Atopic dermatitis is a chronic skin disease. Due to disruption of biochemical processes, excessive dryness, peeling, redness occurs, inflammatory processes develop, and itching is felt. It develops under the influence of allergens, and is often combined with bronchial asthma, food allergies, and allergic rhinitis. It appears in the first years of life, most often before 12 months or at the age of 2-3 years, when the children's diet expands and many allergenic foods enter it. With proper treatment and care, the disease enters the stage of stable, long-term remission, but can manifest itself in adolescents, young and elderly people during contact with allergens, a weakened immune system, and after stress.
Symptoms
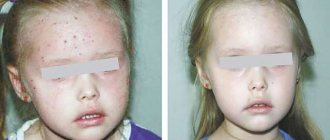
With atopic dermatitis in children, skin tightness, redness appears, the skin flakes, feels rougher to the touch, and thickening may appear. Microscopic bubbles form, around which moisture is released. The child is worried and scratches the affected areas. When an infection occurs, local inflammation develops and the wounds heal poorly. With significant spread in young children, general intoxication of the body manifests itself: the temperature rises, the peripheral lymph nodes enlarge. Due to severe itching, sleep and appetite are disrupted, and the child often cries. Dermatitis most often affects the face, neck, armpits, scalp, groin, areas under the earlobes, popliteal fossae, and elbows.
The expression “skin like a baby’s” implies unusually delicate, soft, silky skin without any defects. However, more and more often mothers, together with pediatricians, allergists, and dermatologists, are faced with skin problems in their children. Is it possible to solve skin problems with a tendency to atopy using special cosmetics? Let’s look at it below.
Yes, indeed, the skin of children in the first years of life is particularly tender and at the same time insufficiently mature, and therefore vulnerable and prone to irritation.
The anatomical and physiological characteristics of children's skin largely determine the composition and use of care products.
The main skin features of young children are listed below:
- the looseness of the epidermis in combination with a thin stratum corneum leads to a tendency to irritation upon contact with physical and chemical irritants
- fragile connection between the epidermis and dermis
– low moisture content and imperfect blood supply
Below we will talk about skin care products for children prone to atopy.
For many years, Atopic dermatitis in children has been considered the number one problem among skin diseases. This is a chronic allergic inflammatory skin disease, accompanied by itching, rashes of varying morphology and severity and requiring an integrated approach in treatment, which includes the mandatory use of drugs for local use - topical glucocorticosteroids, calcineurin inhibitors, agents with antibacterial and antifungal properties, necessary during exacerbation of the inflammatory process, as well as skin care products during periods of remission of the disease.
In addition to the problem of atopy-prone skin, diaper dermatitis occurs in children, which occurs from exposure of the groin and buttocks to the friction of wet diapers. diapers, detergents, as well as low-quality or incorrectly selected care products. There is also the problem of chapping and sunburn. Thus, in each case, it is necessary to correctly select and use medicinal cosmetics to care for problem skin.
Currently, along with basic anti-inflammatory local therapy for atopic dermatitis, the standard of treatment includes moisturizing and emollient medicinal cosmetics. Until relatively recently, children’s skin care products were not known in Russia, especially in such variety as they are now. Previously, they used sterilized vegetable oil, powder, and simple baby cream.
There are a number of requirements for children's cosmetics
— it is permissible to use only high-quality raw materials
— all ingredients must be approved for use in infants and young children
— cosmetic products must pass safety tests and be certified
— the packaging of the products must indicate the manufacturers of the products, as well as all ingredients, including emulsifiers, flavors, and preservatives.
Simplified classification of essential skin care products
They can be conditionally divided into four main categories
- baby lotion
- baby cream
- baby oil
- protective cream
We will consider products for bathing and sun protection separately.
Lotion. This is a water-alcohol solution for hygienic skin care. The difference between children's lotions is the absence of alcohol in their composition. Their main purpose is to cleanse and moisturize the skin when it is difficult to clean it from dirt with water and conventional detergents. The lotion is usually used in the morning as a cleanser; it does not leave a greasy film on the skin.
