Bleeding from the vagina during pregnancy is an alarming sign that requires seeing a doctor or calling an ambulance. Let's tell you more about the causes of bleeding and the actions of a pregnant woman.
Bloody discharge can appear at any stage, and in the Russian Federation up to the 20th week of gestation is grounds for hospitalization.
According to the intensity of the discharge, it can be abundant or scanty (“daub”), bright/scarlet or brownish. However, the severity of bleeding is not always proportional to the severity of the pathology/cause.
Implantation bleeding
Develops 6-12 days after fertilization. It occurs a few days before the expected menstruation, when the woman does not yet know about the pregnancy.
What's happening
When attached to the wall of the uterus, the fertilized egg damages the vessels, which begin to bleed.
Manifestations
Bloody discharge is not abundant, lasting 1-2 days. May be accompanied by slight heaviness or discomfort in the lower abdomen.
What threatens
Not dangerous.
Complications
Let us highlight possible complications of individual pathologies. Doctors consider the consequences of ectopic pregnancy to be the most difficult of them:
- There is a possibility that when a pipe ruptures, blood will flow into other organs, which often leads to death.
- Another serious consequence of tubal abortion is peritonitis (purulent inflammation). It occurs as a result of parts of the fertilized egg entering the abdominal cavity.
Failure to go to the hospital in a timely manner during a miscarriage leads to the loss of the child. For a woman, this primarily threatens nervous shock and prolonged depression. And sometimes more complex mental disorders. Other complications include:
- endometritis;
- infertility;
- formation of adhesions;
- difficulties with subsequent conception, as well as bearing a child;
- salpingo-oophoritis;
- large blood losses.
A frozen pregnancy is fraught with the following consequences:
- embryo decomposition can cause sepsis;
- provoke the occurrence of peritonitis;
- Another undesirable consequence of a frozen fetus is endometritis.
Hydatidiform mole can lead to the following complications:
- there is a high risk associated with problems during childbirth;
- in a malignant course, the disease promotes the formation of metastases;
- almost all women experience absence of menstruation;
- various anomalies of generic functions;
- sepsis.
As you can see, the complications are very serious, therefore, if blood appears at least a little during pregnancy 6 weeks or at another stage, you should not hesitate to go to the doctor.
Bleeding on the days of expected menstruation
They can be observed in the first trimester, but sometimes in some women they continue until the 20th week of pregnancy.
What's happening
Bleeding is caused by hormonal changes occurring in the body of a pregnant woman.
Manifestations
Brownish spotting that lasts 1-2 days. Usually painless.
What threatens
They pose no danger to either mother or child.
Blood at 6 weeks of pregnancy
This is a condition related to a number of obstetric symptoms that requires immediate attention to a gynecologist. Every woman who is looking forward to the birth of her baby is interested in taking care of its preservation and normal development. You should not immediately panic in such situations, since physiological factors also have their place here.
It happens that only a drop of blood is found on underwear. At 6 weeks of pregnancy, such symptoms can be of a different nature, so you should understand all the existing causes.
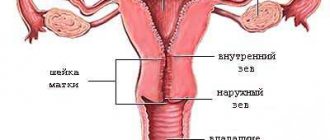
Changes in the cervix
Often there are no symptoms at all, but sometimes they cause minor bleeding from the vagina.
Cervical erosion/ectopia
Mucosal cells from the cervical canal move to the vaginal/outer part (small ulceration occurs).
Causes
Inflammation, hormonal changes, mechanical damage and others.
What's happening
At the site of erosion, the cervical mucosa becomes thinner. During pregnancy, more blood flows to the cervix and the vessels grow. Even a slight mechanical impact on the area of erosion can damage blood vessels and cause bleeding.
Manifestations
Bloody spotting discharge from the vagina may appear after sexual intercourse or a gynecological examination. Lasts 1-2 days..
Is it possible to have sex during pregnancy?Modern obstetrician-gynecologists do not prohibit, but on the contrary, they recommend that expectant mothers continue sexual relations with a partner... |
Reasons for the appearance of blood in the discharge in the early stages of pregnancy
Bloody discharge during pregnancy can be divided into two types:
- physiological, arising due to changes in the ratio of hormones;
- pathological, indicating an abnormal course of pregnancy.
