Cerebral ischemia is characterized by partial blockage and narrowing of blood vessels in the head, most often due to atherosclerotic deposits. Damaged vessels are not able to pass a normal volume of blood, so the brain tissue does not receive the required amount of oxygen and nutrients. Over time, a person notices memory loss, deterioration in performance, sleep problems against the background of chronic fatigue. These alarming symptoms should be a reason to visit a qualified physician. Otherwise, the patient may risk stroke, memory loss and disability.
General information about cerebral ischemia
Ischemia is a deterioration in the blood supply to organs and tissues due to impaired blood flow as a result of narrowing of vascular channels.
There are acute (stroke) and chronic forms of ischemia. About 90% of brain pathologies associated with blood vessels are related to chronic ischemia. The disease is common and has a high degree of disability. Pathology requires professional consultation and treatment. The brain requires more oxygen consumption than other organs. This is due to intense metabolism and accelerated metabolism. When blood supply deteriorates, less oxygen, red blood cells, and glucose enter the brain, its metabolism is disrupted, and hypoxia develops.
As a result, blood stasis occurs, a tendency to blood clots appears, and neurotoxins are produced. These processes provoke cell death. In the chronic form of the disease, the white matter is affected, and connections between the subcortex and frontal lobes are disrupted. Such changes, if left untreated, contribute to the development of dementia. In the chronic form of ischemia, an increase in intellectual-mnestic deficit is observed. At the initial stage, the patient experiences anxiety and depression. Further development of the disease leads to maladaptation in the social and everyday environment.
Treatment is aimed at improving blood circulation, metabolism, eliminating hypoxia, which helps reduce clinical manifestations and preserve brain tissue.
Read also
Transient ischemic attack (TIA)
What it is?
Why is this happening? Is this condition dangerous? What to do if doctors make such a diagnosis? These questions are always asked by patients who come to see a neurologist. According to the classification... Read more
Atherosclerosis
What is atherosclerosis Atherosclerosis is a narrowing of the arteries caused by the formation of plaque. As a person gets older, fat and cholesterol can accumulate in the arteries and form plaque. Accumulation…
More details
Encephalopathy
These can range from minor abnormalities in brain function to serious neurological disorders that require urgent treatment. Encephalopathy can be congenital or acquired. Congenital...
More details
Swelling of the legs
Causes of Swelling in the Legs The legs are common sites for swelling due to the effect of gravity on the fluids in the human body. However, fluid retention is not the only cause of leg swelling. Injuries...
More details
Hemorrhagic stroke
Hemorrhagic stroke is a type of acute cerebrovascular accident, which is characterized by the effusion of blood into the brain substance with the development of neurological deficit, often leading...
More details
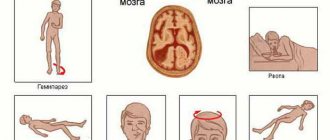
Symptoms of cerebral ischemia
Symptoms of cerebral ischemia may occur periodically. There is a gradual deterioration in the patient's condition and progression of dementia.
Ischemia is manifested by the following symptoms:
- memory impairment;
- irritability;
- constant fatigue;
- sudden change in mood;
- inability to control emotions;
- slow thinking;
- loss of consciousness;
- failure of sleep mode;
- apathy;
- frequent headaches;
- blood pressure above or below normal;
- forgetfulness;
- inadequate reactions to events;
- marble skin tone;
- the appearance of new moles;
- involuntary muscle contraction.
In the last stage, it is difficult for the patient to provide self-care.
Folk remedies
Photo: veronikaa.ru
Therapy for chronic cerebral ischemia lasts for years; doctors often combine methods of traditional and alternative medicine. Folk remedies must be used in combination with pharmacological drugs. Before use, you should consult a neurologist and cardiologist.
Many plants have anti-sclerotic and antioxidant properties, that is, they help reduce the risk of cholesterol plaques and help restore the function of blood vessels. Nonea dark herb, motherwort, mint, dill seeds and thyme thin the blood. All components must be mixed in equal proportions, pour 2 tablespoons of the mixture with half a liter of boiling water and leave. Take, strain, 100 ml three times a day 30 minutes before meals. The course of therapy is 3 weeks.
To speed up the restoration of cerebral circulation, you need to take an infusion of Galega officinalis. Pour two cups of boiling water over the grass and seeds (15 grams), leave for several hours and strain. Drink 100 ml twice a day before meals. An infusion of sweet clover has similar properties. The method of preparation and administration is similar. The course of treatment is 2 weeks. You can repeat it after 10 days.
The information is for reference only and is not a guide to action. Do not self-medicate. At the first symptoms of the disease, consult a doctor.
