28 February 2020
74236
0
3.5 out of 5
Coccydynia is a disease in which pain of varying degrees of intensity is constantly present or regularly occurs in the coccyx, rectum and anus. In this case, it is not possible to detect any organic deviations from the norm, which indicates the neuralgic nature of the pain syndrome.
In women, coccydynia is diagnosed 3 times more often than in men, which is due to the structural features of the pelvic organs. Moreover, most often the disease occurs in people 40–50 years old.
Reasons for the development of coccydynia
The main cause of coccydynia is pinched or injured nerves in the area of the sacrum and coccyx. This can even be the result of prolonged sitting on a hard surface, while driving a car, especially with emphasis on the tailbone. It is especially stressed when sitting in a position with legs pulled up to the stomach. Many people spend a lot of time in front of the TV in this position, which becomes a prerequisite for the occurrence of neurodystrophic coccydynia.
Also, the cause of the development of pain syndrome can be osteochondrosis, especially of the lumbosacral region, and injuries of the sacrococcygeal region:
- fractures;
- sprain;
- bruises;
- soft tissue injuries.
They occur as a result of a fall from a height onto the buttocks or a direct blow to the tailbone area with a heavy object. Against the background of injuries, the development of inflammatory processes and the ischemia that develops as a result, functional and morphological changes occur in the periosteum, and myositis often occurs. The result is persistent pain.
In the absence of proper treatment, the outer shell of the coccyx formed by connective tissue begins to thicken and sclerosis. Gradually, the osteogenic cells of the periosteum change, swelling and compression of the capillaries develop, which leads to the formation of foci of pathological bone formation. In such cases, traumatic coccydynia is diagnosed.
Also, pain in the tailbone can occur due to the formation of a cyst on it. For a long time, the tumor exists unnoticed by the patient. But as it grows, it begins to compress the surrounding tissues or its liquid contents become infected. This starts a chain of inflammatory reactions and requires immediate medical attention.
Often the causes of pain in the coccyx lie in the development of changes and diseases of the pelvic organs, which becomes the cause of false coccydynia. For women, these may include:
- endometriosis;
- ovarian cysts;
- abnormal position of the uterus;
- pregnancy and childbirth.
Also, pain in the coccyx can be felt with colitis, external and internal hemorrhoids, anal fissures, proctitis and paraproctitis, and in men with prostate diseases. After all, prostate adenoma and bladder pathologies are also capable of causing pain in the tailbone.
Obesity is also not good for your health. Increased load on the spine and tailbone in particular leads to an increased risk of damage or dislocation, which will cause pain.
The prerequisites for the development of coccydynia are:
- ankylosing spondylitis syndrome;
- the presence of neoplasms of various nature in the pelvic area;
- systemic connective tissue diseases, in particular rheumatoid arthritis;
- chronic constipation;
- previous operations in the area of the pelvic organs, provoking the formation of rough soft tissue scars;
- weakness of the muscular-ligamentous apparatus.
In a third of all cases, it is not possible to determine the causes of pain in the coccyx, since there are no organic disorders and no injuries were observed. Then they talk about idiopathic coccydynia. It is believed that it is a consequence of damage to the corresponding nerve plexuses, which leads to the development of pain and disruption of the outflow of venous blood.
Contraindications to the use of blockades
The coccyx block procedure has certain contraindications. In addition to the age limit - the blockade is not performed on people under 18 and over 85 years of age - it should not be prescribed if the patient has the following conditions:
- bleeding disorders;
- acute and chronic infections;
- cardiovascular pathologies;
- liver and kidney damage;
- oncopathology;
- arterial hypertension/hypotension;
- epilepsy;
- mental disorders - due to the possibility of inappropriate behavior of the patient;
- period of pregnancy and breastfeeding.
There are no other restrictions for the procedure. In preparation, the patient should undergo the necessary tests. If patients have contraindications, they themselves or their relatives are obliged to notify the doctor about this.
Types and symptoms of coccydynia
The main symptom of the disease is aching, pulling, sometimes burning and sharp pain in the tailbone, which occurs when sitting or standing for a long time. The pain tends to intensify when rising from a sitting position and then gradually decrease. It appears in the coccyx area and can radiate to nearby organs. The pain syndrome intensifies with physical activity, coughing, sneezing, bending over or direct pressure on the tailbone, and in the area below the lower back there is always pressure or a feeling of heaviness.