A woman may secrete secretions of varying volumes with red, pink or brown spots, which indicates the presence of blood in it. They may also contain blood clots or tissue particles.
Bleeding during implantation of the fertilized egg
One of the common reasons for the appearance of bloody secretions in the early stages of pregnancy is the implantation of the fertilized egg into the uterus. Implantation bleeding is common in the first to early second weeks after fertilization. Discharge of pink, brown or transparent color with bright scarlet streaks is a consequence of damage to small blood vessels due to the implantation of the embryo.
Women often mistake the appearance of implantation bleeding for the beginning of menstruation, but it lasts much less - from 1 hour to 2-3 days and is characterized by minor discharge. The presence of such discharge without accompanying abdominal pain is considered normal.
Implantation bleeding can occur earlier or later than the specified period, but not earlier than a week after conception. Blood is never dark in color.
Microdamage to the mucous membranes after sexual intercourse or examination by a gynecologist
Bloody discharge in pregnant women after sex appears quite often. Due to changes occurring in the body, the cervix acquires a loose structure, becomes swollen and susceptible to any pressure, which is why microdamages appear on it during coitus. These injuries are not serious and will not harm the fetus. Their appearance is not a reason to terminate intimate relationships, but subsequent sexual contacts should exclude sudden movements.
Blood may also appear during a gynecological examination. At 4–5 weeks, many women, suspecting pregnancy, go to the doctor for the first time and he may accidentally injure the cervix with a speculum. Such damage does not threaten the baby's development.
A similar situation is sometimes observed after a transvaginal ultrasound. Discharge occurs due to hypersensitivity of the reproductive organs, lasts no longer than 2 days and does not recur.
Menstruation during a normally developing pregnancy
During pregnancy, a very small number of patients may have periods. Popularly this phenomenon is called “fetal washing”, in medicine – breakthrough bleeding. Discharge appears on the day when menstruation began earlier. In addition to the discharge, the patient complains of other symptoms of menstruation: pain in the back and abdomen. The bloody secretion is quite abundant, menstruation lasts several days.
Normally, hormones released during pregnancy prevent menstruation from occurring. However, sometimes a malfunction occurs, and their concentration in the body is too low to stop the established monthly cycle. Bleeding usually stops by 3 months. In rare cases, “fetal washing” is possible even at a late stage of pregnancy.
Doctors are wary of such anomalies and carefully monitor the patient’s condition throughout pregnancy. In women with this feature, childbirth often occurs on time, and babies are born healthy, so there is no reason for alarm.
Gynecological diseases not related to gestation
Pregnancy does not protect against gynecological problems; many chronic diseases, on the contrary, worsen during this period, while others are discovered for the first time. Decreased immunity and changes in the amount of hormones produced lead to various pathologies:
- Cervical erosion. The ulcers formed on the mucous membrane make it very sensitive. The capillaries of the organ become overfilled with blood, red spots on the underwear can appear both after sexual intercourse and when sitting with legs tucked. Discharge comes out once after damage to the epithelium; treatment is prescribed after childbirth. This condition does not pose a threat.
- Varicose veins Since pregnancy increases the load on the vaginal veins, the disease can affect the labia area. The perineum hurts, the secretion of lubricant is impaired, sexual intercourse becomes painful. Discharge with bloody inclusions can be detected after sex or for no reason. The disease slightly complicates the course of pregnancy, but is not dangerous.
- Polyp or cyst. A small amount of blood is released, there is no pain. The neoplasm does not pose a threat to the fetus, but if it has been severely damaged, infection may occur. The polyp can gradually exfoliate on its own; the cyst is treated after childbirth.
- Venereal disease. Activation of trichomonas or other microorganisms leads to the appearance of vaginal discharge with a specific odor and bloody spots. The disease is accompanied by itching in the perineum and an increase in thermometer readings, increasing the likelihood of miscarriage.
Pregnancy pathologies (fading, abortion, placental abruption, etc.)
If a woman has uterine bleeding, it can pose a serious threat to her and the baby. The causes of bloody discharge during pregnancy are the following conditions:
- Abortion. Possible in any period for various reasons - from pathologies of the fetus incompatible with further development and extrauterine life to an infectious disease of the mother. Characterized by sudden painful sensations and bleeding.
