From this article you will learn
- what is dental granuloma,
- her appearance in photographs and x-rays,
- How is granuloma on the root of a tooth treated?
Dental granuloma is an inflammatory formation at the apex of the tooth root, which is a proliferation of granulation tissue. Its development is associated with infection of the root canals and the further development of chronic inflammation at the apex of the tooth root - chronic apical periodontitis. In dentistry, the broader term “apical granuloma” is usually used to refer to this disease, which already implies the location of the source of inflammation directly at the apex of the root (from the word apex - apex).
The granuloma is tightly attached to the root apex, and therefore, when a tooth with a granuloma is removed, the latter usually comes out along with the tooth (Fig. 1-2). It is important to note that granulomas are inflammatory formations only up to 0.5 cm in diameter, but they tend to grow slowly. And if, due to lack of treatment, the granuloma becomes larger than 0.5 cm, then dentists call this inflammatory formation the term “cystogranuloma.” A formation with a size of 1.0 cm is usually called the term “radicular cyst”. Therapy for granulomas is always conservative, but treatment of a cyst may require resection of the tooth root.
What is dental granuloma: photo, diagram
But granuloma differs from cystogranuloma and radicular cyst not only in size. The fact is that a granuloma is not a cavity formation, i.e. inside it there is no cavity filled with pus - like cystogranuloma and radicular cyst. Morphologically, a granuloma is an area of proliferation of inflammatory granulation tissue, surrounded by a fibrous membrane (capsule), due to which the granuloma is tightly attached to the apex of the tooth root.
Outside of periods of exacerbation of the inflammatory process, there is no cavity with pus in the granuloma, i.e. inside the fibrous capsule it is completely filled with granulation tissue. However, during periods of exacerbation, pus forms inside it, the pressure of which on the walls of the capsule from the inside can lead to rupture of the fibrous capsule and the release of pus into the bone tissue and further under the periosteum. The slow growth of granuloma in size leads to its transformation into cystogranuloma (from 0.5 to 1.0 cm), inside of which a cavity is already formed, filled with purulent contents even outside periods of exacerbations.
Tooth granuloma
Granuloma on the root of a tooth - what is it and why does it appear? Granuloma is an inflammatory formation that affects part of the root. It is the initial stage of a granular cyst and differs from it only in its smaller size. The disease is characterized by the formation of a purulent sac of granular tissue. The sac is surrounded by a fibrous capsule that connects to the apex of the tooth root.
The appearance of a granuloma under a tooth indicates that an inflammatory process is underway. Before installing dentures, it must be eliminated, otherwise the granuloma will grow under the crown.
The formation of a focus of inflammation in the jaw bone is the body’s defensive reaction to the attack of pathogenic microbes. A dense connective capsule is formed around the lesion, isolating it from the healthy bone. But this protection does not last forever, so granuloma is often compared to a time bomb.
Classification
Depending on the location and other features of granulomas, there are:
- Subcutaneous - more often found in children, located on the scalp, near the eyes and on the limbs.
- Plaque - usually occurs in women, they are characterized by the presence of erythematous, red-brown or purple plaques without ring-shaped rims.
- Localized and disseminated - as a result of pathology, a single lesion can form or spread to other parts of the body.
- Perforating - this type of dermatosis is quite rare and is characterized by the presence of plugs in the center of formations and gelatin-like discharge, as well as the formation of larger plaques, crusts and further scarring.
- Interstitial form (with a mucin infiltrate between collagen fibers) and frontal form (there is collagen surrounded by histiocytes).
Histology: front garden form of granuloma annulare
Symptoms
Even having an idea of what dental granuloma is, its symptoms are not so easy to determine. The fact is that the disease may not manifest itself for a long time. The tooth under which the formation is located may not outwardly stand out in the dentition. The gums may also look quite healthy.
In some cases, the disease is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- swelling of facial tissues;
- swelling of the gums;
- slight increase in temperature;
- the occurrence of flux;
- acute pain in the area where the granuloma has formed;
- slight discharge of pus between the tooth and gum;
- pain in the eyes, migraine, dizziness;
- On palpation there is acute pain.
