- home
- Coloproctology
- Rectal cancer
- Stages of colorectal cancer and their symptoms
Stages of rectal cancer
Rectal cancer is an oncological disease in which a tumor localized in the distal part of the large intestine occurs against the background of pathological changes in the mucous membrane. There are different forms of cancer: the focus of pathology can grow into the lumen of the intestine, over time blocking it, or spread deep into the intestinal wall. Infiltration of the intestinal wall is possible, and the tissue loses its elasticity, which affects its functionality. Gradually, cancer cells penetrate into nearby tissues, and if left untreated, metastases affect other organs, most often the lungs, kidneys, liver, ovaries, etc.
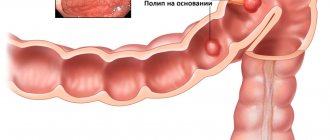
Rectal cancer accounts for 5% of all malignant tumors of the digestive system. For the most part, the disease affects people 40-60 years old, although in recent years, oncologist patients are increasingly becoming younger people. The risk group for morbidity includes patients suffering from ulcerative colitis, proctitis, diffuse polyposis, having fistulas, ulcers, anorectal fissures, rectal polyps - in this case, the risk of malignancy is especially high. Large polyps are dangerous; if the size exceeds 3 cm, then the risk of degeneration into cancer reaches 40-85%. The process of malignancy of a polyp can last several years, but after degeneration the tumor grows rapidly.
How many stages of colorectal cancer are there?
In domestic clinics, the disease is usually divided into stages; rectal cancer has four stages. The classification is based on the size of the tumor, the existing invasion of the intestinal wall and the degree of spread of malignant cells to other tissues and organs.
| Stage | Tumor size and spread | Main symptoms |
| 0 | small tumor within the mucosa; | there are no signs of disease; |
| I | the formation does not exceed 2 cm, mobile, within the intestinal wall, only the mucous and submucosal layer is affected; | asymptomatic; |
| II | the tumor is no more than 5 cm, spreads beyond the intestinal wall, metastases are either absent or present in regional lymph nodes; | indigestion, feeling of incomplete bowel movement, false urge to defecate, rectal discharge; |
| III | the tumor size exceeds 5 cm, the tumor grows into the intestinal wall, there are multiple metastases in the lymph nodes; | persistent constipation, bloating, rumbling in the abdomen, when the intestinal lumen is blocked by a tumor, intestinal obstruction occurs; |
| IV | the tumor is large, immobile, metastasizing to distant organs; | rectal bleeding, pain, stool retention, fever, weakness, vomiting, cachexia. |
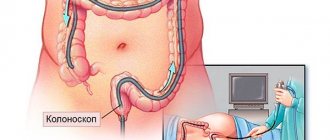
Staging is important for choosing the optimal treatment tactics and prognosis of the disease. If at stage 0 or I of rectal cancer it is possible to get by with polypectomy during colonoscopy or intestinal resection, then in advanced cases extensive intervention is assumed. To determine the stage, it is necessary to undergo an examination. In our clinic, patients have access to the most effective examination methods.
written consultation, in order to determine the indications for surgery, as well as choose the correct surgical treatment tactics, you can send me a full description of the colonoscopy, histology data, if possible, MSCT data of the abdominal cavity with contrast, indicate your age and main complaints.
Then I will be able to give a more accurate answer to your situation.
Among women
Most often, colon cancer occurs in women. Cancer usually appears after the age of forty, as the body prepares for menopause. Very often, cancer arises from the degeneration of polyps. Hereditary predisposition and poor nutrition play a very important role here.
The main symptoms appear after two years. Usually these are abdominal pain, problems with stool, and bloating. When metastasis occurs, the lymph nodes, vagina, and other pelvic organs are affected. In the later stages, the pain intensifies, intestinal incontinence occurs, the patient vomits, the composition of his urine changes, the kidneys are affected, urogenital fistulas occur, and the menstrual cycle may change.
