Blood pressure (BP) is considered the most unstable indicator of the human body. Its level can change a huge number of times throughout the day at any age. This is due to hormonal levels, changes in weather conditions, emotional state, physical activity, etc. The average blood pressure is considered to be 120/80 mm Hg. Art. The numbers increase and decrease, the reasons for which may be physiological and pathological factors.
In this article we will talk about pressure readings of 100 to 60. What does this mean, should adults, children and women be wary of such numbers during pregnancy, and also what to do if the reasons for the appearance of such numbers on the tonometer are pathological processes in the human body.
What does each number mean?
Blood pressure is a measure of the pressure that blood exerts on the walls of blood vessels as it passes through them. The blood flow is created by the heart, which works like a pump. The heart muscle has the ability to contract (systole) and relax (diastole). During the first period, blood is pushed into large arteries, which is accompanied by the highest pressure levels. This is the first number. In this case we are talking about 100. The indicator is called systolic or upper (in common parlance) pressure.
During relaxation, the second number is recorded (in this case, 60). It is also called diastolic pressure or lower. Experts pay attention not only to these numbers, but also calculate the difference between them, calling this indicator pulse pressure. The blood pressure level is formed under the influence of the following factors:
- The force with which the heart pushes blood into the vessels.
- Hormonal background.
- Conditions of the central and peripheral nervous system.
- Conditions and indicators of arterial elasticity.
- The total volume of blood circulating in the body.
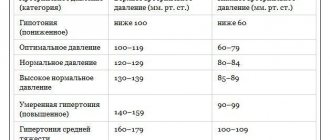
Important! The normal blood pressure level is considered to be 120–129/80–84 mmHg. Art.
Troubleshooting at home
Hypotonic patients should consume at least two liters of clean water per day, this will help maintain the blood in a normal fluid state. It is also recommended to drink one glass of dry red wine or drink a little black tea or coffee. Taking medications when the readings are 100 to 70 is not always appropriate. Good nutrition and physical activity, strengthening the body with sports will quickly bring blood vessels and the heart back to normal. Treatment of hypertension without proper sleep is impossible.
Additional measures to increase blood pressure can include:
- Taking vitamin C. It is found in cabbage, citrus fruits, parsley, spinach, cranberries, strawberries, broccoli, and tomatoes. Vitamin C has a beneficial effect on the adrenal glands, causing them to produce more adrenaline, which will increase the tonometer readings.
- Taking licorice root will allow you to produce hormones more freely, but the risk of swelling increases.
Do not overuse teas and herbs, try to balance your daily diet and this will be enough to raise your blood pressure to 102 to 72.
If you suffer from hypotension in the morning, then sleep at night on a high pillow, so there will be no sudden changes in pressure.
Causes of hypotension
Biophysical factors that are involved in the development of hypotension are:
- Decreasing the amount of venous blood that returns to the heart.
- Decrease in total circulating blood volume.
- Reduced vascular resistance in the periphery.
- Decrease in cardiac output and stroke.
Pathologies of pregnant women
Blood pressure of 100 over 60 during pregnancy, especially in women over 30 years of age, is considered a pathology, especially if symptoms of hypotension are added. Most often, low blood pressure is observed at the end of the first trimester of pregnancy and at 19-23 weeks. Persistent hypotension can cause oxygen starvation of the fetus, which provokes the development of malnutrition and damage to the child’s central nervous system. It is important to monitor the blood pressure of a pregnant woman in order to have time to adjust the numbers.
Teenage years
Adolescents aged 12–13 years experience hormonal changes in the body, which may be accompanied by a decrease in blood pressure. Girls are more likely to face this problem than boys. Hypotension is combined with both accelerated physical development of the body and its slowdown.
Important! A persistent drop in blood pressure during puberty (adolescence) can trigger the development of severe hypertension at a later age.
Psychological characteristics and constitution
Experts say that low blood pressure (for example, 101 to 63, 104 to 64) is more often complained of by patients who are prone to depression and an exaggerated sense of duty. In such cases, treatment is largely aimed not at taking medications, but at using meditative techniques, yoga, breathing exercises, and herbal medicine.
If we talk about the relationship between arterial hypotension and body constitution, then people with an asthenic body type more often complain about a decrease in blood pressure. In such patients, longitudinal dimensions prevail over transverse ones: arms and legs are long, the neck is thin and long, and the muscles are poorly developed.