- Frozen pregnancy. Often observed at 6–7 weeks. The stomach hurts, toxicosis and chest pain disappear. The pathology is characterized by intrauterine fetal death and can be detected during ultrasound, palpation of the uterus or by analyzing the hCG content in plasma for up to 28 weeks. Pain and bloody discharge do not appear immediately, but after a few days. Sometimes the uterus manages to reject the frozen fetus on its own, but more often cleaning is required. Delaying a visit to the doctor can lead to sepsis. With a frozen pregnancy, the risk of miscarriage increases by 15% upon reconception.
- Placenta previa. When it is located close to the uterine os, the muscles are not able to hold it, which leads to the separation of small sections of the placenta. Blood flows like during menstruation. The condition occurs in 2% of women and appears after the 20th week after conception.
- Placental abruption. The phenomenon is diagnosed in 1 out of 200 patients. The process is accompanied by the release of blood clots and cramping pain in the abdomen. Even with partial detachment, there is a threat to the child’s life.
- Umbilical cord tear. A rare occurrence that can result in fetal death. If he is able to survive outside the womb, doctors perform an emergency caesarean section.
- Hydatidiform mole is a pathology accompanied by abnormal growth and increase in the volume of placental tissue (for more details, see the article: Hydatidiform mole: pathological anatomy of the disease). A woman experiences bleeding in the early stages of pregnancy (before the 11th week). The pathology is rare, the cause of its occurrence lies in genetic factors. The pregnancy cannot be saved.
Pregnancy outside the uterus
An ectopic pregnancy is diagnosed in the early stages and occurs due to the fact that the fertilized egg is implanted in the fallopian tube (most often), ovary, cervix, or even in the abdominal cavity, and not in the uterus, as this should normally happen. Vaginal bleeding appears in the 6th week of gestation, when the fallopian tube is stretched to its limit. At the same time, the woman is bothered by nausea and abdominal pain. The discomfort may stop when the pipe ruptures, but after a couple of hours the patient will feel many times worse.
Pregnancy outside the uterus can cause internal bleeding, so it is important to diagnose it early and prescribe treatment. Sometimes this pathology leads to infertility.
Decidual polyp
It is a small outgrowth protruding into the lumen of the cervical canal or beyond.
Causes
During pregnancy, due to hormonal changes, the mucous membrane of the cervical canal grows. Usually the polyp disappears on its own after childbirth, but during pregnancy it can bother the woman.
What's happening
Even a slight mechanical impact can injure the cervix - for example, when using vaginal forms of medications or during sexual intercourse.
Manifestations
There may be slight bleeding from the vagina, which can be observed throughout pregnancy.
What threatens
Risk of infection of the decidual polyp.
Frozen fetus: causes, treatment tactics
This pathology can appear during pregnancy at 6-7 weeks. Blood is released in small quantities, and all signs characteristic of pregnancy suddenly disappear. The mammary glands become soft, the uterus does not correspond to the proper period during a gynecological examination. Along with these symptoms, pain is felt in the lower abdomen with increasing severity and a temperature of 37 to 37.5 degrees is observed.
The causes of the pathological condition include:
- genetic disorders in the fetus;
- acute infections suffered by a woman before or during pregnancy;
- lack of hormones in the mother's body.
Under the influence of any of the above factors, the embryo suddenly stops its development. Ultrasound and hormonal tests will help determine the pathology.
It is important to know that such a condition at the first stage can be asymptomatic for a pregnant woman, therefore, at the slightest such signs, you should immediately undergo a diagnostic examination.
Corpus luteum deficiency
It is more often observed in the first trimester of pregnancy, less often in later stages.
It occurs due to insufficient production of progesterone, the pregnancy hormone, by the corpus luteum.
Causes
Usually not associated with a real pregnancy, but are hidden in problems with the health of the mother - for example, polycystic ovary syndrome.
What's happening
With a lack of progesterone, the tone increases and the growth of the uterus is disrupted - leading to rejection of the uterine mucosa, which is rich in blood vessels.
Manifestations
The intensity of bleeding is related to the degree of progesterone deficiency: the less hormone, the more pronounced the manifestations.
Usually, at the beginning, the bleeding is light and spotting, but then it intensifies.
