(Health Center) There is a lot of talk about high blood pressure (hypertension). But low blood pressure (hypotension) seems to be considered a minor problem. The number of risks associated with hypotension is much less than with hypertension. However, those whose blood pressure is consistently below normal often feel tired and overwhelmed. For such people, knowing the possible causes of hypotension, and especially knowing how to stabilize low blood pressure, means a significant improvement in quality of life.
Causes of low blood pressure and ways to solve the problem
Low blood pressure causes lethargy and fatigue, accompanied by dizziness, decreased ability to concentrate and thus can significantly worsen your well-being. Doctors often tell hypotensive patients that low blood pressure is not as serious a problem as hypertension, and therefore nothing needs to be done.
But for anyone who would like to feel better, such words, of course, are of little use. Therefore, we will tell you about the possible causes of low blood pressure, which even doctors often do not think about, as well as how you can increase low blood pressure.
Causes of arterial hypotension
Causes of low blood pressure may include:
- Dehydration, blood loss, iron deficiency.
- Impaired cardiac function (heart failure, heart defects, pericardial disease, etc.).
- Decreased tone of arterial vessels (poisoning, allergic reactions, etc.).
- Taking large doses of antihypertensive drugs (drugs to lower blood pressure).
- Nervous-psychological stress, neuroses, depression, stress.
- Insufficient physical activity.
- Poor nutrition.
- General fatigue, chronic fatigue.
- Infectious diseases.
- Weather change.
- Hereditary predisposition.
- Lack of body weight.
- Impaired kidney function.
Low blood pressure is not a cause for concern if low blood pressure numbers are observed in a person in most cases and are not accompanied by any health complaints. You should consult a cardiologist if hypotension is not a normal condition for a given person and is combined with a deterioration in general health, greatly reducing the patient’s quality of life.
Low blood pressure - less than 100/60 mmHg
As you know, when measuring blood pressure, two indicators are distinguished: systolic and diastolic pressure.
First, the systolic blood pressure is indicated. This pressure occurs when the heart pumps blood into the arteries. It is always higher than diastolic pressure.
The second indicator is diastolic blood pressure. This is the pressure in the blood vessels between two contractions of the heart, that is, at the moment when the heart is not pumping blood.
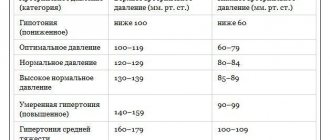
Healthy blood pressure, according to today's understanding, is approximately 120/80 mmHg. Indicators above 140/90 mm Hg. Art. referred to as high blood pressure. If the pressure gauge regularly shows less than 90/60 mmHg. Art. and even less than 100/60 mmHg. Art., then they talk about low blood pressure. If only one of the two indicators is very low, this is already enough for the development of the corresponding symptoms.
Low blood pressure: symptoms and causes
Low blood pressure or hypotension is a pathological change in the human body in which blood pressure drops below generally accepted norms (120/80 mm Hg). Low blood pressure is considered to be reduced to 90/60 mmHg. Art. and below. The disease is treated only if it has a negative impact on the human body.
Physiological norms of hypotension:
- a feature of the body, low blood pressure is the norm for the structure of a certain individual;
- compensatory, adaptive, typical for a person living in the mountains;
- orthostatic hypotension - a sudden change in body position;
- Postprandial hypotension is a decrease in blood pressure after eating food.
Low blood pressure - causes:
- diseases of the cerebral vessels, mainly central;
- stress;
- thyroid diseases;
- cancer;
- anemia;
- hepatitis;
- inflammation of heart tissue;
- brain injuries;
- rheumatism;
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- gastrointestinal ulcer;
- taking certain medications;
- strong physical activity. Acts as a protective reaction of the body;
- change of place of residence to a different climate zone or sudden change in weather;
- change in electromagnetic field;
- exposure to radiation;
- heredity;
- VSD (vegetative-vascular dystonia).
Quite often, hypotension is a symptom of VSD. Vegetovascular dystonia is a disruption of the human body by the autonomic nervous system. This symptom causes disturbances in the functioning of: cardiovascular system (cardiovascular system), heart rate (heart rate), endocrine system, thermoregulation, etc.
Causes of VSD: chronic stress, tension, neurosis, psychological trauma, negative habits, occupational hazards, heredity.
Symptoms of low blood pressure:
- Decrease in pressure to 90/60 mm Hg. and below.
- Weakness.
- Cardiopalmus.
- Sleep disturbance.
- Cold hands and feet.
- Frequent mood swings, aggression.
- Increased sweating.
- State of drowsiness.
- Frequent dizziness.
- Headache in the forehead and temples.
- Shortness of breath after slight exertion.
- Fainting.
- Nausea.
Complications:
- problems with the cardiovascular system, due to rapid heartbeat there is a strong load on the heart muscle;
- Pregnant women experience oxygen starvation of the fetus and disruption in its development. Also, pregnant women with hypotension often experience severe toxicosis and gestosis.
