After reading the article about vaginal suppositories, you will learn:
- 1 What are vaginal suppositories?
- 2
Candle making technology. - 3
Mechanism of action of suppositories. - 4
Medicinal components of suppositories. - 5
Indications for prescribing vaginal suppositories. - 6
How to use vaginal suppositories correctly. - 7
How to increase the effectiveness of candles. - 8
Possible side effects. - 9
In what cases should you consult a doctor? - 10
Benefits of using vaginal suppositories.
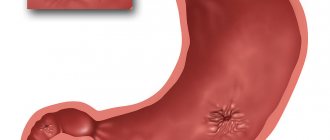
Suppositories (suppositories) are dosage forms that are solid at room temperature and melt or disintegrate at body temperature and are used for administration into body cavities. Vaginal suppositories are used intravaginally, that is, they are inserted into the vagina. Vaginal suppositories can be spherical, ovoid, or flat with a rounded end. Their weight should be in the range from 1.5 to 6 g. If the weight is not indicated, then vaginal suppositories are made weighing at least 4 g.
Candle making technology
The main method of obtaining suppositories is pouring into molds. The method consists of three stages: preparation of the base, introduction of medicinal substances into the base, formation and packaging of suppositories. Bases for the manufacture of suppositories can be lipophilic or hydrophilic. Cocoa butter, its alloys with paraffin and hydrogenated fats, vegetable and animal hydrogenated fats, hard fat, lanol, alloys of hydrogenated fats with wax, hard paraffin and other bases that are approved for medical use are used as lipophilic bases. Gelatin-glycerin gels, polyethylene oxide alloys and other substances approved for medical use are used as hydrophilic bases. The gelatin-glycerin base is made from medical gelatin, glycerin and water.
If you have questions about the use of vaginal suppositories in gynecology, you can read the answers from doctors and user comments in this topic here.
If necessary, medicinal substances are crushed, sifted, mixed with the base directly or after dissolving or grinding with a small amount of water, glycerin, petroleum jelly or other suitable solvent. Heat-labile substances are added to the base immediately before the formation of suppositories. Suppositories are prepared by pouring the molten mass into molds, rolling out or pressing using special equipment. Suppositories are sealed in contour packaging made of polymer materials, combined materials with aluminum foil and other packaging materials.
Mechanism of action of suppositories
Suppositories consist of an active substance and a fat base. At room temperature, candles are characterized by a solid state of aggregation, but at the temperature of the human body, the material from which the candle consists begins to melt, and the substances contained in the candle come out and begin their active action. Some suppositories act exclusively locally, on the mucous membranes, but since the vaginal tissue is saturated with small blood vessels, part of the active substances enters the bloodstream and circulates in the pelvic area, while exerting its therapeutic effect. Absorption of the active substance into the blood occurs very quickly, but the active components affect the general blood flow to a very small extent and almost do not reach the liver and kidneys.
Gynecological suppositories can have different types of action. The most commonly used suppositories have the following effects: anti-infection, anti-inflammatory, tissue repair, vaginal microflora restoration, pain relief. Most often, suppositories have a complex effect, that is, for example, they can simultaneously influence the causative agent of a disease and relieve inflammation.
What are anti-inflammatory suppositories?
Anti-inflammatory suppositories are medications that are used quite often in gynecology. There are many drugs with this effect. The main task of such drugs is to relieve pain and swelling in the area of inflammation. Diclofenac, ichthyol or prednisolone are the active substances that are usually contained in such suppositories. Components of plant origin in candles are also not uncommon. They do an excellent job of relieving inflammation. Many people are familiar with suppositories containing sea buckthorn oil; such preparations have proven themselves on the positive side, and their cost will be affordable for anyone.
Medicinal components of suppositories
Most gynecological diseases are caused by viruses, bacteria, fungi and protozoa, so suppositories may include antiviral, antifungal components, antibiotics and antiseptics.
Antibacterial components of candles are various substances that kill bacteria and prevent their proliferation. Antibiotic suppositories used in gynecology usually contain drugs such as chlorhexidine, metronidazole, penicillins, macrolides, and iodine. Antifungal components are active only against fungi, these include: clotrimazole, ketoconazole, sertaconazole, etc. Often, in the treatment and prevention of gynecological diseases, suppositories are used to restore normal vaginal microflora, which contain lactobacilli and bifidobacteria.
List of suppositories in gynecology
Suppositories for gynecological inflammations
- Indomethacin;
- Neo-Penotran;
- Movalis;
- Flagyl;
- Voltaren;
- Ecofucin;
- Diclofenac;
- Hexicon;
- Flamax;
- Terzhinan.
Suppositories for cysts in gynecology
- Utrozhestan;
- Iprozhin;
- Prajeesan.
Suppositories for cervicitis
- Sintomycin;
- Depanthol;
- Terzhinan;
- Polygynax;
- Hexicon.
