A clavicle fracture is a change in the physiological structure of the bone. The patient, during or after a clavicle injury, experiences pain in the supraclavicular and infraclavicular areas, with disruption of the usual previously available active movements in the upper limb on the injured side. In addition, the person notices swelling and changes in the shape of the collarbone.
When examining a bone injury, a traumatologist or surgeon relies on the patient’s complaints, medical history, general examination, and the results of instrumental studies. X-ray examination has high diagnostic value. Depending on the type of fracture, the doctor will determine treatment tactics. For example, in case of a “green stick” type injury (in this case, the integrity of the periosteum is preserved), a soft fixing bandage must be applied to the child. If a clavicle fracture is accompanied by displacement of fragments, then the tactics change: reposition is used with further fixation using a plaster cast. Finally, if there is a possibility of damage to nearby nerve trunks or vascular structures, the patient needs immediate surgical treatment.
Therefore, if your collarbone hurts , you should definitely contact a traumatologist! The doctor will conduct a qualitative examination and determine the causes of pain.
Causes of clavicle fractures
Often, a clavicle fracture occurs at home, and if symptoms of a clavicle fracture , you should immediately consult a traumatologist. Clavicle injury can occur for the following reasons:
- Direct mechanical impact on the bone. Due to direct trauma (for example, a sharp or strong blow) to the collarbone area, sharp pain in the collarbone may occur - a characteristic symptom of its damage. Direct trauma causes oblique, transverse and comminuted fractures of the clavicle. Situations in which a direct injury to the collarbone occurs are completely varied: a fall of a heavy object, a collision with a protruding part of a structure at work, a fight with the use of bats or large metal objects.
- Indirect bone injury. A broken collarbone can result from a person falling on an outstretched arm, shoulder or elbow. This mechanism causes the formation of oblique and oblique-transverse fractures. Often, indirect injuries occur during difficult weather conditions (ice), as well as when a person is under the influence of drugs or alcohol.
In addition, sudden muscle contraction can be a rare cause of a clavicle fracture. Such situations are observed in patients with epilepsy: after a generalized convulsive attack, the patient notes pain under or above the collarbone, as well as symptoms of limited motor functions of the arm.
Prevention of fractures in old age
Orthopedists recommend thinking about this problem without waiting for old age. At any age, it is advisable to lead an active lifestyle, choose feasible sports, and eat right. In order to prevent osteoporosis and fractures, you can stick to a diet that resembles diet therapy for arthrosis. It is necessary to add sea fish, dairy products, butter, cottage cheese, cheese, yogurt, all types of cabbage, nuts and spinach to the menu.
A special vitamin and mineral complex for bones will also not be amiss. If you are already worried about joint pain, get diagnosed to know the enemy by sight. Degenerative-dystrophic changes in cartilage tissue contribute to bone fractures, so coxarthrosis or gonarthrosis should not be ignored. Timely courses of intra-articular injections of liquid endoprosthesis will help avoid complications.
Symptoms of a clavicle fracture
A closed clavicle fracture is accompanied by the following characteristic symptoms:
- intense pain in the bone, while the intensity of pain in the collarbone area does not decrease when taking any position;
- limitation of available movements on the side of the bone injury, severe pain when performing previously habitual actions;
- the occurrence of swelling in the area of the shoulder girdle, its shortening;
- changing the standard shape of the collarbone;
- drooping of the shoulder, its displacement inward and slightly anteriorly.
Often, a doctor may suspect a clavicle fracture based on the patient’s characteristic posture. So, a person often holds a limb that has been injured with his healthy hand. The patient may also press the injured limb against the body, explaining this by reducing pain when using this position.
As a rule, in the first seconds of a collarbone injury, a person feels a sharp and severe pain in the supraclavicular or infraclavicular area. The pain syndrome intensifies when the limb hangs freely, which explains the forced position - pressing the injured limb to the body. The free position of the injured side leads to the fragments of the collarbone shifting in different directions, changing their position in the wound, causing the person additional discomfort. Thus, a person needs to make a minimum number of movements so as not to provoke displacement of bone fragments when the clavicle is fractured.
