While measuring your blood pressure with a tonometer, did you notice that your blood pressure is higher than normal? It is important to know what high upper pressure means and what consequences it can lead to in the future. You can talk about hypertension and the need for its treatment when the systolic reading regularly jumps up by 20–30 mmHg. Art. Moreover, it is the upper numbers that cause the appearance of characteristic symptoms. The lower levels may be normal or even decreased, but more often they increase almost synchronously. It is important to find out what causes blood pressure to rise, whether the pathology is a primary disease or reflects other processes in the body.
Diagnostics
Have you suspected or discovered that you have high blood pressure?
Make an appointment with your GP as soon as possible. The doctor will conduct an initial examination, which will allow you to establish an accurate diagnosis and select adequate treatment. In most cases, the diagnosis of systolic hypertension includes:
- Anamnesis collection . The doctor conducts a conversation with the patient regarding the existing symptoms of the disease, lifestyle, as well as the presence of concomitant pathologies. All this allows the specialist to make an assumption regarding the possible causes of the increase in upper pressure.
- Physical examination . It involves the doctor listening to the heart using a phonendoscope, during which the specialist has the opportunity to determine the presence of a murmur in the heart, disturbances in its sounds, and other associated abnormalities.
- ECG . The most popular diagnostic method for high systolic pressure, which allows you to confirm the diagnosis of “systolic hypertension”, as well as identify heart rhythm disturbances.
In some cases, the patient may be prescribed Holter monitoring (daily cardiogram).
- Ultrasound of the heart . An auxiliary diagnostic method, during which disturbances in the functioning and structure of the heart valves, and serious defects in the structure of the heart muscle are detected.
- Doppleography . _ A diagnostic method that allows you to assess the condition of the vascular system. With systolic hypertension, it is important to monitor the condition of the arteries leading from the heart to other organs and their systems.
- Laboratory research methods . Most often we are talking about a general analysis of urine, blood, and a blood biochemistry test that determines cholesterol and sugar levels.
If necessary, the therapist can refer the patient for consultation to specialized doctors - a cardiologist and an endocrinologist.
Prevention
The coherence of the heart and blood vessels is a key link in the health of the whole organism. Thanks to preventive measures, it is possible to maintain their harmony, thereby preventing the development of hypertension. These include:
- a measured lifestyle with adequate physical activity;
- weight loss to normal levels;
- balanced diet;
- quitting smoking, alcohol, drugs.
If the symptoms described above appear, you should begin to systematically measure blood pressure using a tonometer. Regardless of the reasons for high blood pressure, its long-term retention at high levels is a reason to contact a therapist or cardiologist.
What is the danger?
The situation when systolic pressure increases one-time due to temporary reasons (for example, strong emotional overexcitation) is not quite dangerous. As soon as a person manages to cope with his experiences, the pressure normalizes on its own.
A frequent increase in the indicator is a rather dangerous phenomenon that can lead to all sorts of complications:
- hypertensive crisis;
- circulatory disorders in the brain - stroke;
- acute myocardial infarction;
- rapid development of heart failure;
- rapid development of irreversible kidney pathologies.
One of the most dangerous complications of increased upper pressure is the development of malignant hypertension. This pathology cannot be treated: 2-3 months after the development of the disease, the patient dies due to the appearance of associated complications.
Classification
| Classification according to changes in diastolic pressure levels | Classification by stream |
| Type 1 (60%) – no increase. Type 2 (40%), or “burnt-out hypertension” - a gradual transition of the form with increased numbers of upper and lower pressure into ISAH. | Stable – fluctuations in upper pressure are insignificant, a crisis increase is extremely rare. Labile or crisis - pronounced fluctuations in systolic pressure with frequent hypertensive crises. |
Why does blood pressure rise?