Clinical picture
At the initial stage of the disease, there are no unpleasant symptoms, but as the tumor grows, a number of signs appear. Symptoms can be divided into two groups: characteristic of a given pathology and general, occurring in many diseases.
| Symptoms characteristic of cancer | General signs |
|
|
The nature of the discharge is of great importance. For example, with a tumor located in the upper, middle or ampullary section, particles of scarlet blood are present in the stool; with a low tumor location, the discharge resembles fresh blood in appearance. The presence of pus in the stool indicates the development of an infection. The presence of a tumor may be indicated by the appearance of ribbon-shaped feces.
Life expectancy at stage 4
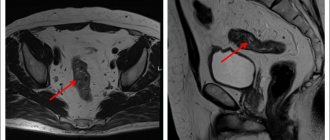
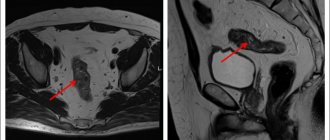
An important distinguishing feature of stage 4 colon cancer is the detection of metastases in distant areas of the body. In the early stages, metastases form in the liver, through which blood passes from the abdominal and pelvic organs. Less commonly, lesions appear in the lungs, genitals, bones, pancreas and adrenal glands. The number and location of metastases significantly influence how long patients with stage 4 intestinal cancer live. In particular, in case of lung damage, additional methods are used - an intensified course of polychemotherapy or embolization of metastases with chemotherapy. Based on the response to treatment, reduction in size of metastases or their complete disappearance on CT/MRI, the doctor can determine how much time a patient with stage 4 colon cancer has left to live.
According to the National Cancer Institute, the 5-year survival rate for patients with stage 4 colorectal cancer is only 11%. This is often due to late diagnosis of cancer or incorrect selection of individual treatment. Despite the disappointing statistics, prognosis for stage 4 colon cancer is extremely individual.
The following factors are of greatest importance in treating stage 4 colon cancer and determining prognosis:
- Age, patients under 60 years of age have a higher chance of recovery
- Gender, with a more favorable prognosis in men
- The presence of concomitant diseases, the most important in this regard are liver and kidney dysfunctions, the state of the cardiovascular system
- A history of oncology; upon initial diagnosis, the prognosis for stage 4 colon cancer is more favorable
- Sensitivity of tumor cells to chemotherapy
To predict how long a patient with stage 4 colon cancer has left to live, it is important to evaluate not only medical factors and the possibility of specialized treatment, but also the patient’s psycho-emotional state. Of course, it is important to perform surgery in a timely manner, as well as chemotherapy to combat metastases. However, competent psychological support helps a person find the strength to fight the disease and believe that remission is achievable.
It matters not only how long patients with stage 4 intestinal cancer live, but also the quality and fullness of life.
It will be useful:
- Attending individual and group supportive psychotherapy sessions
- Selection of a competent physical activity regimen by the attending physician
- Communication with patients in communities dedicated to the disease, meeting those who have recovered from the disease
Treatment
The only effective treatment for rectal cancer is radical removal of the tumor. There are a number of techniques, the choice of the appropriate one depends on the stage.
| Stage | Treatment |
| 0 | polypectomy during colonoscopy or transanal excision of the tumor |
| I | resection, less often abdominoperineal extirpation of the rectum |
| II | resection or extirpation, possibly with chemotherapy after surgery |
| III | resection in combination with pre- and postoperative chemotherapy and radiation |
| IV | resection with chemotherapy, removal of metastases, pelvic evisceration |
Along with surgical treatment for rectal cancer, radiation and chemotherapy are used. Treatment tactics are selected for each patient individually. In some cases, preoperative radiation is recommended, the purpose of which is to destroy cancer cells and reduce the risk of recurrence. For some types of tumors (for example, squamous cell carcinoma), only chemoradiotherapy is effective. Chemotherapy can be prescribed both before and after surgery.
