When you get pregnant, most of your life changes. Sometimes the expectant mother does not know whether to abandon her usual self-care procedures or how to properly celebrate the holiday. Is it possible to fly on vacation or is it better to spend it at home? Let's talk about what a pregnant woman can and cannot do.
Personal hygiene for a pregnant woman
You don't have to live in Ancient Greece to worship the goddess Hygieia, who personified purity and preservation of health. In those distant times, the principles of the science of hygiene were laid down, which explains how to eat, dress, and care for the body so as not to harm the body. Hygiene explains in what conditions you need to live, how to alternate work and rest, and maintain mental health.
Hygiene for a pregnant woman takes into account physiological changes in the body of the expectant mother. Under the influence of the hormone progesterone, local and general immunity decreases, and a woman becomes more susceptible to infections. Therefore, it is necessary to keep the skin and mucous membranes clean.
To do this, you should adhere to the following rules of personal hygiene:
- take a shower 2 times a day;
- use neutral or baby soap;
- do not wash the body and intimate area with antibacterial agents;
- wash the genitals from front to back;
- Do not use depilatory cream.
In pregnant women, the level of estrogen in the blood increases; hormones stimulate the active reproduction of beneficial vaginal microflora. This leads to an increase in the amount of whitish discharge. To prevent them from staining your laundry, you can use personal hygiene pads. But it is better to choose brands without fragrances, so as not to cause an allergic reaction.
Recommendation 1: stop taking medications
The most important rule for women in the first trimester of pregnancy is to avoid taking medications. The medications you took before pregnancy cannot be used in the first trimester of gestation.
In the early stages of pregnancy, the formation of fetal organs occurs, and any drug can negatively affect this process. Therefore, before you swallow a tablet, powder or syrup, think carefully and be sure to consult with your obstetrician-gynecologist. If you have any chronic disease that requires medication, you should also consult a specialist.
Rule 2. Eat right
The need for nutrients and vitamins during pregnancy doubles, and the process of food digestion changes, intestinal motility slows down, and the production of hydrochloric acid in the stomach decreases. Therefore, nutrition during pregnancy must meet the following hygiene requirements:
- balanced in composition;
- contain a sufficient amount of vitamins;
- in small portions, but at least 4 times a day;
- without dyes, preservatives and other toxic substances.
Eliminate alcohol from the diet, reduce the amount of sweets and fatty foods, and increase the proportion of vegetables and fruits. But you won’t be able to increase your vitamin intake through diet alone. For pregnant women, there are special vitamin complexes that contain all the necessary components in the required proportions.
Recommendation 6: avoid hypothermia and overheating of the body
If before pregnancy you liked to take a steam bath or, conversely, plunge into an ice hole, then during pregnancy you need to reconsider your habits. Overheating and hypothermia are dangerous for the fetus, especially in the first trimester of gestation.
Hypothermia impairs blood circulation, which can cause fetal hypoxia. Also, do not forget that during pregnancy, immunity decreases, which means the risk of colds increases.
Overheating of the body in the early stages of pregnancy negatively affects the formation of the fetus and increases the risk of miscarriage. Therefore, in the first trimester of gestation it is better to avoid baths and saunas. In the second and third trimester, if there are no contraindications, you can visit the sauna and bathhouse.
Rule 3. Fresh air
During pregnancy, the need for oxygen increases, so walking in the fresh air is important. From a hygiene point of view, it is better to walk in a park where there is no noisy road or a lot of cars. In the hot season, this is done in the evening, during sunset.
In an apartment, to maintain hygiene, it is necessary to ventilate the rooms as often as possible. Dust that settles on things and floors contains a large number of allergens and harmful substances. Therefore, for the health of the expectant mother, you need to do daily wet cleaning.
How can this affect the child? Can his mother infect him with the virus in the womb?
Apparently, the virus can be transmitted to a child in the womb.
In March 2021, doctors described a case in which a pregnant woman with suspected COVID-19 was taken by ambulance to Skåne University Hospital in Malmö, Sweden. She suffered from sudden severe abdominal pain. Doctors also noticed the baby's heart rate was abnormally low, which could be a sign that the baby was not getting enough oxygen. Doctors performed an emergency caesarean section. Tests of the child's blood and throat swabs showed that both mother and child were infected with coronavirus. The baby also developed antibodies against the virus and had no serious symptoms after delivery.
