Any adult measured their blood pressure. The normal value of the parameter should be within 120 to 80 mmHg. If the number increases, it is called hypertension. If the value is reduced, hypotension is detected. It is important to know what these numbers mean to understand the patient's condition.
Upper and lower pressure value
Blood pressure is the value of the degree and strength of systemic blood flow spreading inside the vessels. It helps to identify the condition of the following parts of the cardiovascular system:
- arteries, veins;
- arterioles, venules;
- capillaries;
- heart.
The characteristics of blood pressure depend on the following indicators:
- blood resistance;
- the volume of circulating blood formed after a single contraction of the heart muscle (systole);
- quality of myocardial contraction.
The following types of blood pressure indicators are distinguished:
- the highest
- observed during the period of contraction of the left ventricle, leading to the ejection of blood; - the lowest
is the transition of blood flow to the right atrium with relaxation of the myocardium (diastole).
Systolic or upper pressure is the degree of saturation of blood vessels that occurs during the contraction of the heart muscle. This is an indicator that characterizes the quality of heart activity. Activity is generated due to the functioning of large arteries. The most important of them is the aorta. Systolic pressure indicators depend on the following factors:
- left ventricular stroke volume;
- degree of elasticity of the aortic walls;
- the maximum rate of blood ejection from the heart into the vessels.
Diastolic or lower pressure is an indicator that indicates the resistance that forms during the passage of blood through the vessels. At this point, the aortic valve becomes closed, so blood does not move back into the heart. But during this period, the heart tissues prepare for the arrival of other blood, which is already saturated with oxygen. Therefore, re-cutting is required. Biological fluid moves through the heart and blood vessels passively.
The following factors influence diastolic pressure:
- number of contractions of cardiac tissue in 1 minute,
- peripheral vascular resistance.
The difference between systolic and diastolic pressure in a healthy human body should be 30-40 mmHg. This indicator depends on the person’s well-being and the state of the cardiovascular system.
Since each organism is individual, the numbers cannot be identical for each patient. But we can judge the presence of the following criteria for blood pressure:
- upper
- 120 mmHg; - lower
- 80 mmHg.
These indicators are typical for a normal blood pressure within 120 to 80 mmHg.
The following factors influence the overall blood pressure:
- quality of lifestyle;
- food consumed daily by a person;
- the presence or absence of bad habits;
- stress, depression, nervous tension.
For example, some types of food can increase or decrease the indicator. Caffeine increases blood flow through the vessels.
Normal difference between systolic and diastolic pressure
The difference between the upper and lower blood pressure readings is called pulse pressure (PP), normally it is 40 units. A deviation in both directions of 5–10 units is allowed; this condition is not considered critical, therefore, if the normal PD is 30–50 units, there is no cause for concern. Both the physical and mental state of a person’s health can affect pulse pressure.
No ads 3
Insufficient nutrition, weather sensitivity, physical activity and emotional stress can temporarily reduce PD values, but when normal living conditions are restored, they return to normal on their own. A large, stable difference between systolic and diastolic pressure indicates pathologies developing in the body, the causes and etiology of which need to be clarified with the help of doctors.
A change in well-being will be noted when the PD deviates by more than 10 units in one direction or the other. For example, if a person has always recorded a difference between blood pressure readings of 50 units, then a drop in the norm to 30 units will already affect his condition, he may be talking about the emergence of health problems. Even if the pulse pressure remains within acceptable limits, it will still be considered low.
The need to determine blood pressure
If the flow of blood into the heart and the tension in the blood vessels increases, each time the blood pressure increases by 10 mmHg. This leads to an increased risk of developing cardiovascular pathologies. If the patient suffers from chronic arterial hypertension, the following pathologies may develop:
- cardiac ischemia;
- hypertonic disease;
- stroke, heart attack;
- vascular damage in the lower extremities.
