Catatonic (from other gr. kata - “along” and tonos - “tension”) schizophrenia is characterized by alternating stupor and excitement in combination with general symptoms of schizophrenia. A person can literally freeze in one position, often even completely uncomfortable for the body, without reacting to external stimuli and without speaking. Such a patient has signs of a narrowing of consciousness, and, which is quite common for the mentioned mental illness, there are fantastic visions, hallucinations, and delusions.
Story
As an independent mental disorder, the catatonic form of schizophrenia was first described by the German psychologist Karl Ludwig Kahlbaum in the sixties of the 19th century. He announced this syndrome at a congress of psychiatrists in Innsbruck, noting that he has special symptoms that, in addition to the emotional sphere, also affect the motor sphere.
Kahlbaum's disease, as it is often called in memory of its discoverer, can appear in people under 50 years of age at any period of life, even in the youngest. In children it can be determined by monotonous movements of the body, in children 5–6 years old - by sniffing and licking surrounding objects. But usually catatonia strikes people aged 16–30 years. The first signs appear earlier in males.
It should be noted that earlier, until the fifties of the twentieth century, such a serious disease occurred quite often, especially among young people, but since then this trend has declined. Currently, only 1–3 patients with schizophrenia are diagnosed with it.
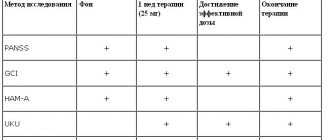
Catatonic disorders in the clinical picture of acute psychotic states
AV Kuznetsov IP Pavlov First St.
Petersburg State Medical University Summary
Catatonia is a psychopathological syndrome characterized by a variety of motor disorders, including stupor, exaltation and multiple symptoms.
Initially, the same cases were qualified as a subtype of schizophrenia, but later the point of view of researchers on this problem was changed towards expanding the diagnosis of catatonic manifestations among patients suffering from affective pathology, neurological and infectious diseases. Finally, the idea of catatonia as a nonspecific syndrome was formed. For syndrokinesis and syndromotaxis of catatonia patterns studying, 150 patients were examined who had acute endogenous psychoses with catatonic symptoms. Several groups were identified, characterized by a different spectrum of acute catatonic symptoms (main, additional and optional) during psychotic attacks. Differences between the groups were revealed depending on the spectrum of residual catatonic disorders. The results of this study allow us to assess the role of the underlying disease in the pathogenesis of catatonia. Keywords
: catatonia, schizophrenia, affective disorders, acute psychosis
For citation
: AV Kuznetsov. Catatonic disorders in the clinical picture of acute psychotic states. Psychiatry and psychopharmacotherapy. 2020; 5:27–31.
Reasons for development
Any form of schizophrenia, including catatonic, develops due to the following factors:
- Unfavorable course of pregnancy. The expectant mother suffered an infectious disease (influenza, measles, hepatitis, chicken pox, etc.). Chronic diseases of a pregnant woman that negatively affect the maturation of the baby’s brain in the womb, drinking alcohol, drugs, and smoking are also dangerous.
- Difficult childbirth, accompanied by head injuries to the baby, hypoxia. Prematurity.
- Genetics. Everything here is ambiguous. A child may receive the defective gene from relatives with schizophrenia. But a gene mutation can also occur at the time of conception.
- Psycho-emotional shock. This can be physical, sexual, psychological violence - death of loved ones, divorce of parents, separation from a spouse, severe stress, bullying, family quarrels, war, etc.
- Neurological diseases - Tourette's syndrome, post-encephalitis syndrome, etc.
- Bad habits – alcoholism and drug addiction. Particularly dangerous are hallucinogens such as psilocicin, LSD, mescaline, which change the perception of reality and have a very strong negative effect on the psyche.
- Mental disorders – autism, childhood developmental disorders, postpartum psychosis.
- Somatic diseases - autoimmune, oxygen starvation, heat stroke, viral infections.
- Problems in the social and domestic sphere. Vagrancy, poor nutrition of the mother when carrying a child and when feeding it, migration.
- Personality characteristics. Perfectionists who strive to do everything as best as possible are under constant stress. This “excellent student syndrome” often leads to the development of schizophrenia.
- Tetraethyl lead or carbon monoxide poisoning.
Why does catatonia occur?
Catatonia was first described in detail in 1874, but its causes have not yet been established. Scientists have several theories about catatonia: pathophysiology, diagnosis and modern approaches to treatment, which approximately explain what changes in the body lead to the appearance of symptoms of catatonia.
Some researchers believe that the problem lies in a disruption in the transmission of nerve impulses in those areas of the brain that are responsible for muscle contractions. Others associate catatonia with a change in the balance of neurotransmitters - substances that are produced by neurons in the brain and are involved in transmitting signals from cell to cell and many biochemical processes. Still others blame the excess or lack of certain hormones of the hypothalamus and pituitary gland, the production of antibodies to brain proteins.
