There are several different hepatitis caused by different viruses. Each of them has its own characteristics and characteristic effects on the body, but they still have similarities.
An infectious disease that is caused by an RNA virus is called hepatitis G. This pathogen is transmitted from one person to another most often through blood.
This disease often runs its course on its own. But sometimes it is combined with other types of hepatitis, for example, B.
The course and prognosis of the disease, as well as the chosen treatment paths, largely depend on this factor. Therefore, it is very important to diagnose it correctly.
In this article we will analyze the disease, the causes of its occurrence, methods of diagnosis and methods of its successful treatment.
Also at the end of the material you will find the names of medications that help in the fight against the disease.
What is hepatitis G
The infectious agent (the main cause of the disease) belongs to the flavivirus family. It was detected in the blood of a surgeon who suffered from hepatitis of an unknown form. The genetic material of the pathogen is represented by RNA. Unlike the type C virus, it does not have a region in its genome responsible for the diversity of genotypes.
The pathogenesis of the disease has not been fully studied, which is due to the relatively recent identification of the pathogen, the high frequency of mixed infection, as well as the low prevalence of hepatitis G as an independent pathology.
A pathogenic agent can cause acute liver damage or predispose to chronic infection. The hepatitis G virus is detected in the body a week after a transfusion of infected blood.
What it is
Hepatitis G is a disease that is caused by an RNA virus. This virus was isolated in the late 60s of the 20th century. Scientists described its symptoms only in the 90s.
Brief medical history
Currently, there is insufficient information about the nature of the disease and the frequency of infection. There is also a lack of information about methods to combat this virus. It is clearly established that the main infection with the virus occurs through blood transfusion or other blood-related events.
Modern researchers have given a name to the new virus - hepatitis G. Another group of scientists named it GBV-C , with the letters GB referring to the surgeon's first name and patronymic. It was he who studied the properties and effects of this virus on monkeys.
The number of works studying the clinical manifestations of this infection is very small. This is because hepatitis G infection is detected very rarely. Most often, scientists study hepatitis, which has a high mortality rate.
Types and forms
Hepatitis A viruses were the first to be discovered by scientists. Later, other viruses of this infection were identified. These include hepatitis,... In addition to these viruses, well known to doctors, new cases of hepatitis soon began to appear. It was difficult to identify them based on existing characteristics. Recently a new form of liver inflammation was discovered. It was called viral hepatitis G.
This disease is considered close in its action and symptoms to hepatitis C.
Prevalence and significance
The prevalence of this type of hepatitis in different countries of the world is very uneven. The infection is spread by patients in the acute stage of the disease. But often the virus can be caught from a patient with a “chronic”. Hepatitis G is very often found together with hepatitis D, B, C. This virus is found in drug addicts in a third of cases.
What consequences
Hepatitis G can lead to dysfunction of the patient's internal organs, such as the liver. Hepatic coma often leads to the death of the patient. The main factor in possible complications is the mixing of several types of virus.
In its acute form, this disease can end happily, that is, with the patient’s recovery. But the degeneration of hepatitis into the chronic stage is also real. A patient may be a carrier of the virus and be completely unaware of it. If this type of hepatitis is combined with hepatitis C, it can develop into cirrhosis.
Clinical manifestations
Hepatitis G is asymptomatic in most cases, which makes initial diagnosis difficult. The first sign of the disease may appear at the stage of progressive liver failure. The course of the disease resembles the clinical picture of hepatitis C.
The difference between hepatitis G is its slower development and the absence of such severe complications as cirrhosis and malignant degeneration of liver tissue.
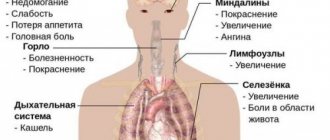
The incubation period is about six months, after which signs of ARVI appear. They are presented:
- hyperthermia, which is characterized by a slow increase;
- myalgia, arthralgia (muscle and joint pain);
- severe malaise;
- decreased performance;
- chills;
- headache;
- decreased appetite;
- skin rashes.
A significant deterioration in the condition is observed after 2-3 days, which is expressed by:
- lack of appetite;
- dyspeptic disorders (nausea, vomiting, intestinal dysfunction in the form of diarrhea);
- painful sensations in the area of the right hypochondrium. They occur when the volume of the liver increases, due to which the fibrous capsule of the gland stretches and the nerve endings are irritated.
