Cytomegalovirus Ig G is detected in the body by
Cytomegalovirus Ig G is detected in the body by laboratory testing of biological fluids:
- saliva
- urine
- blood
- sperm
- vaginal discharge
- cervical mucus
- sputum
- scrapings from mucous membranes
Cmv Ig G cytomegalovirus is detected in saliva and urine sediment using cytological examination.
In this case, using light microscopy, specific viral cells are found in biological material.
But more often this virus is detected using PCR diagnostics and serological blood testing (ELISA).
PCR analysis is aimed at identifying pathogen DNA molecules in biological fluid.
The essence of the ELISA method is to detect antibodies to cytomegalovirus in blood serum.
PCR and enzyme immunoassay can detect cytomegalovirus Ig G with the highest probability and accuracy.
ELISA analysis allows you to evaluate the avidity of Ig G
In addition, serological analysis by ELISA allows one to assess the avidity of Ig G to cytomegalovirus.
What does this term mean?
Avidity is the ability of immunoglobulins to form a bond with virus cells for the purpose of their subsequent inactivation.
In the early stages of infection, the avidity of Ig G antibodies to cytomegalovirus is low.
As the body's immune response increases, its levels also increase.
An increase in the level of immunoglobulin G in blood tests always means an increase in viral infection.
If cytomegalovirus Ig G antibodies are detected, what is it
If cytomegalovirus Ig G antibodies are detected, what does this mean?
This means that there is a viral infection in the blood and the body produces protective cells against it.
If you have been tested and it turns out that cytomegalovirus Ig G is positive, what does this mean?
This indicates that you are a carrier of the infection.
In addition, a positive cytomegalovirus Ig G indicates that the infectious agent has been in the body for quite a long time.
Lifelong immunity has developed to it.
What to do before taking tests?
Correct behavior before donating blood for analysis will help you obtain reliable diagnostic results.
There are no strict recommendations for cytology or ELISA.
The patient is asked to refrain from drinking alcohol and smoking.
Avoid fatty, fried or spicy foods.
The PCR method requires clearer rules.
To obtain an accurate result, you need to stop taking antibacterial or antiviral agents a few days before the test.
Abstain from sexual intercourse for a week.
The period of menstruation in women can influence the survey data.
Diagnosis of infection
In a routine blood test, patients suffering from CMV infection observe:
- Severe lymphocytosis.
- Atypical mononuclear cells (up to 10% or more).
- The total number of white blood cells rarely falls outside the normal range. In newborns, thrombocytopenia and a decrease in the number of red blood cells may be detected. In a biochemical blood test, an increase in the activity of liver enzymes is observed.
In samples of cerebrospinal fluid from patients with central nervous system damage, an increase in protein components, neutrophilic pleocytosis and a significant decrease in glucose levels are detected.
Decoding and interpretation
When conducting serological studies, indicators are used that allow one to understand the result.
- Numerical value less than 0.9 is negative
- A numerical value between 0.9 and 1.1 is doubtful
- Numerical value greater than 1.1 is positive
In this case, the state of the process can be judged by the ratio of IgG to IgM.
If the result is positive for both immunoglobulins, they speak of a secondary exacerbation.
An increase in IgM alone indicates primary infection.
Positive IgG and negative IgM are the stage of formed immunity.
This condition does not require treatment.
The patient is advised to support the immune system to prevent re-infection.
Negative IgG and IgM results - no contact or disease.
But there is always a risk of primary infection.
Causative agents of infection, its sources
Cytomegalovirus (Cytomegalovirus hominis) belongs to the genus of DNA viruses, is distinguished by its large virion size (up to 300 nm), and is part of the herpesvirus family. Several strains of the pathogen have been registered:
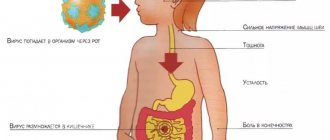
The source of infection is the patient or the carrier. The pathogen is detected in biological fluids and secretions. Routes of entry of the virus:
- Davis.
- Kerr.
- AD-169.
- Towne 125.
