The role of L-carnitine
To determine the effect of vitamin B11 on the health of older people, a double-blind, placebo-controlled study was conducted in Italy in 2007. During the experiment, each participant was supposed to consume 2 grams of the beneficial compound daily for six months, which was 6.5 times the daily requirement for an ordinary person. After the specified period, the subjects improved their muscle mass (increase by 3.8 kilograms) and fat mass (decrease by 1.8 kilograms). In addition, the patients' cognitive function increased, signs of fatigue (mental, physical) decreased, and total cholesterol levels decreased.
Let's look at why vitamin B11 is needed.
- For transport of long-chain fatty acids into the mitochondrial matrix. Triglyceride oxidation and ATP synthesis play an important role in energy production. The key participant in these reactions is L-carnitine. The compound supplies long-chain fatty acids to mitochondria through their inner membrane, where β-oxidation of the substance to acetyl-CoA occurs.
- To control and modulate the intracellular pool of CoASH. Vitamin B11 maintains a stable level of coenzyme A in the body, which is needed to activate carboxyl-containing metabolites. As a consequence, L-carnitine participates in intermediate metabolism, regulating the acetyl-CoA/CoASH ratio in the cell. By maintaining free CoASH at the required level, levocarnitine ensures beta-oxidation, detoxification of xenobiotics and organic acids, and the catabolism of certain amino acids. The compound removes short-chain fatty acids from the mitochondria, freeing intramitochondrial coenzyme A, which is needed for energy metabolism.
- To perform anabolic functions. Systematic use of the drug relieves the athlete of excess fat deposits, accelerates muscle gain and protein metabolism. The anabolic effect of vitamin B11 is caused by increased secretion and enzymatic activity of gastric juice, as well as the intestinal mucosa, which increases the digestibility of food (namely protein) and increases performance when performing strength exercises. In addition, the compound controls the level of accumulated lactic acid in the muscles, reducing the risk of getting soreness after intense exercise, which is especially important for athletes.
- To enhance physical and mental activity.
- For detoxification of organic acids. Thanks to this property, levocarnitine eliminates biogenic waste that accumulates in mitochondria as a result of the oxidation of xenobiotics and triglycerides. Vitamin B11 is effectively used to relieve alcohol or drug intoxication.
- To increase stress resistance. L-carnitine increases the body's resistance to psycho-emotional stress. Research has found that a vitamin-like compound increases a person's ability to adapt to stress. This means that the substance protects nerve tissue from the harmful effects of glutamate, amphetamine, and ammonia.
- To improve eye function. Levocarnitine inhibits the transformation of retinal vessels of the dystrophic type, prevents a decrease in visual acuity and reduces the likelihood of cataracts by 40%.
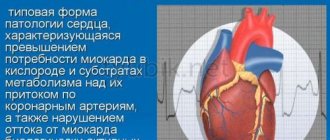
- To protect the heart muscle and blood vessels. Studies have confirmed that after consuming “carnitine-containing” drugs, patients’ myocardial condition improves. This is achieved by improving metabolism in the heart muscle and lowering cholesterol levels in the blood, which prevents the formation of plaques on the walls of blood vessels, narrowing of blood vessels and, as a consequence, the development of heart attack, hypertension, coronary artery disease, atherosclerosis and stroke.
- To protect the body from apoptosis (cell death) caused by inhibition of ceramide synthesis and caspase activity.
- To support the immune system. L-carnitine improves well-being, eliminates chronic fatigue syndrome, increases performance and endurance.
- To slow down the process of leaching calcium from bones. The systematic intake of levocarnitine is especially important for women during menopause and the elderly, since these categories of people are most susceptible to bone loss.
In addition to the above positive properties, vitamin B11 reduces subcutaneous fat.
Determination of the concentration of free and total L-carnitine in urine, used to diagnose primary and secondary carnitine deficiency, as well as to assess its level during treatment with carnitine preparations.
Synonyms Russian
Carnitine, levocarnitine, l-carnitine, vitamin BT.
English synonyms
Carnitine, Levocarnitine, 3-hydroxy-4-(trimethylazaniumyl) butanoate.
Research method
High performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (HPLC-MS).
Units
μmol/L (micromoles per liter).
What biomaterial can be used for research?
A single portion of urine.
How to properly prepare for research?
- Eliminate alcohol from your diet for 24 hours before the test.
- Avoid taking diuretics 48 hours before urine collection (in consultation with your doctor).
