© Author: A. Olesya Valerievna, candidate of medical sciences, practicing physician, teacher at a medical university, especially for SosudInfo.ru (about the authors)
Cystic formations in the cranial cavity always cause well-founded concern among both specialists and their owners. One of the variants of such cavities is a retrocerebellar cyst, which is detected in approximately 4% of healthy people and gives symptoms in only a fifth of its carriers.
Having set out to learn more about this cyst, the reader will find a large amount of information on the Internet, but not all of the information corresponds to reality. Most dubious sources present a retrocerebellar cyst as a kind of intracerebral accumulation of fluid in the place of dead neurons, but in reality it is a cerebrospinal fluid cyst lying outside the brain rather than inside it.
Intracerebral cysts, in other words, cerebral cysts, actually form in the brain itself after necrosis due to a stroke, tumor or injury. The cerebrospinal fluid cyst owes its appearance to the pathology of the arachnoid membrane, therefore it is also called arachnoid, and identifying it with a cerebral cyst is fundamentally incorrect.
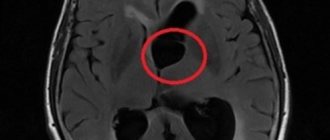
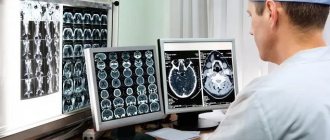
The term “retrocerebellar” is not a characteristic of the cyst itself, but an indication of its location behind the cerebellum (cerebellum), in the region of the posterior cranial fossa, as shown by MRI data, through which these same cysts are detected.
Thus, a retrocerebellar cyst is a cavity formation in the back of the skull, formed by the arachnoid mater, collagen fibers, containing cerebrospinal fluid and lying between the surface of the brain and its arachnoid membrane.
example of cystic expansion of the retrocerebellar arachnoid space
In most cases, a retrocerebellar cyst is discovered accidentally, in young adults who, for one reason or another, have had an MRI. As a rule, the reason for examination is neurological symptoms, which are not always associated with a cyst. A small-sized retrocerebellar cerebrospinal fluid cyst can be asymptomatic and is extremely rarely accompanied by any negative effects on the brain itself.
Indications for the study
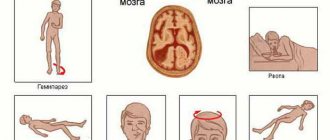
The presence of a retrocerebellar cyst can be suspected by some characteristic symptoms:
- Severe headaches that do not go away even after taking painkillers;
- Unreasonable loss of consciousness or fainting state;
- Sensation of squeezing and pulsation in the head;
- Deterioration of hearing or vision;
- Arterial hypertension;
- Numbness of the limbs;
- Impaired coordination of movements;
- Epileptic seizures.
Magnetic resonance imaging is required if surgical intervention in the brain area is necessary.
Note that the clinical picture and severity of symptoms depend on the exact location and size of the retrocerebellar cyst.
Manifestations of retrocerebellar cysts
When a retrocerebellar cyst is detected in the cranial cavity, the patient has a completely natural question: is it dangerous or not? If it is dangerous, then what actions to take, how to treat, who to contact?
As noted above, usually retrocerebellar cysts do not pose any harm, do not affect health and do not threaten complications. Small cavities are discovered by chance or their existence may never be known.
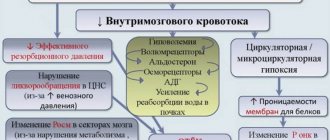
An enlarging cyst, and the behavior of secondary formations rather than congenital ones, can contribute to the appearance of negative symptoms, which are associated mainly with increasing intracranial pressure and concomitant hydrocephalus.
In general, a retrocerebellar cyst is often detected precisely in those people who have symptoms of hydrocephalic-hypertensive syndrome, but caused by other reasons, and the cyst has absolutely nothing to do with it.
The most typical complaints of patients diagnosed with a retrocerebellar cyst are:
- Persistent headaches akin to migraines, which tend to recur at regular intervals (for example, once a year), can last up to several days and are poorly relieved by conventional analgesics;
- Dizziness and episodes of loss of consciousness;
- Attacks of nausea and even vomiting (usually associated with hydrocephalus);
- Headache;
- Autonomic changes - sweating, tremors, hot flashes or extreme pallor, anxiety, emotional lability.
Severe signs of autonomic dysfunction may lead the patient to an examination in which a retrocerebellar cyst is discovered, which, in turn, will be attempted to be associated with the symptoms. Most often, these phenomena are not related to each other, so one should not assume that removing the cyst or its contents will eliminate autonomic dysfunction.
Against the background of increasing pressure in the skull and constant cranialgia, neuroses, anxiety disorders, depression develop, patients experience fatigue, quickly get tired, and performance decreases. Symptoms may intensify under stress, overwork, overheating or exposure to low temperatures, sudden changes in weather, physical activity, long journeys or air travel.