Cream. Basic skin care product. The base of the cream is an emulsion consisting of a water and an oil part. Baby cream has a moisturizing and anti-inflammatory effect. Can be applied from one to several times a day to almost the entire surface of the skin.
Oil. Baby oil forms a protective film that protects against dryness and moisture, and can eliminate incipient irritation. In addition to the softening effect, it has a warming effect. There is a special oil that is added to the bathtub for bathing. In addition, the oil is used for children's massage.
Barrier cream. Its purpose is to treat diaper dermatitis.
Baby powder (talc) is an outdated product and is now used much less frequently. Pediatricians are concerned about the possibility of small particles of powder getting into the baby's respiratory tract.
During the remission stage of AD, skin functions are not completely restored, traces of the inflammatory process remain, and an incomplete water-lipid mantle is formed in the stratum corneum. The consequence is transcutaneous loss of water, which contributes to greater penetration of allergens. The skin is dry and sensitive to external factors.
Let us consider in more detail the types of medicinal cosmetics, which currently cannot be avoided in the presence of manifestations of atopic dermatitis, both in the stage of remission of the disease and during an exacerbation.
Their main action is aimed at restoring the natural hydrolipid film, cleansing and moisturizing the skin. All modern medicinal cosmetics do not contain alkali, fragrances, or a minimum of preservatives. The products are suitable for use from birth, as well as by adult patients. It is important to remember that the duration of action of the products in question is no more than 6 hours, so applications should be frequent, and every 3-4 weeks a change of nourishing and moisturizing agents is necessary to prevent the phenomena of tachyphylaxis (addiction to the drug and, as a result, its ineffectiveness ). When applying to children's skin, it is advisable to use the “distal phalanx rule”. A small amount of the planned care product is applied to the fingertip, then rubbed into a limited area of skin (for example, the wrist) to identify unwanted reactions.
Products based on thermal water - Aven, La Roche Posay, Uriage - are very effective. Each laboratory has a program for dry and atopic skin.
The series presented by the Bioderma laboratory is produced using zinc compounds, as well as active biological components of rhamnose, shea butter, kelp extract, and mineral oils. Cleansing - Atoderm Soap, Atoderm Mousse RR, Atoderm Shower Gel. Atoderm RO zinc cream is used in states of exacerbation and incomplete remission, and can be applied to areas of weeping. Balm Atoderm RR – prevention of exacerbation and prevention of recurrent dryness. Atoderm cream - point of application - constitutionally dry skin of adults, children and newborns.
The Avene Trixera series - nourishing is represented by a softening cream, a softening balm, a softening and cleansing gel and a bath. Avene Cold Cream - moisturizing, Avene lotion and Sicalfat cream have an anti-inflammatory effect.
The Locobase series of Astellas Pharma products contains essential lipids, which not only compensate for their deficiency in the stratum corneum of the epidermis, but can also penetrate into its deeper layers, providing a long-lasting effect. Locobase Ripea and Lipocrem - provide hydration and nutrition.
An important task of local therapy for AD is proper daily cleansing of the skin, followed by moisturizing, which reduces pathological changes in the epidermis, restores its functions, prevents exacerbations of the disease, increases the effectiveness of basic treatment and increases the duration of remission. It is important to note that the previous position on limiting bathing for children with AD is outdated. On the contrary, daily bathing (baths are better than showers) actively cleanses, moisturizes, provides better access to medications and improves the functions of the epidermis. To cleanse the skin, it is advisable to use short daily cool baths (33-35 degrees) with a soft detergent base, with a neutral pH and not containing alkali.
Currently, special oil and emulsion (Mustella and Emolium companies) have appeared among bathing products. Added to a baby bath, these products dissolve in water, soften it, and form a protective lipid layer on the skin; active substances penetrating into the skin help prevent water loss and protect against aggressive environmental influences.
