Oncological diseases are a real scourge of modern humanity. Every year, more and more new cases of cancer of various localizations are registered all over the world, and colon cancer ranks third among them. Early detection of this disease gives a good prognosis and allows the use of more gentle, non-disabling methods of treatment. Therefore, such great importance is attached to preventive examinations using reliable research methods.
The “gold standard” of modern diagnosis of colon tumors is colonoscopy. This procedure is also called fibrocolonoscopy (FCS) or video colonoscopy. Currently, colonoscopy in St. Petersburg is carried out in comfortable conditions for the patient, using general anesthesia (anesthesia).
What is the essence of colonoscopy?
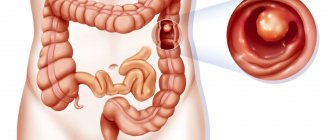
Fibercolonoscopy is an examination of the surface of the mucous membrane of all parts of the large intestine using an endoscope camera. The device used in this case is called a colonoscope; its working part is carefully inserted into the intestinal lumen through the anus. Modern models look like a flexible thin tube; if the doctor is sufficiently qualified, their advancement is not accompanied by severe pain and does not lead to tissue damage.
The image received by the camera is processed and transmitted to the monitor screen. The level of detail depends on the hardware class, screen resolution and the presence of additional software.
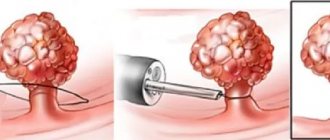
If suspicious (modified) areas of the mucous membrane or space-occupying formations are identified, the doctor performs a biopsy - using manipulators, he separates a piece of tissue for subsequent analysis. It is also possible to simultaneously remove small tumors (for example, polyps).
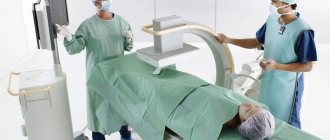
A comfortable option for FCS is to carry out the procedure under anesthesia, when the patient is immersed in a controlled medicated sleep. In this case, the team of doctors includes an anesthesiologist-resuscitator. After completing the procedure, the patient stays in the clinic for some time and returns to everyday life within a few hours.
A delicate problem
Very often, a trip to the proctologist is postponed until the last minute. And talking about any problems with the intestines is considered something shameful. But you need to understand that if you contact specialists in a timely manner, then diagnosing any problem will not be difficult.
In most patients, the imagination often works “in the wrong direction.” They have a distorted understanding of how this research is conducted. Many people think that they are in for torment and inconvenience, but medicine has long stepped forward in this aspect and has created all the conditions for complete comfort for patients.
What can be revealed
FCS with anesthesia allows you to:
- carry out differential diagnosis between chronic diseases with colitis syndrome;
- identify diverticula;
- detect polyps and other benign neoplasms and remove them endoscopically;
- detect malignant tumors (cancer) of any form at the earliest stages, when they are still small in size and limited to the mucous membrane and submucosal layer.
At the moment, FCS is the most informative, reliable and safe way to assess the condition of the wall of the large intestine and identify any neoplasms located here.
Is it possible to replace the FCC with something?
As an alternative, FCS often offers irrigoscopy and CT. In fact, these techniques cannot fully replace endoscopic examination. They do not allow a detailed and targeted examination of the tumor, do not detect small defects in the mucous membrane and do not allow a biopsy. In addition, these techniques involve the use of radiation, which imposes certain restrictions on the timing of re-diagnosis.
Fibercolonoscopy is the optimal method for assessing the condition of the walls of the large intestine and the most informative way for the early detection of colorectal cancer.
Unfortunately, more than 1/3 of malignant colon tumors are diagnosed at late stages, which explains the high mortality rate from this disease. In many cases, this is due to patients’ unreasonable refusal of recommended regularly repeated endoscopy. The lack of information content and reliability of screening studies carried out in clinics, with preference for laboratory or X-ray diagnostics, is also of certain importance.
Possible complications
Colonoscopy is a safe test. The risk of complications during a diagnostic examination of the colon is minimal. The risks of surgical endoscopy of the colon are less than one percent, which allows us to speak with confidence about its safety. Complications during endoscopic examination of the colon are very rare, including:
- Allergic reactions to sedative medications.
- Bleeding after biopsy, polyp removal.
- Perforation (rupture of the wall) of the intestine.
Why is anesthesia needed for FCS?
Colonoscopy under anesthesia relieves the patient of the physical and psychological discomfort associated with the insertion and advancement of the colonoscope tube. He will not experience pain during a biopsy, if there is a need to take tissue samples for histological examination.
