When the coccyx is fractured, the integrity of the bone in this area is compromised due to injury or bone disease. Most often, the disorder occurs as a result of a fall on the buttocks or a blow to the tailbone. A coccyx fracture is manifested by pain, impaired motor activity, increased muscle tone, swelling, etc.
To make a diagnosis, a visual examination is performed, as well as instrumental studies. As a rule, conservative methods are used to treat a fracture. Surgical intervention is necessary for a displaced fracture, when it is not possible to compare the bone fragments and there is prolonged severe pain.
Basic information
The coccyx is located at the very bottom of the spinal column; it consists of 3 to 5 vertebrae that are fused together. The bone is beak-shaped, its base is directed upward, and its upper part is directed downward and forward. Its first largest vertebra is connected to the sacrum by the coccygeal horns, thus forming the sacrococcygeal joint.
In children, a cartilage pad is placed between the vertebrae of the coccyx, so this area is mobile. Over time, these elements fuse and form a single bone.
Reference. The tailbone is an almost motionless area. Movements in it appear in women during childbirth, then the bone bends back, expanding the birth canal.
The functions of the coccygeal bone are very important; muscles and ligaments are attached to it, which are necessary for the normal functioning of the organs of the genitourinary system, the most distant parts of the colon. In addition, bundles of the gluteus maximus muscle, which is involved in hip extension, are attached to its outer surface. The tailbone reduces the load on the pelvic bones when the torso is tilted back. This area is surrounded by nerve fibers, so pain occurs when it is damaged.
In most cases, coccyx injuries are diagnosed in patients 33–45 years old (more often in men). Children and adolescents commonly suffer from dislocation of the vertebrae of the coccygeal bone.
Often a fracture of the coccyx is combined with the following injuries:
- fracture-dislocation (often combined with a fracture of the pelvic bones);
- ligament rupture.
In most cases, the following injuries to the lower spine are observed:
- Injury to only the vertebrae of the coccygeal bone.
- Damage to one or more elements, in which the integrity of the intervertebral joints above or below the injured vertebrae is disrupted.
- A fracture of the coccygeal bone, in which the nerve fibers are torn or torn.
- Combined fracture of the coccyx and other segments of the spinal column.
More often, a closed fracture occurs, in which the integrity of the skin over the injured area is not broken.
The weakest area that is usually damaged is the ossified sacrococcygeal joint. Synchondroses (the joints between the vertebrae of the coccyx) are also often damaged.
The most severe are comminuted fractures, in which the intervertebral disc is destroyed and its fragments move.
With an isolated injury, the spinal cord is not damaged, but the risk of pinching or rupture of the cauda equina (spinal nerve roots) increases.
Depending on the severity, there are uncomplicated and complicated coccyx fractures. The latter type of injury is accompanied by damage to nerve structures.
Complications
Spinal operations in the immediate vicinity of the spinal cord and nerve roots are potentially dangerous. Complications associated with spinal compression fractures include:
- Kyphotic deformity is more common in older people, with severe osteoporosis and a compression fracture caused by it, and in patients with excess body weight. A pointed or flat hump is formed in the area of the thoracic spine. Kyphosis is a source of debilitating pain and abnormalities in the functioning of the cardiovascular system, lungs, and stomach. Patients experience digestive problems, chronic fatigue, fatigue and shortness of breath.
- Segmental instability - the disease occurs with a compression fracture with more than 30% loss of vertebral height. Stability in the spinal segment is disrupted and causes difficulties in performing necessary functions, discomfort and pain. Instability of a segment in the spinal column leads to an acceleration of the degenerative process.
- Neurological complications - as a result of a compression fracture of the spine, bone fragments may be displaced posteriorly, causing compression of the nerve roots and spinal cord. After some time, and possibly immediately, a narrowing of the spinal canal caused by a compression fracture may appear. In addition to compression of the spinal cord, pressure also occurs on the vessels tightly intertwining the nerve structures. The main symptoms indicate a problem with neurology - pain, not only with minor exertion, but also at rest, numbness of the limbs, loss of sensitivity.
To avoid complications with a compression fracture of the spine, you must immediately consult a doctor for examination and timely treatment.
Rehabilitation after a compression fracture of the spine
Post-traumatic rehabilitation, a certain period of recovery after a compression fracture, is of no small importance. The patient’s future health depends on how well the rehabilitation after a compression fracture of the spine is carried out. The main goal of rehabilitation measures is to restore the damaged spine and return to an active lifestyle. The rehabilitation period for a compression fracture may include:
- physiotherapy,
- electrical stimulation,
- massotherapy.