As a rule, a person is being treated for the flu at this time, without even thinking about hepatitis. Suspicion of liver damage arises when the first symptom of jaundice appears - a change in the color of the skin and mucous membranes.
In addition, hepatitis D manifests itself:
- discoloration of feces, which is associated with insufficient intake of stercobilin in the intestines, causing the color of stool to change;
- darkening of urine;
- hepatosplenomegaly (increased volume of the liver and spleen). When palpating (feeling) the area of the right hypochondrium, the doctor discovers a compacted and painful gland.
The severity of icteric syndrome depends on the severity of organ damage. As the infectious process is suppressed, regression of symptoms is observed. The intensity of jaundice decreases first. As for hepatomegaly, it persists much longer and manifests itself as heaviness in the area of the right hypochondrium. Gradually the disease becomes chronic.
Considering the high risk of mixed infection, hepatitis C can lead to cirrhosis and a malignant process, so it is not recommended to neglect the symptoms of the disease.
Disease prognosis
The last resort in treatment is a liver transplant.
There is no exact information yet about how dangerous hepatitis G is for the liver and for health in general. Based on the studies conducted, it can be concluded that infected patients can develop lymphoma. This is the name of cancer of the lymphatic system, which is almost impossible to cure.
If you do not pay attention to the progressive disease, cirrhosis will develop.
Transmission routes
Epidemiological and clinical studies indicate parenteral transmission of the pathogen. The disease is a consequence of infection of the body with the hepatitis G virus (HGV).
It has now been established that the largest number of cases of the disease are recorded among people who frequently come into contact with blood. This applies to donors, patients after blood transfusion and parenteral manipulations.
Transmission of the pathogen in this case occurs through the blood. The risk group also includes injection drug users and people who regularly undergo hemodialysis. There is a significant risk of infection when visiting a dentist, gynecologist and other specialists whose work involves biological fluids. In this case, the cause of infection is a violation of sanitary standards. This can happen in tattoo parlors or when ears are pierced.
There is also information about the sexual way of spreading the infection. Thus, in the group of people suffering from syphilis, HIV and chlamydia, the frequency of hepatitis G is much higher. A greater risk of infection is observed in homosexuals, bisexuals, and those who have multiple sexual partners.
Infection during intimate intimacy occurs when the integrity of the mucous membranes or skin of the genitals is violated.
Another method of pathogen transmission is vertical. Infection of a newborn is registered in 50% of cases when the mother and baby have a wound surface, resulting in contact with blood. The greatest risk of infection is observed if a pregnant woman suffers from acute hepatitis.
According to research, in 40% of cases the cause of the disease cannot be determined.
Causes
Hepatitis G is transmitted in the same way as hepatitis C, that is, through blood . Therefore, drug addicts most often suffer from this type of hepatitis. Pregnant women often infect their unborn child with this virus. Half of children already have this infection in their bodies from birth. The virus cannot be transmitted from mother to child through breast milk. Sexual contact is a common route of transmission of the hepatitis G virus.
Donor blood may also contain the hepatitis G virus. When receiving a blood transfusion, the risk of receiving it becomes quite large. The percentage of donors who are carriers of this virus is relatively small. But now clinics carefully check blood for its presence.
People who require repeated blood transfusions are at greatest risk. Most often, hepatitis G infection occurs as a result of using the same contaminated medical needle.
The risk of complications increases significantly with an active form of the virus. It also increases when the virus and HIV infection . If you pierce your ears with an unsterile needle or perform poor-quality acupuncture, you can also catch the hepatitis virus. But most often the method of obtaining this virus remains unknown. The risk of infection during organ transplantation is approximately 25%.
Incubation period
The infectious etiology of the disease is caused by the penetration of HGV into the human body. On average, about six months can pass from the moment of infection to the onset of clinical symptoms (provided that hepatitis G develops as an independent pathology). If the liver is simultaneously affected by several pathogens, the incubation period can range from two weeks to six months.
During this period, replication of genetic material takes place, as a result of which the number of infectious individuals rapidly increases. As a result of the death of hepatocytes, the disease is accompanied by the appearance of clinical signs of liver damage.