Diagnostic methods
Patients suspected of having rectal cancer should immediately undergo a comprehensive examination and receive recommendations from an oncologist.
Diagnostics includes:
- Examination of the patient and collection of complaints. As a rule, the patient first visits a therapist, and only then goes to an appointment with a specialized specialist - a proctologist, oncologist-surgeon. The doctor will examine the nature of the symptoms and prescribe the necessary tests.
- Tests are prescribed: a general blood and urine test, a biochemical blood test and tumor markers for colorectal cancer. Studies make it possible to assess the general condition of the internal systems of the body, detect foci of inflammation and the extent of their prevalence.
- Investigations: colonoscopy or irrigoscopy, magnetic resonance or computed tomography, and ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity. Allows you to determine the size of the tumor and its location.
- Screening methods. This type of research allows you to identify pathology before the first symptoms appear. This is a digital examination, endoscopy, stool analysis for occult blood.
After tests and studies are completed, observation and treatment is carried out by an oncologist.
IMPORTANT:
Additionally, the oncologist can send the patient for a biopsy. The procedure involves taking a piece of tumor tissue, which is sent for laboratory testing.
Surgery for rectal cancer
Oncological disease is treated by laparoscopic surgery
The goal of surgical treatment is to ensure the unimpeded passage of intestinal contents; for this purpose, the tumor is removed with part of the adductor and efferent intestines, if possible, with the creation of a primary anastomosis. Regional lymph nodes are also subject to removal.
One of the effective techniques is total mesorectal excision (TME), described in 1982 by the English surgeon Richard John Heald. It is based on the isolation of the rectum under visual control in the avascular zone - in the so-called correct layer - between the intestinal fascia proper (mesorectum) and the parietal fascia of the pelvis. The tissue located in the mesorectum contains lymph nodes, which, as a rule, are affected by metastases. When the rectum is isolated in the traditional way, part of the fiber is separated and remains in the small pelvis, which in 25% leads to the appearance of satellite metastases. TME excludes such a development of events. Based on this technique, intestinal resection is performed: anterior, low, abdominal-anal, abdominal-perineal extirpation.
TME is used today by many specialists, but the disadvantage of the method is the high rates of local relapses. I was able to reduce the recurrence rate from 45% to 5% by performing TME through a laparoscopic approach.
Cost of services
Surgical treatment of the sigmoid and rectum
| Service | Price |
| Excision of anal fissure | Cost: 20,000 rub. |
| Excision of external rectal fistula | Cost: 30,000 rub. |
| Removal of hemorrhoids | Cost: 20,000 rub. |
| Removal of polyp of the anal canal and rectum | Cost: 15,000 rub. |
| Resection of the sigmoid colon | Cost: 36,200 rub. |
| Resection of the sigmoid colon using video endoscopic technologies | Cost: 54,050 rub. |
| Robot-assisted resection of the sigmoid colon | Cost: 200,000 rub. |
| Nerve-sparing laparoscopic-assisted resection of the sigmoid colon | Cost: 50,000 rub. |
| Combined resection of the sigmoid colon with resection of adjacent organs | Cost: 50,000 rub. |
| Extirpation of the rectum | Cost: 40,000 rub. |
| Extirpation of the rectum using video endoscopic technologies | Cost: 50,000 rub. |
| Abdominal-anal resection of the rectum with elimination of the rectovaginal fistula, suturing of the vaginal defect | Cost: 45,000 rub. |
| Anterior rectal resection using videoendoscopic technologies | Cost: 50,000 rub. |
| Low anterior rectal resection | Cost: 45,000 rub. |
| Intersphincteric rectal resection | Cost: 45,000 rub. |
| Robot-assisted rectal resection | Cost: 220,000 rub. |
| Combined rectal resection with resection of adjacent organs | Cost: 45,000 rub. |
| Excision of the epithelial coccygeal duct | Cost: 20,350 rub. |
| Mesorectumectomy | Cost: 15,000 rub. |
| Reconstruction of the esophageal-intestinal anastomosis for scar deformities that are not subject to endoscopic treatment | Cost: 20,000 rub. |
| Reconstruction of esophagogastric anastomosis in severe reflux esophagitis | Cost: 50,000 rub. |
| Excision of neoplasms of the perianal region and anal canal | Cost: 15,000 rub. |
| Autopsy of acute purulent paraproctitis | Cost: 16,000 rub. |
| Excision of subcutaneous-submucosal fistula of the rectum | Cost: 15,000 rub. |
| Excision of transsphincteric fistula of the rectum | Cost: 20,000 rub. |
| Excision of extrasphincteric fistula of the rectum | Cost: 20,000 rub. |
Advantages of the laparoscopic technique for total mesorectumectomy
- During the operation, there is a need to intersect nerve fibers, which can lead to urogenital disorders. To prevent such disorders, I use a nerve-sparing technique.