Over time, the body's physiological response to a clavicle fracture is observed. Edema, hyperemia (redness of the damaged area), hyperthermia (increased temperature in the damaged area) is formed. This is a typical inflammatory reaction of the body to trauma to the bone base and soft tissues. Then the pain syndrome increases and the dysfunction of the hand progresses. Above the area of the broken clavicle, a significant swelling is visually visible, corresponding to the area of displacement of the clavicle under the tension force of the sternocleidomastoid muscle.
During an objective examination, the doctor pays attention to the following symptoms of a clavicle fracture:
- the presence of areas of hemorrhage in the damaged area;
- the formation of pathological mobility in the supraclavicular or subclavian region, with any movement causing pain to the patient;
- crepitation (crunching) of bone fragments.
In addition, open fractures are accompanied by the formation of a wound from which some portion of the clavicle protrudes, depending on the area of the fracture. If a collarbone injury has led to a violation of the anatomical integrity of any neurovascular bundle located in the neck, then the patient complains of severe limb weakness, numbness, and crawling.
Often, dizziness and general weakness are added to the list of symptoms of a clavicle fracture, which can be explained by internal bleeding. In severe situations, shortness of breath and lack of air are added to the typical signs of a collarbone injury, which are caused by damage to the pleura covering the lungs by fragments of the collarbone. This leads to the formation of pneumothorax in a person, and is accompanied by symptoms characteristic of such a complication.
Causes of frequent fractures in the “60+” category
As we age, metabolic processes slow down, the body loses its ability to regenerate, and osteoporosis progresses. In older people, bone density often decreases - height decreases, stooping and pathological curvature of the spine appear under its own weight. These processes are accompanied by invisible microtraumas that occur during any sudden movements.
With arthrosis, cartilage tissue wears out - individual areas of the bones rub, causing pain. It is not surprising that they gradually deform, lose strength, and microtraumas and cracks appear on them.
In addition, in old age, due to problems with the cardiovascular system, many people complain of weakness and dizziness. This increases the risk of slipping and falling - both on a slippery road and in everyday life, when performing usual actions.
According to statistics, about 10% of Russian residents suffer from osteoporosis - brittle bones
Complications
Like any disease, a bone injury can be complicated by many pathological conditions if treatment for a clavicle fracture is not started in time. Fortunately, complications from injury are quite rare because patients often seek medical attention immediately. However, possible complications due to poor-quality or untimely medical care cannot be excluded:
- Injury to a vascular or nerve formation. A displaced clavicle fracture can cause damage to a large vascular trunk or nerve formation, which leads to the formation of characteristic symptoms. In the case of damage to the nerve fiber, disturbances in the motor or sensory sphere in the injured area are observed as long-term consequences of the damage. The severity of neurological symptoms depends on the nature and extent of nerve damage, however, one should not forget about the likelihood of injury to nerve fibers. Damage to the vessel often leads to serious bleeding, especially if a sharp bone fragment has injured a large major vessel, resulting in serious blood loss.
- Damage to the pleura . A life-threatening condition for a person, pneumothorax, is formed when displacement during a clavicle fracture causes damage to the parietal pleura. Air enters the pleural cavity, which is accompanied by a characteristic clinical picture (shortness of breath, lack of air, lag of one of the halves of the chest when breathing). Pneumothorax requires prompt action by medical professionals and immediate treatment.
In most cases, fracture complications can be prevented thanks to competent and proper care for a clavicle fracture.
First aid at home
Sudden injury can happen to anyone, so it is important to know how to provide first aid to a person. It is important not to disturb the already painful displacement and follow all the rules.
Some practical tips on what to do with a broken collarbone:
- Before the person waits for the doctor, you should secure the arm using a towel as a loop under the forearm and around the neck;
- the person should move the injured arm as little as possible;
- Provide the victim with over-the-counter pain relievers such as Ibuprofen or Paracetamol to minimize pain;
- Aspirin should not be given to children under 16 years of age;
- An ice pack on the damaged area or a bag of frozen vegetables should be used as an alternative. The ice pack should be covered with a clean towel or cloth to prevent damage to the skin. The cooling effect may help reduce swelling and pain.
