Chronic kidney disease affects 10% of the world's population, and among the causes of death, kidney problems occupy 4th place after heart attack, stroke and diabetes. In the CIS countries, half of the patients die without waiting for a kidney transplant, and of the remaining 50% do not have the opportunity to receive hemodialysis.
Cost of urologist services in our clinic
| Initial consultation with a doctor with the highest category | 1000 rub. |
| Consultative appointment with a doctor based on test results and ultrasound results | 500 rub. |
| Ultrasound of the kidneys in standard mode and using Doppler techniques | 1200 rub. |
| Ultrasound of the bladder | 500 rub. |
| Ultrasound of the pelvis using Doppler techniques | 1200 rub. |
| Make an appointment by phone: 8-800-707-15-60 (toll-free) | |
| *The clinic is licensed to remove tumors |
High-quality treatment of severe pathologies prolongs the patient’s life by 20-30 years, but it is only available to the population of developed countries with high income levels. Chronic kidney disease is irreversible and patients require treatment for the rest of their lives.
What are the common congenital kidney pathologies?
The content of the article
According to statistics, in 70% of cases, serious kidney diseases are congenital or genetic. In the remaining 30%, kidney disease is caused by various external and internal causes. Congenital pathologies are caused by impaired development of the embryo in the early stages (up to 6 weeks), when the formation of internal organs occurs. Under the influence of negative factors (taking medications, ionizing radiation, toxic poisoning), the neural tube develops incorrectly, as a result of which the kidneys are formed with impaired functionality. Congenital pathologies are divided into 4 groups:
Anatomical abnormalities
They occur in various forms in 2.5% of infants. The most common is agenesis (absence of one or both kidneys) or aplasia (underdevelopment of the organ with complete loss of its functions). Agenesis is more often detected in female infants, mainly affecting the right kidney.
It is much worse if there is no left-sided organ, which is more functional than the right and is more adapted to compensatory function. Also, in 7-11% of cases, kidney doubling is diagnosed - complete or partial division of the organ, which does not in any way affect the functioning of the organ, but tends to provoke other genitourinary diseases.
Changes in tissue structure
Changes in the pyelocaliceal system, parenchyma, sinuses, and also the body of the kidney are mainly observed. These pathologies are rarely detected immediately after birth, because the newborn has enlarged renal pelvis for some time, which remove metabolic products accumulated during fetal development. Basically, changes in the structure of the kidney tissue are detected during an ultrasound examination.
Kidney failure
This is an extremely dangerous congenital disease in which the death of nephrons occurs - the structural units of the kidney through which filtration is carried out. In place of the dead nephrons, the parenchyma, a kind of sponge that filters liquid, is formed. As a result, the kidney dies and loses its ability to remove toxins.
In children, as in adults, acute renal failure leads to a sharp deterioration in well-being. After some time, the child falls into a uremic coma. In the absence of emergency assistance, the death of the body occurs. In adults, organ failure occurs against the background of polycystic disease, acute glomerulonephritis (pathological activation of the immune system when an infection enters the kidney), arterial thrombosis.
Pathological changes caused by genetic mutations
Hereditary nephropathy is a kidney disease caused by a gene mutation, which is the cause of 9% of congenital diseases of the organ. Thus, with Alport syndrome, the gene responsible for the structure of collagen in the membrane of the renal tubules, inner ear and eye is affected.
The mutation mainly occurs in boys. The disease leads to loss of function of the kidneys, vision and hearing. Chromosomal abnormalities are accompanied by multiple developmental defects.
Most often, kidney pathologies occur with trisomy of chromosome 21, partial loss of a link of chromosome 18, etc. Congenital anomalies of the organ include a horseshoe shape, displacement, hypoplasia or enlargement of the ureter, as well as multicystic disease.
Why do you need to have your kidneys examined?
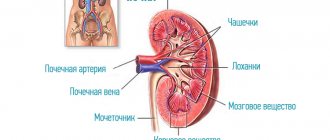
The kidneys are an organ of the urinary system that performs many important functions:
- removes excess fluid, organic and inorganic substances, harmful and toxic compounds from the body;
- secretes the enzyme renin, necessary to maintain normal blood pressure;
- produces the hormone erythropoietin, which controls erythropoiesis - the process of formation of red blood cells;
- maintains a constant composition and pH of the blood;
- participates in metabolism.