General information about the study
Carnitine is a vitamin-like compound that is a derivative of the amino acids lysine and methionine. Its active form is called levocarnitine, or L-carnitine. L-carnitine is a cofactor for many biochemical reactions in the human body. It is necessary for the transport and beta-oxidation of long-chain fatty acids, the processes of glycolysis and gluconeogenesis, and the detoxification of organic acids and xenobiotics. In addition, L-carnitine is involved in the regulation of oxidative stress and apoptosis. It is mainly synthesized in the liver and kidneys; its other source is food (meat products). The body of an adult male contains about 15-20 g of carnitine, up to 95% of which is found in skeletal muscle tissue. The main route of excretion of carnitine is through the kidneys. Normally, the renal tubules ensure the reabsorption of carnitine and prevent its loss in the urine.
L-carnitine and its compounds do not produce toxic effects, and their excess in the body is not dangerous. On the contrary, carnitine deficiency can lead to various disorders affecting almost all systems and organs. Clinical signs develop when its level decreases to 10-20% (or less) of normal. To diagnose diseases accompanied by carnitine deficiency, the concentration of this compound in the urine is determined.
There are primary and secondary carnitine deficiency. Primary deficiency is an autosomal recessive disorder caused by a defect in carnitine transport. As a rule, the disease manifests itself in childhood and is accompanied by severe symptoms. In such patients, carnitine concentrations are significantly reduced. Determining the level of carnitine in urine is particularly convenient in pediatric practice, especially in cases where multiple tests are performed.
Secondary carnitine deficiency is observed in all age groups and can accompany various inborn errors of metabolism (for example, deficiency of urea synthesis cycle enzymes), and also develops during treatment with certain drugs (for example, valproic acid, zidovudine). One of its causes is a violation of its reabsorption in the renal tubules. Secondary deficiency of L-carnitine, caused by its loss in the urine, is observed in Fanconi syndrome, cystinosis, oculocerebrorenal syndrome (Low's syndrome) and some other genetic diseases - they are distinguished by an increased concentration of L-carnitine in the urine. Thus, the determination of carnitine in urine is a method for differential diagnosis of primary and secondary L-carnitine deficiency. It should be noted that the diagnosis of diseases accompanied by carnitine deficiency involves a whole range of laboratory tests.
Recently, new data have emerged on the role of carnitine in the pathogenesis of such conditions as diabetes mellitus, hypertension, heart failure, coronary heart disease, dyslipidemia, etc. The most convincing data have been obtained regarding the use of L-carnitine preparations in patients with peripheral vascular diseases.
Also, measuring the concentration of L-carnitine in urine is a convenient way to monitor the level of this compound during treatment with carnitine preparations.
When assessing the results of the study, it should be remembered that the level of carnitine depends on diet, physical activity and concomitant diseases. The obtained indicators should be interpreted taking into account additional clinical, laboratory and instrumental data.
What is the research used for?
- For the diagnosis of primary and secondary L-carnitine deficiency;
- to assess the level of L-carnitine during treatment with carnitine preparations.
When is the study scheduled?
- For symptoms of carnitine deficiency: non-ketotic hypoglycemia, hyperammonemia, muscle weakness, cardiomyopathy, hepatomegaly;
- when monitoring patients with peripheral vascular diseases, diabetes mellitus, hypertension, heart failure, coronary heart disease and dyslipidemia.
What do the results mean?
Reference values
| Free | Age | Reference values, mmol/mol creat. |
| 0 - 5 months | 1,8 — 105 | |
| 5 – 24 months | 4,2 — 120,5 | |
| > 2 years | 0,8 — 46,0 | |
| General | 0 - 5 months | 18 — 175 |
| 5 – 24 months | 26 — 193 | |
| > 2 years | 8,2 — 82,5 |
Reasons for increased carnitine levels:
- Fanconi syndrome;
- cystinosis;
- oculocerebrorenal syndrome (Low syndrome);
- treatment with carnitine drugs.
Reasons for decreased carnitine levels:
- primary systemic carnitine deficiency;
- ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency;
- carbamoylphosphate synthetase deficiency;
- cytochrome C oxidase deficiency;
- lysinuric protein intolerance;
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- chronic kidney disease;
- diet low in carnitine (milk and vegetables);
- malabsorption syndrome;
- the use of valproic acid, zidovudine, emetine, pivampicillin.
What can influence the result?
- Features of the diet;
- level of physical activity;
- accompanying illnesses.
Daily norm
The body’s physiological need for levocarnitine depends on the person’s type of activity, age, gender, weight, and the presence of diseases.
For newborns and infants up to one year, the daily requirement of vitamin B11 is 10-15 milligrams, for children from 1 to 3 years old - 30-50, for children from 4 to 6 years old - 60-90, for school-age children and adolescents from 7 to 18 years – 100-250, for adults – 300.
The liver and kidneys of healthy children, men and women produce L-carnitine from the amino acids lysine and methionine, fully covering the body's need for this nutrient. However, this occurs only under the condition of proper nutrition and sufficient intake of vitamins, C, and methionine.