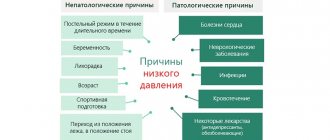
If high systolic pressure is observed with normal diastolic pressure, we should talk about the reasons for the unpleasant situation. Why does blood pressure increase:
- severe stress, emotional shock;
- excess weight;
- negative emotions;
- heredity;
- kidney diseases;
- taking certain medications.
An increase in blood pressure is not dangerous in a one-time event - you can easily get rid of it and forget about it. It is much more serious when it becomes a permanent illness. Chronically elevated upper blood pressure threatens:
- What do upper and lower blood pressure mean?
- impaired blood flow in the brain;
- stroke;
- anemia;
- acute heart attack;
- heart failure;
- kidney pathologies;
- malignant hypertension and death.
Symptoms of identifying indications of increased upper blood pressure with normal lower blood pressure:
- insomnia;
- swelling of the face (fluid retention);
- numbness of fingers;
- headache, dizziness, tinnitus;
- irritability, weakness;
- vegetative manifestations - anxiety, chills, red face, rapid pulse, lack of coordination.
Why is the upper pressure high and the lower normal?
The main factor in the development of a situation in which the upper pressure is increased while the lower pressure is normal is considered to be atherosclerosis of the aorta and its large branches. As you grow up and age, systolic blood pressure increases - the stiffness of the arteries increases, and the elasticity of the arteries decreases. Diastolic up to 50 years of age increases along with the upper one, but after the age limit it begins to decline, while systolic continues to increase.
The reason for this behavior is the stiffness of the blood vessels, the blood flows more slowly into the capillaries. This occurs due to the development of atherosclerosis, diabetes mellitus, thyroid diseases, valve insufficiency between the aortas and veins, and the formation of plaques. Increased blood pressure leads to isolated systolic hypertension. Every fifth elderly person suffers from this variant of the disease.
Symptoms and signs of high blood pressure
Many people know that hypertension is often asymptomatic, but this is noted only at the beginning. Constantly high blood pressure over time results in a number of clinical symptoms:
- The first signs: rare headaches, dizziness, fatigue, weakness, nervousness, sleep disturbance;
- As it progresses: headaches in the occipital region, “tingling” in the heart area, the appearance of shortness of breath during light physical activity (walking, for example), a feeling of heartbeat, “spots” before the eyes, visual impairment.
External signs of hypertension in men and women are no different. The difference in symptoms mainly depends on the level of pressure and the rate of its increase. Often a sharp increase in blood pressure threatens the development of a hypertensive crisis and rupture of the vessel wall.
Definition
Systolic pressure is called top pressure because it is the top number on the sphygmomanometer screen. This indicator characterizes the pressure that occurs at the moment of contraction of the heart muscle - at the moment of blood ejection from the heart into the arteries.
Doctors call a condition in which the upper blood pressure (BP) is elevated systolic hypertension. Most often, this situation is observed at a time when the lower pressure remains within the normal range and does not go beyond 90 mmHg. Art., and the upper one is determined at a level of 140 mm Hg. Art. and higher.
In 90% of cases, the increase is diagnosed in elderly people who have crossed the age mark of 50 years. Most often, women who have concomitant diseases of the cardiovascular system are at risk.
- High lower pressure - causes and treatment with drugs and folk remedies
High blood pressure: diagnosis of causes
The disease we are going to talk about has many faces. High blood pressure and everything connected with it is the topic of our conversation today.
Why is high blood pressure so dangerous? Can you trust a tonometer? These and other questions are answered by the general practitioner, cardiologist at Clinic Expert Voronezh LLC, Angelina Anatolyevna Kalinina.
- Angelina Anatolyevna, there is a lot of controversy around high blood pressure. Russian and Western doctors give different numbers. Let's first define what we mean by high pressure? High – how much?
When talking about blood pressure, we use the concept of so-called “upper” (more correctly, systolic) and “lower” (diastolic) pressure. High blood pressure is a situation where the systolic pressure is 140 mmHg. and higher, and diastolic - 90 mmHg. and higher.