Anesthesia makes it possible to avoid the formation of fear of repeated FCS, so that the patient in the future will not avoid the recommended scheduled regular examinations. According to reviews, after a colonoscopy in a state of medicated sleep, there is no pain in the anus and in the abdomen.
The use of anesthesia also improves the quality of the examination. Moderate muscle relaxation in a sleeping patient and the absence of involuntary resistance on his part give the doctor the opportunity to carefully examine the folds of the mucosa in all parts of the large intestine.
Reviews by patients
Ekaterina D.
Had a colonoscopy in the clinic in a dream. Before this, I was terribly afraid of this procedure, because I once tried to do it in another clinic without anesthesia, there was unbearable pain and I had to stop the examination. They recommended the WMT clinic to my husband, he took me there, and they offered me a “sleep colonoscopy” for a fee. I didn't regret it one bit. The anesthesiologist and nurses are attentive. Dr. Sukhorukov Denis Viktorovich is a pleasant and competent specialist. Thank him very much. It turned out that I had some kind of pathology - 1.5 meters of extra intestine. Yes, this happens too. After giving birth, I felt a terrible condition: bloating, various pains, etc. The doctor examined everything and said that in general everything was fine, there was nothing to worry about. He “corrected and put everything in its place,” so to speak. I’m speaking in my own words, just keep in mind that extra guts can be useful. After this, the bloating and constant feeling of heaviness disappeared, so the procedure is worth it. Next week I will go for an MRI of the brain at the same clinic.
Victoria Kravchuk
Today I had a gastroscopy and colonoscopy in my sleep at the WMT clinic with Viktor Viktorovich Golfand. A wonderful specialist, he explained everything, put me at ease, the nurses are wonderful, they do everything for comfort, the hospital is beautiful! As soon as I came to my senses, they helped me and said: “Everything is fine with you, let’s wake up!” I recommend this wonderful clinic and doctor to everyone!
Dmitry Lobchuk
I had a colonoscopy done in a dream with Alexander Yakubovich. Only positive emotions! The doctor is incomparable and a specialist - nothing hurt after the procedure from the word “at all” (even in the presence of aggravating circumstances in the form of hemorrhoids and fissures), the pain-relieving effect is excellent! He listened to all the complaints, was very tactful and polite, you felt like you were talking with an old friend. I recommend this specialist to everyone! Special thanks to the team, anesthesiologist and nurse, thanks to you the fear of such studies disappears.
Daria Davydenko
I would like to express my deep gratitude to Viktor Viktorovich and the entire team who works with him. FGDS and colonoscopy were performed “during sleep”. Everything is done at the highest level. Everyone was very friendly and helpful. I will recommend it to everyone! Thanks a lot!
Elena Feodorovna
Alexander Yakubovich, please accept my words of gratitude! You know how to put me at ease from the first minutes of the meeting, there is no falsehood, your concern was absolutely sincere, I stopped being afraid as soon as I saw your kind smile. Thank you that there was no formality, you listened to everything, delved into everything, and after your phrase: “We’ll sort it out,” I was sure that I was in good hands. The study took place in a dream, I can’t say anything about it, I didn’t feel it, I don’t remember. No discomfort after it, comprehensive information about the results in addition to what is written. Organization and execution of work at the highest level!
Preparing for the FCC
Preparing the patient for the study includes:
- Examination to exclude contraindications to anesthesia. It is necessary to donate blood for general and biochemical tests, do an ECG (with interpretation), if you have chronic diseases, consult a therapist, and if there are severe hormonal disorders, consult an endocrinologist.
- Following a certain diet aimed at reducing gas formation in the intestines and reducing the volume of intestinal contents. For 3–5 days before the procedure, fruits, vegetables, seeds, nuts, most cereals, legumes, and sweets (sweets, chocolate, baked goods) are excluded from the diet. Consumption of milk and fatty fermented milk products is undesirable. Alcohol, juices with pulp, and strong broths are prohibited.
- Avoid eating for 16–20 hours before your scheduled examination. You can drink water and prescribed medications no later than 3-4 hours before the procedure.
- Limit smoking; it is advisable to temporarily quit smoking a few hours before anesthesia.
- Cleansing the large intestine to the state of transparent, slightly colored and liquid stool. Previously, repeated enema was used for this; now drug preparation for the procedure is preferred. ICLINIC doctors recommend using the drug Moviprep for this; a detailed dosage regimen can be clarified with the clinic’s specialists.
