diseased ear, and after 20-60 minutes it is removed. The procedure is carried out daily for 3-4 days. To prevent the formation of sulfur plugs, the drug is used once every two weeks. |
When should you not use ear drops?
- In case of a defect (violation of integrity) of the eardrum.
- If the patient has chronic otitis or in the past he suffered purulent otitis.
- A-Cerumen is contraindicated for use in children under 2.5 years of age.
Can peroxide be used to remove earwax?
Yes, you can use 3% hydrogen peroxide. Whereas the use of a higher percentage of the solution is contraindicated, since it causes a chemical burn to the skin of the external auditory canal and eardrum. The mechanism of action of hydrogen peroxide When in contact with tissues, peroxide breaks down into molecular oxygen and water. In this case, oxygen oxidizes the tissue (in this case, the cerumen plug), forming foam, which mechanically cleanses the external auditory canal. Moreover, it should be remembered that hydrogen peroxide leads to swelling of the cerumen plug, so ear congestion and hearing loss intensify. However, after cleaning the external auditory canal, the symptoms disappear.
When should you not use hydrogen peroxide?
- If there is a defect in the eardrum.
- If the patient has suffered from purulent otitis media in the past or is currently suffering from chronic otitis media. Hydrogen peroxide should be used with caution as it can burn the skin of the external auditory canal and/or eardrum. Therefore, if during the procedure there is a severe burning sensation and pain in the ear, stop it and be sure to consult an ENT doctor.
Do I need to rinse my ear to remove wax?
Washing out (irrigation) is the most common and effective way to remove wax plugs by an otolaryngologist. However, it is not recommended to remove wax plugs by rinsing yourself at home. Since there is a high probability of damage to the eardrum and/or skin of the external auditory canal.
How to rinse wax plug?
If the sulfur plug is soft, then washing is carried out without preliminary preparation. When the sulfur plug is dry, it is necessary to soften it first. For this purpose, half a pipette of 3% hydrogen peroxide is instilled into the external auditory canal of the diseased ear 5-6 times a day for 2-3 days. Or use cerumenolysis products according to the instructions. To rinse the external auditory canal, use water or any solution of external antiseptic (for example, furatsilin), which are heated to 37°C. There are instrumental (manual) and hardware methods for washing out wax plug:
- Using a Janet syringe, the capacity of which is 100-200 ml. During the procedure, the doctor delivers a high-pressure stream of water into the external auditory canal towards the eardrum. Due to this, particles of sulfur plug move away from the place of attachment. The water then flows into the tray through the outlet of the external auditory canal. However, Janet's syringe is capable of creating pressure up to 10 atmospheres. Whereas the eardrum can only withstand 2 atmospheres. Therefore, the success of the procedure largely depends on the professionalism of the doctor.
- An electronic irrigator is used (Propluse 4th generation) - a new technique that has found wide application. The effectiveness of the procedure is based on the pulsed nature of the jet supply, as well as the ability to regulate its pressure. This ensures complete, painless and safe removal of the wax plug.
When should you not rinse your ear to remove wax?
- Violation of the integrity of the eardrum (perforation) is the result of injury or infection.
- The presence of acute or chronic otitis media.
- Previous history of purulent otitis media.
Because in these cases, water entering the middle ear cavity can lead to an exacerbation of the chronic inflammatory process.
Prevention of wax plugs
It is important for everyone, but especially for people with an increased risk of wax accumulation in the external auditory canal. What do we have to do?
- Clean the pinna and the opening of the external auditory canal with a swab soaked in water, without penetrating the external auditory canal.
- To improve the natural removal of wax, take your earlobe in your hands and pull it down several times. It is recommended to carry out such “charging” daily in the morning.
- If necessary, use ear cotton swabs with a limiter, but do not be too overzealous. Because they clean the external auditory canal from earwax quite well, preventing deep penetration into it.
- If you have an increased risk of developing wax plugs (for example, using hearing aids or working in a dusty room), use cerumenolysis products (for example, Remo-Vax) for prevention.
- Maintain indoor air humidity at least 40% using humidifiers.
- Use earplugs when working in dusty areas.
- When swimming in a pool or open water, protect the external auditory canal from water: put a cap on your head or use protective equipment. There are special earplugs for swimming: wax-impregnated tampons, plugs that protect against water or with a water-repellent effect.
- If the anatomical structure of the external auditory canal is prone to the formation of cerumen, periodically visit an otolaryngologist and follow all his recommendations.
What should you avoid?
- You should not use hygienic cotton swabs that penetrate deep into the external auditory canal. Since the sulfur is pushed closer to the eardrum and compacted. In addition, there is a risk of injury to the eardrum if you are accidentally distracted by another event during the procedure. Young children especially suffer from this, because during cleaning they fidget or break out of their mother’s hands.
- Do not use matches, knitting needles, pins or other sharp objects to remove wax. Since there is a high risk of injury to the eardrum and skin of the external auditory canal.
- Avoid sudden changes in ambient temperature. For example, in the heat - moving from the street to a room where the air conditioner is running.
- Do not use earwax candles to remove wax plugs on your own and without consulting an ENT doctor, as you may harm yourself. For example, cause a burn to the eardrum or the skin of the external auditory canal, and if there is inflammation in the outer ear, aggravate the course of the disease.
Otorhinolaryngologist L.V. Ledova.
Prevention
The basis of prevention is an explanatory conversation between the otolaryngologist and the patient. Improper ear cleaning remains the main cause of earwax in children and adults. The doctor clearly demonstrates the principles of hearing hygiene.
