A biopsy and histological examination of a tissue sample obtained with its help is one of the most accurate methods for diagnosing tumors in the human body. In diagnostics, to monitor the condition and identify pathology of the uterine mucosa, gentle aspiration technology is used - endometrial biopsy pipe. Its results, obtained by examining tissue under a microscope, are necessary to identify the causes:
- hyperplastic growth and thickening of the mucous membrane;
- endometrial carcinomas;
- pathological uterine bleeding;
- miscarriage;
- infertility caused by hormonal and hyperplastic disruptions;
- oncological diseases.
Pipel endometrial biopsy is performed before IVF, during bacteriological examination, including before planned conception, as well as to monitor the results of hormone therapy and its effect on the female reproductive system.
Unlike a conventional biopsy, a painful procedure that requires dilation of the cervical canal and produces a high percentage of complications, this technology is painless and non-traumatic
.
Briefly about the essence
Today, pipell biopsy of the endometrium is one of the most common diagnostic methods in gynecological practice. It is used to study the causes of menstrual irregularities and hormone-dependent diseases, for example, endometritis. The timing of the procedure depends on the specific situation.
The study is carried out on an outpatient basis using local anesthesia. The procedure itself is painless. For it, a flexible plastic cylinder with a diameter of 2.5 to 4 mm is used, inside of which there is a piston. It is introduced into the organ, and when removed, negative pressure arises in the cylinder and the mucosal tissue is drawn into it. The duration of the procedure is less than a minute.
Then a laboratory histological analysis of the biopsy sample is performed. After a week or two, the results are transmitted to the doctor, and based on them he can build optimal treatment tactics.
The study in terms of identifying pathological changes in the endometrium is highly informative and in some cases is not inferior to such a diagnostic method as curettage.
When is a diagnostic procedure prescribed?
The study can be carried out for various diagnostic purposes. Let's consider for what pathologies and disorders it is necessary.
Infertility, failed IVF.
The condition of the endometrium plays a primary role in the onset of pregnancy. The process of successful implantation of the embryo in the uterus depends on the receptivity of the endometrium - structural and functional characteristics.
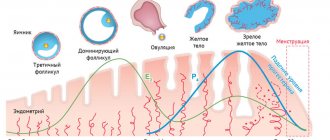
Depending on the phase of the menstrual cycle, the structure and thickness of the endometrium changes. It reaches its greatest maturity during the implantation window, creating favorable conditions for fixation of the embryo in the uterus.
Taking a sample of the endometrium at the expected time of the implantation window and its further immunohistochemical study allows us to assess the receptivity of the endometrium, a decrease in which often leads to reproductive losses, the inability to get pregnant, and unsuccessful IVF programs.
In addition, a pipel biopsy is performed if there is suspicion of:
- anovulatory cycles, in which there is no ovulation and no phase of development of the corpus luteum;
- inflammatory and hyperplastic processes, which can be a source of infertility.
Bleeding of unknown origin, disruption of the menstrual cycle.
The study may be prescribed for bleeding of unknown origin: between menstruation, during menopause.
Also, the diagnostic procedure is performed for women with rare and frequent menstruation, changes in the volume of menstrual blood loss in the direction of increase/decrease. The indication for diagnosis is amenorrhea—the absence of menstruation for six months or more.
The cause of an unstable menstrual cycle and strange bleeding can be inflammatory and hyperplastic processes, endometriosis, and hormonal disorders. Pipelle biopsy of the endometrium allows you to accurately determine the cause of pathological symptoms.
Suspicion of endometrial cancer or other malignant processes in the uterus.
Endometrial cancer is one of the most common malignant diseases in women. Most often, pathology occurs during menopause. Histological analysis of a biopsy (material taken by biopsy) allows not only to detect a cancerous tumor, but also to determine the degree of its malignancy and sensitivity to hormone therapy.
Suspicion of endometriosis.
The disease is characterized by the penetration of cells of the inner layer of the uterus outside the organ. As a rule, the pathology occurs in women of reproductive age. There are many methods for diagnosing endometriosis, and pipel biopsy is one of them.
Endometrial polyps.
A polyp is a benign formation. However, any benign tumor under certain conditions can degenerate into malignant. For example, an adenomatous endometrial polyp is considered a precancer due to the fact that its cells are able to divide rapidly.