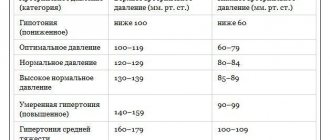
Classification also distinguishes such gradations of blood pressure as optimal (systolic less than 120 mmHg, diastolic - less than 80 mmHg, the lower limit of systolic blood pressure is approximately taken to be 110-115 mmHg, diastolic - 70-75 mmHg), normal (systolic - 120-129 mmHg, diastolic - 80-84 mmHg), high normal (systolic - 130-139 mmHg .art., diastolic - 85-89 mmHg).
- It is known that children have their own blood pressure standards for each age stage. Does blood pressure change with age in adults?
Today, medical opinions on this matter differ. The latest clinical recommendations say the following: if in elderly and senile people the systolic pressure is 140-150 mmHg. If you feel well, it is not necessary to strive to unconditionally reduce it below 140 mmHg. However, diastolic pressure should also not exceed 90 mmHg.
- They say that the tonometer can make mistakes. This is true?
This can often be heard, in particular, about electronic blood pressure monitors. Actually this is not true. If the device is working properly, it shows the correct blood pressure numbers. Another point is that these devices may be more sensitive to the conditions and rules for measuring blood pressure. For example, the position of the patient, his arms, and legs matters.
Ideally, half an hour before taking readings, a person should not eat, worry, exercise, or smoke.
If you have doubts, it is recommended to measure the pressure three times at 2-3 minute intervals, and take the average readings for the upper and lower pressure.
- You don’t always have a tonometer at hand. Therefore, it is important to know what symptoms indicate high blood pressure?
The question is very relevant because high blood pressure is not always accompanied by any symptoms.
Those who make complaints note such manifestations as headache, dizziness, nausea; “flickering of flies” before the eyes; blurred vision; feeling of heat, “hot flush”, sometimes chills; discomfort in the chest area; feeling of fear, anxiety, anxiety; urge to urinate. These are the most common symptoms.
- For what reasons does blood pressure increase in an adult?
This is a complex and, unfortunately, not fully explored issue. There are whole groups of diseases of the cardiovascular, endocrine, nervous systems, and kidneys, in which there is an increase in blood pressure. In these pathologies, the cause and mechanism of its increase are well studied. Arterial hypertension that occurs as part of any of these diseases is called symptomatic arterial hypertension.
Taking certain medications can also increase blood pressure.
Speaking about the well-known hypertension (or, in other words, essential arterial hypertension), it is difficult to clearly judge the reasons, since it is based on a whole complex of pathophysiological changes, the research of which continues to this day. If we talk about the factors contributing to the development of this type of hypertension, we can distinguish two groups. External factors include features of a person’s lifestyle, nutrition, bad habits, overweight or obesity, level of physical activity and stress. Internal factors include, for example, genetic predisposition. The combination of these factors leads to the development of hypertension.
- Angelina Anatolyevna, is high blood pressure always a sign of some kind of disease or can it be a random episode?
No, hypertension does not always indicate the presence of any pathology. The ICD even has such a concept as “increased blood pressure without hypertension.” For example, it may increase in response to physical activity and stress. However, it is recommended to take into account the range of such an increase: after certain numbers it is necessary to be observed by a doctor in order to prevent the development of hypertension in the future.
- And if the pressure fluctuates, sometimes high, sometimes low, what could be the reasons for this condition?
This manifestation is relatively common in young people, with increased anxiety and significant psycho-emotional stress. It is based on a disruption in the functioning of the autonomic nervous system, adaptation mechanisms with a defect in the neurohumoral regulation of the cardiovascular system.
- What actions can be taken urgently at home if a person’s blood pressure has increased?