Sources
- Meier-Stephenson V., Badmalia MD., Mrozowich T., Lau KC., Schultz SK., Gemmill DL., Osiowy C., van Marle G., Coffin CS., Patel TR. Identification and characterization of a G-quadruplex structure in the pre-core promoter region of hepatitis B virus covalently closed circular DNA. // J Biol Chem - 2021 - Vol - NNULL - p.100589; PMID:33774051
- Li Y., Yan L., Wang R., Wang Q., You Z., Li B., Zhang J., Huang B., Chen Y., Li Y., Lian M., Tang R., Qiu D ., Gershwin ME., Xiao X., Miao Q., Ma X. Correction to: Serum Immunoglobulin G Levels Predict Biochemical and Histological Remission of Autoimmune Hepatitis Type 1: A Single‑Center Experience and Literature Review. // Clin Rev Allergy Immunol - 2021 - Vol - NNULL - p.; PMID:33666868
- Thevenot T., Desmarets M. G-CSF, a ray of sunshine in the darkness for patients with alcoholic hepatitis? // Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol - 2021 - Vol45 - N2 - p.101585; PMID:33607376
- Li Y., Yan L., Wang R., Wang Q., You Z., Li B., Zhang J., Huang B., Chen Y., Li Y., Lian M., Tang R., Qiu D ., Gershwin ME., Xiao X., Miao Q., Ma X. Serum Immunoglobulin G Levels Predict Biochemical and Histological Remission of Autoimmune Hepatitis Type 1: A Single-Center Experience and Literature Review. // Clin Rev Allergy Immunol - 2021 - Vol - NNULL - p.; PMID:33512642
- Ito K., Okumura A., S Takeuchi J., Watashi K., Inoue R., Yamauchi T., Sakamoto K., Yamashita Y., Iguchi Y., Une M., Wakita T., Umezawa K., Yoneda M. Dual Agonist of Farnesoid X Receptor and G Protein-coupled Receptor TGR5 Inhibits Hepatitis B Virus Infection in Vitro and in Vivo. // Hepatology - 2021 - Vol - NNULL - p.; PMID:33434356
- Han T.T., Huang J.H., Gu J., Xie Q.D., Zhong Y., Huang T.H. Hepatitis B virus surface protein induces sperm dysfunction through the activation of a Bcl2/Bax signaling cascade triggering AIF/Endo G-mediated apoptosis. // Andrology - 2021 - Vol - NNULL - p.; PMID:33382193
- Wan L., Guo L., Hu Y., Huang H., Zhang M., Xu K., De G., Zheng F., Wu Z., Hu C., Wen Z. Comparing the diagnostic value of serum oligosaccharide chain (G-test) and alpha-fetoprotein for hepatitis B virus-related liver cancer. // Clin Biochem - 2021 - Vol89 - NNULL - p.44-50; PMID:33309517
- Clemente MG., Mauceri C., Grandi N., Marescalco S., Arras M., Bitti A., Galleri G., Manetti R., Schwarz K., Piana A., Castiglia P., Antonucci R. No Hepatitis G virus co-infection in migrants with Hepatitis B or C hosted in Sardinia and Sicily. // Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol - 2021 - Vol - NNULL - p.101566; PMID:33234432
- Wolf JM., De Carli S., Pereira VRZB., Simon D., Lunge VR. Temporal evolution and global spread of hepatitis B virus genotype G. // J Viral Hepat - 2021 - Vol28 - N2 - p.393-399; PMID:33128240
- Bergløv A., Hallager S., Panum I., Weis N. Prevalence of herpes -, measles morbillivirus-, parvovirus B19 - and rubella viruses immunoglobulin G among women with chronic hepatitis B of reproductive age in Denmark: A cross-sectional study. // Int J Infect Dis - 2021 - Vol101 - NNULL - p.269-275; PMID:33011282
Diagnostics
In most cases, diagnosis is made by excluding other types of hepatitis. For this purpose, laboratory research is carried out to identify the genetic material of pathogens. Instrumental methods are used to visualize the liver and assess the extent of the pathological process.
Now in more detail about each diagnostic method.
Laboratory research
Laboratory diagnostics begins with the search for antibodies to the surface type of glycoprotein E2 of the pathogen. Studies have shown that its detection indicates the absence of the disease. The test is designated as follows: anti-E2 HGV;. These antibodies do not last long in the patient’s blood. After the disappearance of viral RNA, only IGGs remain, which confirm the fact of previous hepatitis.