The daily requirement for levocarnitine increases in people who lead an active lifestyle, experience heavy physical activity (during training), mental stress, or have diseases of the digestive system.
At the same time, the opinions of nutritionists regarding taking large doses (2000-4000 milligrams) of vitamin B11 are not clear. Some believe that systematically exceeding the daily dose of 300 micrograms can cause adverse reactions (allergies), addiction of the body, and as a result, reduce the production of its own levocarnitine. As a result, this will serve as a reason for the development of addiction. Other nutritionists believe that increasing the norm has a beneficial effect on the human body: it improves the functioning of the heart, blood vessels, energy metabolism, and “dries out” muscle mass.
Hypovitaminosis and hypervitaminosis L-carnitine
The following types of carnitine deficiency are distinguished:
- primary, occurs as a result of genetic disorders, the first signs of deviation appear in the fifth year of life: the child experiences musculoskeletal weakness, cardiomyopathy and hypoglycemia develop;
- secondary, appears against the background of decreased absorption of nutrients, including foods rich in carnitine.
Characteristic symptoms of vitamin B11 deficiency in the body:
- cardiac dysfunction (atrial fibrillation, cardiomyopathy, angina pectoris, tachycardia);
- increased fatigue, weakness;
- muscle tremors;
- atherosclerosis;
- muscle pain during intense physical activity;
- gaining excess weight;
- asthenia;
- irritability;
- insomnia;
- lowering blood pressure.
Reasons for the development of L-carnitine deficiency:
- lack of B vitamins, iron, methionine in the body;
- raw food diet, vegetarian diet;
- gastrointestinal diseases;
- hemodialysis;
- taking antibiotics or drugs that slow down blood clotting (hirudin, sodium citrate, heparin).
Carnitine deficiency in the body reduces the concentration of fatty acids in mitochondria, as a result, energy production decreases, which leads to the development of degenerative processes in the myocardium.
An overdose of vitamin B11 is an uncharacteristic phenomenon. The medical literature describes only a few cases of hypervitaminosis of a beneficial compound.
Excess levocarnitine causes the following side effects:
- diarrhea;
- increased ammonia levels without hepatotoxicity;
- depression;
- increased blood pressure;
- increased heart rate;
- pain in the epigastric region;
- convulsions;
- fever.
A single dose of L-carnitine (over 10,000 micrograms) can lead to nausea, vomiting, indigestion, increased excitability of the nervous system, and a sharp increase in appetite.
L-carnitine rompharm 200mg/ml 5ml 5 pcs. solution for intravenous and intramuscular administration
pharmachologic effect
Metabolic agent.
Composition and release form L-carnitine rompharm 200 mg/ml 5 ml 5 pcs. solution for intravenous and intramuscular administration
Solution - 1 ml:
- active ingredient: levocarnitine - 200.0 mg;
- excipients: 1 M hydrochloric acid solution - up to pH 6.3-6.5, water for injection - up to 1.00 ml.
5.0 ml of the drug in dark glass ampoules of hydrolytic class I with a break ring. A label is attached to each ampoule.
5 ampoules are placed in blister packs.
1 blister pack along with instructions for use is placed in a cardboard box.
Description of the dosage form
Colorless, transparent solution.
Directions for use and doses
L-Carnitine Rompharm is administered intravenously by drip, slowly or in a stream (2-3 minutes) or intramuscularly.
Before intravenous administration, the contents of the ampoule are dissolved in 100-200 ml of solvent (0.9% sodium chloride solution or 5% dextrose (glucose) solution).
For acute cerebrovascular accidents, 1 g/day is prescribed for 3 days, and then 0.5 g/day for 7 days. After 10-12 days, repeated courses are possible within 3-5 days.
When prescribing the drug in the subacute and recovery period, with discirculatory encephalopathy and various brain lesions, carnitine deficiency, patients are administered a solution of levocarnitine at the rate of 0.5-1 g/day intravenously (drip, stream) or intramuscularly (2-3 times a day) without dilution for 3-7 days. If necessary, a repeat course is prescribed after 12-14 days.
Intravenous administration, slowly (2-3 minutes) is prescribed for secondary carnitine deficiency during hemodialysis - 2 g once (after the procedure); for acute myocardial infarction, acute heart failure - 3-5 g/day, divided into 2-3 doses in the first 2-3 days, followed by a 2-fold dose reduction; for cardiogenic shock - 3-5 g/day, divided into 2-3 doses until the patient comes out of shock. Next, they switch to oral administration of levocarnitine.
Pharmacodynamics
Levocarnitine is a means for correcting metabolic processes; has metabolic, anabolic, antihypoxic and antithyroid effects, activates fat metabolism, stimulates regeneration, and increases appetite. Levocarnitine is a natural substance related to B vitamins. It is a cofactor in metabolic processes that maintain the activity of coenzyme A (CoA).
