Sinusitis is the most common disease for which people consult an ENT doctor. Sinusitis is manifested by inflammation of the maxillary sinuses. This disease is difficult for patients to tolerate, due to unpleasant symptoms that interfere with their usual way of life. Can a child have sinusitis? Yes maybe! And the treatment of a child must be treated with maximum responsibility. How does sinusitis manifest in children? At what age is sinusitis diagnosed in children? How to recognize the first symptoms of inflammation and how to treat it correctly? Read about all this in our new article.
Modern medical statistics provide the following figures: more than ten million people suffer from sinusitis every year. The scale of this type of sinusitis is immediately visible. Sinusitis is a collective name for inflammation of all types of human paranasal sinuses. Sinusitis is manifested by inflammation of the maxillary sinuses. The second name for these sinuses is also used - maxillary sinuses - hence the name of the disease.
Anyone who has been ill at least once will forever remember the unpleasant symptoms of sinusitis and those painful sensations in the bridge of the nose that interfere with leading a normal lifestyle. The disease is severe, regardless of the patient’s age: it will not be possible to sit at home or endure the disease on your feet - the patient requires competent, timely treatment.
Due to the prevalence of the disease, many parents have a question: “Can a child have sinusitis?” We answer: “Maybe!” Young children are also susceptible to inflammation of the maxillary sinuses, and the symptoms of childhood sinusitis are no easier than in older patients.
Diagnosis is complicated by the fact that the child cannot always explain where and how it hurts. Therefore, parents should be able to recognize the first signs of sinusitis in a child in order to promptly contact an ENT doctor for treatment.
How does sinusitis manifest in children? At what age can sinusitis in children be diagnosed? What signs of illness should you look out for? The causes, symptoms and treatment of sinusitis in children is the topic of our new article.
What you need to know about sinusitis?
In humans, in the bones of the skull along the line of the forehead and nose there are sinuses (cavities with air): frontal, sphenoid, maxillary, cells of the ethmoid labyrinth.
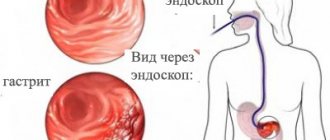
When pathogenic organisms enter, they can become inflamed, resulting in sinusitis. Sinusitis is a disease of the maxillary sinuses. This name is received in honor of the researcher who described this type of sinuses, Nathaniel Highmore. The medically correct name for the disease is maxillary sinusitis.
IRS®19 in the prevention of sinusitis
Prevention of sinusitis in children at home involves proper and timely treatment of acute respiratory viral infections and other respiratory tract infections. In this case, it is the local immune defense in the nose that is important, which will immediately neutralize them when viruses and bacteria enter the mucous membrane. The drug IRS®19 helps activate it. This nasal spray contains 18 bacterial lysates (fragments of destroyed bacteria), which begin to act immediately, triggering a cascade of protective factors, thereby building local immunity5. The sprayer allows you to evenly apply the medicine to the mucous membrane, which contributes to equally strong protection over the entire surface. IRS®19 is approved for children from three months6.
Reasons for development
Due to its occurrence, sinusitis is rhinogenic
,
odontogenic
,
traumatic
,
allergic
.
- Rhinogenic occurs against the background of rhinitis. Provoking factors can be bacteria, viruses, hypothermia, allergies, and side effects of medications. If this disease is not cured in time, it will go deeper, affecting not only the nasal cavity, but also the sinuses.
- Odontogenic sinusitis appears due to a dental infection, which gradually spreads to the sinus mucosa (the tissue around the tooth hurts, a communication is formed between the sinus and the oral cavity), causing it to become inflamed.
- Traumatic sinusitis occurs as a result of mechanical damage to the maxillary sinus, nasal septum or upper jaw.
- With allergic rhinitis, the body reacts in a special way to one of the irritants that causes such a reaction. First, unpleasant sensations appear in the nasal cavity, and then they move to the maxillary sinuses. Allergens include pollen, fur, animal excrement, dust mites, and plant chemicals.
According to the nature of the course, sinusitis can be:
- acute (onset of disease, less than 3 months),
- recurrent acute (repeated up to 4 times a year),
- chronic (appears if the acute stage is not treated, that is, 3 months after the onset of the disease),
- exacerbation of chronic sinusitis (with the appearance of new symptoms in addition to existing ones).