In another case, described in a scientific article in the journal Viruses, the child and his mother were much less fortunate. A healthy 27-year-old woman had a mild infection at 21 weeks' gestation. At the 23rd week, after recovery, an ultrasound showed that the fetus began to grow more slowly and blood flow in the umbilical artery slowed down. Another two weeks later, the premature baby was born by Caesarean section and died in the intensive care unit a day and a half later. Before infection, the patient's pregnancy was normal.
However, so far such tragic cases are rare, while millions of women fall ill with coronavirus. In general, according to a systematic review of studies that together included 100 thousand pregnant women, transmission of the virus from mother to fetus was recorded in 5.3% of cases (if the mother was sick herself). Almost every tenth child born to an infected mother was also COVID-positive.
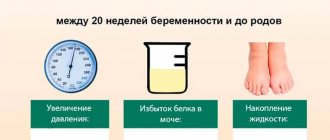
What is the real risk of consequences for the child?
- Newborns born to infected women are nearly three times more likely to have serious medical complications such as neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) admission, mostly due to preterm birth.
- In 26–30% of cases, doctors register distress syndrome (breathing disorder) in the newborn.
- In 25% of cases - low birth weight.
- In 1.4% of cases - asphyxia (suffocation) of newborns (1.4%).
- In only 0.35–2.2% of cases, children of infected mothers die as a result of or after childbirth.
Rule 5. No heels
A feature of pregnant women’s posture is a shift in the center of gravity. Therefore, to maintain personal hygiene, you need to switch to shoes with a stable heel no higher than 2-3 cm. Completely giving up heels and wearing shoes with flat soles is also harmful to health.
Hormonal changes in pregnant women make the ligaments loose. Therefore, many women develop flat feet after childbirth. To avoid this, it is recommended to choose orthopedic insoles during pregnancy.
Recommendation 8: Accept your pregnancy and your new role as “I am a mother”
In the first trimester of pregnancy, hormonal changes occur in the female body, which affects the functioning of the nervous system. In this regard, a pregnant woman may experience conditions and emotions such as tearfulness, anxiety, and excessive sensitivity. And some pregnant women even feel guilty before others for their whims over trifles, frequent emotional breakdowns.
Feelings of guilt are a negative attitude that must be gotten rid of. After all, such an emotion will cause you psychological discomfort.
Irritability in the early stages of pregnancy is nothing more than an attempt by the female psyche to fully realize and accept the fact of motherhood. And the sooner you accept your pregnancy and your new role as a mother, the sooner your calmness, good mood will return, and you will stop feeling guilty before others.
Hygiene after childbirth
In the postpartum period, intimate hygiene acquires new features. During the first month, lochia is released from the genital tract - a mucous-bloody discharge. To absorb them in the first few days, it is better to use urological pads, and replace regular underwear with disposable ones.
The mammary glands require special care. The main cream for nursing mothers is any drug with dexpanthenol. It helps prevent the appearance of cracked nipples and speeds up their healing. A special bra for nursing mothers will support the breasts in the correct position, and round pads for absorbing milk will keep the linen clean.
The life of a young mother is adjusted according to the needs of the baby. But modern personal hygiene products make caring for yourself and your newborn easier.
The first rule is moderation!
Nature is a faithful assistant for those who care about their health. The most important thing is to remember that any medicine is useful only when the dosage is observed. So, one tablet will be your assistant, but if you take the entire package at once, the consequences can be unpredictable.
The same can be said about relaxing in the summer sun and swimming. Even if you are not pregnant, you should not spend the whole day under the scorching rays. And expectant mothers should treat their rest regime with even greater attention.
However, there is nothing complicated about it. And by following the rules mentioned in this article, you can have a pleasant and productive holiday.
Sea, sea... Is it possible for pregnant women to go there?
Not only is it possible, but it is necessary! Sea water contains a lot of microelements and salts that strengthen and tone the body.
What should you pay attention to during a boat trip?
- Abrupt climate change is your enemy. It is best to choose places with a mild maritime climate. In Russia, a great option could be a vacation in the Kaliningrad region on the Baltic Sea or on the Black Sea at the beginning or at the end of the holiday season.