Emolium series products. Moisturizer, bathing product.
The Mustella laboratory has long been known in Russia with series for moisturizing - Stelatopia and the treatment of atopic dermatitis - Stellatry. In addition, Mustella presents a foam product for removing seborrheic crusts from the scalp, as well as products with high UV protection to protect delicate skin from active sun rays both in summer and in winter when staying in the mountains.
The article was prepared by a team of pediatricians from the Tiger Cub Children's Medical Center
Prevention
Atopy is translated from Latin as strangeness. The causes of the disease cannot always be determined. But long-term observation of patients and members of their families has revealed that it develops more often:
- with a genetic predisposition - if the parents are healthy, the probability of developing dermatitis in the child is 20%, if one of them is sick - 50%, if both are sick - 80%;
- in case of unfavorable pregnancy, active or passive smoking of the expectant mother, consumption of food that provokes allergy attacks, use of certain medications;
- when a newborn is in a dusty room, insufficient care for his personal hygiene;
- with prolonged exposure to allergens that enter the child’s body with food through the respiratory tract.
Breastfeeding for up to 6 months and avoiding allergy-provoking foods reduces the likelihood of developing atopic dermatitis.
Forms and complications of atopic dermatitis
Depending on your age, atopic dermatitis rashes may look different. There are infant, child and adult forms of the disease. In addition, there are currently two forms of atopic dermatitis depending on the presence of atopy - atopic and non-atopic.
In the atopic form, there is a connection between exacerbations with food, house dust allergens, and less often pollen. Other atopic diseases are often present: bronchial asthma, allergic rhinitis - both in the patient himself and in his close relatives.
It is assumed that there are other forms of atopic dermatitis, since in different patients the disease may have a different set of symptoms and proceed differently. However, clear markers that allow us to judge which scenario the disease will develop in a particular case have not yet been identified.
Atopic dermatitis can be complicated by the addition of an infection - bacterial, fungal or viral. If the pattern of rashes has changed, or you are concerned about your general condition (fever, lethargy, headache, etc.), you should consult a doctor.
What to feed a child with atopic dermatitis
In order not to provoke an exacerbation of dermatitis, to relieve itching and redness of the skin, you need to follow a diet. Foods that burden the immune system are excluded from the children's diet: citrus fruits, chocolate, eggs, honey, seafood. Red (strawberries, cherries, currants, apples) and exotic (mangoes, coconuts, pineapples) fruits are dangerous.
Split meals are recommended: small portions every 3-4 hours. It is better to boil, stew, bake, but not fry. Do not use spices, black pepper. The diet should be balanced and contain enough protein, vitamins, and microelements.
Avoid giving your child sugary carbonated drinks, chips, crackers and other snacks for as long as possible. If the infant is receiving breast milk, introduce new foods carefully. Add the product once a week to make sure it doesn't cause breakouts. After meals and between meals, offer your baby clean boiled water.
Atopic dermatitis in children
Unfortunately, many children experience the first manifestations of skin allergies at an early age. It's not always possible to understand why. It seems that the parents are doing everything right: they don’t let them eat “chemicals”, they take care of the skin, they bathe the baby, they introduce complementary foods correctly, but the child has itching and rashes.
So what is “atopic dermatitis” or, as it is often called in older children, “neurodermatitis”. How to defeat him?
What is atopic dermatitis? Atopic dermatitis is a chronic inflammatory skin disease caused by various factors, in which the child is bothered by itching.
Typically, atopic dermatitis begins in early childhood, can continue or recur in adulthood, and significantly affects the quality of life of the patient and his family members.
Most often, if a child has allergies, then someone in the family has allergies. If both parents suffer from allergies, then, unfortunately, in 82% of cases the child will also have atopic dermatitis.
What happens in the skin during atopic dermatitis: With atopic dermatitis, immune inflammation occurs in the child’s skin, which is accompanied by an increase in its sensitivity to external and internal factors affecting the skin.