A biopsy is performed if differential diagnosis of a polyp is needed. Examination of the biopsy allows one to exclude the possibility of malignant degeneration of the tumor.
Suspicion of endometrial hyperplasia.
With pathology, thickening of the endometrium and certain changes in its structure are observed. You can suspect a problem during an ultrasound, but to make an accurate diagnosis, a core biopsy is required. In addition, the study allows us to understand whether it is atypical hyperplasia or not. Atypical hyperplasia is accompanied by changes in the structure and shape of cells and is a precancerous condition.
Suspicion of chronic endometritis.
The disease is an inflammatory process occurring in the endometrium. In the chronic form, the pathology leads to irregular menstruation, infertility, miscarriage and other consequences.
If endometritis is suspected, the biopsy specimen is analyzed for CD138 and CD56 markers, which appear in this pathology.
Monitoring the condition of the endometrium after surgical interventions.
Collection of endometrial elements may be necessary after curettage and other surgical interventions on the uterus. A biopsy allows you to evaluate how well the inner layer of the uterus has recovered after surgery.
Methodology
Medicine does not stand still, and today a new approach is being used to study the mucous membrane of the female organ, which allows us to solve many problems that are characteristic of the traditional approach.
Conducting a traditional study is impossible without expanding the cervical canal of the organ. The procedure is performed under hysteroscopic control using intravenous anesthesia. This is not only painful, but can also lead to a number of unpleasant consequences. This is why contraindications arise.
Using a new technique, the doctor gets new opportunities. The procedure itself does not require intravenous anesthesia, and dilation of the cervical canal is also not required.
PET/CT examination
Since the instrument is disposable, it is kept in sterile conditions (packaging) before use, so the issue of possible infection is eliminated.
And another important point: the procedure is more economical than the traditional one.
On what day of the cycle is the study carried out?
Depending on the diagnostic purposes, the study can be carried out on different days of the menstrual cycle. Detailed information is presented in table ⇓⇓⇓
| Purpose of diagnosis | Recommended period of the menstrual cycle for collecting biomaterial |
| Suspicion of oncological processes in the uterus | Any days except the period of menstruation |
| Polyps, endometritis | The period after the end of menstruation |
| Bleeding of unknown origin | During bleeding of unknown origin. It is important to collect biomaterial during the period when pathological signs are observed |
| Heavy menstruation | Days 5–10 of the cycle |
| Search for causes of infertility, unsuccessful IVF programs | Estimated implantation window period |
| Suspicion of an anovulatory cycle | On the eve of menstrual bleeding |
| Diagnosis of the condition of the endometrium in women during menopause, not related to identifying the causes of unknown bleeding | Any day |
| Tracking the results of hormone therapy | Second phase of the cycle |
Stages of manipulation
This test is performed in a doctor's office. It begins with a gynecological examination. Then, after cleaning the vagina with antibacterial soap, the doctor may inject or spray a local anesthetic to numb the cervix.
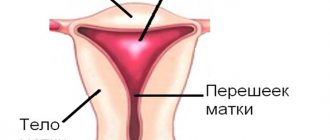
The cervix is the entrance to the uterus and is visible several centimeters into the vagina. In most cases, the doctor will place a clamp on the cervix to hold it still. The doctor will use a flexible, sterile plastic instrument that looks like a drinking straw.
The doctor inserts it through an opening in the cervix and positions it a few centimeters into the uterus. Then he pulls out a thin piston from the center of the pipe. When the rod is pulled out, the pipe becomes hollow and creates suction, pulling some of the cells from the uterine tissue into the device. To get a good sample, the doctor will move the pipette back and forth several times before removing it. The tissue sample is deposited in a special liquid, which must be examined later under a microscope. The whole procedure takes about 10 minutes. It does not cause pain; the patient, most often, does not even feel anything.
Decoding the results
A laboratory assistant will examine the biopsy obtained during the procedure under a microscope. The results of a pipel biopsy can be obtained in person in one or two weeks (in private clinics, as a rule, this happens faster than in public medical institutions). You should contact your gynecologist for a transcript.