In the case of a large cyst (up to 5 or more centimeters), convulsions, disturbances in motor skills and gait, visual and auditory disturbances, a feeling of pulsation or foreign formation in the head associated with compression of the cerebellum and brain stem structures are possible.
In a child, a retrocerebellar cyst is often congenital in nature and does not tend to manifest itself with any symptoms, however, concomitant hydrocephalus will lead to anxiety, emotional lability, poor sleep for the baby, headaches, and slow psychomotor development. An asymptomatic small cyst does not interfere with the motor and mental development of the child.
Contraindications
Magnetic resonance imaging is safe for the body only if all contraindications are excluded.
Magnetic resonance imaging is not recommended in the following cases:
Very often, to obtain more informative images, doctors prescribe additional contrast. In this case, you must ensure that there are no following contraindications:
- Pregnancy of any stage.
- Breastfeeding period.
- Kidney failure.
- Chronic liver diseases.
- Allergic reaction to components included in contrast agents.
How to study a retrocerebellar cyst?
MRI testing with an additional enhancer in the form of a contrast agent helps to distinguish a neoplasm from a tumor. An anomaly of malignant origin can easily accumulate a contrast agent, while a benign cyst is not capable of such a reaction. Doctors identify the causes of the formations to further prevent the formation of new objects and the increase in size of old ones. To achieve this, various diagnostic techniques are used to help identify the sources of infections, problems with the functioning of the circulatory system and autoimmune disorders. These include:
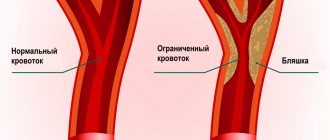
- Doppler diagnostics of the vessels of the head and cervical region - the procedure is prescribed by doctors to identify narrowing of the vessels that serve the function of supplying the brain with arterial blood cells. Due to blood deficiency, gray matter may begin to die.
- Heart check - necessary to determine heart rhythm disturbances and look for insufficiency.
- Donating blood to analyze coagulation and cholesterol levels - an increase in cholesterol and coagulability can become a factor in blocking blood vessels, which will subsequently lead to the formation of a cyst.
- Controlling blood pressure - pressure surges often become a source of strokes and the appearance of post-stroke neoplasms.
- Testing blood cells for infections and autoimmune diseases - prescribed if there is a likelihood of developing a neuroinfection, multiple sclerosis, and other things.
You can make an appointment at any local clinic for diagnostics on the search portal piter-mrt.ru. Here you can apply for an appointment online, find out the current price lists of the centers, the number of vacancies for the coming days and read reviews from visitors.
Preparation rules
During a routine examination, doctors recommend following a few simple recommendations:
- If it is necessary to administer contrast, you must come to the clinic on an empty stomach, that is, do not eat food for 7-8 hours.
- If you are afraid of research or confined spaces, be sure to consult with a specialist. Your doctor may prescribe you sedatives to make the examination process more comfortable.
- Do not bring any metal products inside the tomograph. For this reason, doctors recommend removing metal accessories in advance.
- Prepare a change of clothes that do not have metal or metal-containing accessories.
- The duration of the diagnostic test is about 40 minutes. Empty your bladder in advance to avoid discomfort during the procedure.
Causes
There are two types of origin:
- Congenital retrocerebellar cyst of the brain. Occurs during intrauterine development of the fetus due to defects in the maturation of the central nervous system. It also occurs against the background of problematic childbirth as a complication of birth trauma. In this case, the substance of the brain becomes necrotic and a hollow neoplasm forms in its place. This option is considered as an individual feature of the structure of the brain, that is, it is the norm.
- Acquired education. It occurs due to intravital factors: hemorrhagic stroke, traumatic brain injury, hydrocephalus, encephalitis, meningitis or complications of neurosurgical operations. This is a variant of pathology.
How is an MRI performed?
To ensure that the procedure is as informative as possible and that the images are clear, experts recommend performing magnetic resonance imaging in closed-type tomographs. Before starting the study, the patient must change into clothes without metal structures, take off his shoes and lie down on a retractable table. If the doctor has prescribed additional contrast enhancement, a special drug is injected into a vein, which is distributed throughout the circulatory system in just a few minutes. Then the table moves inside the tomograph, where the research process takes place.
Maintaining immobility is the main requirement for the patient! Remember that even minimal movements can lead to a decrease in the information content of the procedure.
It is also worth noting that when performing magnetic resonance imaging, a specific loud noise is observed. If this scares you, you can use earplugs.
Patients generally tolerate MRI well. Inside the tomograph there is good lighting and ventilation, there is a loudspeaker, as well as a panic button for emergency stop of the study.
