In recent years, perinatal neurologists have diagnosed about 85% of cases of blockage of cerebral arteries in babies, which is a serious pathology that requires urgent correction. Cerebral ischemia in newborns develops as a result of insufficient supply or complete cessation of oxygen supply to brain cells due to external and internal exposure to unfavorable factors. To prevent complications, it is necessary to begin treatment measures as early as possible. Therefore, expectant mothers should know how to recognize the first signs of pathology and what methods exist to eliminate it.
What is this pathology?
Cerebral ischemia in newborns is not an independent pathology, since its formation is simultaneously preceded by several pathological processes in the body. Thus, during the period of intrauterine development of the fetus, an acute oxygen deficiency may occur, as a result of which metabolic reactions in the brain are disrupted, which subsequently leads to its functional changes. These changes become the main cause of inhibition of neuronal activity, as well as the formation of local areas of necrosis.
The severity of the child’s condition and the risk of complications depend on the degree of hypoxia.
Diseases can manifest themselves throughout pregnancy or occur during childbirth. At the same time, early disruption of nervous regulation carries more serious complications for the development of the baby than later ones.
About prevention
To prevent the development of ischemic manifestations in the unborn baby, a woman must:
- Plan your pregnancy carefully.
- Undergo the necessary examination procedures during pregnancy.
- If required, take iron supplements as prescribed by your doctor.
- Completely give up bad habits.
- Do moderate exercise.
- Eat a balanced diet, follow your daily routine, and get plenty of rest.
- If the pregnancy is difficult, you should be treated in a hospital.
This is the only way to minimize the likelihood of cerebral ischemia in the child.
Reasons for development
The fundamental cause of the development of ischemia in children is insufficient oxygen supply to brain tissue as a result of circulatory disorders and ischemia, which are closely interrelated. As a rule, the causes of pathology are associated with pregnancy and childbirth, as well as factors influencing their course.
Premature babies lack automatic self-regulation of cerebral circulation
Experts identify the following reasons for the formation of the pathological process:
- Hypoxia caused by a disorder of placental circulation.
- Infection of the myocardium and vascular system of the fetus during intrauterine development.
- Anemic conditions of the mother during pregnancy.
- Chronic arterial hypotension in a pregnant woman.
- Prolonged compression of the umbilical artery during childbirth.
- Disorder of intrauterine circulation due to hereditary anomalies in fetal development.
- Prolonged or rapid process of delivery.
- Premature placental abruption.
- Entanglement or compression of the umbilical cord around the fetal neck.
Chronic respiratory failure of a woman leads to hypoxia of the baby even during the period of intrauterine formation
There is an increased risk of developing the disease if you have the following conditions:
- Injuries to the child's spine during labor. The risk of injury during childbirth is very often observed in women after 30 years of age, even with normal fetal development. There is a high probability of pathology in the presence of a narrow pelvis in a pregnant woman, strong labor accompanied by spasms, as well as the birth of a large baby.
- The condition of preeclampsia in the mother. It is observed against the background of diseases of the cardiovascular system, with changes in hormonal levels, and hereditary predisposition. The condition is accompanied by a sharp increase in blood pressure, fluid retention in tissues, and an increase in protein concentration in urine.
- Multiple births. The simultaneous development of several embryos requires significant oxygen reserves and its adequate redistribution.
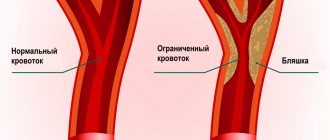
Cerebral ischemia in newborns occurs when there are disturbances in the circulatory system, as a result of which the lumen of the blood vessels narrows somewhat. As a result, a blood clot forms, which clogs the supply vessel, which leads to a lack of oxygen in the body.
Why does it occur
{banner_banstat1}
Hypoxic manifestations are observed if a woman is pregnant or during childbirth. Oxygen starvation is provoked by the following circumstances:
- The presence of infections in the body of a pregnant woman, dysfunction of the cardiovascular and endocrine systems, acute respiratory infections.
- When drinking alcoholic beverages, smoking.
- With late toxicosis, reduced volume of amniotic fluid, pregnancy of more than one fetus, late labor.
- Placental and umbilical cord pathology.
- If the baby is premature.