Lack of physical activity
Modern innovations in technology are causing people to stop moving. Most people prefer to work and relax while sitting at the computer. In this case, not only hypotension occurs, but also cardiovascular diseases, digestive pathologies, and diseases of the musculoskeletal system due to weakness of the muscular system and joints.
Chronic infections
A third of patients who go to doctors with complaints of low blood pressure, dizziness, periodic pulsation in the back of the head and frequent headaches have foci of chronic infection in the body. In this case, hypotension is caused by intoxication, metabolic disorders (metabolism), and circulatory disorders.
Endocrine diseases
The organs of the endocrine apparatus are responsible for the state of the body's hormonal levels. The most common causes of hypotension are Addison's disease (adrenal dysfunction, characterized by a decrease in the amount of hormones produced) and hypothyroidism (lack of thyroid hormones).
Medicines
Long-term or uncontrolled use of medications can serve as a factor in lowering blood pressure. We are talking about the following groups of drugs:
- Sleeping pills.
- Painkillers.
- Antibacterial agents.
- Tranquilizers.
- Sedatives.
- Diuretics, etc.
What does pressure 10080 mean?
Detection of low blood pressure may indicate the following:
- the person is hypotensive;
- an acute attack of hypotension developed;
- when systolic pressure is below 90 – the patient is in a state of shock, there is a violation of microcirculation and tissue metabolism.
Reduced numbers are also detected in children under the age of 16–17 years, which is a physiological condition and is not life-threatening.
The diagnosis of hypotension is established based on repeated measurements of the patient's blood pressure on different days and times of day. In the absence of complaints and pathological symptoms, a person can live a full life without treatment.
Acute attacks of hypotension occur in various conditions, such as:
- injuries to the brain or medulla oblongata;
- metabolic disorders (diabetes mellitus, ketoacidotic coma);
- contusion of the heart muscle;
- pericardial hemotamponade and others.
A chronic physiological decrease in blood pressure is a characteristic feature of tall people with low body weight (asthenics). Their peculiarity is the frequent presence of connective tissue diseases, decreased body reactivity, and a tendency to motion sickness.
Types of hypotonic conditions
Primary hypotension is characterized by a decrease in blood pressure, the causes of which are not pathologies of the heart and blood vessels. Secondary, on the contrary, is a manifestation of a disease. Depending on how long the numbers remain at low levels, acute and chronic forms of the pathological condition are distinguished. In the first case, if we talk about blood pressure 100/60, such numbers remain at a low level for a short time, in the second - over a long period.
Physiological form
We can talk about a physiological variant of hypotension if a pressure of 100/60 (or other low numbers) is discovered by chance, is not accompanied by a deterioration in general well-being and is caused by some physiological reason. Hypotension can be an individual variant of the norm, observed in people actively involved in sports and those living in tropical and subtropical climates.
Pathological form
This type of blood pressure reduction exists in two variations: neurocirculatory and idiopathic orthostatic. The first type manifests itself with a clear clinical picture, the second is characterized by a drop in blood pressure only if the body position changes from horizontal to vertical (for example, when getting out of bed in the morning).
Symptomatic form
She is secondary. It is a symptom of a certain disease. May occur against the background of:
Blood pressure 100 to 80
- Diseases of the heart and blood vessels (heart failure, cardiomyopathy, inflammation of the myocardium, pericardium).
- Pathologies of the respiratory system (pneumonia, tuberculosis, bronchial asthma).
- Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (stomach and duodenal ulcers).
- Diseases of the renal apparatus (econephropathy, nephritis).
- Pathologies of the nervous system (Parkinson's disease, encephalopathy, cerebral infarction, mental illness).
Diagnostics
Diagnostic measures to identify hypotension begin with interviewing the patient. A therapist or cardiologist will ask about changes in tonometer readings over a long period of time and ask about current symptoms and general well-being. Examines the patient and measures blood pressure. After this, the doctor may order several or all of the following tests:
- Cardiogram.
- Echocardiography.
- General blood analysis.
- Blood chemistry.
- Angiography.
- Radiography.
- Ultrasound of the heart.
- Daily blood pressure monitoring.
After establishing the causes of low blood pressure, the doctor will prescribe therapy.