General recommendations
Cysts in the head of an adult and a child can be different in type and method of exposure. Dimensions standards depend on the type of formation. If the cyst has minimal, normal or average parameters, then the following medications are used for treatment:
- means for normalizing blood pressure;
- drugs to reduce the frequency of vascular spasms;
- tablets for normalizing blood cholesterol;
- medications to reduce the risk of blood clots.
The treatment method for cysts is influenced not only by parameters. After all, even with a normal or minimal size, the formation can cause significant harm. The treatment method is influenced by dimensions, localization, etiology, and dynamics of development. Surgical intervention cannot be avoided if the neoplasm creates a critical level of intracranial pressure and has led to rupture of pathological structures.
If the specialist’s recommendations are not followed, a tumor of even normal size can cause a persistent increase in intracranial pressure, neurological disorders, and pathologies of the nervous and vegetative-vascular systems. Periodic sleep problems develop into chronic insomnia, and gastrointestinal and cardiovascular disorders appear.
MRI with contrast
In most cases, magnetic resonance imaging of the brain is performed with contrast, especially if any neoplasm is suspected. This makes it possible to examine the tumor in detail and distinguish a benign tumor from a malignant one.
The contrast agent clearly highlights the vessels, which allows you to see any tissue pathologies. Don't worry, contrast agents are safe for the human body. Most patients tolerate this procedure well. You must first consult a doctor and exclude all possible contraindications.
Relationship between the symptoms of cystic formation and its size
The clinical course of the pathology is directly dependent on its increase (growth). Of course, there are many other factors - the location of the cyst, the source of the disease, but size plays a primary role
. An increase in cyst volume provokes an increase in fluid pressure in it, which entails an active course of the disease. The growth of cystic formation is influenced by:
- neuroinfection;
- chronic disorders of the blood supply to the heart;
- development of autoimmune processes (for example, multiple sclerosis).
Decoding the results
A retrocerebellar cyst is located in the brain behind the cerebellum, in the posterior cranial fossa. During magnetic resonance imaging, it is possible to clarify the exact location and size of the formation.
The report will contain all the information, but the MRI specialist cannot make a diagnosis - this must be done by your attending physician. If the diagnosis of retrocerebellar cyst is confirmed, the doctor will determine treatment tactics. For benign tumors, it is often possible to do without surgical interventions - they are required only in cases of large tumors or rapid growth. To avoid serious consequences, consult a doctor at the first alarming symptoms. Be healthy!
How does the disease manifest itself?
The symptoms of the anomaly have a direct relationship with the size of the tumor. Localization and educational factors are important. If the cyst continues to increase in volume or the pressure of the substance in it increases, the patient may experience pronounced manifestations. At the same time, the formation of small cysts that stop their growth does not provoke symptoms. The main reasons for the progression of the disease are:
- neuroinfectious microorganisms;
- long infectious process;
- malfunctions in the functioning of the circulatory system of a chronic nature;
- autoimmune disorders.
The patient exhibits the following signs of an unstable condition:
- pain in the head area;
- discomfort from a feeling of pulsation inside the skull;
- temporary hearing problems;
- presence of noise in the ear canals;
- a feeling of fullness in the head and a surge in pressure;
- disturbances in visual abilities (formation of spots, blurriness, bifurcation);
- paralysis of the arms or legs, complete or partial;
- seizures;
- sudden loss of consciousness;
- numbness of body parts of a temporary or permanent nature.
Diagnostic measures
To prevent the development of an anomaly and establish a timely correct diagnosis, it will be necessary to rely on all the patient’s existing complaints along with the clinical picture. Medical staff use clinical tests such as magnetic resonance imaging.
Why does dropsy of the brain occur?
In adult patients, acquired hydrocephalus is often encountered, which develops either due to any mechanical damage to the head, or as a result of the development of pathological processes. Why does cerebrospinal fluid accumulate outside the cerebral hemispheres? The explanation is simple: brain structures are disrupted, adhesions appear in the veins, arachnoid villi are destroyed, and as a result, the cerebrospinal fluid does not circulate as it should.
If we delve deeper into the question of the causes of such a disease as external dropsy of the brain, we can identify some factors:
- infectious diseases (tuberculosis, meningitis, encephalitis);
- post-stroke condition, development of sepsis, extensive hemorrhage;
- concussion, head or cervical spine injury;
- malignant tumors that develop in the stem region.
Frequent intoxication of the body leads to the appearance of external hydrocephalus. For example, alcohol abuse, which damages neurons and leads to tissue death. Those patients who suffer from metabolic disorders, diabetes mellitus, multiple sclerosis, encephalopathy, and atherosclerosis are also at risk. Another reason that deserves due attention is irreversible age-related changes that cause aging of blood vessels and brain tissue.
Main services of Dr. Zavalishin’s clinic:
- consultation with a neurosurgeon
- treatment of spinal hernia
- brain surgery
- spine surgery