Severe attacks of pain cause sweating and pale skin. Sometimes they provoke the occurrence of irritable bowel syndrome. This is accompanied by diarrhea, vomiting, disturbances in the functioning of the abdominal and pelvic organs, and discomfort in the lower abdomen. This can cause irritability, sleep problems, increased fatigue and decreased performance.
Seizure triggers may include:
- change of season;
- physical fatigue;
- psychological stress;
- exacerbation of chronic diseases;
- hypothermia;
- repeated injuries;
- gynecological or rectal examinations.
In severe cases, the pain can reach such severity that the person is practically unable to bend his legs at the hip joints, spread his legs to the sides or squat, and gait is also impaired.
If the disease develops against the background of trauma, the primary form of coccydynia is diagnosed. In such situations, pain occurs immediately after the blow and disappears after a few days. After a few weeks or months they return, but the patient can rarely associate their appearance with the injury that occurred.
In cases where the cause of its occurrence is gynecological, urological, or proctological disorders, coccydynia is a secondary disease.
During coccydynia, pain may predominate in different areas. They can also be observed in the buttocks, perineum, anus and rectum. In any case, coccydynia negatively affects a person’s quality of life. She calls:
- pain during defecation, which forces a person to try to defecate as little as possible, resulting in constipation;
- decreased quality and regularity of sexual life, since intimacy provokes increased pain in the tailbone;
- a decrease in social activity, since the patient cannot sit for a long time and is forced to refuse to attend public events or even change his type of work.
How is the tailbone structured?
How many vertebrae are there in the coccyx
In humans, the coccyx consists of 3-5 coccygeal vertebrae. The coccygeal vertebrae are connected to each other by cartilaginous plates. In older people, the coccygeal vertebrae often fuse into one bone.
Muscles and ligaments of the coccyx
Partially the piriformis and partly the gluteus maximus muscles, as well as the coccygeal muscles lying on the sacrospinous ligament, are attached to the outer parts of the lower sacral and upper coccygeal vertebrae.
Below is the muscle that lifts the anus. All these muscles are a structural element of the pelvic floor.
The sacrospinous and sacrotuberous ligaments are partially attached to the anterior walls of the coccyx.
The anal sphincter and anal-coccygeal tendon are attached to the tip of the coccyx.
The coccyx connects to the sacrum through a full intervertebral disc.
In addition to the intervertebral disc, the sacrococcygeal joint includes anterior, posterior longitudinal and lateral ligaments.
Coccygeal nerve plexus
In front of the coccyx is the coccygeal nerve plexus, formed by the anterior branches of the fifth sacral and coccygeal nerves. This plexus is located on the coccygeal muscle and the sacrospinous ligament, is anatomically connected to the lower parts of the sympathetic nerve trunk and provides innervation to the organs and tissues of the pelvis. The anal-coccygeal nerves extending from the coccygeal plexus innervate the skin in the area of the coccyx and anus.
Pain in the coccyx in a child
Coccydynia in children is a rather rare phenomenon. Although in recent years there has been a tendency to increase the incidence of pain in the tailbone in adolescents. This is due to the tendency to spend a lot of time at the computer or with other gadgets, low levels of physical activity and poor diet. Injuries, as well as other diseases, can be one of the causes of pain in the tailbone.
Diagnosis and treatment of coccydynia in children is carried out in the same way as in adults. Moreover, depending on the indications, both conservative and surgical treatment methods can be used to eliminate pain.
Coccyx block and its types
If the effectiveness of the effects of tablets, intramuscular injections and physical therapy is low, the doctor may recommend a blockade - injection of the drug directly into the spine. This allows you to reduce or completely interrupt the pathological conductivity of the clamped areas of the nerve - until the moment when it is unblocked with the help of medical manipulations or naturally. When blocking the coccyx, injections are made into the sacrococcygeal joint. Depending on the severity of the patient’s condition, from two to three to 15 procedures are performed at intervals of several days.