Identification of the pathogen is carried out by amplification. For this purpose, special test systems are used, which are produced exclusively for scientific research.
Using an enzyme immunoassay, it is possible to detect immunoglobulins G, which are synthesized against the E2 protein. At the same time, attempts to develop methods for registering IGM have so far remained unsuccessful.
Numerous studies prove the high frequency of spontaneous recovery of the patient.
As for specific diagnostics, it is carried out using a polymerase chain reaction, which makes it possible to detect the genetic material of the pathogen in the patient’s blood. Test systems can detect HGV RNA.
Additionally assigned:
- biochemistry. The analysis makes it possible to assess the severity of the infectious process and the severity of liver damage. To do this, the level of transaminases (ALT, AST), protein, alkaline phosphatase and bilirubin is determined;
- A coagulogram is necessary to assess the state of the blood coagulation system.
Instrumental methods
In order to visualize the liver and surrounding internal organs, the doctor prescribes an ultrasound examination. It allows you to examine the gland, determine its size, structure and density. If a more accurate diagnosis is needed, computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging can be used.
X-ray examinations are carried out using a contrast agent, which makes it possible to visualize the bile ducts and detect an obstacle to the movement of bile.
In doubtful cases, a biopsy is performed. It allows you to examine the structure of the liver and determine the shape of the lesion. Elastography is considered more informative.
Symptoms and diagnosis
One of the symptoms of hepatitis G is jaundice
The disease is often asymptomatic and is diagnosed during the treatment of another disease. Signs of hepatitis:
- nagging pain in the right side under the ribs;
- jaundice if other hepatitis is present;
- temperature increase;
- itching on the skin.
Changes in the blood are also detected during laboratory tests:
- growth of liver tests;
- high bilirubin;
- to study hepatitis markers.
In acute hepatitis, the incubation period is about 11 days . The duration of the icteric period is about 3 weeks . Moderate intoxication is also observed.
Diagnostics
When making a diagnosis, the main attention is paid to symptoms and laboratory data. These include, first of all, changes in blood biochemistry. The PCR method is also used to diagnose hepatitis G. With its help, the RNA of the hepatitis G virus is detected, that is, the source of this infection.
PCR can detect a DNA fragment. This method also allows us to identify the characteristics of virus reproduction and its further cloning. This method of detecting a virus is one of the most expensive and at the same time very complex methods. Now scientists are trying to create tests for antibodies to this type of virus. For hepatitis G, the doctor also necessarily prescribes a detailed study of serum, plasma and blood cells.
Possible complications
In most cases, no serious complications of the disease are observed. There are several forms of hepatitis:
- typical, characterized by a slow onset of clinical symptoms and a slight change in laboratory parameters. Jaundice may be mild or absent altogether;
- fulminant is characterized by rapid deterioration of the condition, severe jaundice and a sharp change in laboratory indicators of liver function.
Often, the latter form develops with combined damage to the gland by viruses of types B or C. In this case, the risk of developing:
- cirrhosis, when normal organ tissue is replaced by connective tissue, as a result of which liver functions suffer;
- portal hypertension, in which the pressure in the venous system increases, which is manifested by varicose veins of the esophagus, ascites and the appearance of veins on the abdomen;
- bleeding as complications of cirrhosis;
- malignant process, when cells change their structure and form a tumor focus;
- cholestasis (stagnation of bile) when the excretory ducts are blocked.
How dangerous is hepatitis G during pregnancy?
As for the vertical mode of transmission of the pathogen, research is under study. According to statistics, 35-55% of infants born to HGV-positive mothers were infected. The maximum risk of infection is observed during the period when a pregnant woman experiences the acute stage of hepatitis.
Babies delivered by caesarean section have a lower risk of infection compared to babies born vaginally. In the latter case, even with a negative result for HGV in the first days of life, the virus can subsequently be detected in the child’s blood. All this indicates a high risk of intrauterine infection, as well as the possibility of transmission of the pathogen during labor.
During lactation, infection does not occur.
Preventive measures
To avoid contracting hepatitis, it is important to avoid direct contact with blood and always wear gloves. It is also necessary to use your own personal hygiene products and think about the rules of safe sex. It is important to get proper rest, get enough sleep, maintain a healthy lifestyle and normal physical activity.