- In case of a difficult birth, which consists in the fact that the baby is entwined with the umbilical cord, the birth continues longer than expected due to a large fetus, trauma during childbirth and other problems of labor.
- The child’s mother is over 34 years old or under 18.
All these factors disrupt the blood flow between the placenta and the uterus, which is manifested by a hypoxic state.
Provoking factors
Obstetricians-gynecologists identify factors that increase the risk of developing HIE in newborns, including:
- The onset of the first pregnancy over the age of 35 and under 18.
- A long-term therapeutic course aimed at eliminating infertility.
- Incorrect placement of the fetus.
- Insufficient baby weight at birth.
- Trauma to the newborn's skull during childbirth.
- Performing an emergency caesarean section.
- Excessive blood loss during childbirth.
- The woman has a history of endocrine diseases, pathologies associated with the coagulation system.
- The occurrence of gestosis in late pregnancy.
A woman's history of diabetes mellitus is a risk factor for the development of fetal hypoxia.
Provoking factors in the development of pathology are also congenital defects of the hematopoietic system associated with anomalies in the formation of prothrombin genes, a vascular-platelet clotting factor.
Cardiac ischemia
Coronary heart disease is a chronic disease that occurs as a result of insufficient blood supply to the heart muscle. Cardiac ischemia occurs when the need of the heart muscle for oxygen does not correspond to the amount of oxygen delivered through the coronary arteries.
The occurrence of coronary heart disease is directly related to atherosclerosis of the coronary arteries , arterial spasm , which is sometimes provoked by certain medications and biologically active substances. Also, cardiac ischemia can occur due to increased blood viscosity and the formation of blood clots in the coronary arteries.
But still, the main cause of cardiac ischemia is atherosclerosis of the coronary arteries. The narrowing of blood vessels occurs due to the formation of plaques on their inner walls.
Mostly, coronary heart disease occurs in males of working age. Clinically, cardiac ischemia can manifest itself in different ways. Most often, this disease is characterized by the occurrence of angina pectoris . In this case, the patient may feel pain in the chest area. Painful sensations mainly occur during times of severe stress , or as a result of physical activity and are of a compressive nature. As cardiac ischemia develops, such attacks become more frequent over time. After all, when under load, the heart requires more oxygen to flow to it. myocardial ischemia may occur , manifested by compressive pain behind the sternum. Cardiac arrhythmia may also occur. Such attacks subside after taking Nitroglycerin . If the attack lasts about half an hour, then it is considered critical, because after some time some of the cells in the myocardium die, and, as a result, a person may develop a serious complication - myocardial infarction . Another form of cardiac ischemia is post-infarction cardiosclerosis . It is a consequence of a previous heart attack.
A complication of coronary heart disease can be heart failure. In this condition, the heart cannot function normally.
The diagnosis of “coronary heart disease” can be made using ECG data, as well as studies using radionuclide methods of studying the heart, echocardiography, daily ECG monitoring, etc. The coronary angiography method is used to detect atherosclerotic plaques.
Treatment of cardiac ischemia is always primarily aimed at normalizing blood flow through the coronary arteries. It is important to prevent all obstacles that interfere with the flow of oxygen and nutrients to the heart muscle.
Therefore, it is important to properly treat atherosclerosis, prevent the formation of blood clots, restore adequate blood supply to the heart muscle, and correct metabolic processes in the body.
To do this, it is necessary to take into account a number of factors that influence the deterioration of the condition. First of all, you need to fight obesity , lead an active lifestyle, follow a diet , giving up unhealthy foods.
As a rule, the doctor prescribes complex treatment, taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient and the course of the disease. When treating cardiac ischemia, medications are used that reduce the need for myocardial oxygen, drugs that prevent platelet aggregation, heparin , thrombolytics and other drugs.
Currently, surgical methods for the treatment of cardiac ischemia are used more and more often. Surgery is especially strongly recommended for patients with severe attacks of angina. The most noticeable effect is brought by surgical interventions aimed at restoring normal blood flow in the coronary artery. Among such operations are the creation of mammary-coronary anastomosis and coronary artery bypass grafting. An angioplasty technique is also used: a catheter with an inflatable balloon is inserted into the coronary artery, allowing the vessel to later expand.