Reduces basal metabolism, slows down the breakdown of protein and carbohydrate molecules. Promotes penetration through mitochondrial membranes and the breakdown of long-chain fatty acids (palmitic, etc.) with the formation of acetyl-CoA (necessary for ensuring the activity of pyruvate carboxylase in the process of gluconeogenesis, the formation of ketone bodies, the synthesis of choline and its esters, oxidative phosphorylation and the formation of adenosine triphosphate (ATP)) . Mobilizes fat (presence of 3 labile methyl groups) from fat depots. Competitively displacing glucose, it turns on a fatty acid metabolic shunt, the activity of which is not limited by oxygen (unlike aerobic glycolysis), and therefore the drug is effective in conditions of acute hypoxia (including the brain) and other critical conditions.
Causes slight depression of the central nervous system (CNS), increases the secretion and enzymatic activity of digestive juices (gastric and intestinal), improves food absorption.
Reduces excess body weight and reduces fat content in skeletal muscles.
Increases the threshold of resistance to physical activity, reduces the degree of lactic acidosis and restores performance after prolonged physical activity. At the same time, it promotes economical consumption of glycogen and increases its reserves in the liver and muscles.
It has a neurotrophic effect, inhibits apoptosis, limits the affected area and restores the structure of nervous tissue.
Normalizes protein and fat metabolism, increased basal metabolism in thyrotoxicosis (being a partial antagonist of thyroxine); restores the alkaline reserve of the blood.
Pharmacokinetics
After intravenous administration, it disappears from the blood within 3 hours. It penetrates easily into the liver and myocardium, and more slowly into the muscles.
It is excreted by the kidneys mainly in the form of acyl esters (more than 80% in 24 hours).
Indications for use L-carnitine Rompharm 200 mg/ml 5 ml 5 pcs. solution for intravenous and intramuscular administration
L-Carnitine Rompharm is used as part of complex therapy for acute hypoxic conditions (acute cerebral hypoxia, ischemic stroke, transient ischemic attack). The drug is prescribed in acute, subacute and recovery periods of cerebrovascular accidents.
Used for dyscirculatory encephalopathy and various traumatic and toxic lesions of the brain, in the recovery period after surgery.
L-Carnitine Rompharm is indicated for primary and secondary carnitine deficiency, including in patients with chronic renal failure on hemodialysis; for cardiomyopathy, coronary heart disease (angina pectoris, acute myocardial infarction, post-infarction conditions), hypoperfusion due to cardiogenic shock and other disorders of myocardial metabolism.
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to levocarnitine or other components of the drug, pregnancy and breastfeeding.
The drug should be prescribed with caution for diabetes mellitus.
Application of L-carnitine rompharm 200 mg/ml 5 ml 5 pcs. solution for intravenous and intramuscular administration during pregnancy and lactation
L-Carnitine Rompharm should not be used during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
special instructions
L-Carnitine Rompharm is not addictive, because Levocarnitine is an endogenous substance.
An increase in glucose absorption when administering L-Carnitine Rompharm to patients with diabetes mellitus receiving insulin or oral hypoglycemic drugs can cause hypoglycemia. For this reason, in this category of patients, during treatment with L-Carnitine Rompharm, blood glucose levels should be constantly monitored for immediate correction of the dosage regimen of hypoglycemic drugs.
Long-term use of levocarnitine in high doses in patients with severe renal impairment may cause an increase in the concentration of potentially toxic metabolites, trimethylamine and trimethylamine-N-oxide, because these metabolites are usually excreted in the urine. In this case, urine, breath and sweat have an unpleasant odor.
If any of the side effects indicated in the instructions get worse, or you notice any other side effects not listed in the instructions, tell your doctor.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery
The drug does not affect the ability to drive vehicles and other potentially hazardous activities.
Overdose
There are no data on toxicity in case of overdose of levocarnitine. Tolerance to the drug should be monitored during the first week of use and after each dose increase.
In case of overdose, treatment is prescribed to maintain vital functions, symptomatic treatment.
Side effects L-carnitine rompharm 200 mg/ml 5 ml 5 pcs. solution for intravenous and intramuscular administration
Mild symptoms of myasthenia gravis were observed only in uremic patients taking levocarnitine.
Allergic reactions.
With rapid administration (80 drops/min or more), pain may occur along the vein, which disappears when the injection rate is reduced.
Drug interactions
Glucocorticoids promote the accumulation of levocarnitine in tissues (except the liver), other anabolic steroids enhance the effect.
Indications and contraindications
Vitamin B11 is used for:
- relieving alcohol intoxication;
- improving memory in people over 60 years of age due to age-related changes in brain cells;
- reducing depression;
- improvement of sexual activity;
- elimination of B11-hypovitaminosis;
- stimulating growth in children.
