The pharmacy sells drugs that help normalize hypertension, hypotension and get rid of “spikes” in blood pressure. But it is important not to purchase medicine without first consulting a doctor, since the consequences of using the wrong medicine can be very serious.
Hypertension is a disease in which blood pressure is elevated. Pathology most often occurs in people over 45 years of age. Hypertension cannot be cured, which is why patients need to take medications regularly to avoid complications: stroke, heart attack and other equally serious health problems.
The use of one type of drug (monotherapy) has a positive effect only at the initial stage of the disease. In more serious cases, blood pressure is normalized with the help of combination drugs, including two or three active ingredients from different groups. Hypertensive patients should know that the body gets used to the action of any medicine and the effect of the drug is individual. For this purpose, each patient should consult a cardiologist at least once every six months.
Medicines with antihypertensive effects are long-acting (prolonged) and rapid-acting.
The tablets act on various organs to lower blood pressure - the effect depends on the group of the drug. For different people, remedies are selected individually, taking into account the general state of health and the presence of concomitant diseases, which are discovered after a full medical examination.
Tablets for normalizing high blood pressure
List of main drug groups for blood pressure:
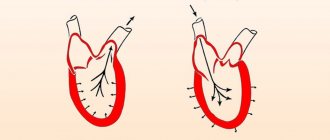
- Beta blockers. They act on the walls of blood vessels, eliminating spasms. Accordingly, the heart rate decreases and blood pressure normalizes. Classic beta blocker drugs include: Atenolol, Propranolol, Anaprilin, Metaprolol.
- The antihypertensive effect of alpha blockers occurs due to the relaxation of muscle tissue that is located inside the blood vessels. As a result, arterioles and arteries dilate. Common tablets: Minoxidil, Hydralazine.
- Calcium channel antagonists block the calcium currents involved in the contraction of the heart muscles, after which the heart slows down and blood pressure returns to normal. Representatives of the group are short-acting and rapid-acting drugs (“Nifedipine”); with a prolonged effect - Amlodipine, Verapamil, Diltiazem.
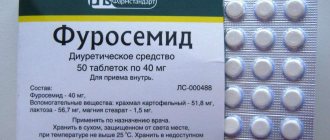
- Diuretics (diuretics) are used to relieve swelling by removing fluid. Thus, an automatic decrease in blood pressure occurs. When using diuretics, it is taken into account that useful and necessary microelements are removed from the body, therefore diuretics should be taken carefully and under the control of a biochemical examination. The most common drugs: Hypothiazide, Furosemide, Diuver.
- ACE inhibitors inhibit the formation of a peptide responsible for the dilation of blood vessels. Names: “Ramipril”, “Anaprilin”, “Captopril”.
Fast-acting drugs
Hypertensive patients from time to time face a situation where the pressure rises sharply. People who have been suffering from the disease for a long time keep on hand means to stabilize the indicator, which can reduce it in a short time.
List of drugs:
- Furosemide has an effect on reducing blood pressure approximately 20 minutes after administration. After 60-70, the maximum effect occurs, which is achieved by expanding the loop portion of the renal nephron and, consequently, increasing urination.
- "Anaprilin" helps reduce the rate in 15-20 minutes. The tablets are able to be quickly absorbed into the blood, and elimination occurs after 5-10 hours. In accordance with the instructions, you should take the drug 80 milligrams in two doses throughout the day. If the prescribed dose is ineffective, then the dosage is doubled. Suitable for stopping episodic attacks of tachycardia.
- "Captopril" is the gold standard for emergency medical care for high blood pressure. The medicine acts quickly, but lasts only three hours, so it is not recommended for continuous use for hypertension.
- "Adelfan" is a combination drug that constricts blood vessels and calms the nervous system thanks to the main active ingredients: reserpine, digidazaline. According to the instructions, take 0.25 milligrams 3 times a day. If necessary, the doctor may increase the dose. After a course of taking it, it is gradually reduced until completely eliminated.
- "Ebrantil" is an excellent choice for tachyarrhythmia due to high blood pressure. A new product with lightning-fast (at the end of a needle) effect. In tablets at a dose of 60 mg.
- "Physiotens" is a drug that affects the vasomotor center and cerebral cortex. An excellent modern medicine that quickly brings the indicator back to normal. It is produced in doses of 0.2 and 0.4 mg and is available for use 2 times a day.
Causes
Cycle disruption is, as a rule, not an independent disease, but the result of other problems or changes in the body.
- Hormonal imbalances or abnormalities. This is the most common cause of menstrual irregularities. Which is not surprising, since it is the endocrine system that completely regulates the menstrual cycle. Moreover, a malfunction can be caused not only by fluctuations in the level of sex hormones, but also by decreased or increased production of hormones of the thyroid gland, adrenal glands, and pituitary gland. However, in approximately 70% of women of reproductive age, cycle disorders are caused by increased levels of prolactin (hyperprolactinemia). In second place among hormonal causes is a change in the functioning of the pituitary gland, in which the excretion of follicle-stimulating and luteinizing hormones or their normal ratio necessary for ovulation deteriorates.
- Climax. Shortening the cycle and its irregularity is one of the manifestations of menopause. During menopause, the production of sex hormones decreases, their ratio decreases, the cycle becomes shorter, and menstruation gradually stops altogether. We must remember that menopause is a normal condition, not a disease. It occurs in all women. However, the appearance of an irregular cycle does not indicate menopause.
- Chronic stress. This reason partly overlaps with hormonal disorders. During stress, a high portion of prolactin is released into the blood; with constant stress, the level of prolactin will be constantly high.
- Diseases of the neuropsychic sphere. Psychiatric spectrum disorders are also often associated with hormonal problems.