Doctors also prescribe surgery for cardiac aneurysm that develops as a consequence of myocardial infarction. This surgery can prevent heart failure in the future. Sometimes during surgery, thrombotic masses in the aneurysm cavity are removed. All surgical interventions for cardiac ischemia are performed only in special clinics, and artificial circulation is used.
The most favorable prognosis for the treatment of this disease is provided that there are rare attacks of angina pectoris. If the patient has a recurrent heart attack and heart failure, the prognosis is less favorable.
As prevention methods, it is important to eliminate all factors that contribute to the development of coronary heart disease. You should follow a special diet that limits the consumption of foods high in animal fats, too sweet and salty foods. A very important step is to completely quit smoking. Regular exercise is recommended, and if the patient has arterial hypertension or diabetes mellitus , then these diseases must be treated correctly and on time. Patients with cardiac ischemia should be regularly monitored by their physician.
Development mechanism
Violation of the metabolism of brain cells during ischemia leads to irreversible processes of destruction of nerve structures and disruption of their activity. As a rule, the mechanism of formation of the pathological process is based on a rapid decrease in the level of adenosine triphosphoric acid, which is the main energy source in the body.
Impaired cerebral circulation creates favorable conditions for the formation of ischemia
For the full functioning of neurons, a balance is required between the concentration of intracellular and extracellular ions penetrating through the membranes. Long-term oxygen deficiency creates an imbalance of transmembrane components of the brain, which subsequently dramatically changes the concentration of potassium and sodium. This leads to a decrease in membrane potentials. In parallel with these processes, there is an increase in calcium levels, which allows the release of the neurotransmitter glutamate, which overstimulates brain receptors, thereby promoting structural and functional changes in the brain.
The body's first response to perinatal oxygen deficiency is to increase blood supply to the main organs. Subsequent arterial hypotension leads to a throughput decrease in cerebral blood flow.
Pathological changes in the brain in a newborn
Thus, the following stages are distinguished in the mechanism of development of pathology:
- Intrauterine oxygen deficiency.
- Decreased oxygen supply to the brain and increased carbon dioxide concentration.
- Increased acid-base environment in the fetus.
- Swelling of intracellular components.
- Increase in brain tissue volume.
- Local decrease in cerebral circulation.
- General cerebral edema.
- Increased level of cranial pressure.
- General blood flow disorders.
- Death of brain cells.
The mechanism of ischemia formation depends on the date of birth of the child, which is associated with age-related characteristics of the structure of the brain.
General information about cerebral ischemia
A disease in which blood circulation to the brain is reduced or completely stopped is called ischemia. The cause of the disorder is a pathological narrowing of the lumen of blood vessels, in which oxygen does not flow in the required volume. Lack of nutrition leads to malfunctions, which are expressed by general malaise and other symptoms.
Medicine has identified two forms of the disease:
- Focal
- in which tissue damage is localized in only one area. The cause is an embolism or blood clot that blocks the blood flow. - Global
- characterized by a decrease or cessation of blood circulation in several areas of the brain.
As a result of oxygen starvation of tissues, ischemia develops. With early diagnosis, complications of the disease can be avoided.
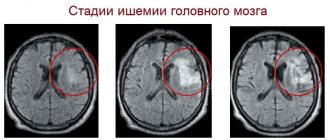
Degrees of impairment
The severity of clinical symptoms, the direction of the therapeutic course, as well as the number of complications depend on the degree of brain disorders.
Functional and structural changes of the brain at different stages of the pathological process
There are three degrees of severity of cerebral ischemia, which have different intensity of manifestations:
- Easy. It is temporary, since after stabilization of the nervous system, ischemic disorders occur without neurological consequences. The condition is characterized by a slight increase in the concentration of carbon dioxide and a decrease in the oxygen saturation of the body. The activation of compensatory mechanisms is observed when the oxygen deficiency is replenished by increasing blood flow.
- Moderately heavy. Intrauterine hypoxia provokes an abnormal heart rhythm, leading to the development of asphyxia, which lasts about 60 seconds after birth. The condition manifests itself as periods of excitement, abruptly alternating with depression of the nervous system. Convulsive seizures of a short-term nature are observed.
- Heavy. It is formed as a result of a violation of intrauterine circulation, when an insufficient amount of nutrients and oxygen reaches the fetus. After birth, the child experiences a decrease in brain activity, progressing to a coma. An increase in intracranial pressure leads to inhibition of the respiratory and cardiac systems, as well as to a disorder of metabolic reactions.