However, with kidney diseases, the functionality of the organ decreases, which leads to a change in the normal composition of the blood, intoxication of the body and other pathological conditions. Without timely diagnosis, many nephrological diseases lead to end-stage chronic renal failure, a life-threatening condition that requires replacement therapy in the form of hemodialysis or kidney transplantation.
To diagnose kidney dysfunction, there are special laboratory tests:
- biochemical blood test for certain indicators that reflect the functional state of the kidneys;
- determination of glomerular filtration rate (GFR), Rehberg test;
- urine tests - general urine test, microalbuminuria test, Zimnitsky test, Nechiporenko urine test.
Where do acquired kidney diseases come from?
The kidneys bear a tremendous burden. In an adult, they pass about 120-200 liters of fluid daily. The organ has a large margin of safety, is resistant to infections and inflammation, but sometimes a person, unknowingly, causes harm and disrupts the functioning of the kidneys.
Many diseases are asymptomatic, so preventive medical examinations should not be ignored even if you feel well. Pain syndrome appears much later, when the disease becomes chronic and changes the functional abilities of the organ. Drugs cause a serious blow to kidney health. This is especially true for self-medication, when the patient takes medications on his own without first consulting a doctor.
According to statistics, only 40% of people with respiratory viral diseases go to medical institutions, and then mainly to apply for sick leave. The remaining 60% self-medicate based on the advice of friends and online recommendations.
However, a number of medications provoke the development of kidney diseases in a completely healthy person. Moreover, these are not some special drugs, but tablets that are available in every person’s home medicine cabinet.
Drugs that kill kidneys
Potentially dangerous drugs include the following: 1. Analgesics , especially those based on acetylsalicylic acid and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Ibuprofen, Aspirin, Diclofenac). They are used to relieve pain and reduce fever. They contain codeine, a semi-synthetic substance extracted from morphine.
The component is highly soluble in both water and alcohol, so painkillers are available in the form of effervescent tablets, capsules, mixtures, ointments and gels.
Codeine affects the nervous system and smooth muscles like morphine, only ten times weaker. Thus, codeine suppresses the excitability of the parts of the nervous system responsible for cough, and also activates the anticicertic part of the nervous system, as a result of which pain is suppressed.
Thanks to drugs containing codeine, smooth muscles relax and peristalsis decreases. However, analgesics and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs have an extremely negative effect on the kidneys. The parenchyma contracts and calcifies, causing disruption of the structure of the renal tissue.
Long-term uncontrolled treatment leads to the appearance of a large lesion caused by exposure to the active substance. For this reason, after treatment of ARVI, bronchitis, pneumonia, as well as frequent use of analgesics, you should definitely check your kidneys. Changes at the initial stage can be prevented by maintaining kidney functionality. 2. Antibiotics (Methicillin, Ciprofloxacin). They help the body overcome pathogenic bacteria, but they have a significant negative property - nephrotoxicity. This is the ability of certain substances to interact with the kidney parenchyma and change its structure.
Hemodynamics change (blood pressure inside the kidney), hemolysis (breakdown of red blood cells with the release of hemoglobin), and acid balance inside the organ change.
Penicillin-based drugs cause inflammation of the glomeruli. Antibiotics interfere with renal circulation, causing ischemia of the organ.
Aminoglycosides (Gentamicin-K, Streptomycin) are highly effective in the fight against gram-negative microorganisms (chlamydia, gonococci, spirochetes), but in combination with diuretics (diuretics) they cause kidney failure and are fatal. 3. Antiviral drugs (Acyclovir, Tenofovir). They are used in the treatment of herpes, HPV, AIDS, and other viral diseases. However, the active substances are extremely difficult to remove from the kidneys, so taking antiviral medications should be accompanied by drinking plenty of water. Drugs that lower blood pressure (Amlodipine, Torsemide, Captopril, Atenolol). Drugs for hypertension lead to vasodilation, and this in turn leads to the expansion of efferent arterioles - small arteries located in the walls of smooth muscles. This leads to an increase in intrarenal pressure.
