Quick transition Treatment of otomycosis
Otomycosis is a fungal infection of the external auditory canal.
Otomycosis can occur as a primary infection or develop together with bacterial external otitis.
Fungal infections account for approximately 9% of all external otitis media. Aspergillus niger (Aspergillus black - a mold fungus from the genus Aspergillus) and Candida (yeast fungi of the genus Candida) are the most common causative agents of otomycosis .
The incidence of otomycosis is higher in tropical and subtropical regions where high humidity persists. Swimming, scratching the ears, and excessive cleaning also predisposes to the development of a fungal infection.
There have been concerns in the past that overuse of antibiotic ear drops may increase the likelihood of fungal ear infections, but studies have not confirmed this.
Fungal infections are often localized in the medial (closer to the eardrum) part of the ear canal. Part of this may be due to the anatomy of the ear, but other suggestions are that the medial portion of the ear canal is darker and warmer, which encourages fungal growth.
Causes
There are several groups of main causes of otomycosis:
- The presence of concomitant diseases that can provoke the development of a fungal infection. This can be eczema, atopic dermatitis, dermatoses accompanied by itching. When scratching certain areas of the skin, saprophytic fungi, which under normal conditions are asymptomatically located on the surface of the epidermis, can get onto the surface of the ear canal. Genital candidiasis present in humans also often causes otomycosis.
- The development of local dysbiosis, provoked by various inflammatory diseases of the ear. The use of antibiotics or corticosteroids included in antibacterial ear drops, as well as inflammatory mediators, make the skin of the ear canal susceptible to any fungal infection. A loose surface that does not have a natural protective film becomes an excellent breeding ground for fungi.
- External reasons, such as the constant presence of dust, high humidity or the presence of a large number of microorganisms in the environment. Otomycosis is often diagnosed in people of certain professions, such as ragpickers, workers at waste collection points, and cloakroom attendants. A certain percentage of patients report constant visits to the pool or frequent visits to public baths or saunas.
- Constant trauma to the ear canal with various foreign objects, including headphones and hearing aids for the hearing impaired.
- Postoperative periods.
Treatment in the network of Nearmedic clinics
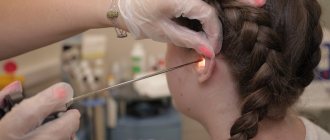
When otomycosis is diagnosed, treatment is carried out only by conservative methods with the mandatory use of antifungal agents. At the first stage, doctors at the Nearmedic center give preference to local antimycotic drugs that do not have a systemic negative effect on the body. Usually, applications are used for this, which are performed professionally (painlessly and highly effectively) by doctors at our centers.
They select a unique combination of local antifungal agents for each patient based on the latest medical advances. It has been proven that the combined approach accelerates recovery and increases the percentage of destruction of pathogenic fungi, because Some antimycotics suppress reproduction, while others cause their immediate death.
But in order to prevent relapses, it is not always possible to cure otomycosis with the help of local therapy. Therefore, Nearmedic otolaryngologists initially identify patients who are candidates for systemic antifungal therapy. This helps not to waste precious time from the first minutes, but to immediately direct all efforts to destroy pathogenic fungi. Indications for systemic antifungal therapy are:
- Mycosis of the middle ear;
- Fungal postoperative infection.
Also, doctors face another main question - which antimycotic drug is best to prescribe. The answer to this depends on what type of fungus caused the mycosis. If it is candida, then Fluconazole is usually used, and if it is aspergillus, then Terbinafine or Itraconazole. This differentiated approach is determined by the different mechanisms of action (points of application) of these antimycotic drugs.
In some cases, surgical treatment may be required, but it is not aimed at curing mycosis, but at preventing its recurrence. Indications for surgery are:
- Ear polyps;
- Granulation.
They can be removed by excision or the use of silver nitrate, which causes necrosis (death) of the pathologically overgrown tissue.