Feeling good with blood pressure 100/60
If the pressure drops sharply, the patient complains of headache, dizziness, pulsation in the back of the head, rapid heartbeat (at a pressure of 100 to 60, the pulse can reach 100 beats/min). Cold sweat, severe weakness appear, trembling in the limbs may occur, and body temperature decreases. The result of a critical drop in indicators is a fainting state requiring emergency assistance.
With chronic hypotension, the patient complains of daily weakness, fatigue, emotional lability, depression, and shortness of breath. With a chronic type of pathology, people get used to attributing their poor health to all sorts of factors, but not to a drop in pressure. The problem is associated with changes in weather conditions, fatigue at work, stress, overeating or, conversely, diet abuse.
Associated symptoms
Hypotension (low blood pressure) is characterized by the following symptoms:
- chronic fatigue and lethargy;
- fainting;
- fast fatiguability;
- constant drowsiness;
- darkening of the eyes, especially during sudden ascents;
- irritability;
- sound and photophobia;
- excessive heartbeat even with light exertion;
- memory impairment;
- problems with concentration;
- cold hands and feet;
- deterioration of libido;
- muscle weakness;
- indigestion;
- intolerance to heat and/or cold;
- regular headaches and/or dizziness;
- low body temperature;
- seasickness.
If a person experiences at least three of the listed symptoms on an ongoing basis without any factors directly causing such symptoms, it is strongly recommended to consult a specialist.
Diagnostic measures
When contacting specialists with a problem of low blood pressure (for example, 100–106 to 60–66), patients are interested in the question of whether this is normal, and if not, how to improve the readings. The doctor must ask the patient about the following points:
- When were such pressure indicators first noticed?
- Associated symptoms.
- What is the patient’s “working” pressure?
- Do the patient and his relatives have any diseases of the cardiovascular system?
- The presence of pathologies of other systems.
- Does the person take any medications, etc.
Hypotension can cause fainting
Blood pressure must be measured several times at intervals of 5–10 minutes. If necessary, daily monitoring of blood pressure with monitoring of pulse and other indicators of heart function is prescribed. Additional methods include ECG, echocardiography, electro- and rheoencephalography, and examination by an ophthalmologist.
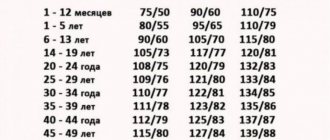
Blood pressure 105 over 65 in children and adolescents
Children and adolescents are characterized by low blood pressure relative to the standard “adult” indicators of 120 to 80. If a young growing body is comfortable with this pressure and there are no accompanying symptoms, it means that this is normal pressure for a particular young person.
However, in cases where a child notices at least a couple of symptoms of hypotension (often lethargy, headaches, fatigue), then it is definitely worth contacting your treating pediatrician.
A blood pressure of 105 over 65 is generally at the lower limit of normal. For women and children, this pressure is very common and normal. The main criterion by which it is worth assessing whether such pressure is normal is the self-perception of each individual person.
Correction of indicators and first aid
To increase the pressure, you must follow the following algorithm:
- Call a team of medical workers.
- Lie on a horizontal surface with the leg end raised or lay the victim down in this way.
- Open a window or direct a fan to provide fresh air.
- Drink sweet warm tea or give the victim something to drink. You can add 10 drops of tincture of eleutherococcus, ginseng or Rhodiola rosea.
- Rub your whiskey with lemon essential oil.
What does pulse pressure mean?
Increased pulse pressure is often observed in people suffering from hypotension. This may indicate vascular disease and ischemic disease, more often tachycardia. It can be calculated by subtracting the “lower” pressure from the “upper” pressure reading. That is, with a blood pressure reading of 100/80, it is 20 beats per minute. But what if the pulse is 100 beats per minute?
To normalize your heart rate, stop activity and relax. Try to breathe deeply and calmly, unfasten tight clothing, and wash with cold water. Take valerian, if there are no contraindications or intolerances to it, open the window to let fresh air in. If your pulse does not return to normal, seek medical help and call an ambulance at home.
Treatment recommendations
First of all, it is necessary to normalize your lifestyle. You should do gymnastics daily, preferably in the fresh air. Evening walking, swimming, cycling, and light jogging are excellent options for low blood pressure. You should stop drinking alcohol and smoking and normalize your sleep. And it is also important to correct the diet: give up fried, smoked and fatty foods, include a large amount of vegetables and fruits, grains in the menu.