Suppositories for endometriosis in gynecology
- Longidaza;
- Indomethacin;
- Galavit;
- Endometrin;
- Antikan.
Candles for adhesions
- Longidaza;
- Dystreptase;
- Lidaza.
Suppositories for dryness in gynecology
- Feminela;
- Beautyful;
- Revitax;
- Vagical;
- Femilex;
- Betadine;
- Vagiferon;
- Livarol.
Suppositories for erosion in gynecology
- Hexicon;
- Polygynax;
- Livarol;
- Depanthol;
- Betadine;
- Suporon.
Indications for prescribing vaginal suppositories
Suppositories can be prescribed for the treatment of the following gynecological diseases:
- inflammatory processes of the organs of the reproductive system;
- cysts, polycystic disease;
- cervical erosion;
- vaginitis (colpitis);
- vaginal candidiasis (thrush);
- bacterial vaginosis;
- sexually transmitted diseases, etc.
Also, suppositories in gynecology are prescribed during the recovery period, after gynecological operations or abortions, to prevent infections before operations, childbirth, installation of an intrauterine device, etc. In addition to the above, there are other cases when specialists choose this method of treatment.
Your doctor may prescribe medication intravaginally if:
- the oral route causes side effects in women;
- there is a history of diseases associated with serious disorders of the liver, kidneys, gastrointestinal tract, and other methods of drug administration are contraindicated.
Suppositories in gynecology: indications for use
Anti-inflammatory suppositories
Many gynecological diseases and pathologies are accompanied by tissue inflammation. Anti-inflammatory suppositories in gynecology help deliver the medicine directly to the site of inflammation. The most common active ingredients in such drugs: diclofenac, indomethacin, prednisolone. Preparations with herbal active ingredients are also available for sale: sea buckthorn or eucalyptus oil, chamomile, sage, calendula.
Suppositories with natural ingredients are allowed for pregnant women and teenage girls. Some suppositories for inflammation in women have an additional analgesic effect.
Indications for use:
- vaginitis;
- vulvovaginitis;
- erosion;
- oophoritis;
- cystitis;
- urethritis;
- endocervicitis;
- endometritis.
Antibacterial (antimicrobial) suppositories
Antimicrobial suppositories for women usually contain iodine, chlorhexidine, metronidazole, miconazole, penicillin, cephalosporin, macrolide, co-trimoxazole or another antibiotic that kills bacteria that cause tissue infection.
Indications for use:
- vaginal candidiasis (thrush);
- inflammation caused by the activity of pathogenic microorganisms, such as vaginitis, cervicitis and others;
- prevention of infectious diseases and inflammation before gynecological interventions.
Painkiller suppositories
Modern suppositories are broad-spectrum suppositories; as a rule, they contain antiviral or antifungal, as well as anti-inflammatory and analgesic components. Anesthetic suppositories in gynecology with ketorolac or indomethacin in the composition can quickly relieve discomfort.
Indications for use:
- algodismenorrhea - severe pain in the lower abdomen during menstruation;
- endometriosis, cystitis, adnexitis and other diseases accompanied by pain;
- postoperative pain syndrome, including after vaginal delivery or CS.
Candles for restoring microflora
The acidic environment in the vagina supports its ability to self-cleanse and provides protection against bacteria and viruses. If the number of lactobacilli that maintain the required acidity is reduced, the protective functions of the system are blocked, and unpleasant symptoms occur.
In this case, it is recommended to use suppositories to improve microflora; they contain probiotic strains of lactobacilli. Such suppositories, which restore microflora, are usually used in gynecology after treatment with antibiotics.
Indications for use:
- unpleasant odor, a large amount of white or yellow discharge, itching, burning, cycle disruption and other symptoms indicating a violation of the vaginal microflora;
- completion of antibacterial therapy;
- prophylaxis before gynecological operations.
Hormonal suppositories
Hormonal suppositories contain a synthetic analogue of the female hormone estrogen. In gynecology, treatment with estradiol suppositories helps to compensate for its deficiency in the body.
Indications for use:
- treatment of genitourinary disorders associated with estrogen deficiency;
- severe symptoms of menopause;
- preoperative therapy and rehabilitation period after surgical interventions in postmenopausal women.
Antifungal suppositories
Antifungal suppositories in gynecology are prescribed when the mucous membranes are damaged by fungi. The active substance damages the cell membranes of fungi and promotes their death.
Indications for use:
- vaginitis, vulvitis, vulvovaginitis and other lesions of the vaginal mucosa caused by Candida fungi;
- prevention of candidiasis during long-term antibacterial therapy.
Antiviral suppositories
Suppositories used in gynecology for infections usually contain interferon or panavir - substances with antiviral and immunomodulatory properties. Such antiviral suppositories for women suppress the spread of the pathogen and increase the body's resistance to the infectious load.