Such disturbances in the functioning of the body appear in many diseases:
- psychiatric Borisova P. O. Nosological dilemma and clinical polymorphism of the phenomenon of catatonia. , for example bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, autism, depression, anorexia nervosa;
- endocrine: Cushing's syndrome, hyperthyroidism, Sheehan's syndrome and others;
- neurological, for example epilepsy, multiple sclerosis, Parkinson's disease, brain tumors, dementia;
- metabolic - this is when substances accumulate in the body that have a bad effect on the brain: this happens with Wilson-Konovalov disease, an increase and decrease in sodium concentration in the blood, kidney failure and other diseases;
- autoimmune, for example systemic lupus erythematosus, antiphospholipid syndrome;
- Catatonia caused by psychoactive substances: alcohol, antipsychotics, sedatives, drugs;
- infectious Catatonia: HIV, typhoid fever, tuberculosis, meningoencephalitis, herpes and others;
- vascular, for example thrombosis of the arteries and veins of the brain, stroke, cerebral hemorrhage.
Symptoms of catatonic schizophrenia
Typical signs of this mental disorder are intermittent stupor and agitation. Let's look at each in detail.
Catatonic stupor - a person is in an uncomfortable position for quite a long time, several hours, days, months and even years. The famous physiologist Ivan Pavlov mentions a case when he was shown a patient who had been in this condition for 20 years.
A person in a stupor retains consciousness, that is, he can then talk in detail about the events that took place at that moment. He has muscle tension or waxy flexibility. He does not move, does not speak or perceive someone else's speech, does not eat or drink, and produces natural relief on his own. To maintain his vital functions, he is fed and watered through a tube. Prolonged stupor can provoke the formation of bedsores, possibly compression of large blood vessels and nerves.
The most characteristic poses for this period:
- hood symptom - twisting of the body in the form of an embryo and covering the head with a tucked-in fabric (a hollow robe, a blanket, a hood);
- Dupre syndrome (air cushion) – the head does not touch the pillow, it seems to be hanging in the air;
- the proboscis symptom is a manifestation of grasping and sucking, i.e. the most primitive reflexes.
Catatonic excitement - the patient commits stereotypical aggressive actions aimed at aimlessly destroying everything that comes in his way. If he is stopped, he stubbornly resists and can tear off his clothes. To prevent the patient from harming himself and others, he must be tied up.
In both periods, the catanonic may exhibit oneiric syndrome . That is, he will be visited by fantastic visions with himself in the leading role. He draws the content of such dreams from heard scary stories about any incidents, thrillers, detective and science fiction films or books. Dream experiences are reflected on the patient’s face, and this is especially noticeable when he is immobilized: the expression of ecstasy turns into horror, etc.
It is worth noting that experts consider the absence of oneiroid syndrome to be a bad sign that worsens prognoses.
Other symptoms accompanying the main ones:
- negativism - everything that is offered to the patient is perceived negatively. There are 3 variants of it - active (the catatonic person performs actions that he was not asked to do), passive - completely ignoring calls to him, paradoxical - the patient performs actions that are exactly the opposite of what he was asked to do);
- mutism – silence, reluctance to communicate;
- Pavlov's symptom - a reaction only to requests made in a whisper;
- stereotypy, motor paradoxicality - over a significant period of time, automatically perform the same action - hitting the wall with the forehead or the back of the head, scratching in one place, literally tearing the skin into blood, shaking off invisible specks of dust, etc.;
- echolalia – repetition of heard words and phrases;
- echochemistry – pretentious and mannered copying of the interlocutor’s facial expressions;
- echopraxia – copying the movements of animals or surrounding people;
- automaticity - thoughtless execution of received instructions and instructions;
- sudden mood swings;
- violation of orientation in space and time;
- confusion, memory impairment, loss of connection with the outside world.
The presence of certain signs determines the type of catatonic schizophrenia. She may be:
- empty – with stupor and agitation without hallucinations, delusions and mood disorders;
- lucid – immobilization without narrowing of consciousness, delirium and hallucination;
- oneiric - stupor or excitement, accompanied by confusion, fantasy dreams, etc.
Differential diagnosis
Catatonia is most common in depression and other mood disorders. In second place is hysteria (dissociative disorder). Catatonic stupor or agitation also occurs with organic brain lesions after traumatic brain injury and other damage to the central nervous system. Epilepsy in its manifestation sometimes includes catatonia. Psychoses against the background of severe infections, intoxications, and vascular diseases of the brain can occur with catatonic disorders. To exclude other mental, neurological and physical diseases, long-term inpatient observation and thorough examination by both a psychiatrist, a neurologist and a therapist are necessary.