The prescription of medications depends on the type of hypotension. In the primary form of the pathology, anticholinergics are used, which have a sedative and antispasmodic effect. In order to increase the heart rate (according to indications) and increase the return of blood to the heart, sympathomimetics are prescribed.
And they also use preparations based on herbal and other natural ingredients (tincture of aralia, ginseng, zamanikha, camphor, Pantocrine, Saparal). In the treatment of symptomatic hypotension, attention should be paid to the treatment of the underlying disease that caused the decrease in blood pressure. To regulate blood pressure numbers, it is important to take vitamins:
- Thiamine.
- Riboflavin.
- Niacin.
- Pantothenic acid.
- Pyridoxine.
- Folic acid.
- Cyanocobalamin.
- Ascorbic acid.
- Calciferol.
Important! Hardening helps well, which can be used to prevent a hypotonic state.
What does a high or low heart rate indicate?
Not much. Heart rate and blood pressure monitor levels are not related. Although the correlation is obvious, it does not exist.
However, the pulse can be used to assess the danger of the process, the need for hospital treatment and the prospects for recovery.
Sinus-type tachycardia (90-100 beats or more while maintaining the correct rhythm and intensifying the work of the natural driver) requires correction of the underlying disease. The acceleration of cardiac activity in itself does not pose a danger.
The paroxysmal type of tachycardia (paroxysmal) is associated with the threat of cardiac arrest and sudden death.
Fibrillation, fluttering, as well as group extrasystoles such as bigeminy and trigeminy, which are recorded during the ECG, provoke a fatal result even more often.
Bradycardia, that is, a decrease in heart rate of less than 60 beats per minute indicates a violation of tissue conductivity or a weakening of myocardial contractility. The prognosis is getting worse.
This is an indirect connection, mostly noted as a result of organic disorders of the heart and blood vessels.
Why might blood pressure drop?
A value of 100 to 80 is not considered normal, but predicting serious pathologies only based on blood pressure and pulse differences is unacceptable. To understand the cause of this condition, you will have to monitor your blood pressure over time, not forgetting to measure your pulse along with your blood pressure. In addition, biochemical blood testing is important.
Low blood pressure in a healthy person
100/80 is not considered a characteristic sign of hypotension, but if a pressure of 120-125 over 80-85 is considered normal for a patient, it is worth thinking about the reasons for the appearance of low numbers. The presence of episodic fluctuations in blood pressure can be explained by external influences; if the drop in the indicator becomes regular, you should look for possible health problems associated with other reasons:
- extensive blood loss, symptoms of dehydration;
- consequence of the development of vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- signs of abnormal heart valve function;
- lack of adrenal and thyroid hormones;
- the development of thromboembolism as a result of heat stroke.
Deviation of pressure from the norm in the downward direction is more often found in adolescents and the elderly. In women during pregnancy, it is subject to fluctuations; a decrease to a level of 100 to 80 may indicate hormonal changes, the development of heart or kidney pathology. But it is not recommended for pregnant women to take medications that increase blood pressure on their own, so as not to harm the fetus.
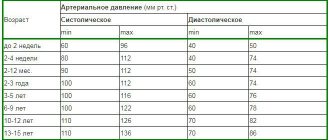
Blood pressure indicators in preschool children are at the level of 95/60 mmHg. Art., which is considered normal, and their increase to 100 units by 80 already borders on a sign of the onset of hypertension. Men are characterized by higher units, which may fall due to an overdose of drugs for hypertension, in case of problems with heart function.
A table of pressure indicators for a relatively healthy person is given below.
Important: A small pulse difference is especially dangerous, which can signal a weak heart and an increased risk of a heart attack. No treatment is given for physiologically low blood pressure
100 to 80 in hypertensive patients
If, during the treatment of hypertension, a patient’s blood pressure drops to one hundred units, this is a signal that it is necessary to adjust the list of drugs used to treat hypertension. Also, the cause of a drop in blood pressure may be associated with the following factors:
- post-stroke period, in this case it is important to monitor the pulse, it may increase;
- overdose of antihypertensive drugs used to reduce high blood pressure units;
- increased physical activity of a hypertensive patient who is unaware of his pathology.