Most strains are little studied, but it is reliably known that all of them can reproduce without destroying the host cell. The virus can survive for a long time at room temperature, but is sensitive to heat and the action of disinfectants.
- Airborne.
- Contact.
- Food.
- Parenteral and transplacental.
According to statistics, the infection rate is up to 95%, depending on the region and country.
Decoding the analysis for pregnant women
Interpretation of diagnostic data for pregnant women has its own characteristics.
A significant increase in the titer of immunoglobulin G indicates an intensive fight of the body against the virus.
Additional diagnostics are required to confirm the active phase of the disease.
If a woman takes tests after 4 weeks from the start of pregnancy, a negative result does not guarantee the safety of the fetus.
The virus could have entered the body earlier than 12 weeks, and the immune response is still weak.
If a high titer of immunoglobulin M and low G are detected, the pregnant woman should be prescribed treatment.
It requires constant monitoring and observation followed by repeated diagnostics.
Pregnant women whose tests have confirmed the absence of an acute form of the disease should undergo regular examinations and monitor their condition.
Maintaining immunity at the proper level will help maintain the health of the fetus until birth.
When to treat and how
Therapy for cytomegalovirus infection should be complex and multicomponent.
To do this, drugs are used that directly affect the pathogen.
These include:
- Virus replication blockers
- Drugs that destroy viral particles
From the first group, Ganciclovir is used.
Megalotect is used to destroy the cell wall.
Additional treatments for patients with cytomegalovirus include immunomodulators, painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs.
To carry out full monitoring, treatment of patients with the acute form occurs in a hospital setting.
This makes it possible to isolate the patient and prevent further spread of infection.
Outpatient treatment is also possible.
For pregnant women and children, the use of antiviral drugs is of particular importance.
Ganciclovir can inhibit the process of hematopoiesis and cause bleeding.
Skin rashes appear while taking it.
Disturbances from the gastrointestinal tract appear less frequently.
Self-medication or use of drugs without the supervision of a physician can harm the body.
Any therapy should be prescribed after an examination and a range of laboratory tests.
Cytomegalovirus
Herpes
19010 April 28
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Cytomegalovirus: causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment methods.
Definition
Cytomegalovirus (CMV, or cytomegalovirus disease) is a chronic infectious disease of viral etiology, characterized by a variety of clinical forms and manifestations - from asymptomatic to severe damage to internal organs and the central nervous system. The causative agent of CMV is a representative of the herpesvirus family (human herpes virus type 5).
The reservoir and source of infection is only humans.
Once in the cells of the body, cytomegalovirus is able to remain in them for life. In individuals with a normally functioning immune system, in the vast majority of cases, the infection occurs as a virus carrier. When the immune system is suppressed, the virus is activated, causing clinical symptoms of the disease.
According to various data, the proportion of cytomegalovirus carriers in Russia is about 73-90% - that is, this is the number of people who have antibodies to CMV.
Causes of cytomegalovirus disease and
Cytomegalovirus is transmitted through biological fluids: saliva, urine, blood, vaginal secretions, tears, semen, feces, breast milk.
Due to the lability of the pathogen and the low concentration of the virus in secretions, long-term, frequent and close contact with the carrier is necessary for transmission of infection.
Mechanisms of transmission of the virus - airborne droplets (aerosol route), contact (household contact and sexual contact), blood contact (parenteral, as well as during organ transplantation), vertical (from mother to fetus), fecal-oral (nutritional - through breast milk) .
Infection of the fetus occurs through transplacental transmission from mother to fetus, which is possible throughout pregnancy. Primary infection in the early stages of pregnancy poses the greatest danger to the fetus, as it often causes the formation of congenital malformations.
A special property of CMV is the ability to cause depression in almost all parts of the immune system and sharply inhibit the production of interferons, primarily IFN-α. In acute infection, the virus primarily affects epithelial cells of the lungs, liver, intestines, kidneys, bladder, mammary and salivary glands, and genital tract. Cytomegalovirus can infect nerve cells, smooth muscle cells, and bone marrow.