Catatonic schizophrenia - a story of a disease
After his marriage, the 30-year-old mechanic developed strange behavior: withdrawn, unsociable. He answered his wife’s questions in monosyllables or ignored the woman. When he did not return home to spend the night, his wife found him sitting on a bench: the man sat motionless and looked into the distance, did not answer questions. He was taken to the hospital, where he did not understand who he was, was in a motionless position and resisted when they tried to change the position of his body. Persistent mutism and negativism were observed for 20 days. After receiving the necessary therapy, I came out of the stupor. When asked about his previous condition, he answered that he “didn’t know how to speak.” For the next two years, no psychopathologies were observed, after which he fell ill for no apparent reason. The speech was broken, incoherent and accelerated. The excited state was replaced by stupor. I stood at the station in a motionless position for several hours in a row. He was noticed by police officers, after which the patient was taken to the hospital. The recovery from the state of stupor took a long time.
Diagnosis and treatment
To determine catatonic schizophrenia, the presence of at least 1-2 symptoms observed over a two-week period is necessary. The patient is placed in a psychiatric clinic for examination and pathopsychological testing, consultation with neurophysiologists and neurologists.
The attending physician talks with the patient and his relatives to compile a medical history. His task, first of all, is to cut off, using differential diagnostics:
- temporal lobe epilepsy;
- cerebral edema;
- encephalitis;
- depression;
- metabolic disorder;
- sodium deficiency;
- Tay–Sachs disease;
- affective disorders;
- neoplasms in the brain;
- hepatocerebral dystrophy;
- consequences of taking cocaine, ecstasy and other similar substances.
The patient undergoes computed tomography and MRI, and an electroencephalogram is taken. If necessary, other studies are carried out.
Treatment of catatonia is also carried out strictly in a hospital setting: this makes it easier to control the patient during agitation so that he does not injure himself and others, and administer nutritional drips during periods of stupor.
Therapy involves prescribing individually selected drugs in tablets and injections:
- Antipsychotics for calming in the stage of agitation. To eliminate anxiety, benzodiazepines with hypnotic and anticonvulsant effects are prescribed. Classic remedies are used carefully if the patient behaves too aggressively. The list of medications includes Diazepam, Triazolam, Lorazepam, Clonazepam, Haloperidol.
- Normotimics for normalizing mood - lithium preparations, Carbamazepine, Olanzapine.
- Nootropics to improve blood supply and activate brain activity are administered for stupor - Cinnarizine, Piracetam.
- Muscle relaxants to reduce excitation in the skeletal muscles – Tubocurarine, Tercuronium.
If the use of medications does not have the desired effect, then electroconvulsive therapy is used. It should be noted that such transmission of electric current discharges is not very comfortable for the patient, so many specialists refuse to use it.
It should be noted that treatment does not always lead to stable remission, but in any case it helps to reduce the frequency of attacks, which makes life much easier for patients.
Unfortunately, the prognosis for this form of schizophrenia is largely unfavorable: the person’s mental state gradually worsens, and he is no longer able to take care of himself.
If you consult a doctor to establish a diagnosis, then correctly selected treatment will prevent the development of catatonic schizophrenia, slow down the course of the disease, put the patient into stable remission, and even stop the disintegration of personality. Your loved ones should remember this and do everything possible to receive qualified medical care in a timely manner.
How successfully is catatonia treated?
The sooner catatonia is treated, the better for the patient. Quick help helps to avoid complications and save life.
But not everyone recovers. According to Catatonia statistics, 12–40% of patients are successfully cured. The prognosis is poor in children and adolescents with schizophrenia, as well as in older adults. They may require Catatonia ongoing psychiatric care.
If a person has long suffered from kidney failure, alcoholism, Parkinson’s disease or other pathology, then the disturbances in brain function are already chronic. Therefore, at any moment, catatonic syndrome can recur. Catatonic syndrome: From detection to therapy. In order not to be late with help, you need to remember the dangerous symptoms and follow the doctor’s recommendations.
How to avoid getting catatonia
Scientists have not yet learned how to prevent catatonia, like other mental illnesses or brain tumors. But, taking into account the causes of the syndrome, we can advise the following:
- Reduce alcohol consumption, and if you have symptoms of addiction, get treatment.
- Never use drugs.
- Don't ignore symptoms of depression.
- Do not take sleeping pills, sedatives, or antipsychotics without a specialist’s prescription. Catatonia: pathophysiology, diagnosis and modern approaches to treatment.
- See a doctor if you have headaches, dizziness, or spots in your eyes.
- Treat kidney and liver diseases in a timely manner.
- Avoid casual sex to protect yourself from HIV and syphilis.
- Monitor your weight and avoid stress so as not to worsen the condition of your blood vessels.
- Pregnant women should register on time and follow the doctor’s recommendations so that the birth goes smoothly.
- Try not to injure your head.