- You should not relax on popular crowded beaches. The weakened immunity of pregnant women requires privacy, not crowds.
- Often the seabed is rocky, and even more dangerous are corals that can cut your feet. Take special rubber slippers with you that will protect your feet from wounds.
- It is also necessary to protect yourself from possible genital infections. Gels and creams for intimate hygiene will help you with this.
The sea is good not only for the body, but also for the soul (or, if you like, the psyche). Contemplating the surf calms you down and sets you up for positive thoughts - what else does a pregnant woman need?..
How to sunbathe correctly and profitably during pregnancy
The body of a pregnant woman is exposed to sunlight much more than during other periods. The fact is that hormonal levels change, and this factor enhances the formation of melanin, the pigment that gives the skin a beautiful tan. Instead, the expectant mother may develop pigment spots on open areas of the skin.
However, this is by no means the most terrible consequence of prolonged exposure to the sun. Much worse is overheating. The fetus has not yet developed the mechanisms of thermoregulation, and therefore the mother’s passion for sunbathing can cause problems in the functioning of the nervous system and brain of the unborn child. To prevent this from happening, you must follow a number of recommendations.
Tanning rules for pregnant women
- Forget the solarium. Your friend is the sun.
- Direct sunlight is dangerous for pregnant women. On the beach it is better to hide under an umbrella; in nature, sit in the shade of trees. Don't worry about tanning: to get a beautiful chocolate skin tone, you don't have to fry in the sun.
- The best time for sunbathing is in the morning, before 11 o'clock, and in the evening, after 15 o'clock. During the day, when the sun is most active, it is better to stay indoors.
- If the temperature rises above 30 degrees, it is recommended to avoid going to the beach. On such days, sunbathing can be taken during leisurely walks.
- On the beach, sit on a sun lounger: the pebbles and sand warm up to 60 degrees and above, which threatens overheating. In addition, a lounge chair allows you to keep your head elevated, which is beneficial.
- Choose the right clothes: they should be spacious and breathable. Don’t forget about a hat (a wide-brimmed hat is best, because you need to hide your face from the rays and avoid age spots) and sunglasses, and chapstick will save your lips from drying out. And, of course, don't go out in the sun without applying sunscreen.
- Drink plenty - at least 2-3 liters per day. Make sure you always have water with you (not sweet and carbonated drinks, but plain water). This way you will avoid dehydration.
We all want to be beautiful, but expectant mothers should not forget: sunbathing for them is not a means to achieve a chocolate skin tone, but a procedure useful for an unborn child. This means you need to sunbathe correctly and not for too long.
Food facts for pregnant women
- A woman's caloric intake increases during pregnancy. Typical weight gain in a singleton pregnancy varies greatly depending on pre-pregnancy weight and other factors.
- Underweight pregnant women are advised to eat the most calories, while overweight women eat lower-calorie foods.
- During pregnancy, a woman's body absorbs iron more efficiently and blood volume increases, so it is necessary to consume more iron to ensure an adequate supply of oxygen to herself and the fetus.
Pregnant women and water: can you swim?
Swimming is a great sport. It trains all types of muscles (including abdominal muscles, which will help during childbirth) and breathing, relieves fatigue and swelling. In the water, the expectant mother will again be able to feel lightness throughout her body.
But don’t rush into the first body of water you come across. First make sure it is clean. Experts do not recommend swimming in stagnant water, that is, in ponds and lakes. The immune system of expectant mothers is weakened, and therefore various infections caused by microorganisms from these bodies of water are most destructive for pregnant women. But visiting the pool will be completely safe.
You should not swim if the water temperature does not exceed 20 degrees. Hypothermia is no less dangerous than overheating.
You should not swim for a long time. As soon as you feel the first signs of fatigue, go ashore and take a break. Try not to swim far, because the likelihood of cramps during pregnancy increases significantly.
Warm up before entering the water. Rub your feet and calves, straighten and bend your legs, stand on your toes. This way you will avoid cramps.
It is useful not only to swim, but also to do simple physical exercises in the water: turns, bends, raising and lowering your arms and legs. But you should forget about diving and diving for a while.
And most importantly: ultraviolet rays affect you even in water. Therefore, add up the time spent on the beach and the time you spend swimming, so as not to stay in the sun for too long.