This type of biopsy causes minimal trauma to the uterine cavity, so the risk of complications is very low. The advantages of pipel biopsy include:
- Carrying out the procedure in a gynecologist’s office, no need to go to the hospital;
- minimal discomfort;
- the procedure lasts several minutes;
- the growth of the endometrium is not disrupted, since in the process it receives minimal damage, unlike the curettage procedure or other biopsy methods;
- good information content of studies of biopsy obtained by this method, since the sampling is made from different parts of the mucosa;
- low cost.
You can perform a pipel biopsy in the medical institutions presented on the website; the price of the service ranges from 2-5 thousand rubles.
After the procedure
After the manipulation, the patient can immediately leave the clinic and return to her usual lifestyle.
Within 1-2 days, minor or moderate nagging pain in the lower abdomen is likely, which in most cases does not require the use of painkillers.
For several days, a woman may experience bloody discharge from the genital tract.
Resuming intimate contacts, as a rule, is allowed 3-4 days after the manipulation.
Similar methods
Pipelle biopsy is deservedly considered one of the most modern methods of collecting material for studying the uterine cavity. In terms of its effectiveness, it can be compared with aspiration biopsy, but at the same time its advantage is its gentle action and, subsequently, the absence of mechanical damage. Aspiration biopsy takes a sample of mucous membrane in a similar manner, but the procedure does not use a flexible tube. This method cannot be indicated in the presence of cervical cancer.
Best materials of the month
- Coronaviruses: SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19)
- Antibiotics for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19: how effective are they?
- The most common "office" diseases
- Does vodka kill coronavirus?
- How to stay alive on our roads?
Indications for pipel biopsy
Aspiration biopsy is prescribed:
- for the purpose of diagnosing the causes of infertility;
- for the diagnosis of hyperplastic processes in the uterine mucosa (including endometrial polyps in the uterus);
- in preparation for an in vitro fertilization program;
- if there is a suspicion of the presence of malignant tumor processes in the uterine cavity;
- with recurrent miscarriage;
- for carrying out bacteriological analysis;
- with a chronic inflammatory process in the mucous membrane of the uterus;
- to monitor the effectiveness of treatment.
How to prepare?
The advantage of the method is simple preparation for the procedure, thanks to which endometrial biopsy pipette saves time and nerves of patients, as well as financial costs for tests and monitoring processes in the reproductive system.
Before the study you need:
- undergo an examination by a gynecologist;
- conduct laboratory tests for hepatitis, syphilis, HIV, sexually transmitted infections;
- take a smear for microflora.
24 hours before the examination, you should refrain from intimacy, the use of vaginal suppositories, tampons
Analysis of pipel biopsy of the endometrium of the uterus: indications and contraindications
Pipel biopsy replaces the painful procedure of conventional biopsy, which is dangerous with complications, from medical practice. It is performed for the same indications
:
- examination of endometrial tissue in female infertility;
- bleeding - in patients over 40 years of age, during hormonal contraception, therapy, during menopause;
- as an element of a comprehensive examination of the uterus simultaneously with transvaginal ultrasound or hysteroscopy.
- when obtaining a tissue sample from patients with diabetes mellitus, the risk of spreading cancer cells and endometriosis.
The ability to obtain fragments of different tissues significantly increases the value of simultaneous comprehensive examinations.
Pipelle biopsy has a minimal number of contraindications
:
- infectious diseases of the genital organs;
- inflammatory processes in the vagina and cervix;
- pregnancy.
Contraindications to the procedure
Contraindications for this procedure may include:
- blood clotting disorders;
- the presence of acute inflammatory disease of the pelvic organs;
- the presence of an acute vaginal infection or cervical infection;
- cervical cancer;
- stenosis, or severe narrowing of the cervix.
Also a contraindication is the presence or suspicion of pregnancy.
How is the diagnosis carried out?
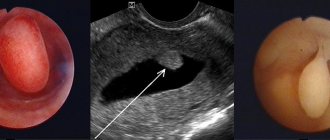
The procedure is performed on an outpatient basis in a gynecologist's office. The woman lies down on the gynecological chair, and after inserting vaginal speculum and fixing the cervix with a bullet, he dilates the cervical canal and inserts a Peipel probe into the uterine cavity, slowly and carefully advancing it. After reaching the fundus of the uterus, the doctor removes the plunger of the rod and eventually creates negative pressure in the syringe. As a result of creating negative pressure, endometrial tissue is taken into it. To obtain a reliable result, samples are taken from several places, after which the syringe is removed and the material is placed on a glass slide for further histological examination. The procedure lasts no more than 20 minutes.