Long-term use of large amounts of drugs for high blood pressure leads to kidney infarction and complete damage to the organ. 4. Psychotropic drugs . They affect the brain and central nervous system, and the situation is aggravated by the need for lifelong medication for mental disorders. People with this problem need to have their kidneys checked regularly, because psychotropics provoke the formation of cysts in the kidneys.
Anticonvulsants can also cause chronic urinary tract disease.
Causes of poor kidney function
The causes of kidney problems can be different:
- Impaired blood supply. Urine is formed as a result of glomerular filtration. In this case, water with substances dissolved in it comes from the blood. If the pressure drops, then not enough blood flows to the kidneys and urine production is reduced. Blood pressure may drop due to injury, heart attack, bleeding, septic shock, or anaphylactic shock. The condition is acute and requires immediate response.
- Damage to the renal parenchyma. We are talking about the tissue that covers the surface of the kidneys. The outer layer is the glomeruli that filter the blood, the inner layer is the tubules through which the fluid passes before entering the calyces and pelvis. Here the necessary substances enter the blood, that is, readsorption occurs. Thus, when the parenchyma is damaged, a disturbance occurs in the processes of filtration and readsorption. How can parenchyma be damaged? With nephritis, pyelonephritis, glomeruloneritis, urolithiasis, the parenchyma can degenerate into connective tissue. As a result, function is impaired and kidney failure occurs. Such a process will not be acute, but chronic. If the parenchyma is damaged due to injury, kidney infarction, then renal failure will be acute.
- Obstruction of the urinary tract. Due to various processes, obstruction of the ureters, that is, their obstruction, can occur. As a result, the outflow of urine from the kidneys is disrupted. Obstruction can be caused by obstruction by a calculus, that is, a stone, hematoma, or as a result of compression by a tumor. Usually the blockage occurs in one ureter.
Pyelonephritis: who does it threaten and who is at risk?
Pyelonephritis is an inflammation of the kidney parenchyma caused by the activity of pathogenic bacteria. The disease affects the entire pelvicalyceal region, it has a tendency to recur and occurs mainly in young people.
Pyelonephritis is found in 1% of the world's population, and in the fair half of humanity it occurs 6 times more often than in males. In its acute form, the disease is diagnosed in 13% of patients, and in 35% a purulent form is observed.
83% of people who have once had pyelonephritis experience a second relapse, and in 58% the disease becomes chronic. In 80% of cases, the causative agent of infection leading to inflammation of the pyelocaliceal system is Escherichia coli, and in other cases it is staphylococcus.
In women aged 15-40 years, pyelonephritis is a complication of cystitis, as a result of which pathogenic microflora passes through the urogenital tract.
Pyelonephritis itself is not dangerous; it does not lead to organ failure or death. However, the greatest danger is posed by the consequences of pyelonephritis - sepsis, which occurs in 10% of cases, and impaired renal function (42% of all relapses).
Who suffers from pyelonephritis and why?
- At autopsy, every 5th elderly patient had kidney damage as a result of pyelonephritis, but did not know about his disease.
- The number of pregnant women diagnosed with kidney inflammation has increased 5-fold over the past 20 years.
Pyelonephritis is exclusively bacterial in nature, i.e. its causative agent is pathogenic microflora. It is not necessary that it came from outside. Most often, the provocateur is one’s own opportunistic microorganisms, which have gained strength due to weakened immunity or other factors. Bacteria enter the bladder from the intestines or genitals, as well as through the blood and lymph. The disease affects not only adults, but also children under 7 years of age. The risk group includes children prone to frequent colds, acute respiratory viral infections, intestinal infections and inflammatory diseases.
Suppression of immunity promotes the vital activity of pathogenic microflora, which is a provocateur of pyelonephritis. Pregnancy itself provokes the development of chronic diseases, so it is advisable to first check the kidneys, because when carrying a fetus, a huge load falls on them.
Diagnosis of pyelonephritis: diagnosis requires a comprehensive examination
Diagnosis of the disease is difficult, because in 80% of cases it makes itself felt only in acute form, when the kidney tissue has undergone changes.
The similarity of the symptoms of the initial stage of pyelonephritis with cystitis leads to an incorrect diagnosis in 30% of cases and the prescription of incorrect treatment, as a result of which pyelonephritis takes on a chronic form.