The blockade can be monocomponent - if one drug is administered, dicomponent - if there are two such drugs at the same time, and multicomponent - when there are three or more of them. The most commonly used widely known analgesics are Novocaine and Lidocaine. More modern analgesic drugs used for blockades of the spinal column, including the coccyx, include Diprospan, which has a rapid analgesic effect and a longer lasting effect. Medicinal substances are injected into the sites of localization of the most severe pain syndrome. For an anti-inflammatory effect, glucocorticosteroids Hydrocortisone, Dexamethasone, Kenalog are used simultaneously with an analgesic.
A powerful analgesic effect is achieved with an epidural blockade into the coccyx for a herniated disc, but this is a more complex procedure. It is carried out by highly qualified specialists only in a hospital setting. The medicine is injected into the area between the hard shell of the spinal cord and its bony “case”. Pain relief is achieved by blocking the transmission of pathological impulses along nerve endings.
Diagnostics
If pain occurs in the tailbone, rectum and genitals, you should consult a neurologist, proctologist or gynecologist. Thanks to visual and manual examination, a specialist will be able to detect signs of organic diseases and prescribe additional research methods: ultrasound, colonoscopy, laboratory tests, etc.
As a result, it is possible to detect or exclude tumors, hemorrhoids, prostatitis, urethritis and a number of other diseases that are characterized by pain in the coccyx and perineum. If such pathologies are not detected, the patient is sent for an X-ray or CT scan of the spine, the results of which make it possible to diagnose coccydynia.
Diagnosis of coccydynia
Coccygeal pain syndrome is difficult to diagnose. Since the pain radiates to the rectum and genitals, gynecologists and proctologists may be involved in the examination, who help to exclude or confirm diseases of these organs.
But the main specialist who diagnoses and treats coccydynia is a neurologist. The doctor makes a diagnosis based on the collected history, physical examination and instrumental examination.
At the initial appointment, the neurologist clarifies the nature of the pain, asks about injuries, falls on the tailbone, and surgical interventions in the pelvis. The doctor studies the patient’s medical history, then proceeds to examine and palpate the spine, in particular the sacrococcygeal region.
Note! With coccydynia, palpation is painful. If there is no pain when pressing on the tailbone, then the pain is associated with osteochondrosis, a herniated intervertebral disc or other pathology.
Mandatory diagnostic procedures include a rectal digital examination, which is performed by a proctologist in order to assess the condition of the pelvic muscles and the presence of overstrain.
To determine the cause of coccydynia, the doctor prescribes the following examination methods:
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs;
- colonoscopy;
- X-ray, CT or MRI of the spine.
Of the instrumental methods, MRI is the most informative. With its help, you can detect post-traumatic changes, tumor neoplasms, and organic disorders. You can get an MRI at the medical office. The clinic has installed a new ultra-precise MRI scanner.
If necessary, create a 3D model of the area under study
The diagnosis is known on the day of diagnosis. After an MRI, additional examination is often not required, since the cause of pain and its etiology can be detected. Treatment is prescribed by the attending physician, referring to the diagnostic results.
Kazieva Aminat Ziyavovna
Neurologist
Rostov State Medical University
Experience since 2012
Treatment of coccydynia
Treatment of pain in the coccyx includes measures aimed at improving the patient’s condition and eliminating the causes that led to their occurrence. The effectiveness of therapy depends on the correct identification of the causes of the disease. Patients with pain in the coccyx are prescribed:
- drug therapy;
- physiotherapy;
- exercise therapy;
- diet.
In some cases, conservative therapy is unsuccessful, and people continue to suffer from excruciating pain in the tailbone. In such situations, as well as in the presence of fractures, surgical treatment of coccydynia is recommended. Modern methods of neurosurgery make it possible to perform full-fledged operations with virtually no trauma to healthy tissue and obtain excellent results. They are characterized by minimal risk, as well as a quick and easy recovery period.
Drug therapy
The goals of drug therapy are to reduce pain, improve the condition of bone and cartilage tissue, nerve conduction, eliminate the inflammatory process and improve the quality of peristalsis. Therefore, patients are prescribed:
- NSAIDs in the form of tablets, products for external use;
- muscle relaxants;
- chondroprotectors;
- B vitamins;
- laxatives.
In case of severe pain, novocaine-alcohol and lidocaine pericoccygeal blockades are performed. To perform it, the patient must lie on his right side and bend his legs. The skin in the area of the sacrum and coccyx is treated with an antiseptic solution, for example, Lugol's solution. The nurse inserts the index finger of the left hand into the patient's rectum. This ensures the accuracy of the blockade.