SEARCH FOR TREATMENT AROUND THE WORLD WITH YELLMED
Causes
The main cause of the development of pathology is atherosclerosis. Fat deposits accumulate on the walls of blood vessels, which leads to a narrowing of the lumen. In addition, the following factors provoke cerebral ischemia are identified:
- heredity;
- heart rhythm disturbances;
- squeezing of blood vessels;
- elevated blood sugar levels;
- diabetes;
- pathologies of the circulatory system;
- changes in blood pressure;
- vasculitis;
- heart pathologies, myocardial infarction;
- taking narcotic drugs;
- thrombosis;
- undergone operations;
- difficult or premature birth;
- abnormalities in the structure of blood vessels;
- pathologies of the central nervous system (CNS);
- severe toxicosis during pregnancy;
- renal ischemia;
- excess weight;
- influence of toxic gases;
- brain tumors (malignant and benign).
Bad habits - smoking, drinking alcohol - have a negative impact on the blood supply to organs. Age-related changes can also contribute to the development of the disease. Elderly people are more susceptible to cerebral ischemia.
Prognosis, disease prevention
If the dynamics of chronic cerebral ischemia are suspected, timely diagnosis and the prescription of adequate drug therapy are important. The course of the disease is significantly worsened by the presence of concomitant pathological conditions - hypertension, diabetes mellitus. In severe clinical cases, the patient may become disabled.
Prevention consists of preventing the development of ischemic factors. Risk factors include: obesity, sedentary lifestyle, smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, frequent stressful situations.
Stages of development and types of cerebral ischemia
The disease develops in stages. There are several stages:
- First stage. It manifests itself as a deterioration in the quality of sleep, mood swings, and a feeling of constant fatigue and heaviness. Symptoms are nonspecific, which complicates the diagnosis of pathology at an early stage.
- Second stage. A disturbance in the functioning of the central nervous system occurs, the patient experiences dizziness, memory loss, coordination of movements, and gait are impaired. Mental work becomes impossible.
- Last stage. Significant neurological impairment is present. The disease manifests itself as loss of ability to work and the ability to care for oneself. Fainting occurs, the patient cannot independently describe his condition.
The form of cerebral ischemia is:
- Spicy.
It manifests itself as a sudden disruption of the blood supply to the brain. The patient experiences severe dizziness and muscle weakness. - Chronic.
Gradually progresses in the absence of therapy. Changes occur as a result of hypoxia. Symptoms appear periodically, and the arteries gradually wear out.
By localization and distribution they are divided:
- Focal.
Develops when a blood clot appears. Leads to the death of cells of the vascular canal. - Global.
Remission occurs when there is a drop in blood pressure or cardiac arrest.
Diagnostics
Photo: uclinic.kymu.edu.ua
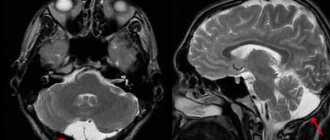
Determining chronic cerebral ischemia requires an integrated approach when examining patients. In addition to the neurologist, related specialists are included in the process: a clinical psychologist, a functional diagnostics doctor, a cardiologist, and a therapist. The difficulty of making a diagnosis lies in the fact that in the early stages the disease manifests itself as subtle deviations in nervous activity, and imaging studies (CT, MRI) do not detect any changes.
Diagnosis of CCI consists of the following procedures:
- Questioning, anamnesis collection. Complaints from the patient and his relatives, as a rule, indicate a cognitive deficit: forgetfulness, absent-mindedness, fatigue when performing usual work. For example, the patient cannot remember a new name and has difficulty counting. Moderate and severe cognitive changes are more noticeable, as they lead to difficulties in performing everyday functions. There are also many nonspecific complaints: headache, insomnia, dizziness. Assuming vascular pathology, the neurologist determines the presence of arterial hypertension, heart disease, and disorders of glycemic control.
- Neurological examination. Vascular cognitive disorders are always accompanied by changes in neurological status. Most often, the patient’s gait is disturbed; upon examination, it is slow and unsteady, difficulties in starting to walk and turning, and shuffling. It appears that the patient is walking very carefully so as not to fall. Tests for the integrity of reflexes also reveal a number of disorders (pyramidal, pseudobulbar, discoordination).
- Neuropsychological testing. A clinical psychologist determines a decrease in intellectual abilities in comparison with the norm and assesses the severity of cognitive disorders. Tests and tests are used to study intelligence, thinking, memory, attention, speech, writing, counting and spatial orientation. Common techniques are the Mini-Cog test, the Montreal Cognitive Function Rating Scale. The more advanced the stage of CCI, the greater the decline in cognitive function and writing and numeracy skills.
