Cough is the most common problem that every child faces sooner or later, and the second most frequently reported symptom after a runny nose. The reality is that most Kaliningrad residents treat children themselves at home, not realizing that this symptom can be a sign of a number of serious diseases. In this regard, parents need to understand how important it is to correctly assess the baby’s condition, promptly respond to dangerous symptoms and show the child to a doctor. Our specialists remind parents of the most important points regarding dry cough that they need to take note of.
Causes of the cough reflex
It's no secret that in most cases the cause of cough is viral and bacterial infections. However, it makes sense to list all the possible causes of irritation of the larynx, these are:
- viruses and bacteria;
- allergies to tree or grass pollen, etc.;
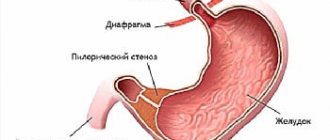
- dysfunction of the organs of the gastroesophageal zone;
- foreign object caught in the respiratory tract;
- psychogenic causes (anxiety).
As we mentioned earlier, an irritating dry cough can be a symptom of many respiratory diseases, including:
- ARVI;
- bronchitis;
- bronchial asthma.
These are the most common diseases, accompanied by coughing attacks, arranged in descending order. Others are much less common, but this does not make them any less dangerous - whooping cough, tracheitis, pneumonia, etc. Consultation with an otolaryngologist is necessary to exclude pathologies of the upper and lower respiratory tract.
Diagnosis of pathology
A pediatrician can perform the initial diagnosis upon treatment. A narrow specialist, an otolaryngologist, is responsible for making an accurate diagnosis and choosing a treatment regimen. An important role in establishing the cause of cough without fever in a child is taken by collecting an anamnesis. It is the responsibility of the attendant to detail the following observations:
- how long and intense the coughing attacks are;
- character of cough: dry, wet, “barking”, “whistling”;
- what becomes a catalyst for coughing: active games and sports, cold air, eating;
- Are there any third-party symptoms accompanying the cough: runny nose, vomiting, snoring;
- is there a correlation between coughing attacks and the time of day;
- whether the child’s emotional state affects the nature and frequency of coughing.
In addition to the conversation, the otolaryngologist will examine the child during the appointment and carry out a number of manipulations and prescriptions, including:
- auscultation, incl. using a phonendoscope;
- radiographic examination and CT;
- examination of bronchial discharge;
- fibrobronchoscopy examination;
- video endoscopic examination of ENT organs.
The nature and duration of the cough, coupled with the accompanying symptoms, allows us to determine the location of the inflammation and make a diagnosis more quickly. During the diagnosis, additional consultation with a pediatric allergist, phthisiatrician, endocrinologist, infectious disease specialist, or immunologist is possible.
Types of cough: wet and dry. How to determine?
The choice of treatment tactics depends on the type of cough, so it is very important to be able to distinguish between them. Distinctive features are as follows:
- Presence of sputum. A wet (productive) cough is accompanied by the discharge of sputum; with a dry irritating type of cough, it is absent, which is why it is called that.
- Characteristic sound. If a dull and gurgling sound is heard when coughing, it is a wet cough. A dry cough has a rolling and crackling sound; due to its similarity to the barking of a dog, it is also called barking.
- Localization of the inflammatory process. With a wet cough, the sound comes from the depths of the chest, and with a dry cough, from the larynx, since the inflammation affects only the mucous membrane of the posterior wall of the larynx and pharynx.
- Duration. A dry, irritating cough usually lasts 3-4 days, after which it turns into a productive wet cough as the infection spreads to the lower respiratory tract, which can last another 2-3 weeks.
Note that a dry cough appears both at the initial stage of a cold and at the end of a cold, as a residual phenomenon.
Physiology
Before determining the reason why the voice is hoarse and the cough appears, let's look at the mechanism of voice formation. When there are no problems with the vocal apparatus, we speak loudly and sonorously. How is this achieved? In fact, voice formation is not as simple a process as it might seem. It involves our lungs, trachea, nose, paranasal sinuses, mouth, teeth, tongue. But the most important role in voice formation is assigned to the larynx, or more precisely, its vocal cords.
The vocal cords are folds of muscle located in the center of the larynx.
The space between the vocal cords is called the glottis. Sounds are produced as you exhale. A stream of air emerges from the lungs and goes up to the larynx. During vocal production, the vocal folds close and the gap disappears. Under the influence of exhaled air, the ligaments begin to vibrate and sounds are formed.
Make an appointment right now!
Call us by phone or use the feedback form
Sign up
The appearance of hoarseness is a consequence of the fact that the vocal cords are hoarse.
Swollen ligaments cannot fully close; accordingly, the glottis does not narrow, and sounds are reproduced distortedly.
In fact, there are quite a few reasons why hoarseness of the vocal cords appears, and infection is not always to blame.
In what cases is a mandatory examination by a doctor necessary?
Parents should be aware of important symptoms, the presence of which should seriously alert vigilant parents and force them to urgently consult a doctor. The “red flags” include the following key points that reflect the child’s condition:
- deterioration in the child’s general well-being;
- no visible improvements within 7-10 days;
- presence of fever for more than 3 days;
- sudden appearance of a rash;
- the occurrence of moist wheezing when breathing.
With the joint efforts of the doctor and parents, we will be able to provide timely assistance to the baby and find out the reasons that aggravated his condition. The parents' task is to immediately respond to the above physiological markers.
First aid
Treatment of a hoarse voice should only be carried out under the supervision of a doctor, since it is very difficult to independently determine what caused the voice failure. But there are a number of recommendations that everyone can and should follow before visiting a doctor.