Nearmedic doctors immediately warn patients about restrictive measures, non-compliance with which can slow down recovery or cause chronicity of the process. Therefore, the entire treatment period is necessary:
- Protect your ear from water getting into it;
- Avoid contact with gases and dust;
- Do not stay in rooms with high humidity.
External otomycosis
The most commonly diagnosed is otomycosis, the frequency of which reaches fifty percent in all examined patients. It is characterized by slight inflammation and narrowing of the ear canal, the absence of a fatty film on the skin, and slight discharge. Acute external otitis should be treated at the first symptoms, without resorting to home methods, since mycoses can affect the entire length of the ear canal, including the eardrum. Attempts to clean the ear canal lead to intensive spread of fungal flora and the appearance of an acute phase of external otomycosis.
During the acute phase, patients note the appearance of pain, which is most intense at night. The volume of discharge increases significantly, the swelling of the ear canal increases, it is so pronounced that it almost completely blocks the lumen. A person cannot even hear loud sounds; he is haunted by a constant noise in the ear. Acute external otomycosis may be accompanied by pain when swallowing, the inflammatory process affects regional lymph nodes and the parotid gland.
Risks of self-medication
Self-medication may not only not lead to recovery, but also cause irreparable harm to your body, so let’s immediately make a reservation about what is strictly prohibited and why this is so.
- Do not use alcohol-based solutions to instill or lubricate the ear. This will lead to a longer period of residence of the antifungal drug in the external auditory canal, causing irritation. And if it gets on the mucous membrane of the eardrum, it will further increase the swelling, cause severe pain and contribute to the development of granulations (they are a common factor in the chronicity of the process).
- Do not prescribe systemic medications for yourself, because... Each type of otomycosis requires a differentiated approach, which is based on the results of sensitivity to antimycotics. Otherwise, the treatment will be completely ineffective.
Mycotic otitis media
Average otomycosis is diagnosed half as often, it occurs in approximately twenty percent of patients, and most often is a complication of purulent otitis caused by the addition of fungal pathogenic flora to a bacterial infection. It is characterized by a sharp decrease in hearing, increased discharge, and sharp pain that does not subside during the daytime. Patients complain of congestion and tinnitus, frequent headaches and tenderness of regional lymph nodes. An increase in temperature and a general deterioration of condition accompany mycotic otitis media.
Treatment of otomycosis
Treatment of otomycosis must be carried out under the supervision of a doctor. Patients with suspected fungal disease of the ear canal can undergo the necessary examination and quickly get rid of an unpleasant and painful disease. It is convenient to undergo treatment while in a day hospital or visiting a clinic for procedures; treatment is carried out confidentially if the patient wishes.
Therapeutic methods include not only the prescription of antifungal drugs, but also local treatment of the affected areas, washing the middle ear, and mandatory cleaning of the ear canal from dead epithelium and exudate particles.
In addition to local treatment, the patient is given restorative therapy aimed at increasing immunity and identifying concomitant diseases. Antiallergic drugs must be prescribed, since fungi cause severe allergization in the body.
Symptoms of fungal otitis
What can worry you about fungal otitis externa?
- Itchy ears
- Pain in the external auditory canal
- Weeping, “squelching” sensation in the ears
- Peeling of the skin of the external auditory canal
The main complaints of patients with mycotic otitis media are: decreased hearing, discharge from the ear, periodic itching in the ear, dizziness. The course of otomycosis is long-term with periodic exacerbations. Exacerbations are characterized by severe ear pain, itching, ear congestion, discharge, headache, and dizziness.
It is necessary to differentiate the diagnosis with inflammatory processes of the outer and middle ear of another etiology, as well as with ear tumors. The final diagnosis for otomycosis is made as a result of a comprehensive mycological study.
Treatment of fungal otitis
At the initial stage of otomycosis, treatment is carried out with antifungal ointments for topical use. In advanced stages, an ENT specialist can prescribe complex treatment using strong drug therapy.