Diagnosis of a clavicle fracture
Diagnosis of a clavicle fracture with or without displacement is carried out by a traumatologist. As a rule, the doctor performs the entire list of diagnostic measures in the emergency department of a hospital or in a trauma center. The main methods that the doctor uses are as follows:
- Objective research data . The traumatologist conducts a thorough examination of the injury site. A clavicle injury is characterized by severe deformation of the area, severe swelling of the damaged area, and in some cases, especially with a displaced fracture of the clavicle, crepitus (crunching) of bone fragments is observed. During an objective examination, the doctor necessarily checks for the presence of neurological damage: determines the sensitivity of the hand on the side of the injury, the presence or absence of active movements. In addition, the doctor needs to evaluate possible complications. Thus, during the examination, the traumatologist determines the presence of symptoms of blood loss due to damage to large vascular bundles or difficulty breathing, shortness of breath as symptoms of the formation of pneumothorax.
- X-ray diagnostics. X-ray is the standard examination method for suspected clavicle injury. With its help, the doctor determines the site of the fracture and the displacement of the collarbone. A clavicle fracture in a child is often accompanied by an angular injury. In this case, displacement of bone fragments occurs, however, the integrity of the periosteum is preserved. X-rays are traditionally performed in a direct projection, but in difficult cases, if the traumatologist is unable to determine the location of all fragments of the clavicle, the diagnosis is additionally carried out in a lateral projection.
- An additional research method, if X-ray diagnostics is insufficiently informative, is computed tomography . Three-dimensional reconstruction allows you to fully see the picture of the clavicle injury and determine the degree of displacement of bone fragments when the clavicle is fractured.
Finally, if the traumatologist suspects complications in the form of trauma to large neurovascular bundles, he refers the patient for consultation with a neurologist and vascular surgeon.
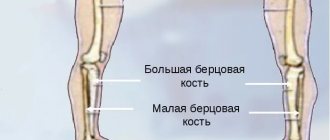
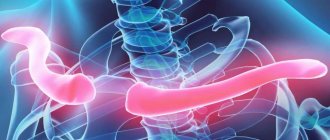
Anatomy of the clavicle
The clavicle is a not very large arcuate tubular bone. It is united on one side with the sternum, and on the other with the acromial end of the scapula. The main injuries to this area are a fracture or dislocation of the collarbone.
Since it contains 2 ends, in this case, dislocation of the acromial end of the clavicle is also distinguished as dislocation of the sternal end of the clavicle. Injuries to the acromial end are more common. We will analyze all the symptoms and causes of injury, without exception, as well as all possible ways to solve the problem.
A dislocated collarbone is a fairly common injury. As a percentage, the number of cases of clavicle dislocation is 5% of the total number of injuries of this kind. In this case, one should strictly distinguish between dislocation of the acromial (external) and sternal (internal) ends.
For a general understanding of the collarbone, we invite you to watch a video that describes in detail the composition of the shoulder joint.
Treatment
The therapeutic tactics chosen by the doctor depend on many parameters. the degree of clavicle fracture matters , whether the clavicle fracture occurred in a child or an adult, and whether there is displacement of bone fragments. In addition, when deciding on treatment tactics, the doctor also evaluates the presence of developed complications. If there is no threat of damage to large nerve or vascular formations, and a person has a well-reduced clavicle fracture, then the patient does not require long-term hospitalization.
If there is a high risk of complications or exacerbation of the clinical situation, then treatment of the collarbone must be carried out in the trauma department. According to statistics, in a significant number of cases, patients do not require surgical intervention; only ordinary therapeutic treatment is sufficient.
About the collarbone
The collarbone (lat. - Clavicula) is a typical S-shaped bone, in simple words, connecting the arm (free upper limb) to the torso.
Like most long bones of the skeleton, the clavicle consists of a body and two ends - internal or sternal, external or acromial. The ends of the clavicle are involved in the formation of 2 joints: sternoclavicular and clavicular-acromial. There are 6 muscles and several ligaments attached to the collarbone. The shape and function of the clavicle is of great importance when it is damaged.