- In the presence of a widespread tumor or small-sized carcinoma, the operation is performed in several stages.
- To form the interintestinal anastomosis, I use modern staplers made in the USA, which helps to minimize the risk of developing postoperative complications, such as stricture or failure of the anastomotic suture.
- Using the LigaSure electrothermal tissue ligation device, ultrasonic scissors, and the Force Triad energy platform, mobilization of the colon is carried out quickly and bloodlessly, there is no need to use surgical clips and threads, and it is possible to preserve nerve fibers.
Considering the psychological state of patients when removing part of the intestine to the anterior abdominal wall, I strive, if possible, to perform organ-sparing operations while maintaining the continuity of the intestinal tube and rectal sphincter.
I have personally performed more than 300 laparoscopic interventions for diseases of the large intestine. The results of the operations are summarized in the monograph “Minimally invasive surgery of the colon.” Information about the surgical treatment methods I use can also be found in numerous peer-reviewed scientific publications.
Original surgical technique
Resection and extirpation are carried out on the basis of an operation - total mesorectal excision - TME. To prevent the appearance of satellite metastases when isolating the rectum in the traditional way, when the lymph nodes located in the mesorectum remain unremoved, I perform the operation through laparoscopic access. This technique allows us to reduce the development of local relapses to a minimum; in our clinic this figure does not exceed 5% (instead of 45%).
Our clinic is equipped with the most modern equipment and instruments, for example, to prevent stricture or failed anastomotic suture after treatment, staplers are used during surgery, mobilization of the intestine is performed bloodlessly thanks to the use of the LigaSure electrothermal tissue ligation device, etc.
Considering that removing part of the intestine onto the abdominal wall can negatively affect the psychological state of the patient, I strive to perform organ-preserving operations, if possible. Therefore, during surgical treatment, my goal is to maintain the continuity of the intestine and anal sphincter, as well as gentle surgery to preserve the nerve structures in the intervention area. If the formation of an anastomosis is impossible, and placing a temporary intestinal stoma on the abdominal wall is the only correct solution, then after a few months the patient can undergo reconstructive surgery, which makes it possible to return to the person’s usual method of bowel movement.
Prognosis for rectal cancer
If the tumor grows within the intestine itself for a long time, then in most patients, with timely treatment, the chances of a complete recovery are very high. The stage of the disease also affects survival in colorectal cancer:
- with 0-I, the five-year survival rate reaches 90%;
- in II – about 60-85% of patients recover;
- III - cure is possible in 25-60% of patients, the effect largely depends on properly prescribed treatment;
- Stage IV - has the most unfavorable prognosis, survival rate is only 7%.
Despite the availability of effective diagnostic methods, most cancer cases are diagnosed late due to a person's reluctance to see a doctor when the first symptoms appear, which reduces the chances of a full recovery.
Causes of the disease
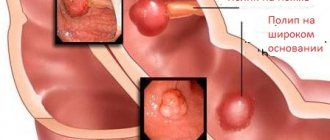
One of the main causes of this cancer is polyps (glandular growths). They develop on the wall of the rectum and, over time, can degenerate into a malignant tumor.