Good to know. Granuloma often makes itself known if a person has had a cold, flu, pneumonia and other diseases that lead to a decrease in immunity.
Dynamics of disease development
The disease is characterized by a slow course, so the intervals between stages can take up to six months, and if there are no provoking factors, then the development of the process slows down even more.
The following stages are distinguished:
- primary;
- active (the height of the disease);
- final.
At the primary stage, due to the activity of microorganisms in the source of inflammation, periodontal tissue thickens. Granulomatous tissue gradually takes up more and more space and replaces dead healthy cells. A sac is formed, in the cavity of which there is liquid with fragments of bacteria, immune cells, and toxic substances released during tissue death.
During the active stage, the tumor becomes larger in size as more and more cells die and more microbial waste products accumulate in the affected region. The granuloma capsule contains a significant amount of inflammatory fluid.
At the last stage, the formation of the focus is completed. The granuloma is already so large that it begins to put pressure on surrounding tissues and cause discomfort to the patient. The root of the tooth and bone tissue can be so damaged by chronic inflammation that the tooth begins to loosen and its destruction will occur.
Causes of granuloma
What causes dental granuloma? Among the main factors provoking the formation of a focus of inflammation, the following should be highlighted:
- treatment of pulpitis was carried out poorly (for example, tissues affected by caries were not completely removed);
- the dentist filled the root canals in violation of the rules of asepsis and antisepsis;
- the tooth was injured directly due to damage to the maxillofacial area, unsuitable orthodontic design or for other reasons.
Granuloma annulare in children
The disease in children manifests itself in the form of widespread benign granulomatous dermatosis. Foci of skin lesions in childhood most often develop spontaneously in the first years of life or after shingles or warts as a result of changes in the functioning of the immune system. For most, they are single - on the limbs or head (as in the presented photo of granuloma annulare in children), but can spread to other parts of the body, for example, joint bends.
Granuloma annulare in a child
If signs of the development of granulomas are detected, the initial treatment of the child should be aimed at treating concomitant chronic pathologies and correcting nutrition.
How is dental granuloma diagnosed?
Diagnosis at an early stage is almost impossible. Even a dentist with extensive experience will not always be able to visually determine the occurrence of a granuloma under a tooth; this will require additional research. Most often, a neoplasm is discovered completely by accident during radiovisiography, which was prescribed for a completely different purpose.
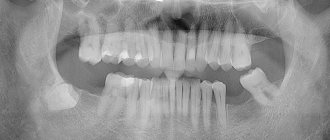
To confirm the diagnosis, the patient is prescribed radiography. Using this study, it is possible to differentiate dental granuloma from other diseases. In the picture, the source of inflammation and its location will be clearly visible. Based on the results of the study, the most suitable treatment method is prescribed.
In the photo you can see what granuloma of the gums and teeth is and what it looks like.
It is important to know. Unfortunately, it is not always possible to save a tooth under which a cyst has formed. If the tooth is already partially destroyed or has a vertical crack, it must be removed.
Symptoms, signs of the disease and diagnostic methods
The clinical picture of granuloma at the initial stage is erased. In most cases, there are no alarming symptoms, and the patient may notice only minor changes in the condition of the affected tooth:
- a change in the color of the enamel, in which it becomes yellow, gray or another shade;
- pus is released from the gum pocket;
- The gums near the diseased tooth become red and periodically swell.
During an exacerbation, the patient is bothered by acute pain. This sign allows you to differentiate dental granuloma from other diseases, because other inflammatory processes of the teeth and gums are accompanied mainly by throbbing or aching pain. Redness of the gums and its swelling is accompanied by the formation of a purulent abscess (flux), and sometimes an increase in body temperature, general weakness, and headache.
The combination of these symptoms should be a signal to immediately contact a dentist, because if left untreated, the granuloma will develop further, destroying an increasingly larger area of bone tissue. Such processes lead to the formation of extensive suppuration with melting of bone tissue. In addition to tooth loss, this pathology can lead to the formation of a fistula in the jaw, which can break not only outward (into the oral cavity, onto the surface of the skin on the face), but also into the maxillary sinuses. In addition, the infection can spread through the circulatory system, negatively affecting the functions of internal organs and systems.