Providing first aid for a fracture
At the first stage, you must definitely call an ambulance . Within a few minutes after a clavicle injury, active swelling begins to form in the damaged area, which subsequently creates difficulties in performing closed reposition of the fragments. The more time passes, the more likely it becomes that the patient will undergo open reduction. Treatment of a broken collarbone by a traumatologist consists of a surgical operation, during which special access to the site of injury is performed, and then comparison of bone fragments. Of course, if closed reduction is not possible, then the open method is used to treat the clavicle. However, when performing an open surgical operation, the risk of infectious agents, pathogenic microorganisms entering the wound, as well as the occurrence of purulent complications (abscess, phlegmon, secondary osteomyelitis) naturally increases. The ambulance transports the victim to the emergency department of the trauma hospital, and during the provision of first aid, medical workers will provide high-quality pain relief, as well as immobilization of the fracture site. Thus, the ambulance carries out primary actions aimed at reducing the likelihood of complications developing in the long term, as well as transporting the patient as carefully as possible. It is important to remember that a certain amount of time will pass before the ambulance arrives, which can be properly used to alleviate the patient’s condition.
The main rule that you need to remember when providing assistance with a fracture of the collarbone is that you cannot independently try to carry out medical procedures to eliminate the displacement of the collarbone by performing sudden movements or jerks. It is imperative to limit the mobility of the injured limb : due to sudden movements, secondary displacement of fragments or complications may occur. Competent first aid consists of immobilizing a limb (reducing its mobility by fixing it to the body) using a scarf. In this case, the arm must be fixed in a special way: press the humerus to the body, and only then bandage it using a scarf. However, there is a rule: if a person reports increased pain during shoulder adduction, then it is necessary to leave the injured limb in a position that provides minimal pain.
Immobilization is considered an important aspect when providing first aid. Primary immobilization before the arrival of the ambulance team will reduce the severity of pain in the patient, because the injured area will be firmly fixed and immobilized with a bandage. Secondly, immobilization will help to avoid the development of complications in the form of traumatization by bone fragments of vascular or nerve formations during transportation of the injured person to the emergency department of a trauma hospital. For immobilization, a scarf bandage is actively used on the arm, during which the limb is bent at the elbow joint and pressed against the body. It should be remembered that during long-term transportation of the patient to the hospital, the supporting function of the bandage weakens over time. Therefore, rewinding of the bandage may be necessary to maintain sufficient fixation force. Often, for immobilization, in addition to the scarf dressing, the following types of dressings are used:
- Velpo;
- Deso;
- 8-shaped bandage;
- Delbe rings.
We must not forget about painkillers . Pain from a broken collarbone is a strong irritant to which a person may have an unexpected reaction. This, in turn, can complicate the provision of first aid to the victim: he may resist and refuse any action. Besides. intense pain during the arrival of an ambulance will complicate the diagnosis of the condition and the collection of anamnesis, because the person will not be able to correctly and clearly answer the doctor’s questions. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are actively used as painkillers at home. Ketanov, Ibuprofen, Spazmalgon, Paracetamol are actively used. However, before using these medications, you need to be sure that the person is not allergic to one or more components of the drug. In addition, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs should be used very carefully in patients with gastric or duodenal ulcers. The drug will begin to act within 15-30 minutes when taken orally, 5-10 minutes after intramuscular administration. If the effect of the drug is not observed, you cannot increase the dosage or introduce a new dose of the drug, because there is a possibility of an overdose of the drug, which requires special assistance for intoxication.
If you do not have the opportunity to use painkillers to relieve pain, then you can use a proven and effective method - applying cold to the injured area. Cold has a local effect without affecting other tissues and systems of the human body. Additionally, applying cold is the only option if you don't know if the person has an allergic reaction to the pain medications available to you. The mechanism of action of cold is very simple: in the area of the collarbone fracture, a cold object reduces the temperature of the soft tissues, where many nerve endings are located. When the tissue reaches a temperature of 4-5 degrees, the intensity of the transmission of pain impulses in it decreases, which means that irritation does not enter the brain. Thus, there is a temporary reduction in the severity of pain in a person. However, a broken collarbone requires a special approach in applying cold. You should not apply a whole piece of ice to the damaged area, but crushed ice. The specificity is explained by the anatomical structure of the area: in the clavicle area there is a supraclavicular and subclavian fossa, which forms an uneven relief. Crushed ice will work much better on the damaged area than a single piece of ice. In addition, you need to apply ice exclusively over the fracture site: if you move the ice pack to the neck area, the body may react in the form of a sharp drop in blood pressure and heart rate. The fact is that in the neck area there is a sinocarotid nerve plexus, and careless influence on this formation can lead to serious consequences.