- Exercise therapy is required.
Competent therapeutic movements in the post-traumatic period are very important. Patients are allowed to make the first movements after removal of the fixing structures, and sometimes even if they are present.
It is better if the exercises after a compression fracture are supervised by a clinic specialist, but you can also perform exercises at home.
A course of exercise therapy, consisting of four stages, will help the patient quickly return to his usual lifestyle.
The main goal of a set of exercises for a compression fracture is to strengthen the muscle corset. To prevent a decrease in muscle strength, exercises have been developed to improve the functioning of the cardiovascular system, gastrointestinal tract, and respiratory organs. The load is increased gradually, extending the time of exercise therapy and introducing new exercises. Then, under the supervision of a specialist, the patient is prepared for vertical loads and exercises with weights and resistance are introduced.
For each patient, the period of physical therapy for a compression fracture is assigned individually.
Causes of injury
In most cases, the injury occurs after a fall on the buttocks. Slightly less often, the lower part of the spine is damaged after a blow with a blunt object. It is possible to break your coccygeal bone during childbirth, but this is rare. This usually happens if the baby is large, and the woman in labor has a narrow pelvis, if the fetus is not positioned correctly, or if the pregnant woman has injured a bone in a fracture.
A fall on the buttocks is one of the most common causes of a fracture.
According to statistics, the tailbone is most often injured in the following situations:
- If a person falls from a height at home or at work, if a person violates safety precautions. In winter when there is ice or on a wet floor.
- After jumping into a body of water that is shallow.
- After being hit on the tailbone with a blunt heavy object.
Reference. With osteoporosis and other diseases of bone tissue, a person can injure the lower spine during a sharp turn, bending, shaking while riding a vehicle, cycling, etc.
People who are intoxicated are often injured.
Damage to the lower spine is possible after a direct blow in the following cases:
- Major accident at a technical facility.
- Natural disasters, such as earthquakes.
- Domestic conflicts.
- Strength sports, group games. In most cases, wrestlers, football players, hockey players, etc. are injured.
The tailbone can also be injured during an accident.
Features of the structure of the coccyx
The coccyx is the lower portion of the spine, which may have three to five fused vertebrae . They are arranged in the form of an inverted pyramid with the base at the top and the apex at the bottom.
Pay attention to the structure of the coccyx
The first vertebra is endowed with modified upper articular processes, the so-called coccygeal horns. Its lateral surfaces have rudimentary (non-functioning) transverse processes. The remaining vertebrae do not have such processes.
Symptoms
A true fracture of the coccygeal bone, when small bone processes are damaged, occurs extremely rarely. More often, the ligaments of the sacrococcygeal joint are damaged or the vertebrae of the lower spine are displaced.
Symptoms of a coccyx fracture:
- sharp pain in the lower back;
- pathological mobility, which is accompanied by crunching bones;
- increased muscle tone in the damaged area;
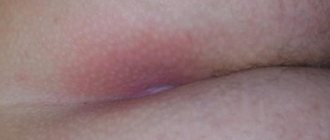
- redness and swelling above the tailbone.
It is difficult for the victim to move his legs, and when sitting and standing, the pain syndrome becomes more pronounced.
A broken tailbone is manifested by a sharp piercing pain, which often spreads to surrounding tissues. Over time, it becomes aching in nature, but intensifies when trying to empty the bowels or sit down. Discomfort often worsens while walking.
Signs of damage to the cauda equina after a fracture of the coccygeal bone:
- pain in the lower back that radiates to the lower limbs;
- impaired sensitivity in the area of the coccyx, sacrum, groin;
- feeling of numbness, tingling in the legs;
- in the worst case, the sensitivity of the lower extremities completely disappears;
- weakening of the muscles below the coccyx, complete paralysis is possible;
- violation of defecation, which is manifested by constipation, impaired control over the process of bowel movement, impaired sensitivity of the anus;
- dysfunction of the bladder functionality, then ischuria (urinary retention) occurs, decreased sensitivity of the urethral sphincter.
With osteoporosis, the likelihood of combined fractures increases, then the symptoms are varied.
With a crushed fracture, pain, nausea, profuse vomiting appears, which does not bring relief, and delayed passage of gas and stool.
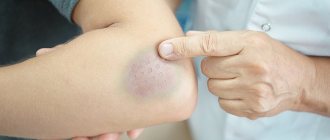
Reference. A fracture of the coccygeal bone differs from a bruise in that in the first case there is a bruise, and in the second there is not. When the integrity of the bone is violated, piercing pain appears, and when there is a bruise, its intensity changes. A fracture of the coccyx is characterized by increased pain during coughing, sneezing, and sitting, but not with a bruise.