- Give yourself a day of silence; try to talk as a last resort, and if you really have to speak, do not whisper under any circumstances. Whispering will have a much more negative impact on the condition of the ligaments than ordinary speech.
- Avoid talking in frosty air.
- Quit smoking and alcohol at least for a while until your vocal cords recover.
- Follow a gentle diet: you need to exclude everything that irritates the laryngeal mucosa. We are talking about too hot, cold, spicy, sour, hard food.
- Maintain an optimal level of humidity in the room.
It is worth noting that these measures are not enough to completely restore voice function and get rid of unpleasant symptoms.
It is necessary to undergo treatment of the underlying disease from a doctor.
Cough treatment is always comprehensive!
The first task facing the doctor is to establish the form of the cough, after which adequate therapy will be prescribed. To identify a cough, the specialist will clarify the patient’s medical history, heredity, allergic and immune status, as well as the effectiveness of previous treatment, if any. In this regard, during the examination, the doctor may ask the parents:
- How long has a child been bothered by a cough?
- Does sputum come out, and if so, what color?
- What causes a cough and how often does a child get sick?
- Is there a genetic predisposition to bronchial asthma?
- What medications were given to the child and how was the cough treated? Etc.
If a small patient has been diagnosed with a dry cough of viral etiology, then the doctor’s task No. 2 is to transform the dry cough into a productive one. No matter how scary a wet cough may seem, it is “useful” because it frees the body from purulent secretions.
To accomplish this task, both medicinal and non-medicinal methods will be used. The first include treatment with drugs (drops, syrups, tablets) that can change the quality and quantity of sputum:
- mucolytics - agents that thin out viscous secretions;
- mucokinetics (expectorants) – affect the mobility of sputum;
- It is advisable to take antitussive drugs that relieve attacks before bedtime.
Non-drug options include:
- increasing the volume of fluid consumed to thin the sputum;
- ensuring sufficient humidity in the room;
- inhalation using special steam inhalers based on solutions of herbs or essential oils.
Timely consultation with a doctor and an integrated approach to the treatment of dry cough will allow you to achieve a positive result and prevent the development of a chronic form or complications.
Physiotherapeutic procedures for a child
Starting from the age of 3, to treat a child’s cough , both dry and wet , using various physiotherapeutic procedures. Inhalations using either special additives or the addition of
- herbal tinctures (chest, chamomile, oregano)
- essential oils (lavender and eucalyptus oils)
- or plain soda.
But you need to do this carefully, otherwise you can provoke an allergic reaction.
Will be useful for treating cough
- rubbing
- compresses
- or mustard plasters.
Ointment for rubbing for dry cough can be bought at any pharmacy.
It is advisable to perform rubbing before bedtime.
You need to rub both your back and chest (but not in the heart area) with your legs. Don’t get too carried away with mustard plasters and apply them maximum once a day.
Memo to parents: how to treat a cough, and how not to...
General recommendations that need to be followed at home, in addition to doctor’s prescriptions, relate to the following important points:
- Provide your baby with rest, plenty of warm water and adequate nutrition. We exclude from the diet spicy and sour foods that irritate the throat.
- Don't forget to ventilate the children's room. If the baby does not have a temperature, you can walk with him in the fresh air.
- Warming compresses and inhalations are permissible only if the child does not have a fever.
Let us also remind you what you should not do if you have a dry cough:
- Place mustard plasters, which increase blood flow to the bronchi. They can be used only for wet coughs to increase sputum discharge.
- Rubbing ointments with a strong smell of camphor or menthol, which can cause further irritation of the mucous membranes and provoke new coughing attacks.
- You should not give your child drugs that increase phlegm and inhibit the cough reflex at the same time. Such amateur activities can harm the child and will not help clear the airways.
We urge Kaliningrad residents not to self-medicate their child and not to ignore his lingering cough. Contact us to determine the cause of the unpleasant symptom and receive effective treatment.
Making an appointment is easy. Simply fill out the online form on our website or call one of the phone numbers: +7 (4012) 357-773 or +7 (4012) 973-100.
What to do if a child has a barking cough with fever
Parents of boys and girls under 6-8 years of age may have encountered nightly attacks of a loud barking cough when a child suffering from acute respiratory infections suffocates at a high temperature.
Acute attacks plus nasal congestion, sore throat, hoarseness, difficulty in breathing, and a preceding barking cough are a sign of acute stenosing laryngotracheitis or false croup (FC). The development of laryngeal edema, accumulation of mucus and muscle spasm against the background of inflammation can create a threat of asphyxia. LC is a complication of viral infections, most often parainfluenza, influenza, and can also occur with measles, rubella, chickenpox, diphtheria and scarlet fever. The likelihood of edema in a dry, overheated room in the autumn-winter period is quite high. Most often, the acute form of laryngotracheobronchitis develops in children of the second and third year of life (more than 50% of cases), somewhat less often - in infancy (6 - 12 months) and in the fourth year of life. In boys, this complication is observed almost 3 times more often than in girls. The cause of LC is not an allergy, but a virus. If a child has a seizure during which he experiences difficulty breathing, it is necessary to urgently call an ambulance. Before the doctors arrive, you can take a number of measures on your own, having previously agreed with your doctor: lower the air temperature in the room and increase the humidity: you can hang the radiators with wet towels, turn on the humidifier, calm down yourself and calm the child. You can distract your baby with a tablet, give him a drink of cold mineral water without gas or a lukewarm compote. It is possible to carry out inhalation with a drug prescribed by your doctor. It must be remembered that a warming compress, which mothers love so much, is contraindicated at high temperatures and fevers, as well as during the active phase of an infectious disease, so it is better to avoid this measure. Since hyperthermia causes additional swelling, a pediatric antipyretic may be given at high temperatures.