Also, with this disease, the protective barrier of the skin is disrupted, which leads to the penetration of allergens through the skin. The amount of fats (lipids) in the skin decreases, which leads to dry skin and itching.
How do doctors diagnose Atopic Dermatitis?
First of all, when examining the child and asking the parents in detail, and only then, based on the results of an allergological examination.
Unfortunately, objective diagnostic tests that can confirm the diagnosis 100% do not currently exist.
Signs of atopic dermatitis:
- Itchy skin
- Typical rashes and their location:
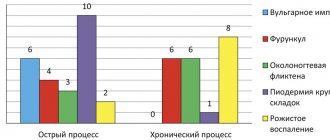
- children of the first two years of life: red spots, spots, weeping skin, most often on the face and less often on the legs and thighs. - older children (2-12 years): severe dry skin, thickening of skin folds, scratching on symmetrical areas of the skin, more often on the flexor surfaces of the limbs, for example, in the elbows or under the knees.
- Early age of onset of allergic rash, most often before one year
- Usually, someone in the family has or has had allergies
- Once allergic rashes appear, they do not go away for a long time
There is also such a non-obvious symptom as “white dermographism”. If you run your finger over the skin of a child’s abdomen, after a while white stripes will appear in the place where the finger touched the child’s skin, which do not immediately disappear.
And yet, what tests can be taken to understand the causes of allergies in a child?
- Clinical blood test
- Skin tests with standardized allergens (they are also called prick tests, skin prick tests). Skin testing is carried out by an allergist when there is no exacerbation of atopic dermatitis in a child, that is, there are no skin rashes and the child is not itching. If a child is taking antihistamines, they must be discontinued at least three days before the test, otherwise the result may be unreliable.
- It is recommended to determine allergen-specific immunoglobulin E antibodies (IgE antibodies) in blood serum. They are also called “allergens”. Using them, you can understand what foods or household factors your child is allergic to, but, unfortunately, they are not always 100% accurate.
What are the manifestations of atopic dermatitis in children like:
There are many skin diseases that allergy rashes in a child may resemble. Here are some of them:
- scabies
- seborrheic dermatitis
- allergic contact dermatitis
- ichthyosis
- psoriasis
All diseases are different and are treated differently.
Therefore, in addition to an allergist, children with regular manifestations of skin allergies should be consulted by a dermatologist.
Treatment There is an opinion that following a low-allergen diet will clear the skin and the itching will go away. This is not entirely true. Treatment must be comprehensive.
There are several areas of treatment and they are all important:
1. Elimination diet 2. Hypoallergenic regimen 3. Proper skin care 4. Taking antihistamines and antibacterial drugs 5. Psychotherapy
Elimination (hypoallergenic) diet
Of course, it is important to identify what foods your child is allergic to. And then, by removing these foods from the diet, you can reduce the manifestations of atopic dermatitis. Please note that it is precisely to reduce, and not to stop altogether, the manifestations of allergies, since a low-allergen diet is important not on its own, but always in combination with proper skin care, which we will discuss below.
But identifying what you are allergic to is often very difficult. Both from laboratory tests and from observing what foods a child eats, it can be difficult to understand what the child is allergic to. In such cases, a so-called hypoallergenic diet is recommended. Foods that can cause an exacerbation of allergies in most people with allergies are excluded from the diet.
Not recommended for use:
- Citrus
- Seafood
- Rich broths
- Processed meat products
- Mayonnaise, vinegar, mustard
- Radish, horseradish, radish
- Spices
- Whole milk
- Honey
- Strawberry
- A pineapple,
- Melon,
- Sweet carbonated drinks,
- Nuts
Hypoallergenic mode
Reducing a child’s contact with an allergen can hardly be overestimated, which is why it is so important to follow household rules. In most cases, it is impossible to completely eliminate contact with the allergen, but as a result of following the recommendations, contact with it is significantly limited, which means that the course of the disease is alleviated and the need for medications is reduced.