How complications are treated
{banner_banstat5}
Encephalopathic manifestations of severe and moderate forms often result in persistent brain symptoms. It may manifest itself mildly or the baby may become disabled. With any prognosis of encephalopathic changes, there are restrictions on the use of drugs:
- Antiepileptic drugs for seizures.
- Muscle relaxants for severe cerebral palsy.
In order for a baby with ischemic complications to develop correctly, you need to regularly work with him:
- If a child has cerebral palsy, then he needs a special massage technique, which should be performed by a specialist at least in the early stages.
- Older children require exercise therapy.
- Special mechanisms are needed to adjust the correct posture. With spastic changes due to incorrect position, they intensify, which will lead to an unfavorable outcome. With the help of strollers, splints, bolsters, and special chairs, the most acceptable, physiological position of the body is ensured.
- The speech therapist will correct the baby’s speech, teach him to be attentive and assiduous.
Features of pathology in full-term and premature infants
The nature of damage to the anatomical structures of the brain during hypoxia or asphyxia depends on the gestational age. Thus, at the birth of a premature baby, there is a risk of developing periventricular leukomalacia. With this disease, damage to the white matter occurs with the further formation of foci of necrosis. Children born before 31 obstetric weeks are susceptible to pathology.
In full-term infants, the gray matter is predominantly affected. The degree of complications depends on the extent of the disorder and the anatomical location of the neurons. In the case of severe, acutely developing hypoxia, pathological changes are observed in the area of the brain stem, which coordinates the work of the heart and breathing. Deviations can cause dire consequences and cause irreparable harm to the baby’s health.
Date of birth and cerebral ischemia
{banner_banstat2}
Manifestations of brain disorders during asphyxial conditions in children who were born on time and in premature infants differ. If the baby is born ahead of schedule (if the pregnancy is less than 31 weeks), then there is a possibility that he will develop necrotic changes in the white brain matter.
In the area of cellular necrosis, cystic changes form, which in many cases leads to cerebral palsy, and the child becomes weak-minded.
When a baby is full-term, he or she has damage to the cortical medulla (gray matter). The consequences depend on the number and location of the defective nerve cells. In acute and severe asphyxial conditions, the cerebral trunk, which is responsible for the respiratory function and rhythmic activity of the heart, is damaged. Such consequences threaten the child’s life.
Symptoms
The clinical picture of cerebral ischemia in infants is determined by the intensity of symptoms, the location of neuronal damage and the severity. The first signs of pathology can be determined by assessing reflex activity, taking into account the physiological maturity of the baby.
A characteristic sign of pathology is excitation of the central nervous system
The first degree disease is manifested by the following symptoms:
- muscle tone disorder;
- involuntary contractions of the lower and upper extremities;
- shallow restless sleep;
- constant crying and screaming;
- strengthening reflexes.
In prematurely born children, the course of the disease is dominated by depression of the nervous system, which is manifested by a decrease in basic reflexes, a decrease in motor activity and lethargy.
At the second stage, the following symptoms are distinguished:
- weakness of the baby during feeding;
- frequent regurgitation;
- disturbances in intestinal function;
- interruptions in the functioning of the myocardium;
- stopping breathing during sleep;
- local cyanosis of the skin;
- decreased reaction of the pupils to a light stimulus;
- sluggish sucking reflex;
- decreased muscle tone;
- constant shuddering of the child;
- convulsive seizures.
A newborn's skin takes on a marbled color.
In severe condition of the child, the appearance of nystagmus, strabismus, vomiting, complete cyanosis of the skin, and arrhythmia are observed.
The third stage of the disease is characterized by the following symptoms:
- lack of basic reflexes;
- convulsive seizures, long-term, at frequent intervals;
- cramps are replaced by a decrease in muscle tone;
- state of complete immobilization;
- respiratory dysfunction;
- decreased heart rate;
- pupils are dilated and do not respond to light;
- increased intracranial pressure;
- decreased blood pressure;
- sluggish bowel activity;
- lack of urination.
The extreme degree of brain damage is manifested by severe depression of the central nervous system, up to the development of coma.
Classification of pathology
According to the time of appearance there are:
- Ischemia of the central nervous system in newborns, which appears during embryonic and natal development. Clinical signs appear in the first few days of life. In 70% of cases, the appearance of symptoms is observed during childbirth or gestation, especially characteristic in the last stages.