Initially, with an increase in blood pressure, dizziness, headache, and a sharp loss of strength appear. In this case, you need to consult a doctor, constantly check the indicator, and begin timely treatment.
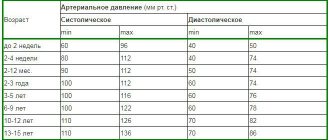
Normal lower pressure by age
Diastolic blood pressure and its norm vary depending on the age category of a person. Undesirable age-related changes are manifested by impaired blood flow, circulatory and microcirculation processes, wear and tear of blood vessels, and the formation of cholesterol plaques, which has a direct impact on blood pressure.
Since physiological changes occur smoothly and gradually, the human body has time to adapt to them. Therefore, a gradual increase in diastolic blood pressure in elderly people is considered a manifestation of the norm, a natural process.
There is a certain classification of normal diastolic pressure by age, presented in table form.
| Age category | Normal diastolic pressure |
| Newborns | Up to 70 mm Hg. Art. |
| Children aged 2 to 10 years | From 65 to 75 mm Hg. Art. |
| Teenagers aged 11 to 16 years | From 50 to 80 mm Hg. Art. |
| People aged 18 to 38 years | From 72 to 76 mmHg. Art. |
| Persons in the age category 39-50 years | From 60 to 80 mm Hg. Art. |
| From 50 to 70 years | Up to 85 mm Hg. Art. |
| From 70 to 80 years | 82-83 mm Hg. Art. |
| 81-90 years | 78-79 mm Hg. Art. |
The Volynsky formula takes into account the weight and age of the patient. The optimal value of individual working diastolic pressure is calculated as follows: 63 + (0.1*number of years) + (0.15*weight in kilograms)
Method of measuring blood pressure
Blood pressure is examined using a specialized blood pressure monitor. It is recommended to adhere to step-by-step methods of carrying out the procedure so as not to obtain overestimated or underestimated results.
- Select a cuff size that fits the shoulder.
- Provide the best conditions. The person should not be under stress or physical activity. The temperature should be room temperature, not cold or excessively warm.
- Taking into account additional factors. It is recommended to measure the indicator 1 hour before active physical activity, eating food and coffee, or smoking.
- Select the optimal table level. It should be of such a height that the cuff on the arm is located in the area of the intercostal line. If it moves by 5 cm or more, the degree of blood pressure will decrease or increase. The error will be 4 mm.
- Location of the pressure gauge scale. It should be at eye level so that the patient does not make mistakes during the procedure.
- Patient location. He should sit straight, leaning on the back of the chair. The body should relax, the legs should be placed straight, and should not be crossed. The hand for measuring pressure is placed on the table and relaxed. Parts of the body should not be tense during the procedure.
- Air pumping. The approximate state of the patient's blood pressure is assessed. During the pumping process, wait until the numbers on the tonometer reach this limit, then pump up another 30 mmHg. If the patient pumps the tonometer above this value, severe pain will begin in the arm.
- Reset. The first sound is formed, which is called the Short tone phase. This is an indicator corresponding to the upper value of blood pressure. When these tons completely disappear, phase 5 will form. This indicator will correspond to the lower pressure criterion.
- Repeated study. It can be carried out only 5-7 minutes after the initial use of the tonometer. During the analysis, the average indicator is calculated, which will be the most accurate and optimal for the patient. A one-time procedure may show an error.
- The first analysis is performed on both hands at once. A secondary study is carried out on only one upper limb.
If the heart rhythm is disturbed, measuring blood pressure becomes difficult. Therefore, it is recommended to evaluate the indicator only with the help of medical personnel.
The main reasons for pressure fluctuations in the body
The main reason for surges in blood pressure is an unhealthy lifestyle. Even minor alcohol abuse or lack of physical activity during the day can lead to changes in blood circulation in the body. In women, hormonal imbalances and age are often the causes of blood pressure surges.