The severity of acute sinusitis varies from mild to severe:
- With a mild course of the disease in a person, the symptoms are moderate: there is no fever, headaches or complications, there is slight congestion, cough, and nasal discharge.
- At the moderate stage, the temperature is within 38 ° C, a cough and runny nose are observed, heaviness of the head (in the projection of the paranasal sinuses) is added when moving and bending, and otitis media.
- In a severe case, the temperature exceeds 38 ° C, all the usual symptoms appear more strongly, periodic or constant pain occurs in the projection of the paranasal sinuses, which intensifies when moving or tilting the head. Over time, intracranial or orbital complications are possible.
What symptoms occur with the disease?
The very first thing we observe in a baby is a runny nose, nasal congestion, and nasal sound. This tells us that mucus is accumulating in the sinuses. If you ignored the first signs, then the following symptoms of sinusitis in a child:
- lethargy, drowsiness, moodiness;
- high temperature (from 38);
- thick discharge from the nasal cavity;
- hard breath;
- possible cough.
When your usually cheerful and cheerful baby does not want to get out of bed, is capricious for no reason, complains of headaches, sweats a lot, and has a bright blush on his cheeks, call the doctor as soon as possible. You cannot joke with the disease, otherwise it will turn into chronic sinusitis.
Reasons for development
Sinusitis develops after pathogens enter the sinuses: viruses, fungi, bacteria. In children, the most common pathogens are pneumococcus, parainfluenza virus, streptococcus, staphylococcus, rhinovirus, hemophilus influenzae and others.
If the child’s immunity is in order, then he can easily overcome the infection, but there are cases when the child’s health is weakened and the body can no longer normally resist the pathogen.
Among the factors that influence the decrease in immunity and help pathogens penetrate the body are the following:
- diseases of the upper respiratory tract (rhinitis, ARVI, tonsillitis, pharyngitis);
- inflammation in the oral cavity (caries or stomatitis);
- enlarged adenoids;
- polyps or other formations in the nasal cavity;
- narrow nasal passages;
- deviated nasal septum.
Important
: sinusitis or maxillary sinusitis is usually bilateral, that is, it penetrates both sinuses.
Children from birth to 3 years old will not yet be able to describe if they are in pain. In this case, it is important for parents not to miss the development of the disease.
Description of the disease
Sinusitis is a common childhood disease in which inflammation (often purulent) of the mucous membrane of the maxillary sinuses occurs.
The main reason for the development of pathology is the blockage of the passages connecting the sinuses with the nose, as a result of which the ventilation of the channels deteriorates and a favorable environment is created for the proliferation of pathogenic microflora. A similar situation can arise after suffering from infectious and inflammatory diseases of the ENT organs, a deviated nasal septum, hypertrophy of the adenoids, etc. Sinusitis brings significant discomfort to the child and greatly disrupts the usual way of life. Symptoms such as nasal congestion, pain in the bridge of the nose, and purulent discharge from the nasal passages occur. Untimely treatment of the pathology can lead to serious complications - meningitis, brain abscess, inflammation of the trigeminal nerve, etc. That is why parents should consult their child with a qualified ENT doctor at the first manifestations of sinusitis.
Diagnostics
At the first symptoms of sinusitis - severe and persistent nasal congestion, weakness, fever - you should consult a doctor. It is important to understand that a small child cannot always say exactly where and how it hurts, so it is important to see a doctor as quickly as possible.
The ENT doctor interviews the patient and conducts an examination. To clarify the diagnosis, you will need to do a blood test for leukocytes and take an x-ray of the maxillary sinuses.
If necessary, a puncture (examination of mucus) is performed. Important: this procedure is quite unsafe, since during sample collection an infection can enter the eye sockets and cause an abscess.
Diagnosis and treatment of childhood sinusitis
For an experienced otolaryngologist, diagnosing sinusitis is not difficult. After a conversation with the parents to clarify the patient’s complaints and collect anamnesis, the doctor conducts a direct examination of the nasal cavity. The most informative diagnostic method is considered to be an endoscopic examination, which helps to examine all the remote corners of the nasal cavity. If necessary, an x-ray examination is performed. A general blood test indicates the presence of an inflammatory process in the body, and a smear taken from the nasal cavity allows one to determine the nature of the pathogen and its sensitivity to antibiotics.