Tanning is not the enemy of pregnant women
Sunbathing is an excellent way to strengthen the body. Heliotherapy (that is, sun treatment) is the key to a good mood, which is important for the expectant mother and her baby.
But the sun's rays also have other benefits. For example, they help speed up metabolism, increase immunity, and improve the functioning of internal organs and glands.
Sunbathing also increases the production of vitamin D3. It is he who is responsible for the body’s absorption of calcium, which is necessary for pregnant women. Some of the most common problems that expectant mothers face are hair loss, splitting nails and, of course, dental problems.
It is for this reason that the doctor prescribes calcium-containing medications for pregnant women, and sunbathing will be an excellent help in taking them. And that’s not all: vitamin D3 is the key to ensuring that the child does not develop rickets, and that the bones of his skeleton are formed properly. Therefore, go out into the sun!
Every pregnancy is individual
And finally, we’ll tell you where to start. More precisely, what you need to do first when planning a vacation. Of course, we are talking about going to the doctor.
Only a specialist, having weighed all the pros and cons, will tell you whether you can sunbathe and swim, whether you should go to the sea, and if so, what type of transport.
SMC Best Clinic doctors will responsibly give recommendations on how a pregnant woman should structure her vacation. Follow their advice, follow the rules of staying in the sun and in the water, and then your summer holiday will become not only enjoyable, but also useful and safe.
About the diet
Pregnant women need to strictly limit their diet. Is it really?
An important rule that applies to the diet of expectant mothers at all stages is: avoid undereating and overeating. The body must receive a sufficient amount of macro and micronutrients. Try to adhere to the principles of a healthy diet - look at the recommendations of the World Health Organization.
But there are no special diets for pregnant women. But there are subtleties that pregnant women need to consider when planning their diet:
- Meat, fish and poultry dishes must be fully cooked, eggs must be hard-boiled.
- Wash fruits and vegetables thoroughly.
- Avoid consuming unpasteurized dairy products - they may contain dangerous bacteria.
- The best way to quench your thirst is clean water. By the way, drinking enough water helps prevent edema, which sometimes bothers pregnant women. Your doctor will help you determine your water level.
- It is better to avoid a cup of Americano, cappuccino and latte: for example, scientists from China in a 2021 study concluded that exposure to caffeine causes intrauterine growth retardation and increases the risk of fatty liver hepatosis in the offspring of experimental rats. Experts add that observations of people have not been carried out, but urge pregnant women to abstain from coffee.
- Avoid alcohol: even a glass of champagne on New Year's Eve or on the occasion of an important holiday. Scientists have not yet determined how much alcohol is acceptable for a pregnant woman and does not pose a risk to the fetus. It is known for sure that all alcohol passes through the placenta to the child - draw your own conclusions.
Drinking alcohol during the first trimester increases the risk of miscarriage, premature birth, and low birth weight of the baby.
What can harm the unborn baby?
The development of a baby during pregnancy depends not only on hereditary factors and the initial health status of the future parents. One of the most important aspects affecting the formation and health of the fetus is the lifestyle that the expectant mother leads during pregnancy. Therefore, it is important to understand what exactly can harm the baby during its intrauterine development.
Smoking
A woman who smokes during pregnancy harms not only her health, but also the health of the baby. This bad habit worsens the course of pregnancy, contributes to the development of various complications, negatively affects the growth and development of the fetus and even the health of the baby after birth.
Clinically proven is a high (up to 83%) percentage of the development of respiratory tract diseases in children whose mothers continued to smoke during pregnancy. Among such diseases are tracheitis, bronchitis, pneumonia, bronchial asthma, etc. These children are at risk for contracting tuberculosis.
Another common health problem for children of smoking mothers is pathology of the cardiovascular system. It is known that smoking during pregnancy can cause the formation of various heart and vascular defects in the fetus. Nicotine causes vasoconstriction, which becomes permanent in chronic smokers. This primarily affects blood circulation in the smallest vessels (for example, fingers and toes). The placenta is made up of such small vessels, through which nutrients and oxygen are delivered from mother to baby. In smokers, placental blood flow is chronically reduced due to the effects of nicotine. In this regard, the fetus in such a woman grows and develops worse. And the result is the birth of a child with reduced weight. Such babies often do not correspond to the gestational age at birth, are weakened, and are more susceptible to infectious diseases. They go through a longer period of adaptation after childbirth and tolerate vaccination less well (they often receive a temporary exemption from vaccinations). After childbirth, babies lose more weight than expected, gain it worse, and cannot stay at the breast for a long time (after all, sucking for a newborn is labor that requires effort).