In addition, L-carnitine is indicated for premature babies, with loss of muscle mass, asphyxia, anorexia nervosa, and in the postoperative period to accelerate tissue recovery.
Contraindications to the use of the drug:
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- diabetes;
- peripheral vascular diseases;
- individual intolerance to the active substance;
- pregnancy;
- breastfeeding period;
- trimethylaminuria;
- hypertonic disease;
- kidney dysfunction.
The possibility of using vitamin B11 for the treatment of mitochondrial myopathy caused by the antiviral drug Zidovudine is currently under study.
L-carnitine for weight loss
In modern life, the amount of calories consumed, as a rule, prevails over energy expenditure. As a result, people begin to develop obesity and health problems appear.
To restore the metabolic process, nutritionists recommend leading a healthy lifestyle: going to the gym, moving more, eating right. During physical activity, metabolic reactions in the body accelerate 2-5 times. Thus, burning excess fat occurs much faster. To speed up the process of getting rid of excess pounds, you can take additional vitamin B11 as a supplement.
Levocarnitine helps the body in the process of burning fat, increasing its efforts. Fitness instructors claim that the supplement is harmless and, in combination with proper nutrition and regular exercise, improves well-being and gives a great figure.
Remember, only an integrated approach will help you achieve your desired goal.
Release form of L-carnitine
- Liquid vitamin B11. This drug is popular among professional athletes and people who want to stay in shape. There is no need to prepare the product before taking it - just open the bottle and drink the contents. Concentrated syrups that have an acceptable taste are also available for sale. The difference between these drugs is not great. Before use, the concentrate should be mixed with water, observing the proportions established by the manufacturer. There is liquid L-carnitine in ampoules. People often get confused when they call the form of release of a substance injectable. It is actually a drug that is taken orally as a drink. Liquid levocarnitine, compared to tablets, is absorbed faster and provides greater flexibility with dosage. However, it has a high cost, a short shelf life (an open bottle is stored for no more than a day), a lot of chemical additives in its composition (flavors, dyes), is difficult to transport, and requires “special” storage conditions - refrigeration.
- B11 in capsules. This drug is taken as tablets: the dietary supplement should be washed down with 150 milliliters of still water or juice. The capsule consists of two gelatin parts. The advantages of this form of L-carnitine release are rapid breakdown in the stomach, good absorption by the body, long shelf life without loss of beneficial properties (up to 3 years). If necessary, the capsule can be opened and the powder contents can be poured into a protein shake. Due to this property, it can be used by people who have difficulty swallowing tablets. Today, one-piece gelatin capsules are also available, which are completely sealed, but have a significant limitation of space, which means that the contents are not compressed to a significant extent. The main disadvantages of this drug: high cost, impressive size.
- Levocarnitine tablets. This form of additive production is the most economical, since it requires the least production costs. Tablets allow you to form a portion of the vitamin (pure material) directly in space, without additional coating or placing it in a gelatin capsule. Let's consider the harm and benefits of this form of vitamin compound. The main advantages of vitamin B11 produced in tablets are ease of use and low price (20% lower than the cost of liquid L-carnitine). The disadvantages of the useful compound include: irritation of the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract, lack of flexibility in dosing, slow absorption of the substance (the rate of absorption of levocarnine taken in liquid form or in capsules is much higher). Recently, American experts have come to the conclusion that tablet vitamins “live” only 7 days after opening the package. After this period, they lose their biological value. Such tablets do not harm human health, but do not provide any benefit. The effectiveness of their use is equivalent to taking candy. In addition, people who have difficulty swallowing “packaged” drugs and have diseases of the digestive tract should avoid purchasing the supplement in tablets.
- L-carnitine powder. Advantages of this form: ease of use, affordable cost, high dosage flexibility, rapid absorption. Disadvantages: negative effect on the walls of the stomach, inconvenience of use associated with the need to accurately calculate the weight of raw materials and prepare a solution. Before taking levocarnitine, dilute the powder in 500 milliliters of water and drink at one time.
Thus, there is no ideal format for releasing vitamin B11. Each of them has its pros and cons.
The active ingredient in all drugs is the same; they differ only in the time of absorption. Any means is suitable for burning fat, the main thing is to eat right and lead an active lifestyle.
The most popular analogues of levocarnitine: “Carnitene”, “Cartan”, “Elkar”, “L-Carnitine300”, “Carnifit”.
What is L-carnitine?
L-carnitine is synthesized in the liver, kidneys and brain of humans and animals from the essential amino acids lysine and methionine.1 Most of it - about 95% - accumulates in the heart and skeletal muscles.2 The body produces approximately only 25% of the total daily requirement of the substance.3 Some the amount of the substance enters the body with food.