Preparing for a colonoscopy is the most important stage of the study. Properly performed bowel cleansing significantly increases the degree of visualization of the upper parts of the colon, expands the diagnostic capabilities of the technique and increases the reliability of the results. And following the rules of preparation for anesthesia makes it easier to tolerate and eliminates the risk of complications.
Colonoscopy is a diagnostic method that is used to assess the condition of the colon mucosa. The examination is carried out using a special instrument - a colonoscope. It is a thin, ultra-flexible tube with a video camera at the end.
Goals of performing a colonoscopy
Using a colonoscopy, the doctor can detect ulcers, polyps, foci of inflammation, tumors, and sources of intestinal bleeding. In addition, during a colonoscopy, tissue samples can be obtained from the intestines for histological and cytological examination, and polyps or other formations can be removed.
The first colonoscopy is recommended at age 40. Further recommendations are given individually, depending on the results of the study. Unfortunately, most colon tumors are detected at late stages. There is only one reason here - late diagnosis of the tumor. The only way to detect a tumor at an early stage is regular examination of the colon, which allows us to identify pre-tumor pathology and remove it, or carry out other necessary treatment to prevent it from degenerating into cancer. The key to curing cancer is early diagnosis. Early diagnosis can be done using colonoscopy.
Diagnostic colonoscopy
A diagnostic colonoscopy is performed to identify certain pathological formations in the intestines. There are two special types of diagnostic colonoscopy:
- A screening colonoscopy is recommended for all people over 50, even if they have no symptoms. For some bowel diseases, screening may need to start at a younger age. This type of screening is used for early diagnosis of polyps that can develop into a malignant tumor and intestinal cancer.
- Control colonoscopies are periodically performed in people with a history of polyps, colon cancer, and inflammatory bowel diseases.
At the Center for Gastroenterology and Endoscopy of the PLATAN clinic in Nizhny Novgorod, there is a promotion “FGDS and colonoscopy under sedation.” The cost of the complex service includes endoscopic examinations of the stomach and colon, light anesthesia (sedation, “medicated sleep”), a preliminary appointment with a specialist, and a stay in the recovery room.
Why is it better to undergo a colonoscopy at the Center for Gastroenterology and Endoscopy at the PLATAN clinic?
In our center, colonoscopy is performed only by experienced endoscopists. Most of the current endoscopists in Nizhny Novgorod were trained in endoscopy from our leading endoscopists - Khabazov I.G. and Teplova O.V.
Our team of endoscopists uses the video endoscope EVIS EXERA III CV-190 from OLYMPUS (Japan) to perform colonoscopy, providing:
detection of 29% more colon polyps and 34% more neoplasms in Barrett's esophagus
the accuracy of diagnosing lesions in the colon and rectum is >90%
complete absence of pain during colonoscopy in >78% of patients
20% reduction in transit time to the cecum
Therapeutic manipulations during colonoscopy
During an endoscopic examination of the colon, the doctor may perform some therapeutic procedures:
- Remove polyp.
- Stop intestinal bleeding, for example, using electrocoagulation or clipping.
Often, a colonoscopy is initially performed as a diagnostic procedure and, if pathological changes are detected, it becomes a therapeutic procedure. Having discovered a pathological neoplasm in the intestine, the doctor removes it using a special instrument inserted through a colonoscope and sends it to the laboratory for histological and cytological examination.
Colonoscopy under anesthesia
Colonoscopy , as a rule, is painless, but the patient may experience discomfort from a feeling of bloating (this goes away immediately after the procedure) and the advancement of the probe through the loops of the intestine. At the PLATAN clinic it is possible to carry out the procedure in a state of medicated sleep. In this case, the patient is given a special sedative, under the influence of which he is plunged into deep sleep. After approximately 40 minutes, the effect of the drug ends, and within 5-10 minutes after waking up the patient can walk and talk, and after an hour he can go home. In addition to comfort for the patient, the use of sedation significantly improves the quality of diagnosis, since the doctor is not distracted by feedback from the patient. In our clinic, most diagnostic procedures are performed under sedation.
How is a colonoscopy performed?
A diagnostic colonoscopy lasts on average 30 minutes. If therapeutic manipulations are required, the procedure time increases.
In order for the patient to undergo the procedure without pain and discomfort, sedation is used - the patient is immersed in a state of “medicated sleep”.