Various instrumental methods are used to confirm the diagnosis. External examination and examination in the dentist’s office are not very informative, because the source of inflammation is located deep in the gums. Instrumental radiological methods are used to visualize granulomas:
- X-ray of the jaw;
- radiovisiography (digital radiography using minimal radiation doses).
On photographs, a dental granuloma appears as a clearly defined, rounded neoplasm that adheres tightly to the roots or partially merges with the apex. It looks like a darkened area, which indicates the presence of pus in its cavity.
Treatment options for granuloma
Treatment of the tumor consists of eliminating the source of infection and preventing relapse. Therapeutic and surgical techniques are used.
Therapeutic method
It will bring results only if the disease is detected at an early stage. The patient is prescribed antibiotics and sulfonamide medications. Timely treatment will help eliminate the infection and save the damaged tooth.
Non-surgical method
It appeared relatively recently, the essence of the method is as follows: the affected tooth canal is expanded and a substance is introduced into it that destroys the infection.
Surgical method
It is used if the granuloma has grown greatly and the use of drug therapy will be ineffective. During the operation, the dentist cuts the gum to allow pus to come out. Then a drainage is installed in the tooth, which the patient must endure for three days. Also during this period, drug therapy is carried out. After three days, another operation is performed, during which purulent sacs, tumors, or a tooth root with a cyst are removed. Then the doctor makes a decision about the fate of the tooth: it is either left or removed.
Removal is necessary in the following cases:
- the tooth is so damaged that it can no longer be restored;
- root canals cannot be treated;
- the cause of inflammation was problems in the periodontal pocket;
- the patient is undergoing a prosthetic procedure;
- cracks have formed in the area of the tooth or its root;
- There are multiple perforations of the tooth.
In other cases, doctors try to save the tooth.
How is the treatment carried out?
To eliminate granulomas, conservative therapy is more often used. The root canals are processed, cleaned, and then filled with temporary material. After 2-3 weeks and after a second photograph, a permanent filling material is installed. If the canals are very narrow, tortuous, and there is a pin in the root, then the granuloma can only be eliminated surgically. Also, such removal is resorted to if a good crown is installed on a tooth, but the patient does not want to remove it. If there is a formation at the root of the tooth, you should not hesitate. Contact qualified specialists of the UniDent clinic. Doctors will perform all procedures efficiently and painlessly. You can make an appointment at the above number.
Expert advice and recommendations
Having figured out what kind of disease this is - dental granuloma, you can protect yourself from it. To do this you need to follow a few simple rules:
- undergo preventive examinations every 6 months;
- contact your dentist in a timely manner if any unpleasant symptoms from the dental system occur;
- treat caries at an early stage;
- carry out hygiene procedures regularly;
- change the brush monthly.
Dentists at the Saint-Dent Clinic in Moscow will offer patients a modern and comprehensive approach to the diagnosis and treatment of dental granuloma. Only the most effective treatment methods and high-quality materials are used. You can find out the cost of services here PRICES. The contact section is located here CONTACTS.
Diet for granuloma annulare
Diet for skin diseases
- Efficacy: therapeutic effect after a month
- Time frame: three months or more
- Cost of products: 1400-1500 rubles per week
Since the etiology and pathogenesis of the granulomatous process are not fully understood, it is important to activate the internal forces of the body and normalize metabolism. This is possible thanks to diet correction and giving up bad habits (alcohol, smoking, irregular sleep).
Many nutritionists consider the main problem of modern society to be carbohydrate metabolism disorders caused by the consumption of large amounts of synthetic sugars and the availability of simple, easily digestible carbohydrates. Therefore, you should start your diet by reducing the consumption of refined sugar, confectionery, bakery and pasta products.
In addition, it is necessary to ensure the supply of all nutrients necessary for normal life - proteins, fats, natural sugars, vitamins. The diet should be balanced, consisting of fresh salads, fruits, cereals, meat and seafood. It is necessary to give preference to dietary methods of preparation - boiling, stewing, steaming.