However, given the ever-increasing pace of modern life, stress and increased physical activity, additional intake of carnitine as a supplement is recommended. The main food source of the product is red meat, which includes beef, pork, and lamb. One hundred grams of raw red meat contains up to 140-190 mg of L-carnitine.4 It should be taken into account that in heat-treated meat, the amount of the substance is slightly reduced. When it comes to supplements, there are four different forms of carnitine available commercially: L-carnitine, propionyl-L-carnitine.
,
L-carnitine-L-tartrate
and
acetyl-L-carnitine
.
How to take levocarnitine
After L-carnitine enters the body, the compound penetrates into muscle cells within 3 hours, where it begins to fight fat deposits. Vitamin B11 works directly during intense exercise, as well as for a long time after training.
Divide the daily dose of the dietary supplement into 2-3 doses of 200 – 250 milligrams. The maximum amount of vitamin B11 (500 - 600 milligrams) on training days should enter the body at least 1 - 1.5 hours before going to the gym. The remaining dose should be divided into morning and afternoon doses. During rest periods (non-training days), levocarnitine should be taken in the morning and lunchtime, 30 to 60 minutes before the start of the meal. Only if this regimen is followed does the substance promote weight loss, otherwise the effect of the supplement is weakened by the food intake.
Let's consider when it is better to drink vitamin B11, depending on the form of release.
- Beginner athletes are recommended to take tablets and capsules 2-3 times a day, 250–500 milligrams before physical activity, and professionals – 500–1500 milligrams at a time. The maximum duration of use of a weight loss supplement is 2 – 6 months.
- The syrup should be taken 3 times a day, 5 milliliters, half an hour before physical activity (dosage for beginners). For experienced athletes, the single dose rate increases to 15 milliliters. The maximum duration of daily intake of liquid levocarnitine is 1.5 months. After this course, you need to take a 3-week break, then, if necessary, repeat the regimen.
- If you purchase B11 in bulk form, before use, 2000 milligrams of powder must be dissolved in 500 milliliters of clean still water. If the amount of liquid is reduced, the drink will turn out cloying and unpleasant in taste. Drink the prepared solution on an empty stomach and immediately an hour before training. The course of taking the drug is 2–4 months. The maximum duration is half a year. Up to 6 courses can be completed in a year, with a minimum break between them of 2 weeks. Today, levocarnitine powder is available for sale in the flavors “Wild berries” and “Green Apple”.
If you missed taking L-carnitine before training, it is recommended to drink the vitamin in liquid form, which is quickly absorbed in the body and promotes a quick release of energy.
How does B11 work?
When taken orally, the vitamin is usually well absorbed. The maximum concentration of the beneficial compound in the body is observed three hours after administration, while the therapeutic concentration remains for 9 hours. In the case of intramuscular administration, the substance reaches the plasma after 3.5 - 4 hours, and when administered intravenously, the drug disappears from the blood after 3 hours. Taken L-carnitine quickly penetrates into the middle layer of the heart (myocardium) and liver, and more slowly into muscle tissue. The compound is excreted by the kidneys as acyl esters.
How to take carnitine?
As mentioned above, there is a wide selection of supplements available on the market that contain carnitine. To increase athletic performance and power output, L-carnitine-L-tartrate is most often recommended .
Its daily dose varies from 1000 to 4000 mg.
This supplement goes well with all types of fat burners and even enhances their effect. It is advisable to consume it after training or during the day, during meals, with high-carbohydrate and high-protein foods. The standard dose of L-carnitine varies from 500 to 2000 mg per day.
Acetyl-L-carnitine should be taken according to a slightly different regimen. It is absorbed much better on an empty stomach, so it is better to take it between meals along with other fat-burning drugs. Recommended dosage is 630 - 2500 mg.
Food sources
Considering the fact that vitamin B11 stimulates muscle growth, oxidizes and removes fats from the body, promoting weight loss, foods rich in the beneficial compound are always present in the menu of athletes and people who want to lose weight.