The patient undresses completely from the waist down and puts on special shorts. He is placed on his left side, with his legs bent and knees brought to his stomach. The doctor carefully inserts the colonoscope through the rectum and slowly advances it, examining the colon lining. In this case, the intestines are inflated with gas to provide a better view. At the PLATAN clinic, carbon dioxide is used for this, because it acts as an antispasmodic, is absorbed through the intestinal walls and eliminated from the body faster than oxygen and nitrogen.
The image from the colonoscope camera is transmitted to the device screen. Videos of the study are recorded and saved on a computer.
After the intestines are examined, the doctor carefully removes the colonoscope. The study is completed.
A unique technique for performing colonoscopy
At the Center for Gastroenterology and Endoscopy of the PLATAN Clinic, a unique method of performing colonoscopy is available - using carbon dioxide. Basically, when diagnosing the intestines, in order to straighten the folds, room air is used, which is unsterile and also gives discomfort after the procedure. Carbon dioxide is used during colonoscopy to achieve absolute image accuracy, since there is no effect of image refraction in the liquid. Sterile medical carbon dioxide enters the intestine through a special hole in the endoscope, and after the procedure, unlike air, it is completely absorbed into the intestinal walls. This provides the patient with maximum comfort, since there are no consequences in the form of bloating and gases.
Preparing for a colonoscopy
Typically, preparation for a colonoscopy takes 2–3 days. It is necessary to follow a diet, limit food intake on the eve of the test, and take laxatives. The doctor who prescribed the procedure tells the patient more about the preparation rules.
Diet before colonoscopy
An important part of preparing for a colonoscopy is proper diet in the preceding days and on the day of the examination. In general terms, the recommendations are as follows:
- A few days before the procedure, you need to switch to a low-fiber diet, reduce the consumption of fresh vegetables and fruits, dried fruits, nuts, and whole grains.
- 1–3 days before your colonoscopy and on the day of the procedure, you should avoid eating solid foods. Broths, clear fruit juices (for example, clarified juice from apples, white grapes), tea and coffee, and jelly are allowed. It is recommended to drink more fluid the day before.
- You should not eat or drink anything 2–4 hours before the procedure The procedure can only be carried out under medicated sleep conditions on an empty stomach.
In parallel with the diet, in the afternoon before, the intestines are prepared for the procedure using laxatives. Recommendations regarding types of drugs and dosage regimens may vary from doctor to doctor.
Indications and contraindications
Indications for colonoscopy are:
- blood and mucus in the stool;
- presence of relatives with colon cancer;
- previous colon surgery;
- chronic abdominal pain of unknown etiology;
- suspicions of cancer, ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease;
- elevated temperature for a long period of time, accompanied by anemia and weight loss.
Regular colonoscopy is also recommended for all people over 50 years of age for the early detection of tumors, polyps and other diseases of the colon.
Contraindications to colonoscopy are the active stage of Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis.
Recording the procedure on video
In our clinic, it is possible to record the colonoscopy process - the image from the camera at the end of the colonoscope is recorded on video, and then the recording is transmitted to the patient. This allows you to avoid repeating the procedure when contacting specialists from another clinic, for example, when sending you for treatment abroad.
Recovery after colonoscopy
Hospitalization is not necessary, and colonoscopy can be performed on an outpatient basis. The patient can leave the clinic as soon as he recovers from anesthesia. But you are not allowed to drive on your own on this day. You need to take one of your relatives to the clinic so that you can be escorted home.
Notes and recommendations regarding the recovery period after colonoscopy:
- When the effect of sedation wears off, a feeling of cramping and fullness of the intestines may appear. It will soon pass. In order for the gas to leave the intestines faster, it is recommended to walk.
- For 24 hours after the procedure, you should avoid drinking alcohol, driving vehicles, and doing work that requires concentration.
- Unless otherwise advised by your doctor, you can begin eating as usual immediately after the sedation ends. A special diet is prescribed after removal of polyps and other surgical procedures.
- It is recommended to rest for one day after the study, then you can do all your usual activities without restrictions, and go to work.
- If a biopsy was performed during a colonoscopy, you may notice some blood in your stool for 1 to 2 days afterward.
- If you need to take blood clot preventative or other medications continuously, ask your doctor how long after your colonoscopy you can start taking them again.
- Because your bowels were cleaned before the colonoscopy, another bowel movement may take a few days. It depends on your diet. If you do not have stool for a very long time after the procedure, consult your doctor.
You should immediately seek medical help if symptoms such as high fever, bleeding from the anus, or abdominal pain appear.