Low blood pressure - diagnosis:
- taking anamnesis;
- inspection;
- blood pressure measurement and daily monitoring;
- examination by doctors: neurologist, cardiologist, endocrinologist;
- blood analysis;
- Analysis of urine;
- Ultrasound of the heart;
- load tests;
- CT;
- MRI;
- Ultrasound of the kidneys, adrenal glands, thyroid gland.
Treatment.
If a concomitant disease causing hypotension is detected, it is treated. In the absence of other diseases, medications are prescribed to normalize blood pressure. Strictly follow the daily routine and proper nutrition. Stop smoking and minimize alcohol consumption. Regular walks.
Prevention:
- giving up bad habits (smoking, minimizing alcohol);
- sleep at least 7-8 hours;
- active lifestyle;
- body weight control;
- blood pressure control.
Blood pressure is constantly changing
However, blood pressure fluctuates and values can change greatly in a short time, even between two heartbeats. The fact is that blood pressure depends on many factors: body position (whether a person is lying, standing or running), breathing rate, stress level, state of health, nutrition, what medications a person takes, and the time of day . For example, at night your blood pressure is usually very low. When we wake up, it increases quickly.
Lower and upper blood pressure
In a healthy person, the heart muscle contracts 60 to 80 times per minute at rest. With each contraction, the heart pumps another portion of blood into the arteries. Accordingly, the maximum blood pressure on the walls of blood vessels is recorded at the moment of contraction of the heart muscle. Between contractions, the heart muscle relaxes. At the time of such rest, blood pressure is at its lowest.
The highest reading is called systolic or upper pressure. The name comes from the word “systole” - the stage of contraction. The lowest pressure reading is called diastolic (from the word “diastole” - the stage of relaxation). Systole and diastole are stages of the normal cardiac cycle.
Pressure readings are traditionally recorded in millimeters of mercury. When measuring, the upper pressure indicator is always indicated first, and the lower pressure indicator second.
Low blood pressure is often a good sign
It is possible that a person’s blood pressure is often low, that is, less than 100/60 mmHg. Art., but I feel excellent and have no complaints. This means that this blood pressure is optimal and helps a person stay healthy as they age.
Athletes tend to have lower overall blood pressure and a slower heart rate than the average person. Non-smokers, those who are of normal weight and who eat healthily also tend to have low blood pressure (which is a good sign), while smokers, people who are overweight, have a poor diet and are sedentary often have low blood pressure. have to deal with high blood pressure.
However, if your blood pressure is constantly low and you do not feel in good shape, then your blood pressure is definitely TOO low and you need to start looking for the causes and solutions to the problem. You may be experiencing the symptoms listed below.
What is the blood pressure of a hypertensive patient?
Doctors recognize normal blood pressure levels as 120 to 80 mmHg.
If it is higher than normal, a diagnosis of hypertension is made, and if it is lower, hypotension is diagnosed. Blood pressure in hypertensive patients can change throughout the day, and short-term increases are caused by physical activity and poor lifestyle. Blood pressure can also rise sharply due to nervousness. Hypertension is a pathology in which elevated blood pressure levels depend on physiological and pathological factors:
- Emotional stress
- Mental fatigue
- Genetic predisposition,
- Age,
- Hormonal changes
- Overweight,
- Concussion and other brain injuries
- Pathologies of the endocrine system,
- Chronic, infectious diseases,
- Exceeding the permissible cholesterol level.
The normal blood pressure of hypertensive patients depends on the degree of the disease:
- 1st degree or mild: systolic blood pressure from 140 to 160 mmHg, diastolic from 90 to 99 mmHg,
- Grade 2 or moderate: systolic blood pressure from 160 to 180 mm. Hg, diastolic - from 100 to 110 mmHg,
- Grade 3 or severe: blood pressure remains stable above 180 to 110 mmHg.
Symptoms of low blood pressure
Low blood pressure is manifested by the following symptoms:
- dizziness to the point of fainting,
- darkness before the eyes when standing up,
- visual impairment,
- noise in ears,
- headache,
- fatigue and decreased concentration,
- dyspnea,
- pallor,
- cold feet and hands.
A sudden drop in blood pressure can be dangerous. Even its decrease by only 20 mm Hg. Art. (eg, from 110 to 90 mm Hg in systole) sometimes causes dizziness and loss of consciousness because the brain does not receive enough blood as a result.
If blood pressure decreases as a result of significant blood loss (in an accident), serious infections or allergic reactions, low blood pressure can be life-threatening. Fortunately, this rarely happens.
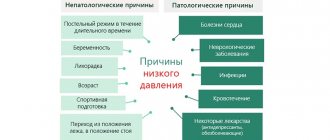
Reasons for decreased blood pressure
The main reason for low blood pressure in hypertensive patients is considered to be drug overdose. Most often this occurs due to a lack of knowledge and taking medications without a doctor’s prescription.