Main causes of rectal cancer:
- Hereditary factor (presence of genetic syndromes - familial adenomatous polyposis, Crohn's disease).
- The presence of other neoplasms in the body.
- Diabetes.
- Papilloma virus.
- Immune system deficiency.
- Abuse of alcoholic beverages, smoking.
- Inflammatory diseases in the intestinal area.
- Work in hazardous industries with chemicals.
- Sedentary lifestyle.
- Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
The risk group includes people with benign intestinal tumors. They need to undergo preventive treatment, which will not allow the tumor to degenerate. A sedentary lifestyle also negatively affects the condition of the body, increasing the possibility of developing a pathological condition.
Forms of bowel cancer
A disease such as intestinal cancer involves damage to various parts of the intestine, from the duodenum to the rectum. However, lesions of the small intestine or duodenal cancer are extremely rare, the stages of the process and symptoms are similar, and digestive disorders predominate. When doctors usually talk about intestinal cancer, they mean the colorectal form of the tumor.
When bowel cancer is diagnosed, additional tests are performed to determine the extent of the disease. The stages of colorectal cancer are as follows:
- Stage I (least common cancer): A tumor that affects only the innermost layers of the colon or rectum. The cure rate for stage I cancer is more than 90%, which emphasizes the importance of early detection of pathology.
- Stage II: cancer demonstrating active growth and spread of the tumor through the wall of the colon or rectum to adjacent structures.
- Stage III: cancer associated with the spread of the process to local lymph nodes (metastases).
- Stage IV (the most common cancer): The tumor cells have spread to distant organs, usually the liver and lungs or lymph nodes far from the original tumor.
Clinics and prices for colon cancer treatment abroad
The cost of examination and treatment in foreign clinics depends, first of all, on the country and the level of the clinic. The cost of the medical program is also affected by the patient’s age, the presence of concomitant diseases, the stage of cancer and the type of tumor. Leading colon cancer treatment clinics abroad:
- University Hospital Dusseldorf, Department of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Infectology
- University Hospital of the University of Munich. Ludwig Maximilian, Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology
- University Hospital Ulm, Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology
- University Clinic named after. Goethe Frankfurt am Main, Department of Gastroenterology, Hepatology, Pulmonology, Allergology, Endocrinology and Diabetology
- University Hospital Würzburg, Department of Gastroenterology, Hematology, Oncology, Hepatology, Infectology, Rheumatology and Clinical Immunology
Average prices for examination and treatment:
- Diagnosis of colon cancer – from 999 euros
- Laparoscopic resection of affected parts of the colon – from 11,593 euros
- Resection of affected parts of the colon using the da Vinci robot – from 25,386 euros
- Treatment of colon cancer with chemotherapy – from 2,255 euros
- Cytoreductive surgery and hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy (HIPEC) for colon cancer – from 38,154 euros
- Oncological rehabilitation – from 951 euros per day
Booking Health helps you get treatment abroad
If you want to find out prices for treatment of colon cancer in Germany, treatment of colon cancer in Israel or other countries, contact the medical tourism operator Booking Health. Fill out the “Send a request” form on the company’s website, and a medical consultant will contact you on the same day.
Booking Health specialists will also help you with such important points:
- Choosing the right clinic based on the annual qualification profile
- Direct communication directly with the attending physician
- Preliminary preparation of a treatment program without repeating previously conducted examinations
- Ensuring favorable prices for clinic services, without surcharges and coefficients for foreign patients (savings up to 50%)
- Make an appointment for the desired date
- Control of the medical program at all stages
- Assistance in purchasing and shipping medications
- Communication with the clinic after completion of treatment
- Control of invoices and return of unspent funds
- Organization of additional examinations
- Service of the highest level: booking hotels, plane tickets, transfers
- Translator and personal medical coordinator services