Possible complications
Colonoscopy is a safe test. The risk of complications during a diagnostic examination of the colon is minimal. The risks of surgical endoscopy of the colon are less than one percent, which allows us to speak with confidence about its safety. Complications during endoscopic examination of the colon are very rare, including:
- Allergic reactions to sedative medications.
- Bleeding after biopsy, polyp removal.
- Perforation (rupture of the wall) of the intestine.
Colonoscopy results
Further tactics depend on whether certain pathological neoplasms were discovered during colonoscopy.
No pathological changes were found
In such cases, no additional diagnostic procedures are required. Your doctor will recommend a repeat colonoscopy in 5 to 10 years. If the intestines were poorly prepared and feces remain in it, which prevented a full examination of the mucous membrane, a repeat colonoscopy will be recommended after a year.
If 1-2 polyps measuring less than 1 cm are found with a low risk of malignancy
The doctor will recommend repeating the test in 5 years.
If “dangerous” polyps are detected
Your doctor may recommend a repeat colonoscopy sooner than five years later in the following cases:
- more than two polyps were found in the colon;
- polyp size more than 1 cm;
- polyps were found, while there are fecal masses in the intestine, which complicate its full examination;
- according to the results of the biopsy, the removed polyps belong to histological types that have a high tendency to malignant degeneration;
- Cancer cells were found in the polyp.
If polyps are identified that could not be removed during colonoscopy
Such patients should consult a doctor. Perhaps the question of abdominal surgery will arise.
If cancer is detected
An examination is prescribed that helps assess the stage and other characteristics of the malignant tumor. The patient is referred to the oncology clinic, treatment begins in accordance with the protocols.
*Why so cheap?
We tell you as openly as possible. Sometimes patients registered for the procedure are discharged for various reasons - illness, work, other reasons. To ensure that space in the doctor’s schedule does not disappear, we offer it at a very attractive price. Please contact our administrators to find out about the availability of discounted seats.
You can make an appointment for a colonoscopy in Nizhny Novgorod from our administrators by phone.
How often should you have a colonoscopy?
According to modern clinical guidelines, indications for FCS include:
- Previously diagnosed chronic bowel diseases.
- The patient has a history of a polyp or other benign neoplasm in the gastrointestinal tract.
- Identification of indirect signs of a tumor according to other research methods (ultrasound, radiography, irrigoscopy, etc.).
- The patient develops symptoms suspicious of tumor growth. These include unstable stools, recurrent or chronic abdominal pain, persistent low-grade fever, detection of blood or mucus in the stool (outside the phase of acute diarrheal infectious syndrome), chronic treatment-resistant anemia (iron deficiency or B12 deficiency), persistent increase in ESR and a number of other signs.
- The patient has cancer risk factors, a hereditary history of gastrointestinal cancer. Currently, permanent residence in large cities and in areas of increased industrial pollution is considered as a predisposition to cancer, including colorectal localization.
Persons with chronic gastrointestinal pathology, previously diagnosed diverticulitis and intestinal polyposis are recommended to undergo fibrocolonoscopy at least once a year. The frequency of visits is determined by the doctor individually; in some cases, diagnostics are carried out every 6–8 months. People from the high-risk group aged 40–45 years are recommended to undergo FCS once every 2 years, and after 45 years – annually.
FCC in ICLINIC: competent approach and modern technologies
ICLINIC Medical Center specializes in the prevention and diagnosis of cancer of the digestive system. Our diagnostic equipment is certified, has high grades and is additionally equipped with special software to increase the information content of studies. The colonoscopes used have a reduced tube diameter, high-precision cameras and monitors, and allow virtual chromoendoscopy of the smallest formations identified. All this ensures high diagnostic information content and reliability of the FCS.
The base price for video colonoscopy at ICLINIC in St. Petersburg is 5.5 thousand rubles. It may change during additional consultations with an anesthesiologist, endoscopist, leading specialist E.I. Levchenko, when using anesthesia of varying complexity, when taking a biopsy.
The affordable price of colonoscopy at our ICLINIC center in St. Petersburg is an opportunity to undergo a highly accurate examination of the large intestine using high-quality equipment and in comfortable conditions. Each patient receives a qualified written report drawn up in accordance with current clinical guidelines and protocols. The ICLINIC doctor also gives recommendations on the prevention and treatment of identified changes, and will suggest the optimal program for further examination.
To do a videocolonoscopy at ICLINIC, you can contact our administrators using the feedback form or by calling the phone numbers listed on the website.