Among the secondary reasons are:
- Low blood pressure - what to do, first aid. Causes of low blood pressure and treatment at home
- Diseases of the cardiovascular system (coronary heart disease, heart failure, endo- and myocarditis, pulmonary edema).
- Vegetative-vascular dystonia.
- Infectious diseases.
- Diseases of the kidneys and adrenal glands.
- Reduced blood sugar levels.
- Mental illnesses – depression, severe and prolonged stress.
- Taking antidepressants, analgesics.
- External and internal bleeding (perforated ulcer, hemorrhoids).
- Anaphylactic shock.
- Severe pain syndrome (attack of pancreatitis, renal colic, peptic ulcer, periodic pain in women).
Provoking factors
Not only the above conditions, but also a number of other provoking factors can lead to a decrease in blood pressure.
Common risk factors include:
- Prolonged bed rest.
- Pregnancy.
- Fever.
- Elderly age.
- Sedentary lifestyle.
- Orthostatic collapse when abruptly getting out of bed (especially in old age).
- Exposure to elevated temperatures that cause vasodilation (thermal springs, baths, saunas).
- Errors in nutrition.
- Prolonged exposure to the sun and tanning can cause blood pressure to drop. When tanning, adrenaline turns into the tanning hormone melanin and very little of it remains to maintain blood vessels in tone. Hence - weakness and hypotension after prolonged exposure to the sun.
A decrease in blood pressure due to hypertension always manifests itself with characteristic symptoms.
The most notable ones include:
- General weakness, lethargy, asthenia.
- State of depression.
- Headache.
- Nausea, vomiting.
- Darkening in the eyes.
- Dizziness.
- Possibly frequent loose stools.
Some symptoms are characteristic of both hypertensive and hypotensive crises. Therefore, you should pay attention to the totality of other manifestations.
| Hypotonic crisis | Hypertensive crisis |
| Skin | |
| The skin is pale, cold. Often - cold sticky sweat. Cold hands and feet. | The skin is pink and warm. The face is hyperemic. Extremities are warm. |
| Headache | |
| The pain is aching in nature, often diffuse. | The pain is pulsating in nature, often localized in the back of the head. |
| Heartbeat | |
| Weak, pulse is poorly defined. | Strong, often rapid. The pulse is frequent and well filled. |
| State of mind | |
| Depressed, increased sleepiness is noted. | Excited. |
| Other manifestations | |
| Nausea, single vomiting. Unsteady gait. Darkening in the eyes. Possible loss of consciousness. | Nausea, repeated vomiting, which does not bring relief. Flashing of flies before the eyes. |
A sharp decrease in blood pressure in a hypertensive patient is much more severe than in an ordinary person. And prolonged hypotension leads to negative changes in organs and tissues.
Types of low blood pressure
In general, low blood pressure conditions fall into three categories:
- Primary hypotension
In this case, the causes of hypotension are unknown. It is believed that slender young women often face this problem. This form of low blood pressure also occurs in people who lead a sedentary lifestyle. However, in general, this group includes all hypotensive patients whose causes of low blood pressure remain unclear from the standpoint of official medicine.
- Secondary hypotension
The adjective “secondary” means that hypotension is a consequence of another disease or the result of other known factors. This could be a hormonal imbalance (Addison's disease, low thyroid function), a side effect of medications taken, heart disease, or a phenomenon accompanying an infectious disease.
The advantage of secondary hypotension is that when the cause of low blood pressure is known, it is easier to find a solution.
- Orthostatic hypotension
This form of low blood pressure manifests itself primarily in the fact that when getting up from a lying or sitting position, you feel dizzy, your vision becomes dark, and you feel like you need to grab onto something to avoid falling.
When a person stands up, the blood naturally goes down to the legs. A healthy body easily compensates for this displacement: the blood vessels narrow, the heart begins to beat faster. Thanks to this, the brain is supplied with blood.
In people suffering from orthostatic hypotension, this regulatory mechanism is disrupted. Blood pressure drops, and in the worst case, the person loses consciousness.
This form of low blood pressure can be caused by various reasons. Blood pressure does not necessarily remain low all the time - it may only happen on some days or only during certain periods, for example during pregnancy, during extreme heat or after lying in bed for a long time. Diabetes, heart problems, certain neurological disorders, and varicose veins also—along with the medications listed below—may increase the risk of orthostatic hypotension.
Those diagnosed with orthostatic hypotension should rise very slowly. You should not get up immediately from a lying position: you must first sit down, sit for one or two minutes and only then get up.
Sometimes blood pressure drops immediately after eating. This form of hypotension is called postprandial hypotension.
Postprandial hypotension
In people with postprandial hypotension, too much blood flows into the digestive system after eating. Compensation mechanisms, which in a normal situation ensure blood supply to the brain as before, despite the digestion of food, do not work in this case.
Postprandial hypotension is often observed in hypertensive patients, which, of course, can be explained by incorrect dosage of drugs to lower blood pressure.