The disease develops against the background of diabetes mellitus, urolithiasis in women and prostate adenoma in men. The first symptoms of pyelonephritis are disguised as ARVI and influenza. Fever, chills, back pain, aching bones - all this should alert the patient.
Only a comprehensive diagnosis, including an ultrasound examination of the kidneys, blood and urine tests will reveal the full picture of the disease. The sooner pyelonephritis is diagnosed and the sooner treatment is started, the fewer consequences there will be for human health.
Signs of kidney problems
- Intoxication – fever, poor health, fatigue and lethargy, even at rest, loss of appetite.
- Swelling – if you notice swelling in the morning, it means that fluid has accumulated in the body, that is, the kidneys have not removed it. In the morning, swelling is localized on the arms and face, but during exacerbation it can be present throughout the body, spreading to the legs. Swelling first appears under the eyes, so the first symptoms will be noticeable on the face. If you press on the swollen tissue with your finger, it will become faded.
- Problems with urination - if you notice that there is less or more urine, urine has begun to be excreted frequently and in small portions, the urge is frequent, even at night, there is a burning sensation, pressure, then this sign will directly indicate that something is wrong with kidneys.
- Changes in urine - we are talking about its color, turbidity, the presence of impurities of pus and blood. The urine may become foamy or the color of meat slop, and the smell may become very unpleasant.
- Pain in the lumbar region - such sensations usually accompany acute disorders of the kidneys, such as urolithiasis. With chronic problems, pain rarely occurs. The pain can be localized on one side or both, can be sharp or aching in nature, and can radiate to the thigh, groin area or lower abdomen.
- Metallic taste in the mouth, dryness and bad breath - the smell of ammonia from the mouth may be present due to a violation of the outflow of urine, since as a result of poor kidney function, the urea content in the body increases. This may cause thirst and dry mouth.
- Vomiting, nausea – when the body is intoxicated, in particular when urea accumulates in the blood, vomiting and nausea may occur. More often this occurs in the morning.
- Increased blood pressure - if your blood pressure is high and it cannot be brought down with antihypertensive drugs, then hypertension may likely be caused by problems with the kidneys.
Nephroptosis or why the kidney drops
Kidney prolapse occurs in 1.5% of women and 0.3% of men in the age group of 20-40 years. Prolapse of the right kidney is more often observed, because the left one is initially located higher than the right one and has a stronger ligamentous apparatus.
The organ changes its position not only vertically, but also deviates to the side or twists around its stem. This disrupts the position of blood vessels, impairs blood flow, and increases intrarenal pressure. Nephroptosis also provokes the development of pyelonephritis, because the incorrect position of the kidney contributes to stagnation of urine and the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria.
In itself, the prolapse of the organ does not affect health in any way, but a bend in the ureter with an incorrect position of the kidney provokes stagnation of urine and the formation of stones. Nephroptosis itself causes increased blood pressure, many times increasing the risk of heart attack or stroke. Kidney prolapse also provokes spontaneous abortion in pregnant women.
Causes of kidney prolapse
The following factors contribute to the development of nephroptosis:
- Pregnancy and childbirth . In unathletic women with poor physical fitness, the fixing apparatus of the kidney weakens during pregnancy and natural childbirth. In addition, the abdominal muscles also stretch, and the kidney loses support. Prolapse is facilitated by sudden weight gain and then weight loss. In general, all pregnant women, as well as mothers who have recently given birth to a baby, should especially closely monitor the health of their kidneys, because in the fair half of humanity, kidney disease worsens in the first year after childbirth.
- Weightlifting , lifting heavy objects. Fascia, sheets that attach the kidney to the peritoneum, pass into the diaphragm. They bear the main burden of keeping the kidney in the correct position.
- Overexertion caused by heavy lifting causes stretching of the ligaments holding the kidney, and it gradually drops. Nephroptosis is typical for weightlifters, construction workers, loaders, and some professional athletes. A serious consequence of the disease is arterial hypertension, which cannot be treated with conventional drugs.
- Sharp weight loss . This problem often arises among teenage girls who have complexes about their appearance and go on strict diets. Metabolism at a young age is good, so the results of the diet are noticeable.