The anesthetic injection itself is made with a long needle inserted along the midline between the anus and the tip of the coccyx. By changing the direction of the needle, the anesthetic solution is injected around the entire tailbone, but special attention is paid to its front part. If necessary, the blockade is repeated after 10–15 days.
Treatment of detected gynecological, urological and proctological diseases is mandatory. Its character is selected individually depending on the type of disorder present, the patient’s age and his general condition.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic treatment methods help improve the patient’s condition and increase the effectiveness of drug treatment. They include sessions:
- electrophoresis;
- UHF therapy;
- rectal darsonvalization;
- diadynamic currents;
- laser therapy;
- therapeutic massage;
- acupuncture;
- paraffin applications.
The procedures are carried out in courses of 10–15 sessions.
Exercise therapy
Therapeutic exercises have a positive effect on the patient's condition. Regular classes according to an individually drawn up plan help reduce pain and normalize blood flow in the pelvic organs.
Diet
All patients are prescribed a diet to improve the quality of digestion. Compliance with it allows you to eliminate constipation and discomfort during bowel movements, which has a positive effect on the patient’s well-being.
The diet should be dominated by vegetable dishes, boiled lean meat and fish, as well as cereals and whole grains. The menu can include fermented milk products, sour fruits, compotes, herbs and vegetable oils.
You will have to give up fried, fatty foods, carbonated drinks and alcohol. Preference is given to dishes steamed or baked in the oven, although boiled food is also allowed.
Surgical treatment of pain in the coccyx
Indications for surgery on the coccyx are:
- severe pain that cannot be eliminated through conservative therapy;
- pathological mobility of the coccyx, which is typical for its dislocations or fractures;
- cystic neoplasm on the coccyx.
Until recently, in case of fractures of the coccyx or the failure of conservative therapy, treatment of coccydynia was carried out only through open surgery, during which the anatomy of the coccyx was restored or it was removed. This surgical intervention is called coccygectomy and is associated with risks of injury to nerve structures, large blood vessels and the development of a number of other complications.
Today, an alternative to the method is radiofrequency ablation, which is characterized by minimal tissue trauma, speed and ease of recovery, as well as a minimum number of intraoperative risks.
Coccygectomy
During the operation, not only the deformed tailbone is removed, but also sections of the nerves. The surgeon also cuts the tendons of the spasmed muscles, which together leads to the elimination of pain.
The operation is performed by removing the coccyx from Co1 to the last coccygeal vertebra (antegrade removal) or in the reverse order (retrograde removal). The methods differ in the type of access created.
Thus, retrograde surgery is performed from a longitudinal approach, which is done parallel to the intergluteal fold at a distance of a couple of centimeters from the anus. This approach involves a high level of soft tissue damage and is associated with the development of a fairly large number of postoperative complications and a difficult recovery period. One of the most dangerous consequences of coccygectomy performed using a retrograde approach is damage to the external sphincter and the membranes of the rectum.
Coccygectomy using the antegrade method is performed through an access formed near the sacrococcygeal joint. The neurosurgeon makes an incision longitudinally or transversely, without touching the intergluteal fold. As a result, the doctor is able to remove the entire tailbone along with the periosteum or parts.
At the first stage, the sacrococcygeal ligament is dissected and the S5–Co1 disc is removed. After this, the vertebrae of the coccyx are sequentially removed according to the principle of disassembling a column of coins, starting with Co1.
But as a result of the removal of the coccyx, a rectococcygeal fossa is formed in its place, in which blood and exudate accumulate. This creates compelling preconditions for the occurrence of a hematoma, seroma, or infection, which subsequently leads to the formation of an abscess. Various attempts are being made to close the resulting defect with the patient’s own tissues, but this only slightly reduces the risk of complications.
Thus, coccygectomy is a rather traumatic operation. Therefore, whenever possible, they try to abandon it in favor of radiofrequency ablation.
Radiofrequency ablation (RFA) for coccydynia
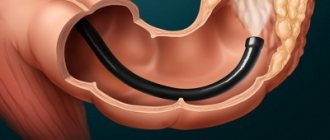
Radiofrequency ablation is a minimally invasive method for treating spinal diseases, widely used in modern neurosurgery to eliminate severe pain. It provides a long-lasting effect by eliminating the path of pain impulse transmission from the site of irritation to the central nervous system.
