Cholestasis
With this pathological syndrome, manifestations and pathological changes are caused by an excess amount of bile in hepatocytes and tubules. The severity of symptoms depends on the cause that caused cholestasis, the severity of toxic damage to liver cells and tubules caused by impaired bile transport.
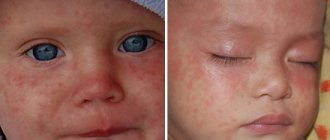
Any form of cholestasis is characterized by a number of general symptoms: an increase in the size of the liver, pain and discomfort in the area of the right hypochondrium, itching, acholic (discolored) feces, dark urine, disturbances in the digestive processes. A characteristic feature of itching is its intensification in the evening and after contact with warm water. This symptom affects the psychological comfort of patients, causing irritability and insomnia. As the severity of the pathological process and the level of obstruction increase, the stool loses color until it becomes completely discolored. At the same time, the stool becomes more frequent, becoming liquid and foul-smelling.
Due to a deficiency in the intestines of bile acids, which are used for the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins (A, E, K, D), the level of fatty acids and neutral fat in the feces increases. Due to impaired absorption of vitamin K during a protracted course of the disease, blood clotting time increases in patients, which is manifested by increased bleeding. A lack of vitamin D provokes a decrease in bone density, as a result of which patients suffer from pain in the limbs, spine, and spontaneous fractures. With prolonged insufficient absorption of vitamin A, visual acuity decreases and hemeralopia occurs, manifested by deterioration of eye adaptation in the dark.
In the chronic course of the process, a disturbance in the metabolism of copper occurs, which accumulates in the bile. This can provoke the formation of fibrous tissue in organs, including the liver. Due to an increase in lipid levels, the formation of xanthomas and xanthelasmas begins, caused by the deposition of cholesterol under the skin. Xanthomas have a characteristic location on the skin of the eyelids, under the mammary glands, in the neck and back, and on the palmar surface of the hands. These formations occur with a persistent increase in cholesterol levels for three or more months; when its level normalizes, they may disappear on their own.
In some cases, the symptoms are mild, which complicates the diagnosis of cholestasis syndrome and contributes to the long course of the pathological condition - from several months to several years. A certain proportion of patients turn to a dermatologist for treatment of itchy skin, ignoring other symptoms.
Description
Cholestasis is a condition characterized by a slowdown or complete cessation of bile secretion, which is accompanied by an increase in the content of substances secreted along with bile in the blood.
According to statistics, approximately 10 out of 100 thousand people experience cholestasis. It can also be noted that cholestasis is diagnosed in men somewhat more often than in women. In most cases, this pathology is observed in people over 40 years of age.
The most common causes of cholestasis include:
- damage to the liver parenchyma as a result of prolonged consumption of alcoholic beverages, taking medications that have a hepatotoxic effect;
- liver infection;
- congenital metabolic disorders, for example, galactosemia, cystic fibrosis and others;
- inflammatory damage to the bile ducts;
- cholelithiasis;
- acquired or congenital obstruction of the bile ducts;
- sarcoidosis;
- oncological disease of the hepatocellular system;
- hormonal changes in the body, for example, during pregnancy.
Cholestasis is usually divided into the following types:
- intrahepatic - occurs as a result of a decrease in the production of bile and its release into the bile capillaries;
- extrahepatic - in most cases indicates obstruction of the bile ducts.
According to the mechanism of development, the following types of cholestasis occur:
- partial – characterized by a decrease in the amount of bile produced;
- total - bile does not enter the duodenum;
- dissociative – characterized by a decrease in the body’s amount of substances necessary for the production of bile.
As a rule, the prognosis is quite favorable. In most cases, with cholestasis it is possible to achieve complete recovery or long-term remission. This is achieved through timely diagnosis and specialized treatment. In some cases, complications develop, in particular, liver failure may develop, which threatens to disrupt the normal functioning of other organ systems. It is also important to follow preventive measures, which include excluding spicy, fried foods and alcoholic beverages from the diet. In addition, it is necessary to promptly treat the pathology that causes the development of cholestasis.