Alcohol
Alcohol, once in our body, undergoes various physical and chemical processes. Alcohol is absorbed into the blood through the intestinal mucosa and enters the general bloodstream. As a result of its processing, half-life products of alcohol are formed, which are toxic to humans. It is with the action of these substances that poisoning, popularly called a hangover, is associated. Since the connection between mother and fetus is carried out through the bloodstream, toxic half-lives of alcohol circulating in the mother's bloodstream can enter the baby's circulatory system. Imagine what harm these toxins can cause to a tiny person with a weak immune system, if even an adult and strong person suffers from a hangover!
Alcohol consumption increases blood pressure (BP). Therefore, for women prone to periodic or systematic increases in blood pressure, alcohol is doubly dangerous. Systematic hypertension (high blood pressure) leads to deterioration of blood circulation in the placenta, the most important organ providing communication between mother and fetus. A decrease in placental blood flow causes disruption of fetal growth and development (FGR - fetal growth retardation syndrome). These are severe and extremely undesirable complications of pregnancy, often requiring long-term hospital treatment.
Another consequence of an increase in blood pressure as a result of alcohol intake may be an increase in the tone of the uterus, which is the main reason for the threat of miscarriage at any stage. Since in this case, uterine hypertonicity is combined with increased pressure in the placental vessels, premature placental abruption may result. This complication requires emergency medical care and threatens the life of the mother and fetus.
Binge eating
Many people think that pregnancy is a wonderful reason to treat yourself to something delicious: extra pounds during this period are natural and will not cause harm. This is fundamentally incorrect reasoning. Extra pounds literally harm the health of not only the mother, but also the baby, sometimes jeopardizing the very fact of pregnancy. Overeating leads to metabolic disorders and the formation of excess weight, increasing the already high load on the cardiovascular system during this period. Against the background of pathological weight gain, the expectant mother’s blood pressure always increases, the tone of the uterus increases, and placental blood flow decreases. As a result of such changes, the fetus experiences a lack of nutrition and oxygen - fetoplacental insufficiency develops, often leading to acute oxygen starvation of the fetus. Pregnant women with significant weight gain (15 kg or more) are at risk for the development of late toxicosis (preeclampsia), characterized by impaired renal function, increased blood pressure, edema and the appearance of protein in the urine. Without timely treatment, this complication can lead to premature placental abruption, heart attacks and strokes, the development of eclampsia (convulsive syndrome), and uterine bleeding. Unfortunately, these dangerous complications, threatening the life of the mother and child, in the vast majority of cases (82%!) develop in pregnant women with pathological weight gain due to overeating.
Physical inactivity
Many women believe that during pregnancy it is safer to give up any physical activity and spend the period of waiting for the baby in the “couch” mode. In fact, completely eliminating physical activity can cause significant harm. The sedentary lifestyle of the expectant mother helps to slow down the general and placental blood flow, which, in turn, negatively affects the nutrition, respiration and metabolism of the fetus. In addition, a decrease in physical activity leads to the formation of venous stagnation in the pelvic area, which usually results in the development of varicose veins of the pelvis, perineum and lower extremities, as well as hemorrhoids. Finally, lying on the couch in combination with an increased diet causes a significant weight gain in the pregnant woman, the sad consequences of which were discussed above.
Excessive physical activity
No less harmful to the fetus than physical inactivity will be increased physical stress. “Forbidden” loads include lifting and carrying heavy objects (over 5 kg), sudden movements, and sports involving abdominal tension. By lifting weights, the expectant mother significantly strains her abdominal muscles, as a result of which the tone of the uterus increases - there is a threat of miscarriage or premature birth (at the end of pregnancy). For the same reason, for the entire period of waiting for the baby, you should avoid any sports, exercises and life situations associated with abdominal tension. It is dangerous for a pregnant woman to make sharp, impetuous movements with raised arms - as, for example, when playing tennis or badminton. With this jerking movement, the diaphragm, the most powerful abdominal muscle that separates the chest and abdominal cavity, sharply contracts. The fundus of the pregnant uterus, located under the diaphragm, also contracts. The placenta, the organ on which the life of the fetus depends throughout pregnancy, is most often attached to this part of the uterus. Through the placenta, the baby breathes and eats, connecting with the mother's body. As a result of a sharp contraction of the uterine fundus, the placenta may separate from its wall. The consequences of premature placental abruption are the saddest - both for the baby and for the mother.