The essence of radiofrequency ablation is the introduction of a long guide needle into the patient’s body directly into the area where the nerve passes through the problem area. Its immersion is controlled by an image intensifier.
A damaging electrode, which has a bare working end, is immersed through the needle. An indifferent electrode is installed on the other side of the coccyx. The first is connected to a radio frequency generator, which maintains the required voltage. As a result, an electric current is supplied to the working end of the active electrode, the required frequency of which is selected individually. Thus, an electric field is formed between the two electrodes, which creates thermal energy, under the influence of which the nerve fibers that provoke the occurrence of pain are destroyed.
After completion of RFA, a solution of local anesthetics and hydrocortisone is injected into the coccyx area. Only after this the guide needle is removed from the patient’s body, and the remaining punctures are covered with a sterile bandage.
After surgery, patients can move independently and return to daily activities within 2 hours.
The only limitation after this is the need to stop lifting heavy objects and squats. Thus, radiofrequency ablation is a one-day operation, which, with a minimum number of risks, can solve the problem of pain for a long time.
But radiofrequency ablation for coccydynia cannot be performed if:
- local or generalized infectious process;
- hemorrhagic diathesis;
- pregnancy.
Methodology of the procedure
To carry out the novocaine blockade, the patient must lie on his stomach. The doctor determines the site of the intended injection by palpation. First, the drug is infused intradermally and the skin is numbed so that the patient does not experience too much pain during further manipulations. Then the needle is replaced with a longer one and inserted between the vertebrae, slightly away from the spinous processes. Having rested on the process, the doctor partially removes it back and, changing the inclination, directs it under it by about 2 cm. The drug is administered at a slow pace: the whole procedure takes about 40 minutes. Novocaine exhibits analgesic properties 15 minutes after the blockade, the deep analgesic effect lasts for about two hours. When using a mixture of novocaine and lidocaine, this period increases.
The epidural block technique looks more complicated. First, the drug is also administered intradermally, then the needle is changed and directed in parallel, for which it is necessary to pierce the membrane of the entrance to the coccygeal canal. Having lowered the needle horizontally no more than 5 cm, partially pull the syringe plunger towards you. If no liquid is detected in the syringe, the medicine can be administered. With epidural blockade, the administration of novocaine, cyanocbalamin, thiamine, and corticosteroid drugs is allowed. The volume of medications administered at one time should not exceed 60 ml. The analgesic effect lasts for several days. Before starting the procedure, a mandatory test is carried out to identify a possible allergic reaction to the drugs in the patient.
Possible complications and consequences
The outcome of the disease largely depends on the timeliness of initiation and correct selection of therapy. If you ignore pain in the tailbone and neglect medical help, this can lead to such undesirable effects as:
- chronic constipation;
- chronic diseases of the pelvic organs;
- decreased performance;
- severe pain during sexual intercourse;
- erectile pain;
- impotence.
Thus, coccydynia is a rather problematic disease that significantly poisons a person’s life, but does not threaten disability or death. However, it causes significant limitations in daily life and can lead to persistent depression. Therefore, you should be attentive to the causes of pain in the tailbone and immediately take measures to eliminate them, for example, using radiofrequency ablation. As practice shows, this particular method gives the best results in the shortest possible time and is not associated with serious risks of worsening the condition.
What happens to the tailbone when pain occurs in it
When the muscles of the lower pelvic floor contract on both sides, the tailbone bends forward; if the muscles contract on one side, the tailbone simultaneously bends and moves to the side.
Normally, movements in the sacrococcygeal segment in the anteroposterior direction are possible within 30 degrees, and lateral deviations are up to 1 cm. Such displacements of the coccyx on an x-ray should not be regarded as a fracture or dislocation. With spastic tension of the pelvic floor muscles, the tailbone in relation to the sacrum takes a position of excessive flexion, and pain most often appears.
Pain in the tailbone may intensify when getting up from a chair. This is explained by the tension of the gluteus maximus muscles, some of the bundles of which are attached to the lateral sections of the sacrum and coccyx.
Sign up for a consultation by phone