Activities and auxiliary things
If the fracture of the limb was uncomplicated, it is enough to wear insoles. They will help not to overload the injured limb. If a person breaks a hip, the recovery time will be more difficult and lengthy. You can’t do it without a special program and devices.
Even in the clinic, the patient’s bed is equipped with a belt. A person grabs it with his hands in order to sit or rise comfortably. Doctors prescribe physical therapy in the first week after an injury, when canes and crutches are still used.
First, breathing exercises are prescribed for the patient. Balloons are used for this. Afterwards, exercises are prescribed, aimed at developing the mobility of the torso. After about a month, the doctor prescribes the following complexes:
- General. Designed for general human health.
- Special. To restore a diseased limb from the day the cast is removed.
Well-thought-out treatment and rehabilitation based on physical education can achieve the following goals:
- Restoring blood circulation through massage;
- Prevention of dangerous complications;
- Serious strengthening of the muscles at the fracture site;
- Restoration of motor ability.
To achieve the above goals, it is important to start exercising while lying down. After this period, quitting classes is not recommended. The features of each gymnastics option should be studied in more detail.
Who should I contact?
Letay.org is the best assistant in finding a doctor!
The organization is engaged in providing treatment for complex orthopedic injuries in clinics in Spain, selecting a attending physician for each patient in accordance with the established diagnosis. Letai will organize a preliminary consultation with a doctor for you, find a hotel and arrange a flight. Letai guarantees examination and treatment in the best Spanish clinics!
Why will you definitely choose Letai? Due to the large number of advantages of the organization:
- Modern equipment and use of innovations. Letai uses only the latest techniques for treating and rehabilitating patients. This allows you to shorten the period of hospital stay or treatment. In addition, innovative approaches ensure maximum restoration of the functions of the human body in a fairly quick time.
- Fast reaction. Letai is not affiliated with any one clinic. This is a significant advantage, because mobility allows you to organize an operation for the patient in the shortest possible time!
- Doctors are professionals. Letai provides patients with the opportunity to be treated by the best Spanish doctors who have significant clinical experience. Specialists from the best clinics in Spain, recognized in European countries, and some throughout the world, guarantee patients high-quality treatment and a responsible approach to therapy!
- Price policy. It is worth noting that the cost of all services provided by Letai is within acceptable limits for each person! Thus, anyone in need of quality treatment can take advantage of Letai’s help in the treatment and rehabilitation of injuries.
Letai's activities cover three main areas:
- Joint diseases. An experienced orthopedic doctor will diagnose and treat diseases of the human musculoskeletal system. Why endure discomfort if you can turn to a competent specialist who will ensure timely diagnosis and correct treatment?
- Treatment of injuries. Often, patients come to Letai because of an injury that causes significant pain and significant discomfort. The doctors of our clinics guarantee treatment of any injuries according to the latest protocols used in the world!
- Rehabilitation after injuries. The recovery period after injury is no less significant. Doctors at Spanish clinics will write you an individual rehabilitation program, and then monitor the dynamics and adjust the plan depending on the activity of restoring the functions of the musculoskeletal system.
Letay.org will find the best doctor for your speedy recovery and quick rehabilitation!
Why should you turn to Scandinavian traumatologists?
Patients with fractures and other traumatic injuries choose the Scandinavia clinic rather than state emergency rooms because:
- We have traumatologists with more than 5 years of experience who can conduct a full diagnosis and select treatment to restore your condition in the shortest possible time;
- The clinic is equipped with modern X-ray machines and tomographs, which allows all necessary studies to be carried out in one place.