A compression fracture of the coccyx may have delayed symptoms that appear after several months. Then a crack appears in the bone, and then with minimal physical exertion the bone fragment comes off. Then pain and swelling occurs.
Signs and symptoms of a compression fracture
A compression fracture is characterized by the following manifestations:
- Pain, which is the main symptom of a compression fracture, gradually increases in the back, upper and lower extremities.
- Manifestation of general malaise, with complaints of weakness, dizziness and fatigue.
- If the nerve endings are damaged, symptoms such as numbness and decreased sensitivity appear.
- A severe form of compression fracture is the worst case scenario, characterized by severe pressure on the spinal cord and excruciating back pain. Severe pain syndrome is aggravated by disruption of the internal organs, the pelvic organs suffer the most.
Get a free consultation by phone
Consequences of injury
Complications are caused by fractures of the coccyx with displacement of bone fragments:
- The spinal cord is damaged. Then the victim feels constant pain while moving (especially when trying to sit down).
- Migraine-like headaches develop, which are difficult to get rid of even after taking analgesics.
- Complications during childbirth. If a pregnant woman has previously suffered a fracture of the coccyx, then during its physiological displacement she will feel severe pain. Such injuries need to be treated at the stage of pregnancy planning.
- Formation of callus (rough growth) at the fracture site. Then chronic pelvic pain appears, which intensifies when a person sits or tries to stand up. Salts may be deposited at the fracture site.
- Cococygodynia is persistent pain in the area of the coccygeal bone. Most often women suffer from it. The pain becomes more severe when the patient sits, walks, or tries to have a bowel movement. Coccydynia is caused by damage to the nerves that surround the coccyx or periosteum.
- The functionality of the genitourinary organs or colon is impaired if the bone moves forward. Severe pain appears when sitting, especially when the back is slightly tilted back.
- A cyst forms with a channel outward between the buttocks.
Coccyx cyst
These consequences provoke constant painful sensations that reduce the quality of life and do not allow a person to perform usual activities.
Classification of compression fractures
Classification according to the degree of vertebral deformity:
- I degree - the height of the vertebra decreases to less than ½ of its size.
- II degree - the height of the vertebra is halved.
- III degree – height decreases by more than half.
A grade I spinal compression fracture is stable and does not disrupt the stability of the spine.
Compression fractures of grade II and III lead to instability of the spinal column.
Classification of compression fractures according to the presence of complications:
- An uncomplicated type of spinal compression fracture can often occur in a latent form and be accompanied by pain in the area of damage to the spinal column. The patient self-medicates and does not seek help from a doctor. In this case, a compression fracture can cause the development of diseases such as osteochondrosis or radiculitis.
- A complicated form of spinal compression fracture, in addition to pain, may be accompanied by a neurological disorder. Particularly dangerous are complicated compression fractures with the formation of bone fragments that damage the nerve roots. Over time, the sensitivity of the limbs gradually decreases and numbness occurs.
Diagnostics
If you suspect that your tailbone is broken, then urgently go to a traumatologist or vertebrologist. If you have neurological symptoms, you will need the help of a neurologist.
Diagnosis of coccygeal injuries begins with collecting an anamnesis. The doctor asks the patient whether he has fallen on his buttocks, been hit in the lower back, or suffers from bone problems.
Then a visual examination is carried out, during which you can notice that the victim tries not to move his pelvis or sit in order to avoid pain. During palpation, muscle tension around the bone is felt, swelling is observed, and the patient feels pain.
To confirm or exclude a displaced fracture, a rectal or vaginal examination is prescribed. During the procedure, the doctor can identify bone fragments that rub against each other, which is why a characteristic crunching sound is heard. These tests help determine abnormal lower spine mobility and pain.
To clarify the diagnosis, the doctor prescribes the following instrumental studies:
What to do if your tailbone hurts
- X-ray (frontal and lateral projection). This diagnostic method does not always allow one to notice a fracture of the coccygeal bone, since it is hidden under a mass of soft tissue. It is especially difficult to identify an injury in the area of the sacrococcygeal joint.
- Computed tomography is a more informative study, which is prescribed if radiography did not reveal a fracture, and the specialist still has doubts. CT scans allow layer-by-layer examination of the lower back to reveal even small cracks in the coccyx.
- Magnetic resonance imaging is an even more effective diagnostic method that allows you to study soft tissues in detail. MRI is usually performed to evaluate the condition of nerve fibers that are damaged by bone fragments.