If you have postprandial hypotension, you should always eat only small portions and ensure that the food is healthy, nutrient-dense and does not contain isolated carbohydrates (sugar, white flour products).
What is the danger?
The cardiovascular system of a hypertensive patient is constantly tense. A sharp drop in blood pressure in such a situation threatens the health and functionality of the entire cardiac mechanism and the body as a whole. Therefore, it is prohibited to sharply reduce high blood pressure in hypertensive patients, otherwise the following dangerous processes will develop:
This condition in the patient provokes a narrowing of the blood vessels in the brain.
- The rapid expansion of blood vessels leads to a lack of blood flow, since it cannot increase in a short period of time.
- As a result of the current difficult situation, a narrowing of the blood vessels in the brain occurs.
- The blood supply to the brain is disrupted, as a result of which it gives the command to reduce the pressure. Oxygen starvation occurs, which leads to the death of its damaged areas. The occurrence of hemorrhage ends in instant death.
Return to contents
Causes of low blood pressure
Often it is not possible to find out the cause of low blood pressure. This may be unpleasant for patients, but does not have serious consequences - unlike patients with chronically high blood pressure.
However, often the doctor is the cause of low blood pressure, which is not thought about at all. Of course, not directly, but indirectly. Many people have had their blood pressure rise during a doctor's appointment at some time in the past. They were prescribed drugs to lower blood pressure, patients diligently took the pills, and it did not occur to them to check whether this was still necessary.
- Blood pressure lowering medications are the main cause of high blood pressure
In the summer of 2021, the results of a study on this topic were published. It covered more than 11,000 patients over the age of 70 years. 1,900 of them had low blood pressure. Imagine: 1,246 of them were taking blood pressure medications. Of those with the lowest blood pressure, 70 percent used such drugs.
Thus, in older people, the main cause of too low blood pressure is blood pressure-lowering medications.
Apparently, they are prescribed very often, without thinking about the fact that the patient's condition may change. Some people are prescribed other drugs over time (see point 2).
The interaction of medications is not always taken into account, and therefore a situation may arise when medications further reduce blood pressure, lowering it below a minimum. At the same time, it is precisely in older people that too low blood pressure often causes death and referral to the hospital - this fact was noted by the authors of the study.
Therefore, if, while taking medications to lower blood pressure, you feel unwell, often feel dizzy and weak, it is possible that the cause of this condition is not high blood pressure, but, on the contrary, too low blood pressure due to the medications. Consult your doctor about this!
The most well-known drugs that lower blood pressure include:
- diuretics (diuretics), such as furosemide and hydrochlorothiazide, which are prescribed for high blood pressure, but also for edema, heart and kidney failure and hyperkalemia (excess potassium),
- alpha blockers, such as prazosin,
- beta blockers such as atenolol.
- Medicines
In addition to special drugs, other drugs can reduce blood pressure and thus cause hypotension. Many of them were developed and are assigned to solve completely different problems.
- Medicines for Parkinson's disease, such as pramipexole, and products containing levodopa.
- Some (tricyclic) antidepressants, for example, doxepin, imipramine, etc.
- Viagra (sildenafil), especially in cases where nitroglycerin is also taken for heart support (against angina).
- Sedatives.
- Antihistamines.
- Pregnancy
During pregnancy, due to increased stress on the body, blood pressure can drop significantly. As a rule, blood pressure returns to normal, at the latest after childbirth.
- Heart problems
If the cause of too low pressure is heart problems, the matter is not limited to slight dizziness. Many other complaints also arise. Heart problems that can cause low blood pressure include bradycardia (very low heart rate), heart valve disease, myocardial infarction, or heart failure.
- Functional disorders of the thyroid gland
Reduced thyroid function can also cause low blood pressure. Because both conditions (low glandular function and hypotension) have similar symptoms, patients sometimes think they “only” have low blood pressure. But in fact, there may be a malfunction of the thyroid gland.
- Adrenal insufficiency
If adrenal function is weakened, low blood pressure may occur along with other symptoms. The adrenal glands, which sit directly on the kidneys, produce hormones including adrenaline and norepinephrine. Both of these hormones activate the body. When needed, they speed up the heart rate, improve blood flow to the muscles, promote the release of glucose and increase blood pressure.
In the case of chronic adrenal insufficiency, such an activating effect on blood pressure is absent, blood pressure becomes chronically low, and the person feels completely powerless.
- Dehydration
Dehydration (lack of water) is also a serious cause of low blood pressure. It occurs in those who consume too little fluid or lose a lot of fluid due to certain circumstances (such as diabetes, fever, vomiting, diuretic abuse, extreme sports without drinking). Even slight dehydration can cause weakness, dizziness and fatigue.
- Deficiency of essential substances
Lack of vitamin B12, folate (folic acid) or iron leads to anemia. The body loses its ability to produce enough red blood cells. As a result, anemia develops and blood pressure decreases. There is a feeling of weakness, loss of strength. Other B vitamins and vitamin C also improve blood pressure and can seriously help with low blood pressure.
