ACVA (acute cerebrovascular accident) is a concept that combines a transient ischemic attack and a pre-stroke condition. ACVA is characterized by sudden development and is very dangerous for human health and life, therefore, when its first signs appear, urgent medical attention is necessary. Timely adequate treatment can reduce the severity of the consequences of an attack. To receive qualified assistance for acute stroke, you can contact the Yusupov Hospital, which operates around the clock and provides the necessary assistance in this situation.
What is ONMK?
The diagnosis of stroke (and the resulting stroke) is established in the event of disturbances in the functioning of the cerebral vessels. When blood circulation is disrupted in a certain area of the brain, part of the nervous tissue dies. This can lead to serious disability or death. A stroke is not yet a stroke, but a condition that can lead to it. The development of stroke indicates that a person urgently needs the help of a qualified neurologist, since a full-fledged stroke or cerebral infarction may soon occur, when the consequences will be much more severe. Decoding the diagnosis of stroke will depend on the type of disorder in the vessels: hemorrhage, blockage or narrowing of the vessel, etc. The name of the disease of acute stroke is deciphered by the attending physician based on symptoms and examination data.
It is important to know about the diagnosis of stroke, that this is the most dangerous condition. According to WHO, approximately 12 million people worldwide die from strokes every year. The disease affects both poor and rich, men and women. People with obesity, diabetes mellitus, alcohol abusers, and smokers are most susceptible to this condition. In women, the risk of stroke increases after menopause. Recently, cases of stroke and subsequent strokes have begun to occur in young people (25-40 years old), which is associated with an unhealthy lifestyle and constant stress.
Excursion into physiology
The uninterrupted supply of substances necessary for the nerve cells of the brain and the cleansing of waste are carried out by the cerebral circulatory system, where arterial blood carries oxygen and nutrition to the brain, and venous blood removes toxins and metabolic products.
The vessels of the brain have a unique, perfect structure that ideally regulates blood flow, ensuring its stability. They are designed in such a way that with an increased flow of blood into large vessels, the strong pulse impulse of the blood coming from the heart is weakened due to numerous bends (siphons) of the vessels along the vascular bed, which contribute to the pressure drop and smoothing of the pulsating blood flow. Due to complex regulatory mechanisms, when total blood pressure increases, the pressure in the brain remains stable for a long time. Regulatory systems allow blood flow to be redistributed from parts of the brain with less load to areas with increased brain activity.
The brain has an autonomous regulatory system, which allows it to be in a healthy functional state and control the processes of continuous adaptation of the body to constantly changing conditions of the external and internal environment. In a state of functional rest, the brain receives 750 ml of blood per minute, which is 15% of cardiac output. In children, blood flow activity is 50–55% higher, and in elderly people it is 20% lower than in adults.
It should be noted that the gray matter of the brain (cell bodies of neurons) is supplied with blood more intensively than the white matter (conducting pathways), which is due to greater cell activity. Thus, during intense mental work, local blood flow in the cerebral cortex can increase 2–3 times compared to the resting state.
The brain has the richest capillary network. Nerve cells are not only intertwined, but also penetrated by capillaries. The vessels of the brain are connected to each other by collaterals (“bridges”). Arterial collateral circulation of the brain, important for maintaining normal blood flow, plays a particularly significant role in compensating for circulatory disorders when one of the cerebral arteries is blocked.
With a high intensity of blood flow in the vessels of the brain, the blood pressure in them is maintained relatively constant. A complex chain of regulatory mechanisms protects the brain from a drop in blood pressure and hypoxia (decreased oxygen). Along the path of blood flow to the brain, there are many sensitive cells (pressoreceptors, chemoreceptors) that can respond to blood pressure and regulate heart rhythm and vascular tone.
The activity of the vasomotor centers of the brain is associated not only with nervous and humoral regulation mechanisms, but also with the autonomic regulation system, which allows, despite significant fluctuations in total blood pressure, to maintain cerebral blood flow at a constant level.