Aching or cramping pain in the lower abdomen often appears, associated with increased tone of the uterus.
What threatens
Difficulty in implantation of a fertilized egg or spontaneous abortion.
Abdominal pain during pregnancyWhat are the types of pain that occur in the abdomen, and what can they signal? Read more |
Treatment for threatened miscarriage
The implementation of therapeutic measures depends largely on when the expectant mother went to the hospital, how severe the blood loss was and whether the pregnancy was maintained. In any case, she must stay in a medical facility for some time and follow all the gynecologist’s instructions. The complex of treatment measures necessarily includes bed rest. Important rules for a expectant mother who is predicted to be at risk of miscarriage are proper rest and emotional peace.
The therapeutic course involves infusion therapy. To restore the body and prevent further complications, corrective treatment is carried out using the infusion of drugs into the systemic bloodstream. The concentration and volume of solutions is prescribed individually by the attending physician in each individual case. Since treatment is aimed at reducing uterine tone, tocolytic drugs and sedatives may be recommended.
Sometimes hormonal medications are prescribed, for example, Utrozhestan, Duphaston or Progesterone. If it was possible to eliminate the reason why blood began to bleed at 6 weeks, and the pregnancy can be maintained, then the expectant mother should be observed by a gynecologist until the very birth.
Hydatidiform mole
The fertilized egg develops incorrectly, and the membrane surrounding it grows in the form of fluid-filled blisters.
Causes
Fertilization occurs in an egg that does not have chromosomes. The embryo is not viable.
What's happening
The bubbles begin to break away from the wall of the uterus, leading to damage to its blood vessels.
Manifestations
From 11 to 25 weeks of pregnancy, dark-colored bloody discharge containing rejected blisters appears from the vagina. There is usually no pain.
The only way to stop the bleeding is to remove the hydatidiform mole.
What threatens
There is a risk of developing malignant tumors, so after termination of pregnancy, antitumor treatment may be prescribed.
Causes of heavy bleeding and the likelihood of continuing pregnancy
Bleeding during pregnancy is not in all situations a sign of fetal death. A woman should not give in to panic - she needs to urgently consult a doctor.
Severe blood loss can be caused by the following reasons:
- infectious diseases;
- uterine fibroids;
- placental abruption;
- uterine rupture (a very rare anomaly that occurs during a hydatidiform mole or after a previous delivery by cesarean section);
- rupture of the fallopian tube;
- lack of hormones;
- spontaneous abortion.
Most often, if the patient is hospitalized in a timely manner, doctors can continue the pregnancy. If there is a high risk of miscarriage, she is admitted to the hospital. Doctors always strive to preserve the life of the baby, but if there is a choice, it is made in favor of the health and life of the mother. However, the consent of the woman (or her relatives when the expectant mother is unconscious) is mandatory.
Early in gestation, it is important to stop bleeding and prevent miscarriage. For this purpose the following are assigned:
- means for increasing the secretion of progesterone (Utrozhestan and Duphaston);
- vitamins (E, B6);
- sedatives (valerian tincture);
- hemostatic medications (Ditsinon);
- antispasmodics (No-Shpa).
When the first positive results of treatment appear, the woman is prescribed rest, bed rest and cessation of intimate life until the time of birth. The drugs are often prescribed over a long period of time and must be taken even in the absence of bleeding. Having crossed the threshold of the 12th week of gestation, you can calm down - the risk of miscarriage is significantly reduced.
Therapy for placenta previa depends on the amount of discharge. If there is little blood and the time of delivery is close, a puncture of the amniotic sac is performed. If there is copious discharge, a cesarean section is indicated, even if the fetus is not full term. Surgical delivery is also required in case of blood loss due to placental abruption.
If bleeding occurs as a result of pregnancy outside the uterus, a frozen fetus or a miscarriage, then one cannot be under any illusions - it is impossible to save the child in these situations. Surgical treatment: the woman undergoes removal of the embryo (or fallopian tube) or curettage of the uterus, respectively.
Ectopic pregnancy
Occurs when the fertilized egg does not descend into the uterine cavity.
Causes
The fertilized egg can attach in the cavity of the fallopian tube, on the ovary or in the abdominal cavity.
What's happening
At the site of its attachment, the fertilized egg damages the blood vessels, which causes bleeding. Tubal pregnancy occurs most often.