Articles about other types of hepatitis:
- About hepatitis A
- About hepatitis B (B)
- About hepatitis D (D)
Treatment
Treatment tactics for hepatitis G have not been developed due to insufficient information about the disease. In this regard, therapy is prescribed, which is usually used for infectious liver damage by other types of viruses:
- interferon-alpha, which prevents infection of new cells and, accordingly, the progression of pathology;
- ribavirin;
- hepatoprotectors necessary for the protection and restoration of liver cells.
Diet is considered an important part of therapy. Its main task is to relieve the hepatobiliary tract (liver, bladder and bile ducts), normalize digestion and metabolism. Table No. 5 includes:
- fractional meals (up to six times in small portions);
- salt restriction;
- refusal of fresh baked goods, sweets, coffee, hot spices, fatty foods, smoked foods, preserves and sour foods (sorrel);
- drinking plenty of water;
- enriching the diet with cereals, low-fat milk, fish and meat products, vegetables and fruits.
During the treatment process, regular examinations are mandatory. With the help of biochemical and immunological analyses, it is possible to monitor the dynamics and severity of the disease and, if necessary, correct therapy.
Treatment options
Treatment of hepatitis G requires mandatory observation by the attending physician in a hospital or in medical centers. Regular blood tests are also important. In addition, it is very important to maintain bed rest. It helps internal organs recover faster and speed up recovery. Oxygen treatment may also be prescribed, but this is done only in exceptional cases.
Medicines are used to treat chronic viral infections. They stop further liver damage and destroy the virus. In the presence of hepatitis C and B, therapy for these diseases is prescribed.
Which doctors should I contact?
Treatment with medications and diet should begin as early as possible
If signs of hepatitis G appear, you should consult a physician and virologist.
What medications are prescribed?
To reduce liver inflammation and prevent the development of cirrhosis, it is important to begin treatment for this disease in a timely manner. As a result, the virus can be completely or partially removed from the body.
The drug Alpha Interferon can be used in any treatment for hepatitis B. As a result, new liver cells are not infected. The transformation of the disease into liver cancer also becomes almost impossible. If the drug is used together with Ribavirin, the effect of this treatment will be much better.
Surgical methods of treatment
In medical centers for hepatitis G, liver transplantation can be performed. This form of hepatitis leads to high mortality if the damaged organ is not transplanted.
Ethnoscience:
- blue plum cuttings with buds are used to treat hepatitis. In the Urals and Siberian region, raspberries with cuttings and buds are ideal for this. Crushed cuttings are poured with boiling water and taken orally before meals for a month. After 3 months, the treatment is repeated. You need to drink infusions every year until the patient is cured. At this time, you should also drink vegetable juices, rosehip drinks, and take fish oil;
- Chanterelle mushroom powder is poured with vodka and left for 10 days. The container must be shaken daily. Take the drug for about 4 months.
Diet
Adjusting nutrition allows you to reduce the load on the diseased organ and effectively supports the body. Moreover, it is prescribed individually to each patient. It is important to completely stop drinking alcohol, coffee, and reduce the consumption of salt, fatty and spicy foods. You need to eat more fermented milk products, vegetables, cereals, fruits, and lean meats.
It is recommended to steam or boil foods. Milk should not be consumed, but it can be used to prepare various dishes and sauces. Pastila and marshmallows can be consumed as dessert. You need to drink more water, compotes, tea or jelly. Split meals help with this disease.
An important component of effective treatment is proper nutrition.
Prognosis and prevention
If hepatitis G is an independent disease, the prognosis is favorable. The pathology will proceed almost unnoticed, after which protective antibodies will remain in the blood. Having an HGV infection does not exclude the possibility of developing hepatitis B or C in the future.
The prognosis for life will be significantly worse if a person abuses alcohol or does not adhere to a diet.
Specific prevention, namely vaccination, has not been developed to date. In this regard, the following rules must be adhered to:
- use barrier contraception (condoms) during intimacy;
- do not visit tattoo and piercing parlors with a bad reputation;
- control which instruments are used to perform manipulations (whether there are traces of blood on them);
- When planning a pregnancy, you should undergo a full examination to exclude the possibility of infection of the embryo.
Regular examination will help prevent the development of complications, so you need to monitor your health and consult a doctor in a timely manner.