Thus, cerebral circulation is provided with complex regulatory mechanisms that make it possible to maintain a constant supply of the substances it needs.
With excessive blood supply to the brain, excessive hydration (fluid accumulation) may occur, followed by the development of edema and damage to vital centers that are incompatible with life. The cause of excess blood supply can be, for example, an increase in systemic blood pressure to 160–170 mm Hg. Art. and higher.
In the problem of impaired blood supply to the brain, much attention is paid to arteries. But venous circulation is no less important. The veins carry out the removal of waste substances (toxins) with the blood - that is, cleansing the brain. Thanks to these vessels, constant intracranial pressure is maintained.
Violation of the venous outflow leads to stagnation of blood and accumulation of fluid in the brain, causes hydrocephalus with compression of the brain centers, and contributes to the occurrence of phlebitis and thrombophlebitis.
There is one more feature of the cerebral veins that must be taken into account. The wall of a venous vessel in the brain does not have a valve apparatus, unlike, for example, the veins of the extremities (valves help withstand loads by moving blood upward and preventing it from moving in the opposite direction). Therefore, venous blood in the vessels of the brain passes freely in both directions, depending on the pressure that arises. This creates a danger of rapid spread of infection from the sinuses and eye sockets, which is facilitated by the atomic structure of the nose and its paranasal sinuses, located in close proximity to the brain. When coughing, venous pressure increases, reverse venous flow, congestion, and brain hypoxia become possible. There are known cases of loss of consciousness during a coughing attack in the presence of a chronic respiratory tract disease and in young children when they “go into a fit” of coughing during illness and crying and screaming until they cough.
It becomes clear why long-term respiratory problems, accompanied by constant swelling and coughing, can cause cerebrovascular accidents. Because they not only cause brain hypoxia, but also disrupt venous outflow and, being a constant source of infection, contribute to its penetration into the brain.
An ophthalmologist, for example, can observe manifestations of congestion in the brain (dilated, blood-filled vessels of the fundus). But this is also visible to the naked eye: red, puffy eyes after sleep (due to drinking alcohol the night before, overeating at night, lack of sleep) are a symptom of congestion in the brain.
After a brief excursion into physiology, it becomes clear that the reasons for the deterioration of cerebral circulation may be associated with disturbances in the flow of blood to the brain and the outflow of blood from the brain.
Classification and code according to ICD 10
ACVA code according to ICD 10 is included in the class of cerebrovascular diseases (I60-I69). The consequences of acute stroke according to ICD 10 codes refer to various hemorrhages, heart attacks, strokes, blockages and stenosis of arteries, as well as other lesions of cerebral vessels. The consequences of acute stroke in ICD 10 can be classified as follows:
- subarachnoid hemorrhage;
- intracerebral hemorrhage;
- non-traumatic hemorrhages;
- cerebral infarction;
- unspecified stroke;
- blockage and stenosis of the precerebral and cerebral arteries.
Also, stroke code according to ICD 10 in adults is divided according to the nature of vascular damage:
- ischemic type;
- hemorrhagic type.
ACVA of ischemic type
Acute ischemic cerebrovascular accident is a brain lesion resulting from the formation of an obstruction in a vessel. Most often, this obstacle is a blood clot or cholesterol plaque. An obstruction interferes with the flow of blood to any part of the brain, resulting in oxygen starvation. Nerve tissue needs a constant, continuous supply of nutrients, since the metabolism in nerve cells is very intense. When the access to oxygen and nutrients transported by the blood is stopped, the functioning of the nerve cells is disrupted, and after a short period of time they begin to die. In the case of an ischemic type of circulatory disorder, a certain obstacle interferes with the normal flow of blood, provoking a cerebral infarction. This type of violation is quite common and accounts for up to 80% of cases. ICD 10 codes for stroke of ischemic type include:
- I63 cerebral infarction;
- I65 obstruction and stenosis of the precerebral arteries;
- I66 blockage and stenosis of the cerebral arteries.