Here's what you need to do - the information below is presented by the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation, that is, it is official and truthful:
1. regularly wash bedding (1-2 times a week) at a temperature above 56°C to kill mites (washing with cold water reduces mite allergens by 90%, and washing with hot water destroys mites) 2. wash pillows and blankets with hot water more than 56°C and mattress covers (covers) made of mite-proof fabric 3. remember that good ventilation of the home reduces humidity, reducing the humidity in the house to 40% is important for controlling the number of mites and fungi
Additionally:
1. use vacuum cleaners to clean your home (preferably with a HEPA filter) 2. use special napkins to remove dust 3. to ensure better conditions for cleaning, it is advisable to replace carpets and rugs with linoleum or parquet 4. it is better to change curtains in the bedroom with washable blinds 5. replace fabric-covered furniture with leather or vinyl 6. remove soft toys from the bedroom; if necessary, they can be washed in hot water (over 56°C) or frozen in the freezer of a home refrigerator to kill ticks 7. considering, that house dust mites are sensitive to direct exposure to sunlight, you can dry mattresses, carpets, rugs in the sun for at least 3 hours (taking into account regional characteristics) 8. In addition, special means can be used to destroy house dust mites - cleaning wipes, aerosols, anti-mite bedding, sprays, washing powders, anti-mite carpet cleaners (based on benzyl benzoate - acaricides), anti-mite cleaners for cleaning vacuum cleaners, etc. 9. To achieve the desired result, an integrated approach is important, since most elimination measures applied individually turn out to be unprofitable and ineffective 10. Important! It must be remembered that allergen-free animals do not exist. It is better to take radical measures - part with pets and not get new ones. After removing the animal from the apartment, it is necessary to carry out repeated thorough cleaning of the room to completely remove traces of saliva, excrement, dander, and animal hair. Cat allergens persist in the living room even after the animal is removed for a long time (about 6 months)
Besides:
1. Carpets, mattresses and coverings should be subjected to regular vacuum cleaning; change clothes when leaving home if there was contact with a pet 2. do not visit the circus, zoo and houses where there are animals 3. do not wear clothes made of wool or animal fur
It is also necessary:
1. limit as much as possible contact with environmental factors that cause exacerbation of the disease 2. ensure optimal room humidity (40%) 3. maintain a comfortable air temperature 4. use indoor air conditioning in hot weather 5. do not use synthetic fabrics or wool clothing , preference is for cotton fabrics 6. ensure a calm environment at school and at home 7. cut your nails short 8. during an exacerbation, sleep in cotton socks and gloves 9. do not prohibit bathing! do not use hot water for showers and/or baths; water procedures should be short-term (5-10 minutes) using warm water (32-35°C) 10. use special skin care products for atopic dermatitis (so-called emollients) constantly, even when the skin is “good” 11. for when washing, use liquid rather than powder detergents 12. minimize contact with allergens that cause aggravation of the disease, as well as irritating substances 13. in sunny weather, use sunscreens that do not cause contact irritation of the skin 14. after swimming in the pool, you must take a shower and apply moisturizer 15. completely follow the doctor’s instructions
Not worth it:
1. use alcohol-containing hygiene products 2. use products with antimicrobial components without the recommendation of the attending physician 3. participate in sports, as this causes intense sweating and is accompanied by close contact of the skin with clothing 4. take water procedures too often 5. intensively while washing rub the skin and use tools for washing that are harsher than a terry cloth washcloth
To achieve the desired result, an integrated approach is important, since most elimination measures applied individually turn out to be unprofitable and ineffective.
Proper skin care
The goal of proper skin care is to relieve itching by restoring the water-lipid layer and barrier function of the skin.
1. Local glucocorticosteroids
In case of exacerbation of atopic dermatitis, to quickly alleviate the child’s condition, it is recommended to apply so-called local glucocorticosteroids to the areas of allergy.