- EPI (electrophysiological study) of the neuromuscular system. This is a comprehensive diagnosis, which is prescribed to assess the condition of nerve branches and identify muscle damage.
- Myelography is an X-ray contrast study that allows you to visually assess the condition of the spinal cord, its roots and liquor pathways.
To distinguish a coccyx fracture from a sacral injury, fracture dislocation of the coccyx and rupture of the sacrococcygeal joint, differential diagnosis is performed. However, the treatment tactics for these pathologies are similar.
Treatment
Every person should know how to provide first aid if a fracture of the coccyx occurs:
- Call an ambulance.
- Calm the victim and do not allow him to move.
- Apply a cold compress to the affected area.
- To relieve severe pain, give him a painkiller, for example, Ketanol, Baralgin, Diclofenac. However, doctors recommend doing this as a last resort, since pain is an important diagnostic sign.
Treatment for a tailbone fracture depends on the severity of the injury. For minor injuries, outpatient treatment is carried out, which follows the following plan:
- The patient must remain in bed for 2 to 3 weeks. It's better to lie on your side. To ensure comfort and avoid bedsores, an orthopedic pillow is used. This device reduces pressure on the damaged area and alleviates pain. Usually a pillow is used if you need to sit down.
- For intense pain, analgesics or NSAIDs are used. However, they should not be taken for a long time.
- If the fracture is closed and the integrity of the skin in the damaged area is not compromised, then painkillers in the form of ointments or rectal suppositories can be used.
- If defecation is difficult, laxatives are prescribed.
- To prevent constipation and displacement of bone fragments, a diet is prescribed. The patient should supplement the diet with foods rich in calcium and silicon. It is recommended to eat cereals, soups, purees, and drink plenty of fluids. For the same purpose, cleansing enemas are performed at home.
If necessary, the victim is given a special splint.
The question of what to do in case of a displaced coccyx fracture is quite relevant. In this case, inpatient treatment is carried out.
Therapeutic tactics for a fracture with displacement of coccyx fragments:
- The damaged area is anesthetized with a solution of novocaine, and bone fragments are compared through the rectum.
- The victim is kept in bed; a rubber cushion is placed under the tailbone.
- Novocaine blockade is used to relieve severe pain. If the pain is moderate, then anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed.
- The patient is prescribed gentle physical exercise, which will speed up blood circulation, metabolic processes, and improve general condition. The load on the lower spine is limited.
- If necessary, antibacterial agents are prescribed, as well as calcium supplements.
- The lower back is secured with a tight bandage.
- If intestinal obstruction occurs, enemas are prescribed.
Important. When comparing bone fragments, the traumatologist must act carefully and gently so as not to damage the mucous membrane of the colon.
After 10 days, complex therapy is complemented by massage and thermal treatments.
If the fracture is caused by diseases of the bone tissue, then, in addition to the above measures, the underlying pathology, for example, osteoporosis, is treated.
Most often, reposition (comparison) of fragments through the rectum is successful. But if the fragments are not held in the correct position, then surgery is prescribed. Surgery will help correct the deformity. During the procedure, the surgeon removes the distal (extreme) part of the tailbone; the procedure is performed under general anesthesia.
If the bone fragments of the coccyx are not held in the correct position, then surgery is performed to remove the extreme part of the bone
The operation is necessary when the pelvic organs are compressed by fused bones, then their functionality is impaired. As a rule, this happens if the fragments of the coccygeal bone have fused incorrectly. This is a fairly complex procedure with a risk of damage to the rectum.
To avoid complications, the patient must remain in bed for 10 days after surgery. In addition, he must follow a special diet.
If the pain syndrome bothers you for a long time, then doctors decide to remove the damaged tailbone. In the postoperative period, the likelihood of developing purulent processes and the appearance of abnormal channels in the body cavity increases.
After surgical treatment, the patient is prescribed painkillers and antibiotics to prevent the development of infection. Restorative measures are complemented by therapeutic exercises, massage, physiotherapeutic procedures (electrophoresis with novocaine, paraffin-ozokerite applications, UHF), acupuncture, hirudotherapy (leech treatment).
Using X-rays, doctors will evaluate how the fragments are fused and will also be able to detect displacement if it has appeared. It is especially important to control this process in pathological fractures.
First aid
If you suspect a fracture of the coccyx, first aid should be provided to the victim, it consists of the following:
- The victim is placed on his side or stomach. You cannot lie on your back; the tailbone area should not be adjacent to any surface. All movements should be kept to a minimum;
- Ice or a cold compress is applied to the coccygeal area. This will help reduce blood flow to the damaged area;
- If you experience severe pain, you should take a pain reliever.