Manifestations
At the initial stage, slight spotting bloody discharge from the vagina may appear, accompanied by nagging or cramping pain in the lower abdomen.
As pregnancy continues, the fallopian tube ruptures, causing bleeding from the vagina and into the abdominal cavity (internal bleeding).
Acute pain occurs in the abdomen on the side where the fertilized egg is attached. Blood accumulates in the space behind the uterus, so pain can radiate to the rectum.
What threatens
If an ectopic pregnancy is not diagnosed in a timely manner, heavy bleeding develops, which is life-threatening.
Treatment is surgical. With timely diagnosis, the fallopian tube can be saved; if it ruptures, it is removed.
Diagnosis and treatment
The doctor will conduct an examination, take a smear from the vagina, and prescribe an ultrasound of the pelvis. The woman also needs to donate blood for general and biochemical analysis and group determination. Based on the results, the gynecologist will prescribe further treatment.
In case of a miscarriage, you will need to clean the uterus; if an ectopic pregnancy is detected, then a diagnostic laparoscopy is performed. If the cause of bleeding is the threat of miscarriage, then the woman will be prescribed medications to maintain pregnancy and bed rest, and hospitalization is possible.
Premature placental abruption
May occur after 16 weeks of pregnancy or during childbirth.
Causes
Diseases of the tissue (kidneys, heart and blood vessels), malformations of the uterus (bicornuate, septum), insufficiency of the corpus luteum, fetoplacental insufficiency, gestosis/toxicosis, polyhydramnios during real pregnancy and others.
What's happening
Small hematomas (containing blood inside) form between the placenta and the wall of the uterus, merging with each other and peeling the placenta away from the wall of the uterus.
Manifestations
With a small detachment, the bleeding is not abundant. Damaged vessels can thrombose (a blood clot forms) and further placental abruption is stopped.
When detachment occurs over a large area, bleeding is usually profuse.
Detachment is accompanied by increased uterine tone. There are nagging pains in the abdomen and lower back, sometimes they are quite pronounced and resemble pushing.
What threatens
Blood flows poorly to the child - the delivery of oxygen and nutrients is disrupted.
There is a risk of developing heavy bleeding, which threatens the life of both mother and child.
Accumulated blood can serve as a substrate for infection and/or lead to premature rupture of the membranes.
Read more - Leakage of amniotic fluid. Signs and diagnosis
Hypertonicity of the uterus during pregnancy
Main reasons
In view of the above, a mother who is worried about the health of her unborn baby may have another question, which is quite appropriate: what can it mean that the implantation process is completed, the 6th week of pregnancy is already underway and bleeding has begun? All reasons associated with such discharge can be divided into two types: physiological and pathological in nature. The clinical picture of bleeding directly depends on this. For example, with progesterone deficiency, biological fluid from the genitals is released abundantly, as during menstruation:
- Physiological factors. During pregnancy, a woman’s body is a rather complex mechanism that undergoes a number of natural transformations. When a new life is born in it, its functioning changes radically. To maintain gestation, it begins to actively synthesize certain types of hormones. Therefore, against the background of restructuring of the body (in some cases), discharge in the form of biological fluid is considered normal and passes without pain. Blood at 6 weeks of pregnancy can sometimes indicate physiological causes. The expectant mother will feel slight dizziness, slight weakness and nausea.
- Abnormal reasons. Pathological bleeding manifests itself in a completely different way, posing a threat to the health of the woman and the life of the baby. This includes abnormal development of the embryo in the fallopian tube, which is unnatural, and gynecological diseases, which usually cause bleeding. Pregnancy at 6 weeks can be interrupted due to spontaneous abortion. In this case, the biological fluid comes out in the form of brown clots. With such bleeding, it is necessary to change sanitary pads at intervals of two hours. This is a rather unpleasant process, accompanied by acute pain in the abdomen. If such signs appear, you should urgently call an ambulance.
Incorrect placement of the placenta (previa)
The normal location of the placenta is the upper or middle part of the uterine body. In case of presentation - in the lower part, completely or partially blocking the pharynx (entrance) of the uterus.
Causes
Poor circulation and/or atrophy (thinning) of the mucous membrane of the uterine wall, making it difficult for the fertilized egg to attach.