Pressure, don't drop!
Probably every adult has heard or knows firsthand how arterial hypertension negatively affects the body when blood pressure is above normal 120/80 mm Hg.
But not everyone knows how dangerous the opposite condition is - hypotension. Moreover, it is not entirely clear what indicators correspond to it.
The conversation will be about where the border between normal and pathological is, and what to do when the Rubicon is behind us.
Arterial peak
The blood pressure value is reflected in two numbers. The first demonstrates the level of pressure blood exerts on the walls of blood vessels during contraction of the heart muscle. This pressure is called systolic.
The second indicator is diastolic, it reflects the blood pressure on the vessels at rest, between heartbeats.
A normal blood pressure is 120/80 mmHg. However, this does not mean at all that 110/70 already indicates hypotension. There is some “play” in indicators that differ from the average statistical norm, both smaller and larger.
This is due to the fact that even in healthy people, blood pressure is not a constant constant. It decreases during sleep and increases when awakening or activity. Sometimes indicators can fluctuate between 30-40 mmHg. during the day!
Have you ever felt a momentary feeling of dizziness and weakness when you suddenly got out of bed? They appear due to excessive blood flow to the extremities and, accordingly, outflow from the brain. A healthy body with orthostatic hypotension—that’s what this condition is called—reacts very quickly by narrowing blood vessels and increasing pressure.
Sometimes low blood pressure (that is, lower than 120/80) becomes permanent and is not accompanied by unpleasant symptoms. This often happens at a young age. This is a variant of the norm.
However, if pressure readings reach 90/60 mm Hg. or fall even lower, we are talking about arterial hypotension.
Causes and signs of hypotension
There is an impressive list of factors that do not allow the body to independently normalize blood pressure. By the way, such a popular diagnosis as vegetative-vascular dystonia does not apply to them. Moreover: such a diagnosis does not exist, but that is a completely different story.
Returning to the real causes of hypotension, we list the most common:
- Decreased blood volume, or hypovolemia, is the most common cause. It may result from insufficient fluid intake, fasting, or excessive water loss through vomiting or diarrhea.
- Heart disease - if the heart muscle cannot pump enough blood, blood pressure drops. This happens with myocardial infarction and heart failure.
- Hormonal imbalance, primarily thyroid dysfunction
- Blood diseases - decreased hemoglobin levels (anemia).
- Taking a number of medications, in particular diuretics (can help reduce blood volume), antihypertensive drugs of various groups, including calcium channel blockers, ACE inhibitors, angiotensin II blockers, beta blockers, and nitrates (nitroglycerin).
Characteristic signs of hypotension: • Dizziness, weakness • Blurred vision • Fatigue • Nausea • Pale, cool skin.
The main danger of hypotension is a decrease in quality of life and a high risk of injury in situations where loss of consciousness occurs against the background of low pressure. In severe, critical cases, hypoxia can develop, and then the brain, heart and other organs suffer from lack of oxygen. To prevent this from happening, it is important to control your blood pressure. If it drops below 90/60 mmHg, you should consult a doctor. It will help you find out why the body cannot cope with blood pressure regulation and offer a way out of the situation.
How to treat?
Let's start with the fact that, alas, there is no magic pill that would increase blood pressure. Therapy is selected individually depending on the cause of hypotension. If the problem is based on a disease, you need to start correct treatment. As soon as the cause is eliminated, the effect will also disappear. When hypotension is associated with other factors, the approach to its correction is completely different.
There is no need to treat simply “low blood pressure”, at which you feel great. Measures should be taken only in cases where hypotension is accompanied by symptoms. And you need to start with simple lifestyle changes. To prevent your pressure from falling below critical levels: • Drink plenty of water • Give up alcohol or minimize its consumption • When changing the position from horizontal to vertical, take your time - get out of bed slowly • Unlearn sitting with your legs crossed • Increase physical activity • Try not to sit and do not stand in one position.
Among the most accessible and effective remedies that help to quickly increase blood pressure are a cup of good strong coffee and adaptogens - tincture of ginseng, lemongrass, aralia, and eleutherococcus extract.
However, you shouldn’t get carried away with them: both caffeine and general tonics can be used in doses, in the first half of the day. Otherwise, the problem with hypotension may result in new troubles, such as insomnia, tachycardia and increased nervous excitability.
And to avoid the temptation to drink a couple of “extra” cups of coffee or another dose of ginseng tincture, take a radical approach to solving the problem - change your lifestyle and allow your body to bring the pressure in order on its own.
Marina Pozdeeva
Photo depositphotos.com
The opinion of the author may not coincide with the opinion of the editors
Low blood pressure: natural ways to improve your health
Even the list of possible causes already given shows that there are many ways to increase low blood pressure again. First you need to find out the cause of low blood pressure. When it is found, treatment begins.
This is not always easy: problems begin already in cases where low thyroid function or adrenal insufficiency is diagnosed. Often official data says that everything is fine, but a person feels completely different.