Classification of the disease
According to the nature of infection:
- congenital (intrauterine),
- postnatal (acquired).
According to the degree of virus activity:
- latent infection,
- persistent infection
- active (low, moderate, high severity) infection.
Primary or re-infection:
- acute infection,
- reactivation of the virus
- reinfection.
Symptoms of cytomegalovirus
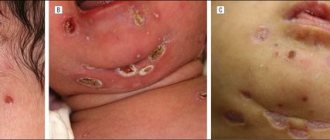
The incubation period of cytomegalovirus disease ranges from 15 days to three months (with a manifest, severe form of the disease). However, more often the primary infection occurs either asymptomatically or as a mild form of acute respiratory infection - the patient experiences slight weakness, fever (temperature 37.1-38.0°C), muscle discomfort, sore throat, sometimes runny nose, enlarged cervical lymph nodes , soreness of the salivary glands, headache, lack of appetite.
In pregnant women, acute primary infection is usually asymptomatic (25–50%) or with nonspecific manifestations (fever, asthenia and headache).
In rare cases, hepato- and splenomegaly, hepatitis with minimal activity of cytolytic syndrome, dermatitis, vasculitis, interstitial pneumonic process, thrombocytosis or thrombocytopenia, and lymphocytosis develop.
In patients with immunodeficiency, cytomegalovirus infection is severe - the virus quickly spreads throughout the body and causes serious complications.
Diagnosis of cytomegalovirus
Diagnostic measures begin with the collection of complaints and medical history, including the mother’s obstetric and gynecological history.
The doctor then conducts an objective examination (physical, neurological and anthropometric).
Laboratory tests - general and specific:
- general blood analysis;
How to monitor after treatment
Stopping medications means ending therapy.
But to ensure a complete recovery, the patient is recommended to undergo laboratory diagnostics.
This will allow you to reliably verify the absence of the virus in the blood.
The PCR method (quantitative) is chosen as the analysis.
Its accuracy will allow you to analyze the effectiveness of treatment.
If the patient or doctor still has doubts about cytomegalovirus infection, tests can be repeated after 2-4 weeks.
Classification
There is no globally accepted classification system for cytomegalovirus infection (CMVI). In practice, the classification developed in 1980 is used. According to this system, CMVI is divided into:
- Congenital, can be acute, chronic.
- Acquired, can be acute, latent, generalized.
CMV infection is classified according to the duration of its course:
- Spicy.
- Protracted
- Chronic
- Recurrent.
Depending on the severity of the course, there are mild, moderate, and severe forms of the course.
Is it possible to completely get rid of
Cytomegalovirus infects cells and penetrates their genotype.
Even after intensive and varied treatment, it is not possible to completely get rid of the virus.
Any therapy in his case is aimed at preventing the development of complications and stimulating the immune system.
It is this that serves as the main barrier between illness and a healthy state.
How to remove immunoglobulin from blood
Unfortunately, this cannot be done completely.
Immune memory persists throughout life.
Prevention
After recovery from cytomegalovirus, there is a risk of re-infection.
Having immunity to particles will only allow the body to quickly cope with the infection.
Therefore, to prevent infection, it is worth following preventive measures.
Unfortunately, no specific methods have been invented.
Patients are advised to maintain a high level of immune defense.
To refuse from bad habits.
To live an active lifestyle.
Undergo regular examinations with doctors and promptly treat inflammatory diseases.
Once a year, undergo an extensive laboratory examination.
Avoid close contacts with little-known people.
Congenital form
In most cases, intrauterine infection of a child does not lead to the development of symptoms. If a pregnant woman encounters cytomegalovirus invasion for the first time, the risk of developing a congenital disease in the newborn increases.
Signs and complications of congenital infection:
- Liver damage, manifested by organ enlargement, jaundice and increased bleeding.
- Intrauterine growth retardation and prematurity.
- Microcephaly and retinitis.
- Enlarged spleen.
The probability of death from congenital infection reaches 30%. The negative consequences of cytomegalovirus infection subsequently become the cause of human intellectual disability.