Instructions for use
pharmachologic effect
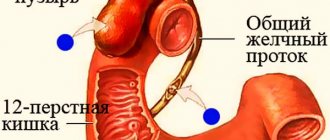
Phospho-Soda indicates the importance of timely detection of polyps during colonoscopy. The action of the drug is based on increasing fluid retention in the lumen of the small intestine due to osmotic processes. Water accumulates in the ileum, promoting increased peristalsis and subsequent bowel movement.
Fleet Phospho-soda has an exclusively local effect, so no thorough pharmacokinetic studies have been conducted.
Sodium phosphate is poorly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, but small absorption of phosphates and sodium ions is present and is dose-dependent.
Indications for use
Flit Phospho-soda is prescribed in the following cases:
- preparation for examination of the colon (x-ray or endoscopic);
- preparation for colon surgery.
Application procedure
You should start taking it on the day before the prescribed endoscopic or x-ray procedure. The medicine is prescribed to adults and adolescents over 15. Elderly patients do not require dose adjustment.
The drug should be taken on the day before the X-ray or endoscopic procedure. If the appointment is scheduled before noon, please follow the instructions for the morning appointment.
If the procedure is performed in the afternoon, you must follow the instructions for scheduling a daytime appointment.
Morning appointment
Day before the procedure
At 7 a.m., replace your usual breakfast with a glass of light liquid (water or soups freed from solid particles, coffee and tea without milk, fruit juices, clear still and carbonated soft drinks, etc.).
The first dose of Fleet Phospho-soda is taken immediately after breakfast. To do this, the contents of the bottle are dissolved in 1/2 cup of chilled water. Drink the prepared solution immediately and wash it down with a glass of cold water.
- Lunch at 13.00 is replaced with three glasses of light liquid.
- Dinner at 19.00 is replaced with one glass of light liquid.
The second dose is taken immediately after dinner. The solution is prepared and taken exactly the same as last time.
If desired, you can drink more liquid. In this case, light liquids are allowed to be drunk until midnight.
Daytime appointment
Day before the procedure
During lunch at 13.00 a light snack is allowed. Eating solid food after lunch is completely avoided.
At 19.00 you should replace dinner with a glass or large volume of light liquid.
The first dose of Fleet Phospho-soda is taken after dinner.
You should drink light liquids (at least three glasses) throughout the evening.
Day of procedure
Instead of breakfast at 7 am, drink a glass of light liquid.
The second dose is taken immediately after breakfast.
Light liquids are allowed up to 8 hours.
Typically, Fleet Phospho-soda causes bowel movements within 30 minutes to 6 hours.
Release form, composition
The drug is sold as a clear, colorless solution for oral use with a ginger-lemon aroma. The medicine is supplied to pharmacies in bottles packed in cardboard boxes.
The solution consists of sodium hydrogen phosphate dodecahydrate, sodium dihydrogen phosphate dihydrate and additional ingredients - glycerol 99%, sodium benzoate, sodium saccharin, purified water, lemon and ginger flavor (partially stabilized lemon oil, alcohol, water, ginger oil, citric acid, lemon oil) .
The doctor prescribes the drug as an oral medication, which is taken according to a clear schedule.
Interaction with other drugs
Patients taking lithium-based drugs, diuretics, CCBs and any drugs that can affect electrolyte levels should use Fleet Phospho-soda with caution. This is associated with the likelihood of developing hypocalcemia, acidosis, hypokalemia, hyperphosphatemia and dehydration against the background of hypernatremia.
During therapy with the use of Flit Phosphosoda, the absorption of other drugs in the gastrointestinal tract may be stopped or delayed. As for the effect of regularly taken medications (including oral contraceptives, antibiotics, hypoglycemic and antiepileptic drugs), it may be reduced or absent altogether.
Morning appointment for colonoscopy
Day before the procedure
At 7 a.m., instead of breakfast, drink at least 1 glass of “light liquid” (including soups freed from solid particles, fruit juices without pulp, tea and coffee, clear carbonated and non-carbonated soft drinks) or water.
The first dose of the drug should be taken immediately after breakfast. The contents of 1 bottle (45 ml) should be dissolved in half a glass (120 ml) of cold water. Drink the prepared solution and wash it down with one (or more) glass (240 ml) of cold water.
At 1 p.m., instead of lunch, you should drink at least 3 glasses (720 ml) of “light liquid” or water.
At 19:00, instead of dinner, drink at least 1 glass of “light liquid” or water.
The second dose of the drug should be taken immediately after dinner. The contents of the second bottle (45 ml) should be dissolved in half a glass (120 ml) of cold water. Drink the prepared solution and wash it down with one (or more) glass (240 ml) of cold water.
If desired, you can drink more liquid. “Light liquids” and water can be drunk until midnight.
This drug usually causes bowel movements within half an hour to 6 hours.
Side effects
| Digestive system | bloating, nausea, abdominal pain, vomiting, diarrhea; extremely rarely - multiple or single aphthae-like formations may be observed on the mucous membrane of the rectum and sigmoid colon during endoscopy (they are not clinically significant and disappear spontaneously without treatment). |
| CNS | weakness, dizziness, headaches, asthenia. |
| Metabolism | in some patients at risk, electrolyte imbalance (for example, hypocalcemia, hypernatremia, hyperphosphatemia, hypokalemia, acidosis) and/or dehydration. |
| Others | allergic reactions. |
Overdose
There are known cases of the development of hyperphosphatemia with hypocalcemia, acidosis and hypernatremia, ending in death. These cases were caused by the use of the drug in large doses in people with constipation and children.