stroke of hemorrhagic type
Stroke of the hemorrhagic type is classified as a pathological condition caused by a violation of the integrity of the vessel, resulting in hemorrhage. Depending on the location of the disorder and its extent, the result of hemorrhage is a hematoma in the brain tissue or penetration of blood into the space surrounding the brain. ACVA of the hemorrhagic type in ICD 10 includes:
- I60 subarachnoid hemorrhage;
- I61 intracerebral hemorrhage;
- I62 other non-traumatic hemorrhage;
The condition after an acute stroke, related to any code according to ICD 10, is severe and requires urgent intervention from a specialist. The consequence of stroke is the death of nerve cells, which occurs very quickly. The consequences of acute cerebrovascular accident can be stopped if the person receives help within 4-5 hours after the attack.
What is a stroke
The essence of a stroke is the cessation of blood supply and functioning of a part of the brain as a result of damage to a vessel.
The larger the affected area, the more severe the stroke. Necrosis of a portion of the brain substance is called an infarction [3]. There is a high risk of death in the first few hours, and then in the period up to 28 days after a vascular accident. The annual mortality rate from stroke in the Russian Federation is 374 cases per 100,000 [10]. In 2018, 35% of patients died in the acute period of stroke; by the end of the first year, this figure increases by 15%, and in general, in the first 5 years, the mortality rate of strokes is 44% [11]. The mortality rate from stroke was 92.9 per 100,000 population, and the hospital mortality rate was 19.1% [5].
Long-term disability is most likely for patients who have suffered a stroke. The prevalence of primary disability due to stroke in 2018 was 3.2 per 10 thousand population [2]. Of these, 31% need constant care, 20% have severe mobility limitations, and only 8% return to work [3]. The prevalence of recurrent strokes in 2014 was 0.79%, of which ischemic
strokes account for 87.5% [9].
Causes and symptoms of cerebrovascular accident
To assess the degree of brain damage, the Rankin scale is often used for stroke and subsequent stroke. Cerebrovascular diseases (CVD) and stroke can significantly reduce a person’s performance and lead to disability. Therefore, conditions such as acute coronary syndrome (ACS) and stroke, associated with disruption of blood vessels in vital organs (heart and brain), require urgent treatment to the hospital.
The Rankin scale presents six degrees of disability after stroke and stroke:
0. There are no clinical symptoms; 1. The vital systems are not significantly impaired, there are minor symptoms, but the person can perform all daily activities; 2. Mild disturbances in vital activity systems: the performance of some actions is limited or inaccessible, a person can take care of himself without outside help; 3. Moderate disability: some assistance is required, the person can walk independently; 4. Severe disabilities: a person is unable to walk independently, requires care and assistance in everyday life; 5. Severe disabilities: complete immobility, urinary and fecal incontinence, the person requires constant assistance from specialized medical personnel.
Each grade of the Rankine scale has its own symptoms, which make it possible to determine clinically how affected the brain is. With minor lesions of the 1st degree, a person has no signs of disability, he is able to care for himself and perform daily work. However, slight muscle weakness, speech disorders, and loss of sensitivity may occur. These disorders are mild and do not lead to restrictions on daily life.
In grade 2, mild signs of activity impairment are observed: the person is unable to perform previous work involving complex manipulations or fine motor skills. However, he can take care of himself independently, without the help of others.
At grade 3, moderate signs of brain dysfunction are observed:
- the person needs some outside help in performing hygiene procedures;
- he cannot prepare food or dress himself;
- speech impairments are pronounced (difficulties arise in communication, expressing one’s thoughts);
- It is possible to use a cane or other walking aids.
Symptoms of acute cerebrovascular accident of the 4th degree are clearly expressed, there are clear signs of disability. A person cannot walk independently, take care of himself, he needs round-the-clock assistance.
With the 5th degree of disability, a person is bedridden, he cannot speak, cannot eat independently, and does not control bowel movements. A person needs constant help and supervision.