Indications for use:
- genital herpes;
- trichomoniasis;
- chlamydia;
- chronic endometritis;
- urea and mycoplasmosis;
- papillomavirus infection
- gardnerellosis;
- relapse of candidiasis;
- other diseases of a viral nature.
Rectal use of suppositories
In the treatment of gynecological diseases, various rectal suppositories can be used: anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial and others. Once in the intestines, the medicine is quickly absorbed into its walls and then enters the blood, providing a general, rapid effect on the entire body.
When asked whether rectal suppositories can be used in gynecology or placed in the vagina, the answer will be negative. If the packaging for the drug contains instructions for rectal use, the suppository should be administered only into the rectum. Some suppositories, such as Nystatin, are available in both vaginal and rectal forms. Be careful when purchasing a prescribed drug.
Healing candles
Healing suppositories used in gynecology contain dexpanthenol or other stimulators of tissue repair. They accelerate the healing of the vaginal and cervical mucosa.
Indications for use:
- therapy for diseases that cause damage to the mucosa;
- ending local treatment with electric current, laser, liquid nitrogen and other traumatic methods;
- postoperative, postpartum period.
Suppositories for prevention in gynecology
Sometimes gynecologists prescribe suppositories for the prevention of female diseases after successful completion of treatment or before surgery. Even those types of vaginal suppositories that contain exclusively herbal ingredients and are classified as dietary supplements should be taken only after consultation with a specialist.
How to use vaginal suppositories correctly
In order to use the suppository correctly, you must follow the instructions that come with any drug. However, there are general rules for their application.
First of all, you need to wash the intimate area using hypoallergenic soap, but only from the outside, you do not need to wash the inside of the vagina. Then wash your hands thoroughly. Rinse your external genitalia to completely remove the soap. Pat the area dry with a clean cotton towel to remove excess moisture. These actions are very important, since this is the only way to prevent the spread of bacteria into the vagina when inserting a suppository.
Stand with your legs and knees apart. Raise one leg up on a stool or on the edge of the bathtub or toilet. You can also lie on your back with your knees bent and spread out to the side to approximately shoulder level. Using your left hand, separate the labia majora and vulva, thereby opening access to the vagina. Hold the vaginal opening open and insert the suppository with your right hand, then use your index finger to push the suppository deeper. Try to insert the suppository as deeply as you feel comfortable. You should not feel the suppository after insertion, and you will not need to remove it, as it will completely dissolve in the vagina. After inserting the suppository, it is better to lie down for at least 15 to 20 minutes to give the suppository time to dissolve.
Simultaneously with the introduction of the suppository, you should not use sanitary pads or tampons. The entrance to the vagina should be open so that there are no obstacles to the release of secretions. Please note that some suppositories must be moistened with water before administration; it is better to clarify this issue in the instructions for the drug. It is not recommended to use vaginal suppositories during menstruation (some drugs allow such use); this issue should be clarified with your doctor.
Trade name: ZALAIN®
International nonproprietary name: Sertaconazole
Dosage form: vaginal suppositories
Composition for 1 suppository
Active ingredient: sertaconazole nitrate 300 mg; excipients: vitepsol 1.305 g, suppotsir 1.305 g, colloidal anhydrous silicon dioxide 0.09 g.
Description: oval-shaped, waxy, white suppositories.
Pharmacotherapeutic group: antifungal agent
ATX code: G01AF
PHARMACOLOGICAL PROPERTIES
Sertaconazole is an antifungal agent derived from imidazole and benzothiophene. It has fungistatic and fungicidal effects in therapeutic doses. Active against fungi of the genus Candida. The mechanism of action of sertaconazole is to inhibit the synthesis of ergosterol and increase the permeability of the fungal cell membrane, which leads to lysis of the fungal cell.
It also has antibacterial activity against gram-positive bacteria (staphylo- and streptococci).
PHARMACOKINETICS
There is no absorption after intravaginal use.
INDICATIONS FOR USE
Local treatment of infections of the vaginal mucosa caused by fungi of the genus Candida (vulvovaginal candidiasis).
If necessary, please consult your doctor before taking the medicine.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Hypersensitivity to imidazole derivatives, benzothiophene and other components of the drug.
Pregnancy and lactation
There are no sufficient data on the use of sertaconazole during pregnancy and lactation. However, taking into account the method of administration of the drug (single administration), as well as the lack of systemic absorption of the drug after intravaginal administration, the use of sertaconazole during pregnancy and lactation is possible if the potential benefit to the mother outweighs the possible risk to the fetus or child .
If necessary, please consult your doctor before taking the medicine.
METHOD OF APPLICATION AND DOSES
Intravaginally, once.
Before using the drug, you must wash the external genitalia using neutral or alkaline soap.