2. Calcineurin inhibitors These drugs are recommended to be applied to the skin of a child when atopic dermatitis often worsens, the exacerbations do not subside for a long time, and the child is constantly bothered by itching and irritation of the skin. These drugs are prescribed only by a doctor.
3. Moisturizers and emollients
They are called "emollients". They do not contain hormones or parabens. These products nourish and moisturize the skin, reduce dryness and reduce itching.
It is important to apply them to the skin daily, at least twice a day, even when the skin is smooth, without allergies and without itching.
Emollients are selected individually by parents, on the recommendation of a doctor, so that the child finds their texture pleasant; for some children, it is important that the emollient does not have any odor.
To cleanse the skin, it is advisable to use daily short cool baths (10 minutes) with a soft detergent base with pH 5.5, which does not contain alkali. When cleansing the skin, do not rub it. After bathing, it is recommended to only blot the surface of the skin without wiping it dry.
And it is more effective to use bathing products of the same brand as the emollient. Then they reinforce each other.
Taking antihistamines and antibacterial drugs
1. Antihistamines, or as they are also called, antiallergic drugs, reduce itching. They are prescribed by a doctor.
2. Taking antibacterial drugs Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) often grows on the skin of patients with atopic dermatitis, which increases the manifestations of allergies. Therefore, sometimes it is necessary to use antibacterial drugs in the form of cream/ointment or in the form of syrup, which the child takes orally.
Psychotherapy
Working with a psychotherapist and a psychologist is also important. These specialists teach the child techniques for relaxation, stress relief and behavior modification. But these methods are only suitable for older children.
What's next?
Atopic dermatitis has a wavy, relapsing course: unfortunately, 60% return throughout life. Therefore, a hypoallergenic lifestyle, proper skin care (constant use of emollients), and a hypoallergenic diet are important throughout the life of a child with atopic dermatitis.
Atopic dermatitis is a chronic skin disease that significantly reduces a child’s quality of life due to constant itching and dry skin, but it can be managed thanks to the achievements of modern medicine. It is important to find a doctor you trust and follow his recommendations.
Skin care
To relieve itching and prevent infection of the affected skin, you need to properly care for your skin:
- It’s better not to take a shower, but to take a cool bath for about 10 minutes; use medicated bathing products with a soft base that cleanse but do not dry the skin;
- moisturizing and softening – the skin should not be dry to prevent flaking and cracking; regularly apply a moisturizer recommended by a dermatologist;
- Do not let your child scratch the affected areas to avoid infection - apply anti-itching products to the atopic areas.
Cream or gel relieves discomfort during an exacerbation and allows you to sleep, eat, and play peacefully. Apply the drug to cleansed skin, treat atopic lesions and the areas around them. Do not exceed the recommended dosage and frequency of use.
Rating of the best remedies for atopic dermatitis
To treat atopic dermatitis, use special children's products recommended by a dermatologist. During exacerbations, medications are prescribed for oral administration, application to atopic areas and general body care:
- preparations for removing allergens from the body - Enterosgel, Lactrofiltrum, Enterodes;
- skin softening products – Atopic cream for daily care;
- drugs that relieve itching - Panthenol spray;
- bathing products - soft shower gels for atopic dermatitis should be purchased at the pharmacy: dermatologists recommend using Atopic bathing gel from head to toe.
Types of emollients
There are three main types of emollients.
- Natural.
They contain vegetable oils: peach, almond, shea butter, jojoba, cocoa, lanolin, wax. Their advantage is that they are of natural origin. The disadvantage is that they can cause an allergic reaction. More often, natural components are not tolerated by adult patients. Therefore, a natural-based cosmetic product is a good choice for a baby. - Chemical.
They use substances obtained during oil refining. These include: paraffin, silicone, mineral oils, petroleum jelly. Such emollients create a dense film and make it difficult for the skin to breathe. However, they rarely cause an allergic reaction. For children, this is the least preferred type of cosmetic product. - Synthetic.
