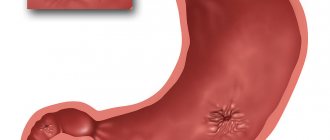
Sinusitis is an inflammation of the mucous membrane of the maxillary (or maxillary) sinus.
We have two maxillary sinuses; they are located in the thickness of the maxillary bone on both sides of the wings of the nose. The paranasal sinuses (which, in addition to the maxillary sinuses, include two frontal sinuses, the ethmoid labyrinth and the sphenoid sinus) are designed to prepare inhaled air for further movement within the body (entering the lower respiratory tract). In the sinuses, the air is warmed and humidified. In addition, thanks to the sinuses, the weight of the facial part of the skull is reduced. The sinuses also play the role of a resonator, setting the timbre of our voice.
The sinuses open into the nasal cavity through small openings called anastomoses. This makes them vulnerable: when the nasal mucosa swells, the sinuses may become blocked. There are few nerve endings in the mucous membrane of the sinuses themselves, so the inflammatory process here can take place without causing pain until a certain point.
Chronic sinusitis
Chronic sinusitis is diagnosed if the inflammatory process in the maxillary sinuses continues for more than 4 weeks. In the chronic form of the disease, periods of relatively good health are followed by exacerbations, when the symptoms of sinusitis appear again.
Between exacerbations, the symptoms of sinusitis are usually mild. The temperature, as a rule, does not rise or rises slightly - up to 37−37.5 °C. The most indicative symptom of chronic sinusitis is attacks of dry night cough, which does not respond to traditional treatment. A cough is caused by phlegm running down the back of the throat.
Chronic sinusitis is very difficult to completely cure. Therefore, if you get sinusitis, you should immediately consult a doctor before the disease becomes chronic.
Method of using ointments
All ointments are applied externally. This medicine can be used after clearing the sinuses. To administer it, the product is applied to cotton wool and placed in the nasal passages. Doctors recommend avoiding the use of vasoconstrictor drops when applying ointments, as they can reduce the effect of their effects by narrowing the vessels of the nasal passage.
Only when applied externally to the site of inflammation, the ointment has an antiseptic effect and helps reduce inflammation of the mucous membrane and remove mucous secretions.
Causes of sinusitis
Most often, sinusitis occurs as a complication of colds and infectious diseases (such as influenza, ARVI). Reduced immunity, structural features of the nasal passages (for example, a deviated nasal septum), susceptibility to allergic rhinitis, and increased sensitivity of the vegetative-vascular system to irritants (the so-called vasomotor rhinitis) can contribute to the occurrence and development of sinusitis.
The inside of the sinuses is lined with a membrane that produces mucous secretion. If a person is healthy, the small amount of mucus produced is easily removed through the sinus anastomosis into the nasal cavity, and with this constant flow, microorganisms and dust particles that have entered there along with the air are removed from the sinuses.
As soon as a runny nose begins, the mucous membrane of the nasal cavity swells, sometimes including the mucous membrane of the anastomosis. The entrance to the sinus is blocked. If the swelling is significant, oxygen stops flowing into the sinus, creating favorable conditions for the development of anaerobic pathogenic microorganisms. Pressure increases in the sinus, a bursting sensation occurs, and then pain. Pathogenic bacteria produce toxins that, when released into the blood, can cause signs of general intoxication. Inflammation of the mucous membrane of the sinus itself develops, that is, sinusitis itself. The mucus turns into pus, which, having a more viscous consistency, even when the swelling has subsided, cannot leave the sinus naturally. Sometimes pus fills the entire sinus, and the severity of pain increases.
Typically, inflammation is not limited to just one sinus, but immediately affects both the maxillary and frontal sinuses, as well as the ethmoid labyrinth deep in the nose. In this case, they talk about polysinusitis (sinusitis is an inflammation of any paranasal sinus; sinusitis is a special case of sinusitis).
Sinusitis, which manifests itself in the form of isolated inflammation of only one sinus, may be of odontogenic origin, that is, be a consequence of inflammation in the dentofacial area. If the maxillary sinus has a significant volume, only a thin bone separates it from the tops of the tooth roots, and in some cases the tops of the tooth roots are adjacent directly to the mucous membrane of the sinus. In this case, advanced inflammation in the area of the four outermost upper teeth or unprofessional tooth extraction surgery can lead to infection of the maxillary sinus mucosa.
Complications
Sinusitis is a fairly serious disease, and if treated carelessly, it can become a source of complications.
The most common consequence of the disease is chronicity of the inflammatory process, and as a result, interruptions in the normal functioning of internal organs. With chronic inflammation, air circulation in the nasal cavity is impaired; accordingly, the brain is not sufficiently saturated with oxygen, which affects other body systems.
Inflammation of the sinuses and the presence of a constant source of infection in them cause frequent exacerbations of sinusitis, as well as tonsillitis, bronchitis and pneumonia.