The largest amount of the nutrient is found in offal and meat. The second place in terms of the content of the “fat burning factor” belongs to lactic acid and dairy products. The smallest amount of levocarnitine is concentrated in plant foods. For this reason, adherents of a strict vegetarian diet often suffer from B11 hypovitaminosis. List of foods rich in L-carnitine
| Name | Content of vitamin B11 in 100 grams of product, milligrams |
| Venison | 210 |
| Mutton | 160 |
| Veal (schnitzel) | 105 |
| Cheddar cheese | 100 |
| Beef | 90 |
| Rabbit | 30 |
| Pork | 24 |
| Duck | 24 |
| Bacon | 23,3 |
| Turkey | 23 |
| Goose | 22 |
| Salmon | 19 |
| Cancers | 15 |
| Goat cheese | 13 |
| Herring | 12 |
| Condensed milk | 10 |
| Milk | 7 |
| Shrimps | 7 |
| Flounder | 6,3 |
| Mackerel | 6 |
| Cottage cheese | 6 |
| Cod | 5,6 |
| Sea bass | 5 |
| Yogurt | 5 |
| Chicken | 5 |
| Duck liver | 4,3 |
| Pollock | 4 |
| Pike | 4 |
| Cream | 3,8 |
| Ice cream | 3,5 |
| Tuna | 3,4 |
| Mussels | 2,8 |
| Sour cream | 2,6 |
| Squid | 2,1 |
| Avocado | 2 |
| Mozzarella | 1,8 |
| Hazelnut | 1,4 |
| Pistachios | 1,3 |
| Cashew | 1 |
| Champignon | 1 |
| White whole grain bread | 0,5 |
| Asparagus | 0,195 |
| Pasta | 0,126 |
| Peanut butter | 0,083 |
| Boiled rice | 0,0449 |
| Eggs | 0,0121 |
| Orange juice | 0,0019 |
Thus, levocarnitine is widely used in the food industry.
A pattern has been noted: the redder the meat, the more vitamin B11 it contains. When food is frozen, the loss of the beneficial compound reaches 70%; after thawing, the remaining nutrient passes into melt water.
Interaction of L-carnitine with various compounds
Vitamin B11 enhances the effect of anticoagulants.- Antibiotics remove carnitine from the body, which leads to depletion of the nutrient.
- Phenobarbital and valproic acid reduce the concentration of the vitamin in the blood.
- When taking levocarnitine and thyroid hormones simultaneously, B11 suppresses their effect.
- Glucocorticosteroids help accumulate vitamin compounds in body tissues (with the exception of the liver).
- Lipoic acid and anabolic drugs enhance the therapeutic effect of L-carnitine.
- Vitamin B11 reduces the toxic effects of zidovudine and doxorubicin on muscle tissue and cardiac muscle cells.
- Levocarnitine alleviates the side effects of isotretinoin.
- Sports nutrition goes well with vitamin B11. The simultaneous intake of carnitine and coenzyme Q10 is considered effective.
Contrary to popular belief that in no case should you combine taking a medication and ethyl drinks, this rule does not affect L-carnitine. Of course, the medicine puts additional stress on the liver, since the organ needs not only to break down the compound into simple particles, but also to remove its breakdown products. Alcohol entering the body disrupts this process and interferes with metabolic reactions. However, in the case of vitamin B11, things are much easier.
The nutrient does not react with ethanol, which means it is not prohibited to take the dietary supplement and strong drinks at the same time. It is important to follow safety measures - control the level of alcohol consumed.
FAQ
How to enhance the effects of levocarnitine?
It's no secret that if you do not follow the recommended conditions for taking biologically active supplements or medications (by the manufacturer and your doctor), therapy will not bring the desired result.
In order for the beneficial properties of L-carnitine to be fully revealed, it is necessary to exercise physical activity while consuming the compound. The best option is aerobic exercise. Only when body temperature rises slightly and tissues are saturated with oxygen can the vitamin capture fat molecules. Fitness trainers recommend calculating your heart rate for cardio training and sticking to this indicator. To increase your heart rate, do brisk walking, aerobics, and running. The minimum training duration is half an hour. This time is enough to launch the natural processes of fat burning, as a result, levocarnitine will take effect.
In addition to physical activity, for the drug to work, you need to eat right. Focus on foods rich in iron, vitamin C, and protein, which stimulate the production of your own vitamin B11. Low-calorie diets should be abandoned, otherwise the body will not have the strength and “building material” to gain muscle mass and start the process of losing weight.
A balanced diet, regular physical activity, drinking 2 liters of clean water per day is the best way to activate and enhance the effect of L-carnitine to combat extra pounds on the way to a slim and toned body.
What is the difference between vitamin B11 and fat burners?
Levocarnitine is absolutely safe. Many manufacturers add various stimulants to fat burners, which negatively affect the state of the digestive tract and the functioning of the nervous system (caffeine). In addition, there are clandestine supplements that are not certified in the country because they contain prohibited components. As a rule, such substances of the “non-stop” category stimulate the central nervous system, completely depleting it.
Vitamin B11, unlike prohibited components, does not affect the nervous system; the compound works exclusively with the utilization of triglycerides and fatty acids.
How to combine exercise and taking levocarnitine?
First of all, the result of losing weight depends on the correctness of the diet and the choice of physical activity. To get rid of extra pounds, it is recommended to perform cardio exercises 4 times a week, lasting no more than 45 minutes. Remember, too frequent and exhausting workouts will not bring the desired result, since in order to lose weight the body must have time to rest. The muscle recovery period is 48 hours.