One vaginal suppository is inserted deep into the vagina, lying on your back, before bed.
If clinical symptoms persist, the suppository may be reintroduced after 7 days.
Use the drug only according to the method of use and in the doses indicated in the instructions.
If necessary, please consult your doctor before taking the medicine.
SIDE EFFECT
Rarely: burning sensation, itching in the vagina, which disappear on their own during treatment and do not require discontinuation of the drug. These side effects are classic for topical medications and reflect the effectiveness of the drug. Allergic reactions are possible.
Consult your doctor if you experience any of the side effects mentioned or other side effects not listed above.
OVERDOSE
Not installed.
If you accidentally take the drug orally, you must rinse your stomach and consult a doctor immediately.
INTERACTION
Simultaneous use of the drug with local contraceptives may lead to a weakening of the spermicidal effect of the latter.
SPECIAL INSTRUCTIONS
In case of simultaneous infection of the labia and adjacent areas (candidal vulvitis), additional local treatment with ZALAIN cream should be carried out.
When using the drug, it is recommended to abstain from sexual intercourse.
To prevent urogenital reinfection, it is recommended to consider simultaneous treatment of the sexual partner.
The risk of condom or diaphragm rupture increases when used simultaneously with the drug.
Treatment can be carried out during menstruation.
Zalain does not affect the performance of potentially hazardous activities that require special attention and quick reactions (driving a car, etc.).
STORAGE CONDITIONS
At a temperature not exceeding 300 C. Keep out of the reach of children.
Best before date
5 years. Do not use after the expiration date stated on the packaging.
Release form
Vaginal suppository 300 mg.
1 vaginal suppository in a PVC/PE blister. 1 blister along with instructions for use in a cardboard box.
Conditions for dispensing from pharmacies
Over the counter.
Registration Certificate Holder
CJSC Pharmaceutical Plant EGIS, Hungary
1106 Budapest, st. Kereszturi ut 30-38 (1106 Budapest, Kereszturi ut 30-38, Hungary)
Phone: (36-1) 803-5555,
Fax: (36-1) 803-5529
Under license from Ferrer International A.O., Spain
Manufacturer
Trommsdorff GmbH and Co. KG, Germany, Trommsdorffstrasse 2-6, 52477, Alsdorf (Trommsdorffstrasse 2-6, 52477, Alsdorf, Germany) (all stages of production);
CJSC Pharmaceutical Plant EGIS, Hungary
1165, Budapest, st. Bokenyfoldi 118-120 (1165 Budapest, Bokenyfoldi ut 118-120, Hungary) (quality control issuer)
Name and address of the organization authorized by the holder or owner of the registration certificate of the medicinal product to accept claims from the consumer
LLC "EGIS-RUS", Russia
121108, Moscow, st. Ivana Franko, 8, phone: (495) 363-39-66
How to increase the effectiveness of candles
To increase the effectiveness of suppositories, it is necessary to store the drug correctly. Suppositories usually consist of fats or water-soluble polymers and, once in the vagina, they begin to melt. To prevent suppositories from melting, they should be stored at room temperature. If the house is too hot and there is a risk that the suppositories will melt, they can be stored in the refrigerator.
It should also be taken into account that it is better to administer suppositories at night. Suppositories dissolve in the vagina and may leak out along with discharge, so they are best inserted before bed. If you need to insert suppositories during the day, use a panty liner to catch the discharge. When inserting a suppository, do not use tampons, as they absorb the drug, making it less effective, and they also irritate the vaginal walls.
Benefits of using vaginal suppositories
The main advantage of the intraginal method of drug administration is that the drug is delivered directly to the destination. Suppositories in the vagina quickly dissolve and begin their therapeutic effect almost immediately. Such a quick effect is very important in the treatment of infection and inflammation, since if the process is not stopped in time, it will begin to spread from the vagina to the uterus and beyond. The medicine administered intravaginally not only has a therapeutic effect, but also prevents the spread of infection, becoming a kind of barrier to its path. With this method of treatment, there are practically no side effects, which cannot be said about other methods of taking medications, for example, oral ones.
Thus, the advantages of using suppositories compared to tablet drugs include:
- rapid penetration of the drug to the source of inflammation, which accelerates the achievement of the therapeutic effect;
- maximum absorption of the active component into the systemic bloodstream ensures high effectiveness of treatment;
- the absence of direct contact with the digestive organs eliminates the risk of side effects from the gastrointestinal tract and the occurrence of serious allergic reactions.
That is why, in the treatment of many gynecological diseases, doctors quite often prescribe intravaginal administration of drugs.
Remember that self-medication with suppositories is unacceptable, since many suppositories have contraindications for certain concomitant diseases and their use can only cause harm. Also, not all suppositories can be used during pregnancy. Vaginal suppositories can only be prescribed by a doctor if there are appropriate indications!