After first aid measures have been taken, the victim must be sent to the emergency room for examination. To do this, it is advisable to call an ambulance. If the patient is transported independently, he should lie on his side.
Crack in the tailbone after a fall
A crack in the coccyx is an injury in which the integrity of the bone is broken, but not completely.
Reference. If cracks in bone tissue appear frequently, this may indicate increased bone fragility, which is characteristic of osteoporosis. In a child under 5 years old, frequent cracks are a sign of rickets.
There are these types of cracks:
- Vertical – occurs with excessive flexion or extension.
- Horizontal - appears after a fall on the buttocks.
- Oblique - is a consequence of falling at an angle.
After a whiplash external impact, a longitudinal crack appears. The integrity of bones can be impaired due to excessive weight, a passive lifestyle, and regular constipation. Then the bodies of the coccyx shift, their tissues become more fragile and with a slight impact (a sharp landing on a hard surface), a crack appears.
Symptoms of a cracked coccyx:
- Pain in the lower back, aggravated by sitting or lying in a horizontal position.
- Difficulty moving.
- Redness, swelling, bruising.
- Painful sensations radiate to the legs.
A crack in the coccyx is treated with conservative methods. The patient must stay in bed and eat properly. To relieve pain, analgesics are used in the form of tablets, ointments, and creams. After eliminating the pain syndrome, exercise therapy, physiotherapy, and massage are prescribed. If you follow the doctor's recommendations, the crack will heal in 4 to 8 weeks.
How long does it take for a coccyx fracture to heal?
Victims are interested in how long it takes for a fracture to heal. There is no definite answer to this question; much depends on the severity of the injury, the timing of the visit to the doctor, the age of the patient and the literacy of therapy. To speed up the process, the victim must strictly follow the doctor’s recommendations during treatment and rehabilitation.
The first steps can be taken approximately 4 weeks after the injury. But if the fracture is light and heals quickly, which is proven by instrumental studies, then you will be able to walk within 2 weeks.
The period of fusion of the coccyx bones ranges from 4 weeks to 6 months or more. The recovery period takes approximately 3 months. In general, treatment and rehabilitation can take about a year, and sometimes more. For example, with a mild fracture of the coccyx, the bones heal in about 6 months, and with a displaced injury – up to 1 year.
Treatment for elderly patients is delayed because their bones are more fragile and not as elastic as those of younger people.
Rehabilitation
Rehabilitation after a tailbone fracture usually lasts at least a month. It is during this period that the bones grow together and their lost strength is restored. For severe injuries, the rehabilitation period can reach 2-3 months and includes the following procedures:
- exercise therapy;
- massage;
- herbal medicine;
- acupuncture.
In addition, it is important to organize a nutritious diet, avoid increased physical activity and use special orthopedic devices to reduce pressure on the damaged tailbone. With this pathology, it is recommended to sleep and lie on your stomach.
A month after the therapy, the patient returns to his normal lifestyle. However, it is recommended to give up sports and increased physical activity for one year.
Orthopedic pillow
When the coccyx is injured, treatment is mainly carried out using an orthopedic pillow. It resembles a wide circle in the form of a lifebuoy with emptiness inside. With the help of such a device, it is possible to ease the load on the musculoskeletal system and achieve a positive result:
- unload the spinal column;
- relieve muscle tension;
- prevent blood stagnation;
- cope with pain.
An orthopedic pillow can be used even after recovery of an injured tailbone. Thanks to it, a person is able to sit for quite a long time without harm to health.
Proper nutrition
If the coccyx is damaged, proper nutrition is important during the recovery period. The patient's diet should be filled with the following products:
- greenery;
- hazelnuts;
- persimmon;
- fish;
- sesame;
- dairy products.
In addition, it is necessary to introduce into the diet foods that provide microelements such as calcium.
The most important
A fracture of the coccyx should be treated as early as possible, then the bones will heal faster. Displaced injuries are more dangerous; they are accompanied by severe pain and neurological disorders, and therefore are more difficult to treat. For a mild fracture, conservative methods are used: bed rest, analgesics, diet, exercise therapy, physiotherapy, etc. For comminuted damage, bone fragments are compared through the rectum. If after this the coccyx fragments are not held in the correct position, then surgery is prescribed. Surgical intervention cannot be avoided if neurological disorders are present, the functioning of the pelvic organs is disrupted, or the pain persists for a long time. After the main treatment, rehabilitation is carried out. It is important to follow the doctor’s recommendations at all stages of therapy, then the bones will heal faster and you can return to a full life.