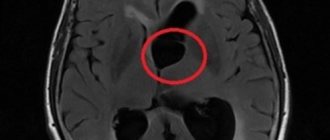
- Imaging studies. To confirm the vascular nature of existing neurological and cognitive disorders, neuroimaging diagnostic methods are used - CT and MRI of the brain. The results are characterized by a decrease in the density of white matter, especially in the area of the anterior horns of the lateral ventricles, multiple small post-infarction foci in the subcortical ganglia and white matter, and dilated ventricles of the brain. However, structural changes in the brain take a very long time to develop and do not always correlate with the severity of CCI symptoms.
Diagnosis of ischemia
The first priority is to take a history and examine the patient. A hardware examination and collection of analyzes are also carried out:
- Ultrasound Dopplerography of the vessels of the cervical spine and head;
- MRI;
- magnetic resonance angiography;
- CT;
- ophthalmoscopy (to examine the fundus);
- ECG (to identify pathologies of the cardiovascular system);
- blood chemistry.
If cognitive impairment is detected, neuropsychological testing is necessary. Using Doppler ultrasound, it is possible to detect atherosclerotic plaques and differentiate them. In addition, the study helps to determine arterial stenosis, their changes, and cerebral vascular spasms. To study cerebral vessels, triplex scanning and color duplex scanning are also used. Using MRI, “silent” infarctions, enlarged ventricles of the brain, and changes causing cortical atrophy are determined.
Prognosis and prevention
The consequences of cerebral vascular ischemia can be minimized if you consult a qualified doctor in a timely manner. This should be done when symptoms of the 1st degree of complexity appear. At this stage, preventive actions are sufficient:
- maintaining physical activity;
- nutrition correction;
- abstaining from nervous stress.
Even with symptoms of the 2nd degree of severity, the prognosis is positive, provided the patient follows all the doctor’s prescriptions. Seeking help at the 3rd stage of the disease is in most cases ineffective.
Treatment
The main task in the treatment of cerebral ischemia is to normalize cerebral circulation. It is necessary to improve blood circulation and tissue metabolism. Drug therapy is aimed at the main links of pathogenesis. Patients are prescribed a course of drugs with different principles of action:
- neurometabolic;
- vasoactive;
- antiplatelet agents.
In addition to taking medications, it is necessary to eliminate risk factors such as arterial hypertension, atherosclerosis and others. Correction of nutrition and lifestyle is necessary. If blood pressure is high, antihypertensive medications are prescribed. For a complex effect on the central nervous system, nootropic drugs are prescribed. In the treatment of cerebral ischemia, antioxidant agents are of great importance. To improve reparative functions, drugs that have a metabolic effect are used.
In case of established cerebral ischemia, as a complex drug therapy, the doctor may prescribe: antihypertensive medications to control blood pressure (amlodipine, atenolol, anaprilin, enalapril, etc.). Attention! All medications prescribed by a doctor should be taken under control. There are contraindications.
What to do if MRI shows chronic ischemia?
If, when decoding the results of a head scan, the presence of ischemic brain disease is detected, it is recommended to consult a neurologist. You may need to consult a therapist or cardiologist. To slow the progression of ischemic damage, it is necessary to achieve target levels of blood pressure, blood glucose and cholesterol levels. Doctors will evaluate metabolic changes and select treatment to compensate for chronic diseases.
The diagnostic department performs MRI of the brain from 2,690 rubles. Contrasting is carried out from the age of 12. You can ask the administrator any questions you may have by calling +7 (812) 407-32-31.
Treatment of cerebral ischemia in the elderly
The treatment plan takes into account the existing pathologies of the elderly patient. The set of activities includes:
- Taking anti-sclerotic drugs. Recommended for hyperlipidemia not corrected by diet. Provides improvement of lipid metabolism, prevents neurodegenerative changes.
- Taking antihypertensive drugs. Antihypertensive drugs and blood pressure control are the main measures to prevent manifestations of ischemia. However, with a long history of high blood pressure, its normalization can aggravate chronic pathology and cause an increase in cognitive impairment of the “frontal” type.
- Use of antiplatelet agents. Necessary for severe atherosclerosis of the vessels of the head, for diagnosing disorders of the rheological properties of blood.
- Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors. They have an effective effect on cognitive disorders.
- Membrane protectors. Improves intellectual and mnestic functions. After taking a course of drugs, improvement in memory and communication is observed.
- Antidepressants. Prescribed for severe astheno-depressive disorders.
Complications
The lack of an effective treatment plan leads to a long-term lack of oxygen supply to the brain. This can provoke:
- stroke;
- necrotic changes in brain cells;
- epileptic seizures accompanied by fainting;
- inflammation of the veins of the lower extremities, the appearance of blood clots;
- atherosclerotic changes in blood vessels;
- paralysis.
In addition, sensitivity is impaired, and pain becomes chronic. The patient develops a depressive syndrome.