Folk remedies
Photo: Ponchikov.net
As is known, in some cases surgical intervention is required to eliminate the cause of cholestasis. That is why it is strongly recommended not to self-medicate at home, but to immediately consult a specialist at the first symptoms of cholestasis. It is important to understand that the use of traditional medicine in this case will not only not provide any help, but can also cause harm. However, there are folk remedies that can be used for preventive purposes. We offer to your attention the following:
- take 20 g of pre-prepared rose hips and 10 g of crushed nettle leaves. Mix the listed ingredients and pour two glasses of boiling water over them, then place in a water bath and boil for 15 minutes. After which the resulting decoction should be infused for 1 hour, having previously wrapped the container containing the decoction. The drink becomes ready for use after careful straining. It is recommended to consume 50 ml throughout the day;
- Dry the birch leaves and chop them finely. Take 1 tablespoon of plant material and pour one glass of boiling water, then heat over low heat in a water bath for 30 minutes. Then the resulting decoction must be allowed to brew for half an hour, after which it should be strained. It is recommended to consume 1/3 glass 3 times a day 30 minutes before meals;
- mix chopped chicory root and dried peppermint leaves in equal proportions. To prepare the infusion, you will need 10 g of the resulting plant collection. Pour 10 g of the collection into glasses of boiling water and let it brew for 1 hour. After this, the resulting infusion should be filtered through a strainer. One glass of infusion is drunk during the day. The course of treatment varies from 1 week to 1 month;
- Grind 1 glass of flax seeds and pour them with three glasses of milk. Then place on low heat until approximately 1/3 of the original volume of liquid remains in the container. After this, the solution is carefully filtered through a strainer. It is recommended to drink one glass per day. The duration of use of this recipe is 10 days, after which a break is taken;
- take 3 drops of peppermint oil and one teaspoon of honey. Mix the listed components thoroughly. The resulting mass should be consumed 3 times a day. The duration of the course is 1 month;
- mix red beet juice with black radish juice in equal proportions. It is recommended to consume 1 glass per day, preferably in the morning. The duration of the course is 1 month.
The information is for reference only and is not a guide to action. Do not self-medicate. At the first symptoms of the disease, consult a doctor.
Treatment
Photo: img2.vitaportal.ru
To eliminate the phenomenon of cholestasis, the cause of its occurrence should be identified. In some cases, surgical intervention is required to eliminate the factor that caused the development of cholestasis. For example, if there are stones in the gallbladder, a cholecystectomy is performed.
You should also follow a special diet for cholestasis, which consists of limiting the consumption of fried, smoked and spicy foods. In the diet, it is recommended to replace animal fats as much as possible with fats of plant origin. Preference should be given to vegetables and fruits that contain large amounts of vitamins and microelements necessary for the normal functioning of the body. It is important to choose low-fat varieties of meat products. Low-fat dairy products are also allowed. It is strongly recommended not to forget about the existence of various cereals rich in grains. It is strictly forbidden to consume alcoholic beverages, strong coffee and tea. In addition, it is important to give up bad habits such as smoking and drug use.
The following groups of drugs are used as symptomatic treatment:
- hepatoprotectors necessary to protect hepatocytes (liver cells);
- cholesterol, the action of which is aimed at binding bile salts, thereby eliminating skin itching;
- vitamin K. Used for bleeding associated with cholestasis;
- vitamin or vitamin-mineral complexes. Prescribed when the clinical picture of hypovitaminosis develops.
During the rehabilitation period, non-drug treatment methods are used, the use of which is aimed at stimulating the protective mechanisms of the human body. For example, physiotherapy, massage or physical therapy may be prescribed.
Proper diet
Together with drug treatment for a patient with bile stagnation, the doctor creates a proper nutrition menu. Patients exclude spicy, fried, various types of baked goods, canned goods, spices, rich meat broths, and any fatty foods from their diet. The diet is formed from dishes containing vegetables and fruits.
The patient's morning should begin with drinking medicinal mineral water; it is also recommended to consume fermented milk products daily. Eating before bed is prohibited, and during the day you need to eat in modest portions, but often (from five to seven times a day). Without strict adherence to dietary recommendations, cholestasis cannot be cured.
More than half of all food consumed must be heat-treated and served warm. You can eat oat and buckwheat porridge. Please note that you need to cook by steaming, in a slow cooker and in the oven. It is recommended to exclude cold drinks or warm them to room temperature before drinking; to do this, you can leave the drink in a warm room for a while.