Tight clothes
The problem with tight clothing is that it tightens the tissue and impairs blood circulation in it. With a general deterioration in blood flow, blood circulation at the level of the uterus inevitably decreases. This, in turn, leads to deterioration of nutrition and the development of fetal hypoxia.
In addition, tight clothing limits the growth of the uterus, and for full growth and development the baby absolutely needs a certain living space. Moving in the amniotic fluid, the embryo increases its blood circulation, acquires new skills, and implements reflexes. Finally, limiting the size of the uterus leads to slower fetal growth. Insufficient living space and the amount of fetal fluid can provoke abnormalities in its development: the formation of fusions of organs with each other and with the walls of the uterus, curvature of the skeleton, etc.
Household chemicals
During pregnancy, you should not come into contact with paints, varnishes, acetone and household chemicals. These substances are toxic. For the expectant mother, chemicals are especially dangerous: they have a teratogenic effect, that is, they have a damaging effect on the fetus. Fumes from common household chemicals used for cleaning or repairing a room can cause various developmental disorders of the fetus. Therefore, the expectant mother should firmly refuse personal participation in repairs or home cleaning using such products for the entire period of pregnancy.
Industrial “hazards”
This is a broad concept that includes all types of physical and chemical exposure in the workplace where the expectant mother works, which can harm the health and development of the fetus: noise, significant vibration, too high (hot workshop) or low (refrigeration units, working outside in cold weather). year) ambient temperature, dust and chemical fumes, radiation. All of these work features can have a detrimental effect on the course of pregnancy and indirectly affect the development and health of the baby. Such “harmful things” as contact of the expectant mother with chemical reagents, fumes, harmful radiation, directly affect the fetus and can lead to the formation of severe malformations of the baby. Therefore, a woman working in conditions of harmful production factors has the right to demand that she be transferred to another, safer position during pregnancy.
No self-medication
It is important to understand that an expectant mother who independently “prescribes” herself treatment or “cancels” medications recommended by a specialist risks herself and puts her baby’s health at great risk.
When making independent decisions about the need for a particular examination method or taking a medication, expectant mothers are guided only by their own unprofessional opinion. The most common sources are Internet forums. Unfortunately, the information provided there is often completely unprofessional, is someone’s purely personal experience, and in most cases has an emotional overtones. Without special medical education, it is quite difficult for an expectant mother to distinguish professional advice from word of mouth, determine the applicability of the found recommendation to her specific case, and make the correct diagnostic conclusion. After all, the same symptoms occur in several diseases at once! In order to correctly make a diagnosis and individually select the necessary treatment, you need an objective view of a professional - a doctor who knows and takes into account all the features of the health and course of pregnancy of the expectant mother. Articles on the topic 10 reasons why you shouldn’t be nervous... What you need to know about intrauterine... Treatment with the Andro-Gyn device... Pregnancy calendar Preparing for pregnancy or... Step-by-step instructions for happy... Cervical erosion during pregnancy
Adventurers
There is an opinion that air travel and sudden climate change do not have the best effect on pregnancy. Indeed, after the seventh month of pregnancy, it is not recommended to fly on an airplane - the threat of premature birth is strong. As for flights in general, everything is very individual - much depends on the course of pregnancy and the woman’s health. If the mother does not complain about anything and everything is fine with her unborn baby, then there are no special contraindications for travel. If a pregnant woman has a weakened body, suffers from high blood pressure, or has a high risk of miscarriage, then in this case it is better to avoid traveling by air.
As for visiting exotic corners of the world or places where it is too hot, we must remember that when entering many Asian, African and Latin American countries, it is necessary to be vaccinated against a number of infections, and this is a very big threat to the unborn baby. It is also not known how your body will react to sudden climate change and high temperatures, so doctors recommend refraining from such extremes and choosing more traditional tourism. But no matter how you feel, before you go traveling, you must definitely visit the gynecologist leading your pregnancy.