- The chronic type appears in adults and older people. It occurs especially often among pensioners. May lead to ischemic stroke.
Ischemic diseases of newborns are divided into 3 stages. Hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy grade 1 is the mildest form of neurological disease of the central nervous system. It is characterized by mild symptoms that appear 3-5 days after birth.
The most characteristic manifestations:
- severe nervous excitement or depression;
- the muscular system is constantly tense;
- tendon reflexes are strengthened.
With this form, it is not necessary to place the patient in a hospital. The disease goes away with time.
Cerebral ischemia of the 2nd degree in a newborn manifests itself in the first day of the child’s life. Symptoms usually appear within a month. Obligatory requirement is supervision by a doctor. During your stay in the hospital, therapeutic measures are required. If the pathological condition of the central nervous system is caused by blockage of blood vessels with a blood clot, surgical intervention may be required.
Hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy grade 3 in newborns is considered the most severe. Characteristic manifestations:
- lack of reflex activity;
- coma;
- problems with heart rhythm;
- severe hypertension;
- impossibility of normal functioning of the respiratory system;
- problems with oculomotor function.
Upon consultation with a specialist, the presence of severe symptoms can be determined within a few minutes after birth. The patient is necessarily sent to intensive care. If the baby has problems with independent breathing, then connection to an artificial life support apparatus is required. The phenomena are often observed in prematurity.
Assessing the degree of complications
Ischemic disorders provoked by oxygen deficiency lead to the death of brain cells, which creates conditions for the formation of irreversible neurological disorders, the severity of which depends on the localization of structural changes.
As a rule, cells located in the pyramidal zone, cerebellar cells, ventrolateral neurons, midbrain nuclei, and stem neurons are affected.
With large-scale ischemic damage to brain cells, their complete death occurs, which leads to death.
The most common complications are decreased memory and mental performance
The consequences of ischemic disorder include the development of the following conditions:
- epilepsy;
- one-sided blindness;
- impaired mental function;
- motor function disorder.
Full assessment of complications occurs at the age of 3 years.
Consequences and how dangerous the pathology is
When the diagnosis itself is made in a timely manner and treatment is prescribed, then, as the doctors themselves note, 5 of the patients have every chance of a successful, full recovery.
Other patients who have had this disease may experience in the future:
- frequent headaches and fatigue;
- poor memory;
- the likelihood of frequent attacks of convulsive spasms, especially at high body or environmental temperatures.
That is why children are not recommended to stay in the sun, live in hot climate zones, excessive stress, or great mental and physical stress.
If there is focal, atrophic damage to certain areas of the brain, the patient’s condition will be more serious.
The most common negative consequences of the pathology suffered are:
- frequent attacks of headaches and dizziness;
- sleep problems and increased excitability and irritability;
- the child’s inability to remember basic things and concentrate on one task, even the simplest action;
- frequent attacks of epilepsy;
- mental retardation;
- mental abnormalities.
In the most advanced cases, a small patient may develop cerebral palsy of varying severity, ranging from partial dysfunction in the musculoskeletal system to complete immobility of the patient. We wrote in more detail about the causes of cerebral palsy in another article.
But the child grows, and his cells divide, and due to a correctly selected course of treatment, mild manifestations of the pathology disappear - the baby, as they say, outgrows his illness, and when the second and third degrees of pathology are diagnosed, the negative symptoms will weaken.
Severe consequences are determined not only by the diagnosis of one or another degree of development of cerebral ischemia, but also by the presence of concomitant pathologies.
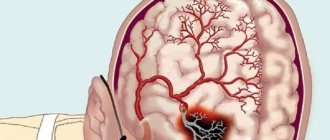
The main negative factors that develop when diagnosing this disease are hypoxia and metabolic failure. They are the ones that can provoke diseases such as ischemic stroke or heart attack, as well as sclerosis of the vascular network of the brain, paralysis and muteness, epilepsy and thrombophlebitis.
Diagnostic criteria
The initial diagnosis consists of examining the child and assessing his condition using the Apgar scale.
Determination of pH of venous blood to detect acidosis
Examination of a newborn includes the following studies:
- Blood test (reduced oxygen concentration).
- Neurosanography.