What you can and cannot eat if you have bile stagnation
The diet includes rye bread, savory products, honey, and jam. Dairy products include sour cream, cheeses, and curd products (low-fat). Juices and drinks made only from sweet berries and fruits. You can also drink compotes and weak tea. You should eat a lot of greens, vegetables, fruits, and berries. Soups should be vegetable with cereals, pasta, or lean meat: rabbit, veal, chicken, turkey. It is recommended to limit vegetable fats in the diet to 50 g per day.
When dieting, it is prohibited to consume lard, animal fats, soup made from fatty meats and fish. Not all greens are allowed; green onions, sorrel leaves, and spinach should be avoided. You can't have radishes, radishes. As for drinks, alcohol, strong coffee, and any cold drinks are prohibited. Nutritionists also do not recommend canned foods (pickled vegetables, caviar, smoked foods) for consumption. Exclude from the menu confectionery pastries, chocolate, ice cream, spices, mustard, horseradish, sour varieties of fruits and berries.
For treatment, it is very useful to drink skim milk - it is a good source of calcium. When a sign of cholestasis occurs in the form of itching, you need to see a doctor for a liver examination; this symptom may appear much earlier than others; it should not be ignored, because delays often lead to liver failure. Treatment started in a timely manner can relieve symptoms and improve liver function.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter
Diagnosis of intravesical and intrahepatic cholestasis
The media and the Internet should not become sources of treatment for the disease. Only special diagnostic methods reveal pathology, and competent specialists prescribe the necessary treatment.
The patient is physically (externally) examined by a doctor. At this stage, abrasions, rashes, redness, scratching, and icteric skin color may be detected.
Biochemical laboratory experiments and analysis of the concentration of serum bile acids will help diagnose the disease with greater accuracy. If the syndrome is detected, blood biochemistry will show elevated cholesterol, bilirubin, phospholipids, acids, and enzymes.
Patients continue to be evaluated to identify extrahepatic “surgical” cholestasis. It may appear at first glance to be intrahepatic in symptoms.
The next step in diagnosis will be an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity, where an enlarged gallbladder is observed and manifestations of blockage of the bile ducts are identified.
If an increase in the volume of the ducts is detected, cholangiography is prescribed, otherwise the diagnosis is indicated by the clinical picture. For example, if the presence of stones is suspected, then ERCP is performed. When this study does not detect stones, they may be referred for a liver biopsy, but before that the doctor determines the absence of an extrahepatic type.
Causes of pathology
The disease can develop for various reasons. The intrahepatic form of cholestasis is manifested by a smaller flow of bile into the duodenum. This may occur due to hepatocellular pathology. If the tubules are damaged due to damage to the intrahepatic interlobular duct, then the syndrome is called canalicular, as well as extralobular ductular cholestasis, and if hepatocytes are destroyed, then hepatocellular.
Viruses, medications, alcohol, and toxic effects make it difficult for the liver to function normally. Canalicular cholestasis with hepatocellular cholestasis can be caused by any form of liver damage, as well as impaired metabolism and heart problems. The etiology of introlobular cholestasis is in the malfunction of the vacation, basolateral membranes. If the epithelium of the bile duct is damaged, patency is complicated, the composition of bile and acid metabolism are disrupted, then ductular cholestasis develops.
Intrahepatic cholestasis may appear due to factors such as ductopenia, hypoplasia of the extrahepatic and intrahepatic ducts, Alagille syndrome, infection, viruses, exposure to the drug Thiabendazole, cystic fibrosis, sarcoidosis, istiocytosis X, reactions associated with transplant rejection, cholangiocarcinoma, hepatitis, autoimmune deficiency A1- antitrypsin, cholangitis, amyloidosis, congestive liver, circulatory disorders, hepatic vein thrombosis.
Extrahepatic cholestasis begins to manifest itself when the positive effect of the main intrahepatic and extrahepatic ducts is counteracted. One of the common causes is the presence of stones in the bile ducts.
The progression of the extrahepatic form of the syndrome may be due to the presence of stones, malignant neoplasms in the ducts, damage to the duodenum, hepatic artery aneurysm, pancreatitis, malfunction of the pancreas, the appearance of cysts, hemobilia, abscess, parasitic and other infections.
Intravesical cholestasis (mild chronic) can occur in the chronic form of non-calculous cholecystitis, when the activity of the gallbladder decreases - an unbalanced composition of bile is formed.