What's happening
As the gestation period increases, the uterus grows, but the placenta does not stretch, which leads to its detachment and damage to blood vessels.
Manifestations
Starting from 16 weeks of gestation, light, painless bleeding from the vagina periodically appears and disappears.
What threatens
Weakness of labor, insufficient oxygen supply to the fetus, risk of heavy bleeding in the early period after childbirth.
Diseases
In addition to abnormal phenomena and emergencies, various diseases can develop in a woman’s body. It is important to be vigilant, since blood at 6 weeks of pregnancy without pain can be observed with the development of fibroids, polyps and erosion. Often the presence of such diseases does not affect the general well-being of a woman, and therefore they cannot be detected immediately.
Cervical erosion occurs during pregnancy in many women, including nulliparous women. Gynecologists advise treating it until the moment of conception. This reduces the risk of epithelialization and possible complications throughout the entire period of pregnancy. With erosion, any mechanical stress can lead to unwanted discharge from the reproductive system. Doctors do not advise immediately treating this disease. If you wait a little, the erosion may go away on its own; most often this happens after delivery. However, in some cases, therapy is carried out only for specific clinical indications.
With varicose veins, very little blood may leak from the genitals. Pregnancy of 6 weeks with this disease is a difficult stage for some. It happens that it is accompanied by a rupture of a blood vessel passing in the area of the uterus. In this case, heavy bleeding is observed.
Spontaneous termination of pregnancy
More often it occurs in the early stages (miscarriage), less often in the later stages (premature birth).
Causes
Almost all of the above conditions can lead to spontaneous abortion.
Most often occurs with:
* thrombophilia - the blood clotting system is disrupted and the risk of thrombosis increases (antiphospholipid syndrome, congenital insufficient production of certain clotting factors, etc.);
* endocrine diseases: gestational diabetes mellitus, thyroid diseases, increased levels of male sex hormones;
* immunological incompatibility of spouses, insufficiency of the corpus luteum;
* chromosomal and genetic abnormalities of the fetus;
* malformations of the uterus, etc.
What's happening
Gradual rejection of the fertilized egg (in the early stages) or placental abruption (in the later stages).
Manifestations
The onset of the threat is manifested by nagging pain in the lower abdomen and lower back. If the fertilized egg passes or placental abruption begins, light brown or deep red bloody discharge appears from the vagina.
What threatens
Development of bleeding and loss of the child. However, it is not necessary to continue the pregnancy in all cases; sometimes it is better to trust Nature, which gets rid of an obviously non-viable or sick baby.
What vaginal discharge is considered normal during pregnancy?
Any vaginal discharge can be a variant of the norm or a sign of pathology; a gynecologist can differentiate one from the other, based on the results of the diagnosis. In the early stages of pregnancy, the hormone progesterone is responsible for the functioning of the reproductive organs, and in the second trimester - estrogen. They are responsible for the nature of the secretion released from the vagina.
At different times, discharge is normal (by week):
- 1–3 – mucous discharge with red streaks or yellow, brown discharge, lasting several days;
- 4 – thick white secretion, reddish inclusions are possible;
- 5–12 – clear or white discharge, which can sometimes have a slight sour odor;
- 13–25 – liquid transparent secretion, the amount of which, compared to the 1st trimester, is increased;
- 26–36 – copious white discharge with a sour odor;
- 37–40 – moderate volume of secretion with a whitish color;
- before childbirth - mucus with blood streaks.
Bloody discharge that appears from 4–6 weeks and lasts until the end of the 12th week of pregnancy can be:
- transparent with 2–3 drops of blood;
- pink;
- brown;
- scarlet.
If they happen once and are not accompanied by painful sensations, then there is nothing to worry about. However, the ideal option is light, almost transparent discharge. They indicate normal functioning of the genital organs, a change in the epithelial layer of the uterus and the absence of signs of the presence of pathological microorganisms.
What can I do to prevent miscarriage?
A woman cannot stop a miscarriage on her own. The main thing is to calm down and call a doctor. The doctor will prescribe the necessary tests, which will tell you about the cause of the miscarriage and the possibility of continuing the pregnancy.