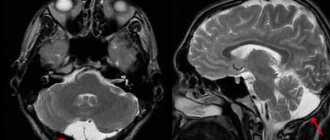
- CT scan.
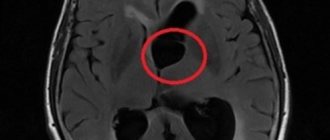
- Magnetic resonance imaging.
- Doppler encephalogram.
Diagnosis of cerebral ischemia
To identify a dangerous disease, neurologists use an integrated approach to diagnosis. During the examination, the doctor collects anamnesis and conducts a primary examination, for example, a finger-nose test. To do this, the patient is asked to stand up, align his legs shoulder-width apart, spread his arms to the sides, bending them at an angle of 90 degrees, and close his eyes. Next, the patient should touch the tip of the nose with the index finger. With developing ischemia, contact between the two surfaces will not occur, and the missed finger will certainly point in the direction of the damaged lobe.
In addition to the finger-nose test, the doctor will examine other abilities of the patient, such as facial expressions, pupil reaction, facial symmetry, clarity of speech and coordination. Along with the examination, the necessary tests are additionally collected:
- Blood pressure is measured in a doctor's office.
- Detection of vascular lesions of the fundus is carried out by an ophthalmologist.
- Undergoing electrocardiography for correct diagnosis.
- Dopplerography of blood vessels is mandatory.
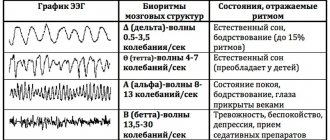
- Electroencephalography reveals inactive areas of the brain.
- CT (computed tomography), MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) perform an in-depth examination.
- A biochemical blood test evaluates cholesterol levels.
Doctors use differential diagnostic methods, since the symptoms of the pathology are similar to the manifestations of other diseases of an infectious, allergic, neurological and oncological nature.
Treatment methods
Treatment at the initial stage of pathology requires the following measures:
- Resuscitation techniques (artificial ventilation, normalization of hemodynamic parameters).
- Maintaining temperature conditions (for several days the child is kept in a state of hypothermia with gradual normalization of temperature).
- Conservative therapy aimed at eliminating pathological symptoms.
- Convulsive seizures are stopped by the administration of anticonvulsants (Phenytoin, Trimethine).
- For muscle hypertonicity, muscle relaxants (Mydocalm) are administered.
- To activate the functional abilities of the brain, nootropic drugs (Piracetam, Ceraxon) are prescribed.
In parallel, vitamin therapy is carried out, including the use of vitamins B6 and B12, which are administered with a glucose solution.
Symptoms of cerebral aneurysm
Symptoms of a brain aneurysm usually only appear when it breaks or leaks and when it presses on an area of the brain, but this is rare because the aneurysm must be quite large.
The symptoms of the disorder are similar to those of a hemorrhagic stroke.
But in most cases, an aneurysm is silent, and so it is usually diagnosed during tests when other diseases are being looked for. However, the symptoms when it ruptures are:
Headache
When a brain aneurysm ruptures, it causes a very severe headache, and many surviving patients have reported that it was the worst headache of their life.
It is often called a “thunder headache” because it is extremely severe, sudden and instantly reaches its peak pain and can even cause imbalance and fall.
Headache associated with an aneurysm is not always a thunderstorm, but it is common.
Sensitivity to light
Greater sensitivity to light may occur soon after the pain. The stronger the sensitivity, the more severe the aneurysm.
Fatigue
Lethargy, or fatigue, is a common symptom when an aneurysm ruptures and should be addressed as it can worsen and lead to coma. Like light sensitivity, the stronger the symptom, the more serious the condition.
Stiff neck
Like meningitis, a cerebral aneurysm can cause a stiff neck. This occurs because blood flowing through the artery accumulates in the area and increases intracranial pressure.
Seizures
As a result of a cerebral hemorrhage, seizures can occur, which is abnormal electrical activity in the brain, as neuronal damage caused by blood in the region can lead to electrical problems.
Confusion
Brain damage caused by blood may manifest as severe confusion
It is important that the patient goes to hospital for emergency treatment as soon as possible
Neurological problems
Difficulty speaking, moving, paralysis of certain areas of the body, and other neurological problems can occur after a ruptured aneurysm caused by damage to blood in the brain.