For patients who are indicated for osteosynthesis, we have equipped a comfortable hospital with television and Wi-Fi in the clinic. We also accept nonresident citizens: you can find out more by calling the clinic.
There are never too many promotions Read more
Treatment in children
The main method of therapy is strong fixation, that is, immobilization of the limb. In children, the immobilization time is 2-3 weeks. To firmly hold broken bone fragments, special Delbe rings are often used. Pediatric clavicle fractures often occur as a “greenstick” type, that is, with preservation of the integrity of the periosteum. In this case, a fixing bandage on the collarbone is used. A fixing bandage is sufficient even if the clavicle injury is not accompanied by displacement.
In cases where the fracture is characterized by displacement of fragments, reposition is performed.
Rehabilitation
Regardless of what methods were used in the treatment of clavicle dislocation, rehabilitation is an important and necessary link in therapy. With its help, the healing process of muscles and ligaments is accelerated, the motor activity of the limb is restored, the collarbone is strengthened, which serves to prevent relapses.
After 3 months after the injury, the doctor prescribes special physical exercises, with the help of which the collarbone and arm acquire their previous shape and function. If you start doing exercises ahead of schedule, there is a possibility of recurrence of the injury, the treatment of which will take more effort and time.
Treatment in adults
Immobilization of the limb is carried out for 1 month, using a Chizhin frame or other bandages. If displacement of the fragments occurs, then reposition is required (returning the fragments to their normal physiological position) with local anesthesia. Then fixation occurs with a soft or plaster cast.
The reposition is followed by a recovery period, and after some time a control photograph is taken. It is actively used during the rehabilitation period of UHF; in the presence of severe pain, the doctor prescribes painkillers. As soon as the need for immobilization disappears, the doctor refers the patient to massage and physical therapy.
Conservative treatment consists of using soft or plaster casts, as well as fixing the limb. This type of therapy is used for uncomplicated fractures in both adults and children. Immobilization is carried out by a traumatologist who actively monitors the restoration of the integrity of the patient’s bone.
The main goal of conservative therapy is to ensure the correct position of the bone and rigid fixation of the clavicle in this position for a certain time. If displacement of the fragments has not occurred, then immobilization of the shoulder girdle is sufficient for high-quality healing to occur. In cases where displacement has occurred due to a clavicle fracture, preliminary reposition is required; at the next stage, immobilization occurs. In traumatology, there are two types of reposition - closed and open techniques.
Closed reduction is non-invasive, that is, the doctor does not perform an open surgical approach. Using non-invasive medical techniques, the traumatologist performs temporary immobilization, and then x-rays are taken. If the bone fragments have been juxtaposed correctly, then temporary immobilization is changed to permanent plaster fixation. In the case where the bone fragments could not be compared as accurately as possible, a repeated closed reduction or open reduction is performed according to the decision of the traumatologist.
Open reduction has a number of strict indications, because during its use open surgical access to the fracture area is performed. Then the doctor compares the bone fragments in the wound and fixes them, which is called intraosseous osteosynthesis and refers to the surgical treatment of a clavicle fracture.
Working with gait
Along with the listed exercises, you need to add a complex for quick gait restoration and rehabilitation. Here are some effective options:
- Use your toes to grab and hold a small object;
- Roll a ball with the foot of the sore limb;
- Standing on your toes, on your heels;
- Walking sideways and backwards.
If possible, you can exercise on exercise bikes. The listed exercises and prescribed treatment after an injury cannot be neglected. Physical education during rehabilitation quickly restores and heals the body from the day the cast is removed.
Recovery after a fracture should continue until the body is completely restored. You can stop exercising after you have regained mobility, swelling has subsided, and there is no pain. The success of rehabilitation depends not only on the will of the patient and the treatment program.
Surgery
surgical treatment is necessary if the patient has an open fracture of the clavicle or a closed injury, however, complicated by acute conditions. For example, a bone fragment damaged a large nerve trunk, which caused a disruption of the innervation on the side of the injury or a major vessel, which caused bleeding. In some cases, bone fragments damage the parietal layer of the pleura, which threatens the development of an emergency condition - pneumothorax.