- Infectious and inflammatory diseases of the genital organs, ovarian cysts, fibroids. Naturally, any disease of the reproductive system will somehow affect its functioning. When the temperature rises, which accompanies inflammatory diseases, ovulation may be disrupted; with genital infections, problems can affect the ovaries and uterus.
- Eating disorders – malnutrition or obesity. With insufficient weight, the activity of sex hormones decreases, since the body “understands” that in conditions of lack of nutrition it will not be possible to bear, give birth and feed viable offspring. Increased weight creates a problem for the proper functioning of most organs and systems.
- Taking medications: hormonal drugs, including contraceptives, corticosteroids, anticoagulants, tranquilizers, antidepressants. These drugs inhibit various functions of the endocrine and reproductive systems.
It is not always possible to establish the cause of menstrual irregularities and ways to return it to normal without additional examination. Therefore, if the cycle begins to differ from the usual in any of the parameters, you should definitely visit a gynecologist.
The initial examination for menstrual irregularities includes anamnesis (frequency of sexual activity, contraceptive methods, medications), external examination (allows you to get an idea of nervousness, stress level, the possibility of anemia), gynecological examination and smears, pelvic ultrasound, blood tests - general, biochemical, hormonal.
After the examination, the doctor will determine what caused the malfunction and how the cycle can be normalized, or he will prescribe clarifying examinations and, possibly, refer you to other specialists.
Long-acting tablets for hypertension
Prolonged pressure stabilizing agents are characterized by long-term effectiveness. Because of this, they are used for course treatment, and not for a one-time reduction in the indicator.
Many patients are prescribed by doctors to take the drug throughout their lives. It is important not to stop taking the medicine, as this will significantly increase the patient's risk of dying from heart problems.
List of drugs:
- "Bisoprolol" . The spectrum of action is wide - lowering blood pressure, normalizing heart rate, preventing and stopping the development of angina pectoris. In case of second and third degree hypertension, it is prescribed for complex treatment or monotherapy (taking one drug). Following the instructions, you need to drink the medicine 50-75 milligrams 2 times a day during or immediately after meals. The dosage is doubled if the disease is extremely severe, or the patient is overweight.
- "Diroton" helps reduce blood pressure, but does not affect the heart rate. The highest level of effectiveness is six hours after taking the drug, and the duration is approximately a day. In accordance with the instructions, the daily dose should not exceed 40 milligrams.
- Prestarium dilates blood vessels, lowering blood pressure. Maximum effectiveness occurs five to six hours after administration and lasts at least a day. The drug helps to quickly lower blood pressure. If you take it regularly, the overall result of the treatment will be visible after 10-14 days. The doctor determines the dosage individually, based on the complexity of the disease. Following the instructions, you need to take a tablet once a day.
Groups of drugs for low blood pressure
- Alpha-agonists should be kept in the medicine cabinet if attacks of hypotension occur with complications (loss of consciousness).
- A group of anticholinergic drugs is popular among doctors and is often prescribed to patients with low blood pressure.
- Adaptogens of plant origin have a beneficial effect on the central nervous system and stimulation of heart activity (no evidence base).
Names of drugs:
- “Gutron” promotes vasoconstriction, resulting in increased blood pressure. The drug helps eliminate uncontrolled urination. After taking it, it takes about an hour for the indicators to stabilize, and the effectiveness lasts four to six. As written in the instructions, people over 12 years of age should take the tablet, divided into 2 doses throughout the day.
- “Ecdisten” increases performance, enhances protein synthesis processes, and tones. Positively affects memory and retention of information. Following the instructions, you need to take no more than 25 milligrams at a time, 3 times a day.
- "Rantarine" normalizes blood pressure, has a tonic effect on the central nervous system, and increases mental and physical performance. You can take no more than three tablets (one per dose) per day, half an hour before meals.
- "Heptamil" helps normalize the tone of blood vessels and the heart. The medicine significantly increases the number of contractions of the heart muscle. The instructions state that you can take the drug in a dose of up to 0.45 grams per day, divided into 3 doses.
- "Citramon". There is a misconception that this medicine lowers blood pressure, but in reality it increases the level. The effect of the product lies in the work of three main components: paracetamol (reduces body temperature, eliminates pain symptoms), aspirin (prevents inflammatory processes), caffeine (increases blood pressure and enhances the effect of paracetamol and aspirin).
Changes in blood pressure cannot be ignored, since the patient’s well-being significantly worsens. In order to normalize blood pressure in a timely manner, you need to have on hand a drug that corresponds to the symptoms: to increase or decrease it.
Types of menstrual irregularities
Cycle disorders can be different, depending on which indicator is outside the normal range: the interval between menstruation, its duration or the amount of blood loss. Here are the main types of deviations and their names.
The interval between menstruation is disrupted:
- Complete absence of menstruation for 3 months or longer is amenorrhea.
- Very infrequent periods, with a period from 36 days to 3 months - opsomenorea.
- Too frequent menstruation, with an interval of less than 21 days - proyomenorrhea.
Abnormal amount of discharge:
- Scanty periods (a few drops during the day) – hypomenorrhea.
- Too heavy periods - hypermenorrhea.
Deviations in the duration of menstruation:
- Less than 3 days – oligomenorrhea.
- More than 7 days – polymenorrhea.
- More than 7 days with heavy bleeding – menorrhagia.
Sometimes uterine bleeding that occurs outside the days of expected menstruation is mistaken for a cycle failure. This phenomenon is called metrorrhagia. As a rule, it is accompanied by severe discomfort, pain, and fever. All these symptoms are reasons to consult a doctor as soon as possible. However, in case of other deviations, it is advisable to visit a specialist.