Material collection
In most cases, aspiration biopsy is performed on an outpatient basis without the use of anesthesia.
The Peipel catheter, which is used to collect biomaterial, is a thin (2-4 mm in diameter) plastic tube with a piston, which is then removed, causing fragments of endometrial tissue to be drawn inward.
After receiving the biomaterial, it is immediately sent for histological examination.
It usually takes about 1 minute to aspirate a piece of endometrial tissue.
Research methods
For women of reproductive age, pipel biopsy is most often prescribed on days 25-26 of the menstrual cycle. For postmenopausal patients, the procedure can be performed at any time. The collection of biological material is carried out in a medical institution; hospitalization is not required. The gynecologist must mentally prepare the patient and explain to her how the manipulation is performed.
A pipel is a tool in the form of a hollow tube with a diameter of 2-4.5 mm, ending in a small hole. There is a piston inside the cannula, and the device functions on the same principle as an injection syringe.
The dimensions make it easy to insert the pipel into the uterine cavity without first expanding the cervical canal. The instrument is marked, so it can be used to probe the uterus. Each instrument is individually packaged and sterile, so the risk of infection is minimized.
The patient is located in a gynecological chair. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia or without it.
The doctor conducts a standard examination and fixes the cervix using a mirror.
Then a flexible thin tube is inserted into the uterine cavity, and the doctor pulls the piston approximately. Due to this, negative pressure is created in the tube, and endometrial tissue is aspirated from the uterine mucosa.
In this case, most patients do not experience significant discomfort, since the cervix is not damaged, and when taking a biopsy sample, extensive wound surfaces do not appear. A woman experiences the most intense sensations at the moment when biological material is directly collected. In response to the alienation of living tissue, the uterus reacts with spasm. In this case, the patient feels pain similar to what happens during menstruation.
After removing the instrument, the resulting endometrial tissue sample is sent to the laboratory.
Despite the fact that the procedure is minimally invasive, it is associated with tissue sampling, and, consequently, with a violation of their integrity. Normally, after a pipel biopsy, there is slight painless bleeding that lasts one or two days. Sometimes the discharge is quite abundant and is accompanied by pain in the lower abdomen.
At the end of the procedure, doctors advise using a sanitary pad. The use of tampons is strictly prohibited. To relieve pain, you can take a painkiller.
To prevent the negative consequences of the procedure, you should follow some rules:
- do not engage in sexual contact;
- carefully carry out intimate hygiene;
- do not take a bath, do not swim in the pool or open water;
- avoid visiting the bathhouse, sauna, solarium;
- prevent hypothermia of the body;
- Avoid sports, heavy lifting, and heavy workloads.
Restrictions apply until the release ceases.
You should immediately consult a doctor if you experience the following symptoms after a pipel biopsy:
- heavy bleeding;
- severe pain in the lower abdomen, difficult to relieve with medications;
- unpleasant odor of discharge, presence of blood clots in it;
- temperature increase.
Such signs indicate the development of complications. It is very important to find a doctor who will correctly conduct an examination before prescribing a pipel biopsy and will carefully perform the procedure itself.
Preparatory stage
Before the study, the woman undergoes a thorough examination, which may include:
- clinical blood test;
- blood test for HIV infection, RW, hepatitis B and C;
- coagulogram;
- cytological and microscopic examination of gynecological smears.
During the period of the cycle in which a biopsy is planned, you need to avoid hormone therapy, which can distort the results of the study. It is also important to stop taking blood thinning medications a week before the test. Such medications may cause bleeding during the procedure.
If the study is carried out in the second phase of the cycle, then after the end of menstruation you need to protect yourself during intimacy. Contraception is necessary to exclude pregnancy at the time of biopsy.
A few days before the procedure, it is recommended to refrain from sexual intercourse, the use of vaginal suppositories, and douching.
The study is carried out on a full bladder.