The treatment regimen for the disease may include:
- taking antibacterial drugs;
- vasoconstrictor drops;
- hormonal nasal sprays;
- solutions for rinsing the nose based on sea water;
- antipyretic drugs;
- rinsing the sinuses using the “cuckoo” method;
- physiotherapeutic procedures.
Treatment
Medicines, home remedies and specific therapy should be prescribed according to the type of disease.
When treating sinusitis, a person does not need to be hospitalized, since home and outpatient procedures are usually sufficient.
Treatment is complex: taking medications that eliminate individual symptoms of the disease, physiotherapy, taking medications to strengthen the immune system, taking antibiotics.
The main methods of treating sinusitis:
- Broad-spectrum antibiotics for internal use. Prescribed by a doctor, when used correctly they are almost harmless to the body. The product can only be used if the child has a high fever and intoxication. Important: To protect the gastrointestinal tract while taking the medicine, you need to take probiotics or prebiotics along with the medicine.
- Antiseptic drugs for topical use are drugs that act on the cause of the disease - pathogenic bacteria. These drugs also include drops based on silver proteinate, which help get rid of a runny nose. It is worth noting that now in pharmacies there are a lot of such drops from different manufacturers, but for safe use it is better to choose the company that produces the original drug
- Strengthening the immune system with the help of folk and medicinal remedies: mustard plaster, rubbing, herbal teas, propolis (roll cotton pads and put in the nostrils for 5 minutes), vitamin C.
- Physiotherapeutic procedures: inhalations, electrophoresis, “blue lamp”.
- Home physiotherapy: inhalations using a nebulizer, steam inhalations.
If none of the remedies work, the doctor may prescribe surgery. As a rule, this is a puncture through which the pus accumulated in the sinus is removed.
Complications of sinusitis in children
Lack of timely drug therapy can lead to the development of serious complications. These include:
- ear infection;
- conjunctivitis and purulent eye lesions;
- damage to the adjacent sinuses;
- inflammation of the bone shell in the sinus with the formation of flux (inflammation of the shell covering the bone - the periosteum);
- meningitis (inflammation of the meninges);
- the occurrence of autoimmune reactions with damage to the kidneys, heart, joints;
- general weakening of the immune system with a high risk of developing frequent colds, sore throats, and rhinitis4.
The most common complication is the formation of chronic inflammation in the maxillary sinus. At the same time, children constantly suffer from runny noses and headaches.
Additional remedies for the treatment of sinusitis in children:
- vasoconstrictor nasal drops strictly according to the instructions;
- anti-inflammatory drugs;
- local immune activators to protect the nasal mucosa and prevent an increase in the number of pathogens3.
If conservative treatment is ineffective, the child needs to undergo surgery (sinus piercing). Sinusitis is a serious problem that is best not allowed to arise. To do this, you need to promptly treat ARVI and influenza in a child, and pay attention to local respiratory tract protection.
To activate the immune system of the nasal mucosa, IRS®19 is used. The drug helps reduce the risk of developing complications from ARVI and influenza, including the likelihood of inflammation of the maxillary sinuses5.
Differences from a runny nose
The pathology of the maxillary cavities can be quite difficult to distinguish from a common runny nose, especially when it comes to young children. The doctor must pay attention to complaints, medical history, examination data, and also conduct diagnostic tests. When collecting complaints, it is recommended to talk not only with parents, who may distort information due to misunderstanding, but also with the child, especially if he is already of a conscious age and can answer the doctor’s questions.
Pay attention to the following signs of sinusitis in children, which will help distinguish it from a runny nose:
- clarify whether breathing is complicated through both nasal passages or only through one: unilateral sinusitis is usually accompanied by unilateral congestion on the affected side, while a runny nose is characterized by congestion on both sides;
- be sure to pay attention to the pain symptom and its features: for a runny nose, the appearance of pain is not a characteristic sign at all, unlike sinusitis, which is characterized by complaints of pain that intensifies when trying to tilt the head to the side, and also relieves when blowing the nose for a while;
They clarify whether there is pain when pressing in the sinus area: with a runny nose, the child will calmly allow his face to be touched; with sinusitis, he will complain of pain or initially begin to be capricious when trying to conduct an examination.
If symptoms resembling sinusitis appear, it is necessary to contact an ENT doctor who will competently assess the patient’s complaints, conduct an examination and, using diagnostic measures, finally confirm the diagnosis. Only after this can you begin to treat the pathology.