Surgical interventions are routinely performed for a clavicle fracture if the patient has a significant displacement of bone fragments or the shoulder girdle area is externally significantly deformed. Surgical treatment consists of performing osteosynthesis of the clavicle using one of the following techniques:
- Intraosseous method. Used for comminuted fractures. During the operation, a special pin or Bogdanov nail is used.
- Bony technique. During the operation, a curved plate is used. This method is used for injuries with many fragments in the wound.
- Spoke method . Rigid fixation is performed using wires that are literally passed through fragments of the bone base. The ends of the knitting needles are fastened, and they are first brought outside the collarbone.
In the postoperative period, antibiotics are used to prevent the development of infectious complications, and painkillers are used to relieve pain. Physiotherapeutic procedures provide faster and more complete restoration of the functions of the injured limb. Discharge from the hospital becomes possible after the stitches are removed, which occurs on the 8-10th day of hospital stay.
We suggest adding your company to a thematic directory of organizations, for example in Sport365days - this is an excellent example of a thematic aggregator tied to topics such as sports, health, sporting goods and beauty. If you are the owner of a business focused specifically on these areas, you can create your own website absolutely free, find business partners with the ability to post information on your page or a partner’s page. (Example: Medart).
Clavicle dislocation
- Anatomy of the clavicle
- Classification
- Dislocation of the outer (acromial) end of the clavicle
- Dislocation of the internal (sternal) end of the clavicle
- Symptoms of types of dislocations
- Prosternal type of dislocation
- Suprasternal type of dislocation
- Substernal type of dislocation
- Photo of a dislocated collarbone
- First aid for acromial dislocation
- Treatment of clavicle dislocations
- Conservative treatment
- Surgery
- Rehabilitation
Content
Recovery
Physiotherapy is widely used in medicine for more active recovery.
Physiotherapeutic methods of rehabilitation after a clavicle fracture are actively used in medicine to accelerate the healing of the injury, as well as reduce pain and discomfort for the patient. In addition, physiotherapy has an anti-inflammatory, anti-edematous effect, stimulates metabolism in the area of damage and tissue regeneration.
The classification of physiotherapeutic procedures is based on the time of their implementation. Thus, there are methods of physiotherapy that are used only during the period of plaster immobilization, after removal of the plaster, and also regardless of whether the patient has a plaster cast.
During plaster immobilization, SUV irradiation in erythemal doses . At the local level, the procedure provides relaxation of muscle tissue in the damaged area, expansion of the capillary network, which stimulates blood flow in the irradiated tissue. Finally, tissue swelling is reduced, as well as the severity of pain due to a decrease in the sensitivity of pain receptors. The general effect of SUV irradiation in erythemal doses is manifested in stimulating the formation of vitamin D, which accelerates the process of callus formation. The second procedure, electrophoresis of painkillers, ensures the accumulation of painkillers in the subcutaneous fat and muscle tissue, which long-term reduce the intensity of the patient’s pain syndrome.
After the moment when a person's plaster cast is removed, it is possible to use new physiotherapeutic procedures. If the traumatologist has removed the plaster, then the callus has already formed quite well, which means that it is possible to put small loads on the bone to increase its strength. For this purpose, therapeutic massage, high-frequency magnetic therapy, amplipulse therapy, UHF therapy, ultrasound therapy, and remote shock wave therapy are used.
Therapeutic massage provides active and persistent dilation of blood vessels in the injured area. Active blood flow accelerates the transformation of formed callus into healthy functioning bone tissue. Therapeutic massage has a significant overall effect through a reflex effect on the vasomotor center located in the brain. Thanks to therapeutic massage, blood pressure in patients is normalized.
High-frequency magnetic therapy provides an analgesic effect by influencing nerve tissue. In addition, the tension in the patient's skeletal muscles decreases.
Amplipulse therapy creates an analgesic effect and leads to relaxation of muscle fibers. The physiotherapeutic method actively influences blood vessels, dilating them, which enhances tissue trophism. Thus, amplipulse therapy stimulates the reduction of swelling, the resorption of infiltrates, and also activates recovery processes in the injured area.