If an adult, due to age-related metabolic characteristics, cannot quickly lose weight, then teenagers are able to lose up to 10 kg per month, which will have the worst impact on the condition of the kidneys.
The organ is located in a fatty capsule, which protects from cold and mechanical injury, and also allows the kidney to be fixed in a certain position. With a sharp decrease in weight, the fat layer becomes thinner, which causes sprains and prolapse of the organ. It is not advisable to lose more than 3 kg per month, otherwise it will affect not only your general well-being, but also the condition of your internal organs.
Nephroptosis is diagnosed at the earliest stages, when health has not yet suffered much damage. Clinical examination of the kidneys is the most effective method of preventing renal pathologies.
In what situations are tests prescribed?
A doctor may prescribe a kidney screening if a patient has symptoms characteristic of kidney pathologies. For example, such signs include swelling in the face and body, high blood pressure, nausea, and decreased diuresis. Also, the reason for prescribing screening may be questionable results of a general blood test, general urinalysis and other basic studies.
Screening is indicated for people at high risk of developing kidney disease. These include patients with diabetes, systemic lupus erythematosus, and hypertension. Screening may also be prescribed after taking nephrotoxic drugs.
In addition, regular monitoring is necessary for people with chronic kidney disease to assess the course of the disease and the effectiveness of treatment.
Why do kidney stones appear?
Kidney stones are mineral-salt deposits caused by a failure in metabolic processes. They are formed when urine becomes concentrated and its constituent substances - calcium, oxalate and uric acid - crystallize.
Oxalate is an enzyme produced by the liver and also found in fruits, vegetables and chocolate. With metabolic disorders or poor diet, the amount of oxalate in the urine increases, creating the preconditions for stone formation.
Struvite stones form when an infection enters the urine. Urate stones occur when there is an increased concentration of uric acid. The prerequisites for their formation are dehydration, excess protein foods and gout. When there is an excess of the amino acid cystine, cystine stones are formed.
Basically, stone formation is of a hereditary-genetic nature. People living in countries with hot climates are more prone to stone formation, because dehydration contributes to the formation of stones. Also at risk are people with excess body weight and lovers of salty foods. According to statistics, men are more susceptible to stone formation. Among them, 13% of the male population aged 30-60 years are affected by the disease, while women are 2 times less.
Removing kidney stones is much more difficult than avoiding the crystallization process. A thorough diagnosis in the clinic will identify the disease at the initial stage and prevent further stone formation.
Kidneys hurt when it’s too late, or Why you need to take a urine test once a year
What kidney diseases do Belarusians most often encounter and why does treatment so often involve dialysis? What can you do to protect your kidneys and what tests, depending on your age, should you take to avoid problems in the future? We talked about this, as well as about the myths that surround kidney diseases among the people, with Viktor Gromyko, associate professor of the Department of Urology and Nephrology of the BelMAPO, nephrologist at the Center for Urology and Andrology.
— Viktor Nikolaevich, according to statistics in Europe, about 5-12% of the population suffers from chronic kidney disease. Is the situation different in Belarus?
— In the Republic of Belarus, the prevalence and incidence of chronic kidney disease is not very different from that in Europe. However, the number of our patients is growing, especially those who require renal replacement therapy. And here, not only primary renal diseases, for example, glomerulonephritis, but also other diseases that are accompanied by kidney damage - arterial hypertension, diabetes mellitus and some others - contribute.
In addition, we have low access to nephrologists in the initial stages of diseases. After all, the kidneys themselves do not hurt. And since nothing bothers a person, then he doesn’t go to the doctor. Unfortunately, when a person realizes that he has a problem with his kidneys, we can often talk about chronic renal failure and the need for dialysis.
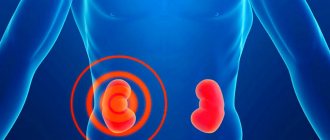
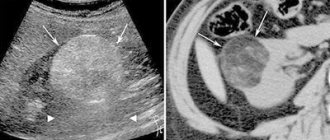
Here's a good example: a 45-year-old man completely accidentally did an ultrasound of his kidneys. It was World Cancer Day and he just decided to get tested. Nothing bothered him, but an ultrasound revealed a tumor. Fortunately, it was an early stage, there were no metastases and it all ended with the removal of the kidney.