Pathogenic microorganisms can enter the ear cavity from the nasopharynx and cause otitis media.
The most dangerous consequences are meningitis and sepsis.
Remember, treatment of acute inflammation and chronic forms should be carried out in a timely manner and only under the supervision of an ENT doctor.
Symptoms of sinusitis
Acute sinusitis is characterized by the following symptoms:
Runny nose
Sinusitis is characterized by a prolonged runny nose with purulent or mucous discharge. A normal runny nose should go away within 7-10 days. If the runny nose drags on and there is no improvement in the condition, then the inflammatory process has probably spread to the mucous membrane of the paranasal sinuses. One of the signs of a runny nose turning into sinusitis may be alternating congestion in the right and left nostrils.
More about the symptom
Morning sputum
Mucus from the sinuses flows into the nasopharynx, causing frequent expectoration and copious sputum production in the morning.
Sinus pain
A characteristic symptom of sinusitis is an unpleasant feeling of heaviness or pain in the cheek area. Sometimes not only the area of the inflamed sinus itself hurts, but also the teeth, eyes, and temples. The pain, less noticeable in the morning, intensifies in the evening. Pain also increases when bending forward.
Weakness
General weakness and fatigue with sinusitis are caused by produced toxins.
More about the symptom
Temperature
In acute sinusitis, the temperature may rise to 38°C or higher.
More about the symptom
Prevention and reviews
Prevention of the development of sinusitis is timely initiation of treatment for various respiratory diseases.
It is necessary to monitor your health and strengthen your immune system. Any ointment for sinusitis should be used carefully and with caution. All contraindications should be taken into account. If adverse symptoms occur, therapy is stopped immediately.
All medications are allowed after prescription; self-treatment can provoke an exacerbation of the disease.
Reviews
Anna:
When the first signs of sinusitis appear, I immediately smear my nose with oxolinic ointment. At first there is an unpleasant sensation, then the cream is absorbed and relief comes. The disease goes away very quickly.
Elena:
Sinusitis occurs frequently. At first I try to smear my nose with Levomekol. After just a couple of days it becomes much easier.
Vladimir:
For sinusitis, the doctor advised using Vishnevsky ointment to lubricate the mucous membrane. Its smell is very pungent, but if you endure it, the result will not be long in coming. I'm recovering pretty quickly.
Methods for diagnosing sinusitis
Diagnostic procedures for sinusitis are designed to determine the condition of the maxillary sinuses: the degree of swelling of the mucous membrane, the presence and level of fluid in the sinus. For this purpose the following are used:
X-ray of the sinuses
The radiography method of the paranasal sinuses is used most often.
More information about the diagnostic method
MSCT of the paranasal sinuses
A CT scan of the sinuses also uses X-rays. But it allows you to get a more detailed picture of bone structures. This diagnostic method is used, as a rule, for chronic sinusitis.
More information about the diagnostic method
Ultrasound of the sinuses
An ultrasound of the nasal sinuses is usually performed if an x-ray is undesirable (during pregnancy, examination of children, or during a repeat examination). Ultrasound can be performed using the Sinuscan ultrasound diagnostic device.
MRI of the sinuses
MRI of the sinuses is used if it is necessary to evaluate the condition of the sinus mucosa.
Sign up for diagnostics To accurately diagnose the disease, make an appointment with specialists from the Family Doctor network.
Levomekol
Levomekol ointment is famous for its antibacterial properties. Its use is justified for purulent forms of sinusitis. Main ingredients of the drug:
- chloramphenicol,
- methyluracil.
They actively fight many types of pathogenic bacteria, help cleanse the nasal sinuses and passages of purulent contents, reduce swelling, resulting in relief of headaches, restoration of nasal breathing and elimination of nasal congestion. The use of the medicine is quite simple: cotton wool is soaked in the ointment and placed in the nose for 10-15 minutes.
Treatment methods for sinusitis
Treatment of sinusitis should be timely. It is very important to prevent the disease from becoming chronic and developing complications. Therefore, if symptoms of sinusitis appear, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Treatment of sinusitis in the “Family Doctor”
Removing pus from the paranasal sinuses
can be carried out
using the YAMIK sinus catheter
, which uses the creation of controlled pressure in the sinuses and nasal cavity. This is a painless and effective procedure. In cases where there is no other way to ensure the outflow of pus from the sinus, a puncture (or puncture) of the maxillary sinus is performed. The puncture is carried out with preliminary anesthesia and is performed using low-traumatic needles, which makes the operation painless.
When visiting a doctor in the early stages of the disease, there is usually no need for a puncture; washing and drug treatment are sufficient.
You can receive qualified medical care for sinusitis by contacting an ENT doctor at any of the Family Doctor clinics. Select a clinic that is located in the area of Moscow you need.
Treatment of sinusitis in pregnant women
During pregnancy, women's immunity decreases slightly. Therefore, a runny nose during pregnancy is a fairly common occurrence. And as a complication of a runny nose, sinusitis often develops.