One of the most clinically striking and health-threatening strokes is damage to the VBB (vertebrobasilar region). In this case, the pathological process affects parts of the brainstem, thalamus, cerebellum and occipital lobes of the brain. ACVA in the vertebrobasilar region manifests itself as follows:
- partial facial paralysis;
- impaired motor activity of the hands;
- difficulty moving the leg and arm on one side of the body;
- impaired coordination of movements;
- the appearance of muscle weakness in the lower extremities;
- mild arm paresis;
- swallowing disorder;
- nausea, vomiting;
- hearing and speech impairment;
- headache and dizziness.
When developing stroke, it is important to consult a doctor as soon as possible. To do this, you need to pay attention to the first symptoms of pathology:
- severe acute sudden headache;
- sudden loss of consciousness;
- sudden muscle weakness;
- sudden disturbance of speech and its understanding;
- sudden visual impairment;
- sudden numbness of the limbs or areas of the face;
- impaired coordination of movements;
- nausea, vomiting.
The severity of symptoms will depend on how severely the brain is damaged. ACVA occurs spontaneously and cannot be predicted. But you can try to exclude factors that increase the risk of developing strokes and strokes:
- smoking;
- alcohol abuse;
- unhealthy diet;
- lack of physical activity;
- chronic fatigue and stress.
People with diabetes, arrhythmia, and overweight need to be especially responsible about their health. These conditions quite often become the causes of the development of circulatory disorders in the brain.
Recommendations
ONMK: what is it?
ACVA of ischemic type.
Many people ask the question of what an acute stroke is and what consequences there are after it. This article will examine the main causes of stroke and consequences.
ONMK - what is it?
Many people who have nothing to do with medicine probably do not know what stroke is. So, an acute circulatory disorder in the brain is a stroke, which causes damage and death of brain cells. The cause of this disease is the formation of a blood clot in the blood vessels of the brain or the rupture of some blood vessels, which causes the death of a huge number of nerve cells and blood cells. According to statistics, acute stroke ranks first among diseases that cause human death. Every year around the world, as the federal register of patients with acute stroke indicates, 14 percent of people die from this disease, as well as 16 from other types of diseases of the circulatory system.
Reasons why stroke may occur.
In order to prevent the occurrence of this disease, it is necessary to pay attention to your lifestyle from an early age. For example, constant exercise can significantly reduce the possibility of developing stroke. You already know what it is; some of the causes of this disease will be discussed further.
As a rule, this disease does not come suddenly; very often the diagnosis of stroke can be established as a consequence of certain diseases.
Often the cause of this condition can be:
- hypertension;
- obesity;
- diabetes;
- high cholesterol;
- heart disease;
- alcohol and smoking;
- various types of medicines;
- high hemoglobin level;
- age;
- traumatic brain injury;
- genetic predisposition and so on.
Now it’s clear what ONMC is. These are the consequences of an incorrect lifestyle. Therefore, it is very important to monitor your health and physical condition.
Ischemic stroke.
Ischemic stroke is a stroke caused by damage to brain tissue and disruption of blood flow to one or another part of it.
Most patients with stroke of ischemic type have common diseases of the cardiovascular system. Such diseases also include arteriosclerosis, heart disease (arrhythmia, rheumatic disease), and diabetes. This type of stroke is characterized by sharp and frequent manifestations of pain, the consequence of which is a deterioration of blood circulation in the cerebral cortex. As a rule, such attacks can occur several times an hour and last for 24 hours.
Causes of ischemic stroke ACVA.
The main reason for the manifestation of ischemic stroke is a decrease in blood flow to the brain. Very often, this is why the cause of death of a person is ischemic stroke. So, we found out the features of ischemic stroke, what it is and what its symptoms are.
This is usually the result of damage to the vessels of the neck and some arteries of the brain in the form of occlusive lesions and stenosis. Let's find out the main reasons for its occurrence.
The main factors that can affect the decrease in blood flow include the following:
- Occlusions and stenoses of the main arteries of the brain and vessels of the neck.
- Thrombotic layers on the surface of an atherosclerotic plaque.
- Cardiogenic embolism, which occurs when there are artificial valves in a person’s heart.