What determines blood pressure fluctuations:
- Improper lifestyle (sedentary lifestyle, difficult working conditions, poor sleep);
- Abuse of alcohol and nicotine;
- Unhealthy diet (spicy, salty, unhealthy);
- Chronic diseases: heart disease, atherosclerosis, diabetes, vascular pathology, kidney disease, etc.;
- Overweight and obesity;
- Hereditary predisposition;
- Stress, nervous disorders, depression;
- Heavy physical activity in sports or at work;
- Spending a long time at the computer;
- Sudden change in weather or air temperature (sauna);
- Taking medications;
- Incorrect distribution of work and rest.
- The age of the person.
Table Risk factors for hypertensive patients
| Demographic characteristics and laboratory parameters |
| Genderª (men > women) |
| Ageª (≥ 55 years - men, ≥ 65 years - women). |
| Smoking (current or past)ª (IB) |
| Total cholesterolª and LDL cholesterol levels |
| Increased uric acid levels in the blood |
| Diabetes mellitusª |
| Overweight or obesity (IA) |
| Family history of CVD at a young age (<55 years for men and <65 years for women) |
| Development of hypertension at a young age in parents or in the family |
| Early menopause |
| Sedentary lifestyle |
| Psychological and socio-economic factors |
| Heart rate (resting value >80 beats/min) |
| Asymptomatic organ damage mediated by hypertension |
| Arterial stiffness: Pulse pressure (in elderly patients) ≥60 mm Hg. Carotid-femoral PWV >10 m/s |
| ECG signs of LVH (Sokolow-Lyon index >35 mm, or R wave amplitude in lead aVL ≥11 mm, Cornell product >2440 mm×ms or Cornell voltage index >28 mm for men and >20 mm for women) |
Echocardiographic signs of LVH:
|
| Microalbuminuria (30-300 mg/24 h) or increased albumin-creatinine ratio (30-300 mg/g; 3.4-34 mg/mmol) (preferably in morning urine)ᵇ |
| Moderate CKD with GFR >30-59 ml/min/1.73 m2 (BSA) or severe CKD with GFR <30 ml/min/1.73 m2b |
| Ankle-brachial index <0.9 |
| Severe retinopathy: hemorrhagic or exudative, papilledema |
| Diagnosed CVD or kidney disease |
| Cerebrovascular diseases: ischemic stroke, hemorrhagic stroke, TIA |
| IHD: MI, angina, myocardial revascularization |
| Presence of atheromatous plaques on imaging |
| Heart failure, including HFpEF |
| Peripheral artery disease |
| Atrial fibrillation |
_________________
| CV risk degree | The presence of at least one of the following criteria: |
| Very tall | Established diagnosis of CVD (according to clinical data or indisputably according to imaging data):
|
| High |
LVH due to hypertension;
|
| Moderate |
|
| Short |
|
Evaluation of results
After receiving the results, it is important to evaluate 1 parameter:
- presence of normal blood pressure:
- arterial hypertension;
- arterial hypotension.
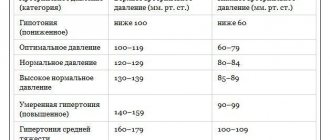
In 1999, a table was developed, according to which it is possible to determine the norm and increase in the level of pressure that negatively affects the patient.
| Pressure parameters | Upper, mmHg | Lower, mmHg |
| The best | 120 | 80 |
| Normal limits | 130 | 85 |
| Increased performance | More than 130 | More than 85 |
Attention! To assess the quality and degree of activity of the cardiovascular system, they look at the upper and lower values in combination. If they differ significantly, choose the parameter that has increased.
The table shows the degree of development of arterial hypertension, hypertension and pressure indicators:
| Degrees of hypertension | Upper value, mmHg | Lower value, mmHg |
| 1 | 140-160 | 90-100 |
| 2 | 160-180 | 100-110 |
| 3 | More than 180 | More than 110 |
| Border | 130-140 | No more than 90 |
| Systolic hypertension | More than 140 | After 90 |