Adrenal insufficiency is detected by examining saliva. Specific measures should be discussed with a specialist in alternative medicine.
Contrast shower and Kneipp douches
Master the contrast shower and practice Kneipp douches. Yes, you can prescribe what is called hydrotherapy if your doctor agrees that it will help combat low blood pressure.
When dousing, the following must be taken into account. Warm water relaxes and relieves spasms, while cold water mobilizes. If you have low blood pressure, you should either use cold water or change the temperature of the water: this activates blood circulation and helps increase blood pressure.
Kneipp foot soaking is commonly practiced. To do this, cold water (temperature 20 degrees) is poured onto the foot from the knee, then directly onto the foot and again up the calf to the popliteal fossa, and then down again. After a warm shower, you can quickly douse yourself with cold water. If this is difficult for you, limit yourself to cold pouring on your feet.
Drink still water regularly
With low blood pressure, water helps not only from the outside, but also from the inside. If you are one of those people who often forgets to drink enough, the first thing you should do at the first symptoms of low blood pressure is drink a large glass of water. Often this is already enough.
As stated above, not drinking enough fluids can seriously aggravate, if not cause, low blood pressure. Therefore, regularly drink 30 ml per kilogram of weight per day. To do this, it is best to choose high-quality still or lightly carbonated water.
To enhance the effect of a glass of water for severe dizziness, cook vegetable broth and drink it or simply add a little salt to the water.
Check the level of vital elements in the body
Get tested for essential minerals and vital substances (vitamin B12, vitamin D, iron, zinc, etc.) and check whether your diet contains enough of the necessary elements. To do this, you can contact a healthy nutrition consultant. If in doubt or found to be deficient in specific substances, take appropriate nutritional supplements.
You can almost always take magnesium and a high-quality B vitamin complex, even without testing. Magnesium is a mineral that is involved in many reactions in the body and at the same time is present in insufficient quantities in modern food. Therefore, in most cases, taking it is only beneficial.
The same can be said about B vitamins. In addition, these vitamins dissolve in water, and therefore, in case of excess intake into the body, they are simply excreted in the urine. Along with vitamin B12, vitamin B5 is also especially important for low blood pressure: its deficiency can provoke hypotension.
Vitamin C deficiency is also a cause of low blood pressure. This is because vitamin C stimulates blood circulation, and therefore blood pressure.
What foods can help with low blood pressure, and which ones should not be consumed?
– For low blood pressure, as I said earlier, it is recommended to consume large amounts of table salt (up to 10 g/day) and liquids (up to 3 l/day), and caffeine-containing drinks.
With postprandial hypotension, you need to adhere to a certain type of diet: eat often, in small portions, more proteins and fats, avoid carbohydrates (especially refined ones), eat warm or cold (not hot) foods. And you should give up alcohol.
In what situations should you definitely consult a doctor – and which one? – Patients with fainting, especially those that occur for the first time, need to consult a cardiologist, and, if necessary, a neurologist.
If blood pressure was previously normal or elevated, and then became chronically low, you should also contact a cardiologist to find out the cause. How to monitor your blood pressure and control its reduction?
– In order to prevent another decrease in blood pressure, it is necessary, firstly, to determine the cause (hypothyroidism, anemia, adrenal insufficiency, taking high doses of antihypertensive drugs, etc.) and, if possible, eliminate it.
Secondly, try to avoid provoking situations and factors, observe safety conditions during verticalization, and lifestyle recommendations.
And in situations where a person anticipates developing hypotension or fainting (increased sweating, nausea), you can help yourself by using the physical counterpressure maneuvers that I described earlier.
Check your vitamin D levels
Vitamin D levels are particularly important: today in Central Europe there is usually not enough vitamin D, which is responsible for many chronic diseases. Vitamin D is the sun vitamin, that is, the vitamin that is formed in the skin when exposed to ultraviolet radiation. Food contains very little of it. Thus, a lack of sunlight usually means a deficiency of vitamin D.
Among other things, it is involved in regulating blood pressure. Therefore, a lack of this vitamin can contribute to low blood pressure. A study published in 2014 found that vitamin D deficiency increases orthostatic hypotension, especially in older people.
Rule out cryptopyrroluria
If you have symptoms other than low blood pressure, such as depression, hair loss, cracked lips, skin problems, or hormonal imbalances, consider getting tested for cryptopyrroluria.
This metabolic disorder also causes low blood pressure.
If the cause of low blood pressure cannot be found or if the condition does not improve despite all efforts to improve your lifestyle, it is usually recommended to simply move more or drink small amounts of alcohol or strong coffee. These measures, with the exception of physical activity, cannot be called healthy. Caffeine and alcohol have only a short-term effect, which means they cannot solve the problem for a long time.
However, there are methods and solutions that allow you to increase blood pressure not only reliably, but also without harm to health.