- What to do if nothing really hurts? Just go for examinations?
— First, remember a simple rule: once a year you need to take a general urine test. If there are any deviations - they will be highlighted on any form with test results - it is worth consulting with a specialist. Possible problems with the kidneys can primarily be indicated by an increase in protein and red blood cells in the urine.
By the way, sometimes, if the test result is not very good, you can simply try to retake it in a couple of days. Maybe the fact is that you ate a lot of meat the night before and that’s why protein appeared in your urine. But if the test is bad the second time, you can’t do without a visit to the doctor.
You need to understand that our body is also a kind of machine. You have driven 15 thousand kilometers on your car and the car needs to undergo maintenance - change the oil, filters, and so on. Here it is: a year has passed - go and get a urine test.
— And when should an ultrasound of the kidneys be done?
- It all depends on age. If you are under 35 years old, then do it once and, if there are no pathologies and good tests, you can repeat it after 2 - 3 years. If a preschool child has had an ultrasound, and again there is no pathology, then an ultrasound of the kidneys may not be repeated until adolescence if there are no complaints. But if you are over 40 years old, then I would advise doing an ultrasound of the kidneys once a year.
“They say that if there’s a pain in the lower back, it’s the kidneys.” Is it worth contacting a nephrologist with such symptoms?
“The fact is that the kidneys begin to hurt when there are some obstacles to the outflow of urine. For example, when a kidney is blocked by a stone and begins to expand. This is accompanied by a very pronounced pain syndrome, this pain cannot be forgotten. If your lower back hurts, then most likely it will be pain of a spinal nature - you lifted too much weight, turned around incorrectly, and so on. In any case, if ultrasound does not reveal kidney pathology, then lower back pain is not associated with the kidneys.
— One of the most common kidney diseases is glomerulonephritis. What is its danger and how to cure it?
“This is a diffuse kidney disease that leads to decreased renal function over time. With glomerulonephritis, both kidneys are affected simultaneously, and subsequently they shrink, that is, decrease in size. And if some patients have pronounced clinical symptoms of the disease - swelling of the legs and face, then in another part the disease is asymptomatic and manifests itself in the later stages, when there is already renal failure.
— Is a general urine test and ultrasound enough to detect this disease?
- Enough to draw attention to the presence of a problem. In modern nephrology, not only in the Republic of Belarus, but throughout the world, there is a gold standard for diagnosing diffuse kidney diseases, in particular glomerulonephritis - puncture nephrobiopsy. To put it very simply, a column of kidney tissue is taken from the back under ultrasound control with a special needle for further morphological examination under a microscope. Without this, no one will make a diagnosis or prescribe treatment.
Because the same clinical picture - edema, protein in the urine, red blood cells - can manifest itself with different morphological changes in the renal tissue and require different treatment options. By and large, there are two options: symptomatic treatment, which reduces blood pressure, reduces the load on the kidney, etc. The second is aggressive immunosuppressive therapy, which can last quite a long time (from several months to several years) and which can be prescribed only based on the results of nephrobiopsy. And to know how the kidney will respond to this treatment and whether it will, you need to perform a nephrobiopsy.
If glomerulonephritis is detected, then with rare exceptions it will be a chronic disease. And here the goal of any treatment is to achieve remission, that is, a reduction or disappearance of changes in urine analysis and normalization of renal function. If remission cannot be achieved, renal failure will develop and the patient will need dialysis.
— It turns out that it is no longer possible to completely cure the kidneys?
- If the kidneys are sick, then it’s forever. A person must understand that this is his weak point. It may be that after treatment for 5-6 years or more, everything is fine, that is, there are no changes in the general urine test, and then you got hypothermic somewhere, caught an infection and the disease came back, which means there was a relapse that will require treatment, including, possibly, immunosuppressive therapy.
— What is the cause of kidney diseases and is it possible to somehow prevent them?