The scope of first aid for high blood pressure should be determined by a doctor (including the ambulance team, if necessary). Firstly, medications to lower blood pressure may not be at hand, and secondly, you need to understand exactly what medications are required in this particular case and how to administer them. Only a doctor can answer these questions competently. As a last resort, until the doctors arrive, and the increase in blood pressure is accompanied by a feeling of fear, anxiety, anxiety, then if you have Valocordin or Corvalol at home, you can take one of these medications (of course, if they are tolerated).
It is necessary to calm the person down; it is better to give him a horizontal position. You can apply a cool towel to your face and forehead.
If we are talking about a patient already taking medications to lower blood pressure, you can take the usual drug in the dosage recommended in such situations by the attending physician.
-Which doctor should I contact with a high blood pressure problem and what diagnostics should I undergo?
Hypertension is treated all over the world by internists and general practitioners. In addition to them, in our country, cardiologists also deal with this disease.
In terms of examination, routine, additional and in-depth methods are distinguished.
The first group includes a complete blood count, a complete urinalysis, albumin in the urine, measurement of fasting blood glucose, total cholesterol, low- and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, triglycerides, creatinine with determination of the glomerular filtration rate, potassium and sodium in the serum, uric acid in serum, 12-lead ECG. Additional methods may include ultrasound of the heart and blood vessels, abdominal organs, kidneys, echocardiography, 24-hour blood pressure monitoring, Holter monitoring and some others.
-Does high blood pressure respond well to treatment? Is this problem curable?
If we are talking about essential arterial hypertension (hypertension), then there is no cure in the sense of “treated with a course and recovered” today. This disease requires continuous lifelong treatment.
But the level of development of modern medicine is already such that this pathology can be easily corrected. The answer to the question of how to reduce high blood pressure and keep it under control lies in the correct selection of medications and strict adherence to all recommendations of the attending physician.
- What preventative measures are needed to keep your blood pressure under control?
You should maintain normal body weight, get rid of bad habits (smoking, alcohol consumption), ensure regular adequate physical activity, eat right and limit your salt intake.
If a person already suffers from high blood pressure, then prevention includes proper self-monitoring, keeping a blood pressure diary, regularly taking prescribed medications, and monitoring with your doctor.
Other related articles:
What to do when the head is cast iron?
How to relieve tension headaches?
What should a child's blood pressure be?
For reference:
Kalinina Angelina Anatolevna
Graduate of the Voronezh State Medical Academy named after. Burdenko 2007.
In 2008, she completed an internship in the specialty “Therapy”.
In 2010, she underwent professional retraining in the specialty “General Medical Practice (Family Medicine)”, in 2017 - in the specialty “Cardiology”.
Since 2015, he has been working as a general practitioner at Clinic Expert Voronezh LLC.
Difference between systolic and diastolic pressure
There is another term for this indicator - pulse blood pressure. If the difference between the higher and lower tonometer readings exceeds 50, it means that the heart muscle is overly strained when pumping blood.
Pulse BP = systolic minus diastolic
It is equally important to note which blood pressure indicator exceeds or lags behind the norm. In many cases, this helps in determining the cause of the blood pressure problem.
For maximum reliability of blood pressure measurements, they must be done at least twice a day, and on each arm.
The tonometer readings for each arm may vary slightly. A difference of up to five millimeters is acceptable. If the difference is greater, then there is reason to suspect blood flow problems in one of the arms. The situation requires attention if it does not change within several days.
Pressure norm
For a healthy adult, normal systolic blood pressure ranges from 110/80 to 139/89 (units of measurement are millimeters of mercury). Therefore, indicators of 110 – 140 mmHg are the norm for systolic blood pressure.
The table below gives a visual representation of the level classification:
| Category | Upper (systolic) blood pressure level | Lower (diastolic) blood pressure level |
| Optimal | < 120 | < 80 |
| Normal | 120 – 129 | 80 – 84 |
| Increased (normal variant) | 130 – 139 | 85 – 89 |
| Hypertension | Above 140 – 159 | 90 – 99 |