The main mistake most people make is dipping cotton swabs into the ear canal. This leads to compaction of sulfur accumulations and the formation of plugs. Cleansing procedures should only affect the auricle and the skin around the auditory opening. Other manipulations are fraught not only with the formation of sulfur lumps, but also with damage to the internal tissues of the ear.
It is beneficial for children and adults to attend preventive examinations every 6 months. An otolaryngologist will diagnose the condition of the ear canals and ensure their professional hygiene. This option is indicated for people suffering from regularly formed sulfur plugs.
An important component of prevention remains the timely treatment of viral infections and systemic pathologies of the body, which can lead to complications, including sulfur plugs. If there is severe overproduction of earwax, the patient should consult with a dermatologist, endocrinologist, therapist, or gastroenterologist. Finding the reasons that provoke increased work of the glands will help doctors develop an effective treatment strategy.
Parents raising small children are advised to clean their children's ears themselves. A child's undeveloped motor skills can lead to injuries when using cotton swabs. Moms and dads should pay special attention to explanatory conversations about the inadmissibility of placing small foreign objects in the child’s ear canals during games with peers.
How to remove a cork at home
Removing ear plugs at home is a last resort, which can be resorted to only if there is no way to visit a doctor. If, after several attempts, a positive result has not been achieved, treatment on your own must be stopped and you must find an opportunity to contact an otolaryngologist.
There are three ways to remove a lump of wax from your ear yourself:
- washing the ear canal using an antiseptic solution and a syringe without a needle;
- phytocandles for sulfur plugs - they create a vacuum effect and thanks to this, like a vacuum cleaner, they pull out the plug;
- drops from earwax plugs - a special composition allows you to soften and dissolve the plug, after which it will be removed from the ear.
If these procedures are carried out carefully, they cannot cause harm. Unfortunately, if the plug is very dense, it may not be possible to remove it using home remedies. This phenomenon is most often observed if the lump is in the ear cavity for a very long time, or if it consists not of compacted wax, but of crumpled desquamated epithelial cells. In the latter case, the formation is tightly connected to the walls of the ear canal, and therefore removal of such a lump is possible only by a doctor using local anesthesia and further antiseptic treatment of damage to the ear mucosa.
How to make an appointment with the specialists of JSC "Medicine" (clinic of academician Roitberg)
You can make an appointment with the specialists of JSC "Medicine" (clinic of Academician Roitberg) on the website - the interactive form allows you to select a doctor by specialization or search for an employee of any department by name and surname. Each doctor’s schedule contains information about visiting days and hours available for patient visits.
Clinic administrators are ready to accept requests for an appointment or call a doctor at home by calling +7 (495) 775-73-60.
Convenient location on the territory of the central administrative district of Moscow (CAO) - 2nd Tverskoy-Yamskaya lane, building 10 - allows you to quickly reach the clinic from the Mayakovskaya, Novoslobodskaya, Tverskaya, Chekhovskaya and Belorusskaya metro stations .
Phytocandles or funnels
This medicine for wax plugs can be bought at a pharmacy. When used correctly, it will not cause any discomfort and will not only remove the plug from the ear, but will also prevent the development of inflammation, and will also have a calming effect on the nervous system. The funnel, which is also called a candle, during the combustion process will create the necessary draft to remove the plug and will warm up the sore ear. It is useful to use this remedy not only for traffic jams, but also for inflammation, when heating is allowed. Candles can improve the health of the ear, but only if there is no purulent process, damage to the ear canal, damage to the integrity of the eardrum, otitis, fungal infection or allergy to wax.
The patient lies on his side with the ear in which the plug is located facing up. They cover his head with a cloth so that only his ear is exposed. A phyto-funnel (phyto-candle) is inserted into the auditory canal with its narrow end and set on fire. The cut should burn to the level marked on it by the manufacturer. They extinguish it in water, preventing it from burning any more. If you unwrap the rest of the candle, you will see an elongated plug in it. Thanks to the heat, the wax softens well, and the vacuum effect removes it from the ear canal. This procedure also helps improve nasal breathing, which is useful for viral infections.
Hydrogen peroxide
In most cases, hydrogen peroxide can even cope with a dense plug, which requires strong softening, which a phytocandle is not capable of. The use of this remedy may not be very pleasant, as it often causes discomfort and burning, but it is effective and helps prevent infection. In addition to a 3% peroxide solution, cotton wool is required for the procedure.
The patient lies on his side with the blocked ear up and pours a few drops of peroxide into it. It is required to remain in this position for a quarter of an hour. This time is enough to dissolve the plug. During this process, hissing and foam formation occur. It is also possible that severe deafness may occur, which should not frighten you - your hearing will return after the plug is removed. When the effect of the peroxide ends, the patient, applying cotton wool to his ear, turns over to the other side and allows the liquid to flow out. If the plug is not completely removed, then the antiseptic is refilled. The sulfur plug and peroxide usually come out quickly after this.
Washing
The procedure is carried out using a large-volume syringe, as well as saline or antiseptic solution. The second option is better, as it will prevent inflammation from occurring due to infection. As an antiseptic solution for washing, it is best to use a weak solution of manganese or a solution of furatsilin, prepared at the rate of 2 tablets per 1 liter of water.
Before washing the ear, wipe it with chlorhexidine. After this, bending over the sink with the affected ear down, pour liquid into it in small portions. There should be no pain during this procedure. When it appears, rinsing is stopped immediately. If it is not possible to wash the cork three times, stop trying to remove it on your own.