— The main reason for diseases that cause complications on the kidneys is still lifestyle. For example, excessive salt consumption leads to arterial hypertension; uncorrected sugar levels in diabetes mellitus cause kidney damage, as does excess body weight. If we are talking about primary kidney diseases, in particular glomerulonephritis, then the trigger mechanism will be disruptions in the immune system caused by an infectious onset, for example, the same untreated tonsillitis, as well as other conditions.
— Is it true that kidney problems are most often women’s diseases?
- No, this is a stereotype. There are forms of diseases that affect men more often, and there are forms that affect women more often. But in general, there are no gender differences here.
— On the one hand, everyone says that you need to drink as much fluid as possible, they say, it’s good for the kidneys. On the other hand, everyone argues about what exactly to drink. They say that soda is bad for the kidneys. Well, on the third hand, in case of kidney failure, it is advised to drink less. So how can you help your kidneys?
- Let's go in order. Everyone needs to drink water! If we talk about norms, then this is an average of 30-35 ml per kilogram of body weight per day. I won’t surprise anyone if I say that the best choice is clean drinking water. As for soda, it is not as dangerous for the kidneys as mineral water. This is where excess consumption can provoke stone formation.
If we say that a person is diagnosed with chronic renal failure, then everything depends on the specific situation. If the patient does not have edema, then you can drink water without restrictions in the amount indicated above.
- They say that the kidneys especially do not like cold, meat and alcohol...
— Yes, Belarusians tend to overeat meat products, there is a lot of protein in the diet - as a result, the kidney begins to work harder. The harder the kidney works, the faster it “wears out.” On average, in the absence of renal dysfunction, you need to consume 1 gram of protein per kilogram of body weight per day. If we take 100 grams of meat, then there will be an average of 20-25 grams of protein, depending on its type (beef, pork, rabbit, etc.). So the safe amount is not so small. But whether you eat fried or stewed meat is not important for your kidneys.
The same is true with alcohol: it is a toxin that passes through the kidneys. So this is not only a blow to the liver, as everyone is accustomed to believe.
Well, everything is clear with the cold: the body becomes hypothermic and, against the background of this, infectious processes are launched that have a bad effect on the kidneys. By the way, there is another problem here. At elevated temperatures, patients often take large dosages of antipyretic drugs, either individually or in combination. But all these drugs can cause kidney damage, impairing their function, up to the need for dialysis. Therefore, any drug must be used according to indications and strictly according to the instructions, but they are often not read at all.
— Is it possible to go to a bathhouse or sauna if you have kidney disease?
— If there is no arterial hypertension, then there are no restrictions here. It’s not for nothing that in Soviet times they went to the resort in Turkmen Bayram-Ali to help their kidneys.
— Nowadays there is a fashion for a healthy lifestyle: everyone runs, goes to the gym. How to avoid harming your kidneys when playing sports?
— Any physical activity implies the possibility of muscle breakdown and the appearance of protein, which cannot normally be present. This is myoglobin. This protein can damage the kidney, resulting in anuria (lack of urine) and acute renal failure, followed by the need for dialysis. And there have been such cases after active sports. The load must be proportionate and increase systematically.
For example, regular jogging is good, intense jogging depends on the body. So if you are planning to run a half marathon or actively engage in sports, then get tested to know the condition of your kidneys, liver and heart.
conclusions
To avoid kidney disease, you need to carefully monitor your health: eat right, do not take medications unless prescribed by a doctor, and do not lift heavy objects. Timely diagnosis by a urologist - expert ultrasound and tests - is of utmost importance.
ONLINE REGISTRATION at the DIANA clinic
You can sign up by calling the toll-free phone number 8-800-707-15-60 or filling out the contact form. In this case, we will contact you ourselves.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter
Treatment of chronic kidney diseases
The direction of treatment for kidney disease strictly depends on the cause of its occurrence. If an infectious agent is isolated from the urinary tract, treatment is aimed at eliminating it with the help of antibiotics and antifungal agents. If the cause is urolithiasis, the issue of drug removal of stones, lithotripsy or surgical intervention is decided.
In any case, to restore the full functioning of the kidneys, it is necessary to involve highly qualified specialists and the availability of new diagnostic and therapeutic methods. Such services can be offered by the Urology Clinic named after. R.M. Fronstein, where with an individual approach with minimal intervention it is possible to obtain the most optimal treatment result.