Cases have also been described in which children and patients with constipation fully recovered after an accidental overdose.
Contraindications
The medicine is not prescribed to patients under 15 and people with:
- complete or partial intestinal obstruction;
- hypersensitivity to the ingredients of the drug;
- megacolon (acquired or congenital);
- violation of intestinal integrity;
- heart failure;
- acute inflammatory bowel diseases;
- vomiting, nausea, abdominal pain;
- renal failure.
During pregnancy
Phospho Flit Soda should not be used during pregnancy, since there is not enough reliable information about the ability of the drug. Flit Phospho Soda should not be prescribed to pregnant women, since it is unknown whether the drug can cause abnormal development of the fetus or have a toxic effect on it.
Sodium phosphate, which is part of the drug, is excreted in breast milk. In this regard, pregnant women are advised to stop breastfeeding after taking the first dose of the drug.
You can resume breastfeeding one day after taking the last dose.
Phosphosoda, 2 pcs., 45 ml, oral solution
The drug is not used as a treatment for constipation.
Severe and potentially fatal cases of electrolyte imbalance have rarely developed in elderly patients treated with Phosphosoda. Before starting the use of Phospho-soda in this category of high-risk patients, it is necessary to carefully assess the risk-benefit ratio.
When prescribing Phospho-soda to any patient, special attention should be paid to known contraindications and the importance of adequate hydration; in addition, in high-risk patients (see sections “Contraindications”, “With caution”), it is important to measure the initial level of electrolyte concentrations and the level of electrolyte concentrations after using the drug Phospho-soda.
Dehydration (Dehydration)
This drug usually works within half an hour to 6 hours after taking it. If within 6 hours after taking Phospho-soda the patient has not had a single bowel movement, it is necessary to ask the patient to stop taking this drug and immediately contact the doctor, since dehydration may develop .
Patients should be warned that they should develop frequent loose stools. They should be asked to drink as much fluid as possible to avoid dehydration. Inadequate fluid intake when using any effective laxative can lead to excessive fluid loss with possible development of dehydration and hypovolemia. Dehydration and hypovolemia under the influence of a laxative may be exacerbated by insufficient oral fluid intake, nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, or by the use of diuretics, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEIs), angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs), and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs); in such a situation, acute renal failure may develop. Rare cases of acute renal failure have been reported with the use of laxatives, including sodium phosphate derivatives and polyethylene glycol (PEG)-3350.
Patients with conditions that may contribute to dehydration or who are receiving medications that may reduce the glomerular filtration rate should be assessed for hydration status before initiating bowel preparation with laxatives and appropriate measures should be taken.
Nephrocalcinosis
In rare cases, nephrocalcinosis with acute renal failure and deposition of calcium phosphate crystals in the renal tubules has been reported in patients taking sodium phosphate for bowel cleansing. Nephrocalcinosis is a serious adverse event that can cause irreversible deterioration of kidney function with the need for dialysis over a long period of time. Most cases of nephrocalcinosis occur in older women receiving antihypertensive drugs or other drugs (eg, diuretics or NSAIDs) that can cause dehydration.
When prescribing the drug Phospho-soda, it is necessary to follow the recommendations, and special attention must be paid to known contraindications and adequate replenishment of lost fluid.
Patients at risk
Caution should be exercised when using Phospho-soda in patients with an increased risk of renal dysfunction, existing electrolyte imbalance or an increased risk of developing it (for example, dehydration, gastric retention, colitis, inability to take sufficient oral fluids, hypertension or other conditions , in which patients receive drugs that can lead to dehydration (see section "Interaction with other drugs"), arterial hypotension with clinical manifestations or associated with hypovolemia; heart disease, acute myocardial infarction, unstable angina, as well as weakened patients and patients elderly Patients at risk should check the initial concentrations of sodium, potassium, calcium, chloride, bicarbonate, phosphate, plasma urea nitrogen and creatinine, and should also check the concentration of these indicators after using the drug.
Electrolyte imbalance
There is a risk of increased serum sodium and phosphate levels, as well as decreased calcium and potassium levels; thus, hypernatremia, hyperphosphatemia, hypocalcemia, hypokalemia and acidosis may develop.
Rarely, prolongation of the QT interval on the electrocardiogram may be observed as a result of electrolyte imbalance such as hypocalcemia or hypokalemia.
These changes are not clinically significant.
Slowing down peristalsis
The drug should be used with caution in patients with disorders accompanied by decreased peristalsis, after surgery on the gastrointestinal tract, or with other medical conditions that slow down peristalsis. This drug should be used with caution in patients with a colostomy or ileostomy, or on a salt-free diet, as electrolyte imbalance, dehydration, or acid imbalance may develop.
Focal changes
During endoscopy, single or multiple aphthae-like changes were observed on the mucous membrane of the sigmoid and rectum. These were either lymphoid follicles, or discrete inflammatory formations, or changes in the epithelium caused by the preparation. These abnormalities are not clinically significant and resolve spontaneously without treatment.
Sodium content
One 45 ml dose of Phospho-soda contains 5 g of sodium. Therefore, the possibility of potential harm to the health of patients who are on a low sodium diet (salt-free diet) must be considered.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery.
Does not affect.