If you follow an exercise-rest regime, eat right, but there is no visible effect, it is recommended to introduce L-carnitine into your daily diet. You need to drink the supplement 1 – 1.5 hours before training. Despite the fact that the nutrient is safe for human health, consuming the compound for a long time is not recommended. The duration of taking levocarnitine without interruption depends on the form of the drug. As a rule, it does not exceed 1.5 months, then the course must be interrupted for 2-3 weeks, after which it can be repeated.
Is it possible to take a “fat burning” vitamin at night?
Yes. At night, growth hormone is produced, which regulates fat metabolism. Due to this, fats are involved in the energy exchange reaction during sleep. It is recommended to eat salads and protein foods at night to maintain growth hormone at the proper level. Taking L-carnitine before bed promotes the complete processing of waste fatty acids. In fact, while a person is resting at night, the body burns triglycerides and loses weight.
Is it possible to drink fitness drinks during a workout? Which to choose?
Best materials of the month
- Coronaviruses: SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19)
- Antibiotics for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19: how effective are they?
- The most common "office" diseases
- Does vodka kill coronavirus?
- How to stay alive on our roads?
If the main task of losing weight is to utilize fat, it is better to avoid taking sweet, concentrated sports drink. To get rid of excess weight, the body must quickly burn carbohydrates accumulated in the liver in the form of glycogen, in order to use internal reserves to “melt” fat. When taking fitness drinks, it turns out that after the energy has run out, the body again receives a dose of carbohydrates, which the body “takes to work” first. As a result, the turn to consume (burn) fat never comes.
If the main goal is to build muscle, bars with levocarnitine, fortified and energy drinks will help the athlete replenish energy, increase performance, relieve fatigue, give strength, and dry out subcutaneous fat.
What is the best fitness drink?
When choosing a “sports drink,” we recommend paying attention to the manufacturer and the composition of the supplement. Products must be certified. During intense workouts, give preference to fitness drinks that contain: taurine, ginkgo biloba, ginseng, guarana, casein.
Which brand is better for L-carnitine?
Let's look at the TOP 11 vitamin compounds from branded manufacturers:
- Alcar 750 from SAN;
- Acetyl L-carnitine from Dymatize;
- L-Carnitine L-Tartrate from Al Sports Nutrition;
- L-Carnitine L-tartrate from Allmax;
- L-Carnitine xtreme from Dymatize;
- L-Carnitine from Source Naturals;
- Acetyl-L-Carnitine from Now Foods;
- L-Carnitine from Optimum;
- L-Carnitine Liquid from Now Foods;
- L-Carnitine Concentrate from Multipower;
- Power System L-Carnitine from Power System.
When to take carnitine?
An interesting fact is that this supplement can be used both during cutting and when gaining muscle mass.
- During the drying period:
If you use carnitine during the cutting period, it will help you burn fat, since it will be used as an additional source of energy - we have already discussed this mechanism of action.
- When gaining muscle mass:
Most people want to gain not just mass, but muscle, without fat. This is why additional intake of carnitine is needed during mass gain - it will help prevent the formation of fat, thereby ensuring a set of “clean” muscles.
In addition, research has shown that carnitine supplementation may promote a more careful use of amino acids as an energy source, thereby creating the potential for new protein synthesis.10 This effect may explain carnitine's ability to increase muscle mass in animal studies and people.11
A 2006 study found that three weeks of L-carnitine L-tartrate increased the number of androgen receptors in muscle fibers by 15%.12 This, in turn, increased muscle sensitivity to androgens (testosterone). Testosterone is known to trigger the process of muscle growth and increase in muscle mass. An unexpected quality for a “fat burner”, as many consider him to be, isn’t it?
Use of vitamin B11 in medicine
After the discovery of L-carnitine, the beneficial compound was first used in medical practice, and only a few years later the nutrient became popular among athletes. Initially, vitamin B11 was used as a biological supplement to the diet of people undergoing rehabilitation after a heart attack. Today, to increase the effectiveness of the nutrient, it is combined with coenzyme Q10. In addition to stabilizing the condition of “cores,” levocarnitine is used in gastroenterology. The compound normalizes the acidity of gastric juice and has a beneficial effect on liver function.
Instructions for use of the drug
- To improve immunity and lose weight, it is recommended to take vitamin B11 from 1500 to 3000 milligrams per day.
- For the treatment of kidney diseases, liver diseases, and heart pathologies, the daily requirement for levokartina is 1000 milligrams.
- For the rehabilitation of professional athletes after injuries, the daily requirement of L-carnitine is 2000 – 3000 milligrams.
In addition to consuming a synthetic form of the vitamin, patients are advised to enrich their daily diet with foods rich in the beneficial compound (see section Food sources).