Their basis is substances obtained as a result of chemical synthesis. For example, dimethicones and cyclomethicones. Such substances perform their barrier function well, interfere with skin breathing to a lesser extent and rarely cause an allergic reaction.
Additionally, emollients include moisturizing substances: urea, lactic acid, hyaluronic acid, glycerol, and the like. Some cosmetics also include fat-soluble vitamins: A, E, PP.
Ready-made cosmetics based on emollient are divided into types:
- Ointments
are products made from fats. They have the densest consistency and are applied to skin with severe dryness and flaking. Children rarely need this type of emollient. - Creams
are water-fat based products. They have a pleasant consistency, absorb well and moisturize the skin. Such products are the most common option for skin care in children and atopic dermatitis. - An emulsion
is a water-fat based product that has a thinner consistency than a cream. This product is convenient to apply to large surfaces of the body. They are usually sold in large bottles. - Lotion
is a water-based product. It is preferable to use it on skin prone to weeping (inflammation with the formation of blisters). This type of cosmetic product is not suitable for dry skin.
In the line of skin care products, there are special products that are added to the water when bathing: shampoos, shower gels, hand soap.
Bathing
After a light shower to thoroughly cleanse your entire body, apply Atopic Bathing Gel to damp skin from head to toe, massage lightly and rinse thoroughly. Dry your baby with a soft towel using blotting, but not rubbing, movements. After water treatments, apply Atopic skin softening cream for daily care. Apply it several times throughout the day: after washing your hands and washing your face.
When taking a bath, the water temperature should not exceed 36 degrees. Place your child in the water and offer him toys or other entertainment. After 5-7 minutes, apply Atopic Bathing Gel from head to toe and rinse well. After bathing, use Atopic cream for daily care, and if itching bothers you, let the cream absorb, and then treat the affected skin with an anti-itching drug.
Do emollients have any contraindications or disadvantages?
Emollients are not a medicine, but a care product. This means that there are no special indications for them. Such cosmetics can also be used for ordinary skin to maintain or improve its condition. However, there are still some restrictions on the use of such cosmetics:
- As with any other skin care product, emollients can cause a contact allergic reaction. Therefore, before generously applying the product to the entire surface of the skin, test it on a small area of the inner surface of the forearm. Apply a small amount of emollient and observe the reaction during the day;
- Do not apply emollient to skin with an acute inflammatory rash, weeping or fresh scratching. Creating a film will increase the risk of spreading infection. Such skin must first be treated with medications.
- emollient containing urea or ammonia should not be applied to areas with injured skin. When such products are applied to injured skin, a burning sensation occurs in these areas.
- Before you start using emollient, you should show your baby to a doctor. Your doctor may recommend using a care product and medicine at the same time. Either cure dermatitis first, and then select a cosmetic product;
There are some inconveniences when using emollients. For example, with abundant and frequent application, underwear and bed linen become dirty. Some mothers of my patients over one year old pay attention to the fact that children do not like the feeling of a thick layer of cosmetic product on the skin. However, most kids quickly get used to it.
Another inconvenience occurs when emollients added to the water during bathing, or applied before bathing, leave a residue on the surface of the bath. This plaque must be washed off with detergents.
How to choose products that are right for your child
A dermatologist may recommend not one, but several drugs to choose from. They have a similar mechanism of action, but their prices may differ significantly. It depends on the active and auxiliary substances, manufacturer, and release form. When choosing a cream for a child’s atopic skin, you need to take into account possible individual intolerance to individual components.
You need to purchase drugs from well-known manufacturers with a good reputation: Russian, European, American. It is equally important to contact large pharmacy chains that work directly with manufacturers and control the quality of drugs on sale - this will protect you from purchasing counterfeit drugs. Consider the age of the child: choose creams and gels with a pleasant smell so that the child enjoys going to the shower.v
When choosing drugs for oral administration, it is preferable to buy syrups, powders, drops, rather than tablets and capsules that are difficult for a child to swallow.