Very rarely, the cause of miscarriage is the mother's wrong actions. The main thing that future parents should do when planning a pregnancy is to undergo a medical genetic examination to find out genetic compatibility. There you can also obtain information about the risk of a genetic disease in a child, if one occurred in the family of one or both parents.
How will the doctor determine the cause of my bleeding?
Vaginal bleeding, spasms and pain are a reason for additional examinations. First of all, the gynecologist who is managing the pregnancy will prescribe an ultrasound examination, blood and urine tests.
If the cause of ongoing bleeding is not a serious pathology, then the doctor will limit himself to the following recommendations:
- rest;
- bed rest;
- ban on having sex.
For more serious causes of vaginal bleeding, hospitalization and further diagnostics will be required.
Your doctor will want to know the answers to the following questions:
- Have you had any bleeding during this or a previous pregnancy?
- When did the bleeding start?
- Is the bleeding heavy or is it blood spots?
- Does the bleeding start and stop or go on and on?
- Approximately how much blood was lost?
- What color is the blood (bright red or dark brown)?
- Is there any discharge along with blood?
- Does blood have a smell?
- Any cramping or pain?
- Are you feeling weak, tired or dizzy?
- Have you had vomiting, nausea or diarrhea?
- Has your temperature risen?
- Have you had any recent injuries (such as a fall or car accident)?
- What was your last physical activity?
- Was there any additional stress?
- When was the last time you had sexual intercourse? Was there any blood after sex?
- Do you have a bleeding disorder? (women with bleeding disorders are at risk of complications during and after pregnancy - iron deficiency anemia, postpartum hemorrhage and bleeding during childbirth; before planning a pregnancy, a woman with bleeding disorders should consult a doctor, in addition, you can undergo special genetic testing, so how this pathology is often inherited).
- What is your blood type and Rh? (if a woman has a Rh-negative blood type, additional treatment with Rho (D) immunoglobulin will be required. This prevents complications in future pregnancies).
Vaginal bleeding is usually blood without clots. If clots are released along with the blood, they must be collected in a separate container and then shown to the attending physician.
An additional test will be to determine the level of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG). This is a specific pregnancy hormone that rapidly increases every two days after conception. During an ectopic pregnancy, hCG is greatly reduced, which may alert the doctor. Then he will send the patient for further examinations.
Recommendations from experts
It would be good for every expectant mother to know how to behave correctly in emergency situations. For example, what recommendations do experts give regarding when bleeding starts at 6 weeks of pregnancy, what should be done, and what should be avoided. Taking into account the various causes of such conditions, you should contact the hospital immediately, while observing some rules:
- With minor spotting that goes away painlessly, you can get to the hospital on your own, if it is located near your place of residence.
- Excessively massive bleeding and the bright color of biological fluid are reasons to call an ambulance at home and under no circumstances go to the doctor without waiting for her.
- While the doctor arrives, you need to take some measures: lie down on a flat surface, take a horizontal position and place a pillow under your feet.
- It is strictly forbidden to take any medications before the ambulance arrives. This can blur the symptoms and complicate the gynecologist’s task in establishing the correct cause of what is happening.
- Even at the initial stage of bleeding, you should not shower or wash with too hot water. This will only increase pathological discharge.
- Signs such as cold sweats, fainting and intense pain may indicate an ectopic pregnancy. In this case, every minute counts because a pipe rupture may occur.
What improves pregnancy?
In order for the pregnancy to develop normally, the child in the womb to grow strong and healthy, you should follow some tips:
- limiting smoking and drinking alcohol by the mother herself and people living next to her;
- prohibition of drug use;
- ban on the use of tampons, they can cause infectious-toxic shock.
It is worth talking to your doctor about additional medications that have a beneficial effect on pregnancy. Folic acid is usually prescribed. However, both low and high folate status can trigger the development of complications. Therefore, the use of this drug should be strictly under the supervision of the attending physician.
What to do if you notice vaginal bleeding?
Any vaginal bleeding during pregnancy may be a symptom of a larger, more serious problem. Therefore, be sure to contact your doctor or your midwife as soon as you notice it, even if the bleeding has already stopped on its own. Also, if you call an ambulance, it is very important to be prepared to talk about the amount of blood you have lost and correctly describe your general condition. You should see if the bleeding is ongoing and also notice if you have any other symptoms, such as pain, fever or dizziness.