Diagnosis and treatment of arterial hypotension at GUTA CLINIC
Diagnosis of arterial hypotension is made by regularly measuring blood pressure. An experienced cardiologist will not ignore the data of a clinical examination, will pay attention to the patient’s complaints, and will most carefully collect anamnesis - all data that may support the diagnosis of arterial hypotension. In the Cardiology Department of GUTA CLINIC, diagnosis of low blood pressure is also carried out using the following examination methods:
- Electrocardiography (ECG).
- Echocardiography (ultrasound of the heart).
- Duplex scanning of cerebral vessels (transcranial method).
- 24-hour blood pressure monitoring.
- Electroencephalography (EEG).
- Ophthalmoscopy.
- Functional diagnostics of the autonomic nervous system, etc.
Treatment of arterial hypotension at GUTA CLINIC is carried out comprehensively, using both classical drug therapy and non-drug treatment methods.
The basis of drug treatment of arterial hypotension is the use of tonic drugs, adaptogens, and general strengthening (including immunomodulating and biostimulating) agents. In addition, the patient is prescribed rehabilitation treatment with normalization of sleep and rest patterns, dosed physical activity, physiotherapy (electrophoresis, electrosleep, water treatments, individual massage course), and dietary adjustments. One should not think that arterial hypotension, low blood pressure, is a less life-threatening condition than arterial hypertension or high blood pressure. If until recently you have not experienced low blood pressure or it was not accompanied by a deterioration in your health, it is better not to delay and immediately consult a cardiologist.
As in the case of arterial hypertension, when a hypertensive crisis may occur, with low blood pressure there is a possibility of developing a hypotensive crisis. Hypotonic crisis is an acute condition characterized by a sharp drop in blood pressure, fainting, convulsions, loss of consciousness, and the development of shock. Often a hypotensive crisis ends in a stroke - an acute cerebrovascular accident that can be fatal.
Rosemary - a remedy for low blood pressure
Rosemary essential oil is believed to effectively stimulate blood circulation, increase blood pressure and refresh the body, so much so that patients with high blood pressure should not take it.
However, those with low blood pressure can use rosemary oil in a variety of ways.
Buy a bottle of rosemary essential oil. If necessary, open it, bring it to your nose and inhale deeply. You can add a few drops to an aroma lamp.
In addition, rosemary essential oil is added to shower gel (1 drop per serving) or to the bath (so many drops for the scent of rosemary to be intense).
Camphor (Spanish) rosemary is best suited - it contains more camphor, which is the active ingredient in rosemary oil that affects blood pressure.
You can drink rosemary tea in the morning if you like it.
Forms of arterial hypotension
There are primary and secondary arterial hypotension:
- Primary (essential hypotension) can be caused by a genetic predisposition to low blood pressure (physiological hypotension), or be an independent disease (neurocirculatory asthenia).
- Secondary arterial hypotension can be a consequence of certain diseases (iron deficiency anemia, hepatitis, cirrhosis of the liver, etc.) or develop as a result of taking certain medications (for example, to lower blood pressure), etc.
Licorice - a remedy for low blood pressure
Licorice is often used for coughs, as it has an antiviral effect, and for inflammation of the gastric mucosa, since this plant successfully fights even Helicobacter pylori.
Licorice contains so-called glycyrrhizic acid (also called glycyrrhizin), which, in addition to these effects, is known to increase blood pressure.
In 2015, the results of a study on one 65-year-old patient were published. She had high blood pressure, but it was stabilized with medication. Suddenly she needed emergency help: her blood pressure rose to 200/140 mmHg. Art.
Intravenous administration of blood pressure-lowering drugs did not produce results. The woman spent seven days in the hospital, five of them in the intensive care unit. Finally, the blood pressure was lowered with the help of three appropriate medications. It later turned out that this patient loved licorice candies, and ate two to four packages a day. Licorice is made from licorice root extract.
A similar study published the same year involved a 45-year-old woman who told her doctor that she had been experiencing hot flashes, sweating, and headaches for 4 months. It turned out that she had high blood pressure and her calcium levels were low. It was later learned that this patient drank six cups of licorice tea daily to wean herself off coffee. Two weeks after she stopped drinking this tea, the symptoms disappeared.
Thus, it is clear that licorice root can increase blood pressure. If your blood pressure is already high, it is better not to drink licorice tea. When blood pressure is too low, this tea in moderation can be very beneficial.
Glycyrrhizic acid from licorice root blocks certain enzymes, resulting in the activation of the stress hormone cortisol, which then increases blood pressure.
Today, experts do not recommend consuming more than 100 mg of glycyrrhizin per day - precisely because this substance affects blood pressure, and for most people it is already very high.
50 mg of licorice (some varieties) contains 100 mg of glycyrrhizin. If licorice contains more than 200 mg of glycyrrhizin per 100 g, in Germany it can only be sold in pharmacies and not as a sweet in supermarkets.