Modern pharmaceuticals offer a number of antifungal drugs that help cope with otomycosis. For candidal external otitis, a combination of a 1% solution of clotrimazole and a 1% solution of naftifine in the form of applications is indicated. For candidomycosis, it is possible to use bifonazole, miconazole, natamycin, econazole or oxyconazole. For external otitis caused by mold fungi, the drugs of choice for local treatment are chloronitrophenol and 1% naftifine solution, also used as applications to the skin of the external auditory canal. This treatment must be continued for 14 days after clinical signs have subsided. In addition to local treatment, it is recommended to prescribe a systemic antifungal drug - fluconazole. The criterion for the effectiveness of treatment is recovery within a month, confirmed by both the clinical picture and negative results of a mycological study.
Prevention and rehabilitation
It is worth being prepared for the fact that the recovery process after treatment will be long, but often with properly selected therapy the fungus is cured without a trace. To prevent a relapse, avoid deep cleansing your ears with cotton swabs. They can only be used to remove wax outside the outer opening. In other parts of the ear, it performs a protective function, so it should not be removed.
Do not self-medicate using antibiotics - these drugs should only be prescribed by a doctor, taking into account the indications. Treat any underlying conditions promptly. Visit your otolaryngologist regularly at least once every six months. Avoid getting water in your ear (eg, wear a shower cap, avoid diving). Lubricate the skin after the main stage of treatment for 1.5 months with antifungal drugs prescribed by your doctor.
Back to articles
Complications
Lack of timely treatment of otomycosis can lead to extensive damage to the entire ear canal, eardrum and tissues surrounding the ear. Fungal infection is dangerous due to its rapid spread, threatening damage to internal organs; this threat increases in the postoperative period.
If the pathological process is localized in the middle ear, then it can become chronic, expressed by periodic exacerbations. Over time, adhesions form in the ear canal, complicating normal sound perception, and hearing loss occurs that cannot be healed. Otomycosis in an infant or a child of primary preschool age is especially dangerous due to various complications and adverse consequences.
What happens if otomycosis is not treated?
See also Treatment of ENT diseases Treatment of otomycosis
Fungal infection of the ear poses a significant danger due to the close location of the source of direct infection to the membranes of the brain. Separately, it is worth mentioning the likelihood of fungal infection of the bones of the base of the skull, especially if the patient has low immunity and the disease is not treated for a long time.
The main sign of an unfavorable course of fungal infection of the ear or the ineffectiveness of treatment is an increase in regional lymph nodes, which indicates the presence of a pronounced infectious process.
Prevention of otomycosis
With timely treatment, otomycosis of the ear can be completely cured, avoiding relapses. But it is much easier to resort to simple prevention methods:
- It is imperative to eliminate local or chronic foci of infection in the ear.
- Avoid injury to the ear canal.
- Do not touch the skin of the ear canal with dirty hands or foreign objects.
- Children should not use cotton swabs to clean their ears, as they can damage the delicate skin, causing infection.
Many patients ask their doctor if otomycosis is contagious. Since the disease is caused by a fungal infection, if the disease is detected in one of the household members, it is imperative to ensure compliance with preventive measures. You cannot share a towel with a sick person; all personal hygiene items must be treated with steam or disinfectant solutions.
Diagnostics.
Diagnosis and treatment of otomycosis - the profile of an otorhinolaryngologist. Diagnostics includes a set of measures and studies. First, the ENT doctor interviews the patient about complaints and collects his life and health history. History helps determine the cause of the disease.
During diagnosis, the patient undergoes:
- otoscopy (examination of the ear cavity using a special funnel);
- endoscopic examination to examine distant areas not visible during otoscopy;
- laboratory testing of ear discharge (to determine the type of pathogen);
- hearing studies (audiometry, acoustic impedance measurement, otoacoustic emissions).
Based on the data obtained, the doctor selects effective treatment tactics.