UHF therapy creates an active warming effect, which directly affects cellular metabolism. Thus, microcirculation processes are activated, the muscle layer of blood vessels relaxes, and the swelling of the damaged area decreases. As a general effect, UHF therapy reduces the tone of the sympathetic nervous system, increasing the tone of its parasympathetic department.
Ultrasound therapy actively stimulates blood circulation processes, as well as lymph circulation. At the local level, capillary permeability increases, which affects the intensity of wound healing.
Remote shock wave therapy activates the synthesis of special biologically active components. They provide vasodilation in the area of injury, which stimulates the processes of proliferation of cells and tissues in the injured area. Cell division ensures the direct process of repair of the bone and cartilage base.
Regardless of immobilization, electrophoresis of vasodilators, low-frequency magnetic therapy and mineral water intake can be performed. Low-frequency magnetic therapy becomes an excellent stimulating factor for reparative processes. In addition, this method has a good anti-inflammatory effect. Mineral waters restore the balance of electrolytes in the human body and provide the necessary minerals for the active healing of damaged bone and cartilage tissue.
Recovery period
Rehabilitation is absolutely necessary, because... Due to prolonged immobilization, the arm muscles partially atrophy. Exercises should be started as soon as possible. The load and type of activity is determined by the attending physician. Typically, the recovery course lasts from three to seven weeks.
The rehabilitation period can be divided into 3 stages:
- during immobilization, perform passive exercises;
- after the growth of callus and removal of the fixing bandage, use gymnastic sticks and expand the range of exercises;
- introduction of strength loads using expanders, dumbbells, clubs, exercise machines.
For a speedy recovery after a fracture, physiotherapeutic procedures are continued, hydrotherapy and massage are used. An integrated approach guarantees high rehabilitation results. Thanks to electrophoresis, magnetic therapy, ultrasound, laser therapy and UHF, blood flows more strongly to the damaged area. Sufficient blood supply promotes rapid tissue repair.
How to develop a collarbone after a fracture?
Exercises after conservative treatment and surgery are slightly different. But in both cases they become more complex step by step.
A set of exercises for the postoperative period:
- breathing and general tonic exercises;
- light active-passive rocking in the shoulder joint (arm on a bandage);
- alternate tension and relaxation of the muscles of the shoulder and shoulder girdle;
- active movements in the elbow and wrist joints, as well as in the fingers and hand;
- pronation-supination (inward-outward rotation) of the forearm;
- shrugs;
- general strengthening exercises for all parts of the body;
- dosed walking and running;
- training hand speed and strength endurance;
- sports-assist exercises;
- exercises to restore coordination of movements;
- sports training.
First, the exercises are performed with outside help for several minutes. Then they are repeated more often and longer. From smooth and slow movements they move to jerks. In order to quickly develop a collarbone after a fracture, you need persistence and patience.
Question answer
What is the prognosis for clavicle fractures?
In the majority of cases, if a bone injury occurs without complications from other pathological conditions, doctors note a favorable prognosis for the patient. As a rule, bone fragments heal well, and even if there is some residual displacement, this does not affect the active movements of the arm on the injured side. In the case when a person develops complications (for example, damage to the pleura or a large nerve trunk, a great vessel), the outcome of the disease depends on the quality, time and literacy of first aid provided to the patient.
What is the patient's recovery time after surgery?
Absolute restoration of the structure of the clavicle and the function of the damaged limb occurs within 6 to 8 months. After surgery, removal of auxiliary structures (wires, screws or medical plates) is performed approximately 6-12 months after the intervention, depending on the intensity of the restoration processes in the bone.
What are the dangers of fractures in old age?
Despite innovative technologies in the field of bone healing and an extensive arsenal of painkillers, fractures are still very dangerous for older people. Among such patients, each illness is severe, and even a seemingly mild injury can lead to death.
- Bones take much longer to heal than in young people due to slow metabolism and insufficient blood supply to skeletal tissue.
- Temporary immobilization and mandatory bed rest weaken the body and negatively affect the emotional state.
- The risk of thromboembolism increases - the formation of blood clots in the lower extremities and, as a result, blockage of the pulmonary artery.
Elderly people who have suffered fractures often lose faith in recovery