Many modern sweets containing licorice contain artificial flavors anyway and only a little real licorice, which means little glycyrrhizin. Therefore, licorice is a very unreliable source of glycyrrhizin if it is necessary to increase blood pressure. Exceptions are possible only if data on glycyrrhizin content are obtained from the manufacturer.
Dried licorice root, which is sold cut into slices in tea shops, contains 200 to 600 mg of glycyrrhizin per 5-15 g. Thus, you can brew a tea from 5-10 g of licorice root daily and drink it throughout the day.
It is officially not recommended to consume licorice products for more than four to six weeks, but this advice applies to all medicinal teas. Periodic breaks avoid addiction and prevent possible side effects.
The glycyrrhizin found in licorice, when taken over a long period of time, can actually cause symptoms in susceptible individuals that indicate elevated cortisol levels. These are, for example, accumulations of fluid, which are manifested by swelling in the face and joints of the feet, increased blood sugar levels, disturbances in the functioning of the heart and, of course, increased blood pressure, although for hypotensive patients this effect is desirable.
But two cups of licorice root tea a day won't cause any problems and will still help raise your blood pressure.
Old and reliable - help yourself!
- Sleep at an angle
Raise the head of the bed by placing a stand under its legs so that your head is approximately 20 cm higher than your feet. The blood circulation will now be forced to work against gravity to better supply the brain with blood. With this method, your blood pressure will not drop to lower limits at night and you will feel some relief when you get out of bed in the morning.
- Eat less, but more often!
Spread your food over 4-5 meals throughout the day! This will prevent you from dropping your blood pressure after eating a large meal. Also, keep your sugar intake constant to prevent hypotension from adding to your blood sugar levels.
- Rosemary
Rosemary is an old home remedy that helps keep low blood pressure from spiking. You can use it in various forms.
Wine: Use rosemary to make a strong white wine, as its bioactive compounds are best suited for fermentation. Pour 20 g of rosemary leaves into 750 ml of wine. Allow the wine to steep for 3 days before drinking a small glass regularly with lunch and dinner.
Bath Additive: Together with lavender, rosemary acts as a stimulant and at the same time relieves tension when used in a bath that has received the historical name of the “Austrian Queen Elizabeth” bath. This bath additive can be purchased ready-made at the pharmacy.
Tea: 1 tsp. with a top of finely chopped rosemary leaves, pour 1 cup of boiling water, leave for 10 minutes, then strain. Drink this tea 2-3 glasses a day.
- Water treatments
You will strengthen your heart and improve vascular tone with cold washes in the morning. With a wrung-out sponge, move from the back of your right hand to the shoulder, and then along the inside back to the hand to then repeat the movement up the outside of the rye. Then move to the shoulder, neck, chest and stomach, and then down to the thigh. Now repeat this procedure for your left hand.
Walking on water: Practice this in the evening. Pour cold water into the bath no more than mid-calf and walk for 5 minutes in a “stork gait”, completely extending your legs out of the water. After the procedure, put on warm socks.
- Acupressure
To eliminate low blood pressure, you can try massaging the “Sea of Energy” point, located approximately 5-10 mm below the navel. Make circular movements with your thumb, middle and ring fingers, rhythmically changing the pressure, but without causing pain. The duration of the massage is 1 minute. Repeat this massage several times a day, especially when you feel tired.
- Aromatherapy
Low blood pressure cannot be completely cured, but when fatigue and loss of performance occur, certain aromatic substances have a very beneficial effect. Massages or baths with camphor, peppermint, sage, thyme and hyssop have a stimulating effect. Rosemary aromatic oil can be used for both high and low blood pressure.
You will need 15-20 drops of one of the above aromatic oils or a mixture of them to taste. Mix them with 1-2 tbsp. l. cream, milk, liquid honey or neutral juice. You can also use vegetable oil. Pour this mixture into a bathtub with running water.
Massage oil: use 50 ml of jojoba oil or almond oil as a base. Add 15-20 drops of aromatic oil to taste and shake this mixture well.
Aroma lamp: You can try using an aroma lamp at work or at home. Add 5-8 drops of rosemary to a cup of aroma lamp water. You will be surprised how the aroma that spreads into the room will bring fresh energy. The active substances of the aromatic oil will penetrate the respiratory tract and skin pores into the body and have a beneficial effect on the entire body.
Tulsi - a remedy for low blood pressure
In 2013, the results of a study were published on the effects of the so-called holy basil (tulsi) on low blood pressure in women aged 18 to 30 years. Participants in the experiment were given juice from 15 mixed basil leaves twice a day. After mixing, the juice was filtered and a teaspoon of honey was added to it for sweetness.
After 30 days, it was found that the blood pressure, which had previously been too low, had increased significantly. Today tulsi is sold in stores and in our latitudes, which means you can stock up on this plant and make juice or smoothie from the leaves.
Medicinal herbs and plants such as marjoram, ginger, lovage and hyssop will also help you increase your blood pressure. They can be brewed or used in cooking, such as added to salads and sauces.