Diagnosis and treatment of sinusitis in pregnant women has its own characteristics: X-rays and computed tomography of the head are not recommended, especially in the early stages. Certain medications (antibiotics) should not be used.
More information about sinusitis in pregnant women
Make an appointment Do not self-medicate. Contact our specialists who will correctly diagnose and prescribe treatment.
Rate how useful the material was
thank you for rating
Liniment Vishnevsky
Everyone is probably familiar with this “fragrant” drug. But not everyone knows about its healing properties for sinusitis. Liniment consists of xeroform, birch tar and castor oil. Xeroform has strong antiseptic properties and effectively copes with most pathological microorganisms characteristic of purulent inflammation. Birch tar also has an antiseptic effect. In addition, tar increases local blood circulation, accelerating the resorption of infiltrates and the removal of purulent exudate. Castor oil improves tissue permeability and has a regenerating effect.
Vishnevsky ointment can be used in its pure form, but more often it is recommended to add additional components to it:
- take cyclamen and aloe juice in equal quantities,
- add a little honey and garlic juice.
It is important to make sure that the person being treated with this composition does not have hypersensitivity to any of the components of the drug.
All ingredients are thoroughly mixed with liniment, the resulting mixture is applied to cotton swabs and placed in the nasal passages for 10-30 minutes. If a strong burning sensation is observed, it is better to stop the procedure earlier so as not to damage the nasal mucosa and not to prolong the recovery period.
- What medications should be used to treat sinusitis?
Using this remedy for sinusitis allows you to speed up the cleansing of the nasal passages and sinuses from pus and secretions accumulated there, eliminate swelling of the nasal mucosa and reduce inflammation.
Frontitis and sphenoiditis
Frontitis is the most severe manifestation of inflammation. It affects the frontal sinuses. Patients experience severe headaches in the forehead area. If a person tilts his head down, a sharp pain occurs in the forehead, because at this moment the purulent masses move and put pressure on the front wall of the frontal sinus from the inside. Patients with this form of the disease try not to get up too much and spend the entire day in a lying position. The chronic form of the disease can cause vision problems, swelling of the upper eyelid and orbital area.
Friends! Timely and correct treatment will ensure you a speedy recovery!
Sphenoditis often occurs in conjunction with ethmoiditis, but as an independent disease it is quite rare. With this type of sinusitis, the sphenoid sinus becomes inflamed. This inflammation, pressing on the walls of the sinus, creates pain in the very middle of the head and the back of the head. Patients sometimes think about high blood pressure or neurological problems, not knowing about the presence of a sinus, which is located so deep. The pain radiates to the temples and eyes. Sphenoiditis can also cause damage to the optic nerve, and as a result, visual impairment.
Classification of sinusitis
Based on which of the paranasal sinuses is affected, sinusitis, ethmoiditis, frontal sinusitis, and sphenoiditis are distinguished. Each type of disease (except for sphenoiditis) can be unilateral (when one sinus is affected) or bilateral (if both). The second option is less common.
Depending on the patient’s condition and the severity of symptoms, mild, moderate and severe forms of the disease are distinguished.
Based on the factors that caused inflammation, infectious and non-infectious forms of the disease are distinguished. The first include bacterial, viral and fungal sinusitis. The second group includes allergic, vasomotor, medicinal, traumatic, mixed.
The inflammatory process in the sinuses occurs in different ways - hence another division of sinusitis into: exudative and productive. The main sign of the exudative form is abundant mucous discharge. Productive is characterized by strong growth of the mucous membrane.
The exudative form of the disease, in turn, is divided into catarrhal, serous and purulent forms. With catarrhal sinusitis, the discharge is abundant, transparent, and there is no pus. With the serous form, noticeably more mucus is released, but the discharge is also transparent. The purulent form indicates that bacteria are joining the inflammatory process. The discharge in this case has a greenish tint and smells bad.
Productive sinusitis manifests itself in the parietal hyperplastic form, when the surface of the mucous membrane noticeably increases in size, and in the polypous form, when polypous tissue grows (as a rule, it occurs if a person has been suffering from the disease for more than a year).
Ways to prevent sinusitis
To reduce the risk of developing sinusitis, follow a number of rules:
- do not get too cold;
- don't get a runny nose;
- treat nasopharyngeal diseases in a timely manner;
- visit the dentist in a timely manner and treat caries;
- if you are allergic, avoid contact with the allergen;
- if full nasal breathing is hampered by a deviated nasal septum and enlarged nasal turbinates, it is necessary to undergo surgery to eliminate these defects;
- strengthen your immune system: walk in the fresh air more often, eat a balanced diet, engage in physical activity, quit bad habits;
- Monitor the microclimate in the apartment: maintain a comfortable level of humidity and temperature for the body. If the nasal mucosa is sufficiently moistened, it is more resistant to the negative effects of viruses and bacteria.
- Try to avoid contact with sick people. During epidemic periods, minimize visiting crowded places.