In hypertension, low blood pressure is often recorded during waking hours, which is manifested by a sudden loss of balance due to dizziness. A person may even lose consciousness due to such a jump. If you have a similar symptom without measuring your blood pressure, you should not immediately take a pill that lowers it, this will only worsen the condition.
100 to 80 and high pulse
The pulse reflects the heart rate; 80 beats per minute is considered normal. If, with low pressure, the pulse rises to 100 beats or higher, this is a possible onset of tachycardia, which accompanies psychosomatic disorders. A drop in blood pressure with an increase in heart rate can be observed in men who are professionally involved in sports, as well as under stress or taking antidepressants.
Please note: Tachycardia when the pressure drops to 100 to 80 can result in shock due to a deterioration in the ability of the cardiovascular system to get rid of carbon dioxide and metabolic products. This condition poses a threat of death
The effect of age on blood pressure
Continuing the study, taking into account the above information, we will try to establish: is the above blood pressure value - 100/80 - the norm?
Blood pressure largely depends on age. So, let's look at blood pressure standards by age. In infancy, for example, for one-year-old babies 96/66 is the norm, also the norm for men from 40-49 years old is 135/83, and for old people 80 years of age and above, their own norm is 147/82. For women, these figures are slightly lower - by 5-10 units. During pregnancy, blood pressure is often elevated. It changes several times during the day. Its indicator depends on many factors:
- One-time physical activity and sports lead to increased blood pressure.
- Taking medications can lead to both an increase and a decrease.
- Time of day - at night blood pressure is lower.
- Taking stimulants, such as alcohol, tea, coffee - an increase followed by a sharp decrease.
- Psychological state: stress provokes surges in blood pressure.
It is noteworthy that one-time maximum loads usually lead to an increase in blood pressure, and with stable high physical activity, when the body gradually adapts to it, blood pressure normalizes and even decreases slightly.
Blood pressure 100/80 - in pregnant women, elderly people (usually a consequence of high cholesterol), in men (their norm is usually higher than in women) - can be considered a sign of hypotension or, more correctly, hypotension. True, initial level. Arterial hypotension (hypotension) is a concept meaning low blood pressure. This is a “beacon”: the tone of blood vessels and muscles is reduced.
How to prevent the situation from getting worse
When your blood pressure is 110 over 80, it is very important to make a few adjustments to your lifestyle. This will help improve the condition and prevent the progression of hypotension
Rules for living when blood pressure deviates from the norm:
- Active lifestyle. Play sports or get into the habit of walking in the evenings. This will significantly improve the condition of the body.
- Stop smoking. The results of this innovation will be noticeable almost immediately.
- Normalize your sleep. Sleep at least 8 and no more than 12 hours a day. It is also advisable to take a fifteen-minute rest every two hours of hard work.
- Maintain drinking regime. To calculate your fluid intake, you need to multiply your weight in kilograms by 30 ml.
- Avoid stress. Try not to get into conflict situations or create them.
- Eat right. Avoid fried, fatty and low-quality foods. Avoid drinking alcohol. Eat plenty of fresh vegetables, fruits and dairy products.
- Get rid of everything unnecessary. To improve your condition, you need to fight extra pounds. However, strict diets are prohibited. The best way to lose weight is proper nutrition and exercise.
A pressure of 100 over 80 is a non-critical indicator . Separately, such values of systole and diastole are within the normal range. However, due to low pulse pressure, such blood pressure has a negative impact on health and may be a symptom of problems within the body. Therefore, it requires consultation with a specialist.
Possible complications
Outside of therapy or with an insufficiently high-quality regimen, the following consequences may occur:
- Heart failure. As a result of a drop in output, blood stagnation and a decrease in myocardial contractility.
- Stroke. Acute malnutrition of cerebral structures. Potentially fatal condition.
- Heart attack. Necrosis of the muscle layer. Leads to deficiency, dysfunction and lifelong disability. The possibility of death always looms on the horizon.
- Cardiogenic shock. Carries the greatest danger. Even with timely assistance, no one guarantees the patient’s life. Statistics show that death occurs within 3-4 years, which happens less in almost 100% of people. The cause is a repeated episode of cardiac arrest or massive heart attack.
- Vascular dementia. As a result of constant disruption of nutrition of cerebral structures. Forms a clinical picture similar to that of Alzheimer's disease.