- Dissection of the main arteries of the cervical spine.
- Hyalinosis of small arteries, as a result of which microangiopathy develops, which leads to the formation of lacunar infarction of the human brain.
- Hemorheological changes in blood composition, which occurs with vasculitis, as well as coagulopathies.
Very rarely, the cause of this disease can be external injuries to the carotid arteries and various inflammatory processes, which can significantly impair the flow of blood through the vessels. Also, very often, the main cause of stroke in the brain can be osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, during which blood vessels are significantly pinched, which can lead to a decrease in blood flow. Patients with osteochondrosis are constantly recommended to massage the cervical spine and smear it with various warming preparations, which can significantly dilate blood vessels and improve blood circulation.
Symptoms of stroke.
Signs of this disease can often appear abruptly or increase gradually. As a rule, the main symptoms of this disease include speech and vision disorders in the patient, disturbances in various reflexes, movement coordination, headaches, disorientation, sleep disturbances, noise in the head, memory impairment, paralysis of the face, tongue, lack of sensation in some limbs, etc. Further.
In acute cerebrovascular accident, the following consequences occur: cerebral stroke, circulatory disturbance in the cerebral cortex due to the formation of blood clots in the vessels and main blood arteries of the head, etc.
When symptoms of acute cerebrovascular accident last more than a day, a stroke is diagnosed. In the first stage of this disease, severe headache, dizziness, nausea, gag reflexes, and so on may also occur. If you do not immediately pay attention to these manifestations, this can cause a person’s death.
According to the register of patients with stroke, according to statistics, the main cause of these manifestations may be high blood pressure, which can be observed during severe physical exertion. A sharp increase in blood pressure can cause rupture of cerebral vessels, followed by hemorrhage and intracerebral hematoma.
In most cases, the above symptoms are observed before ischemia. Typically, they can last several hours or several minutes. As a rule, with the manifestation of ischemic stroke, the symptoms constantly become more active. According to experts, when these symptoms appear, most people experience disorientation, as a result of which the person loses vigilance, coordination of movements worsens, so many patients simply fall asleep. According to statistics, 75 percent of ischemic heart attacks occur during sleep.
Diagnosis of acute cerebrovascular accident of ischemic type.
To identify the problem, it is necessary to conduct diagnostics and various studies using the ICD system. Doctors will be able to diagnose stroke after the following procedures:
- Blood test for electrolytes, glucose, hemostasis, lipid spectrum, antiphospholipid antibodies.
- Electrocardiography of changes in blood pressure.
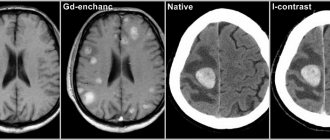
- Computed tomography of the cerebral cortex, as a result of which it will be possible to detect the affected parts of the brain and the resulting hematomas without any problems.
- Cerebral angiography and so on.
Treatment of acute cerebrovascular accident in ischemic type.
The most common cause of death is stroke. Treatment should therefore take place under the supervision of experienced doctors. For this disease, the following therapy is carried out:
- Maintaining vital functions of the human body. The patient should take antihypertensive drugs when the blood pressure in the body is 200 to 120 mm. Hg Art. The use of anticoagulants (used for concomitant pathologies and used for a long time after normalization of the condition), vasoactive drugs, antiplatelet agents, decongestants, neuroprotectors, and so on is also prescribed.
- Various sets of exercises are performed - speech therapy classes and breathing exercises.
- The issue of thrombolysis is being considered when a patient is admitted to a medical facility within 3-6 hours from the onset of the disease.
- Secondary prevention of disease.
- Various rehabilitation measures are carried out and so on.
As a rule, the main points of treatment will be prescribed only by a doctor, who will become more familiar with the victim’s illness.
If there is a suspicion of acute cerebrovascular accident, it is necessary to contact highly qualified specialists in this field of activity. As a rule, first of all it will be necessary to undergo magnetic resonance imaging, which can accurately determine all pathologies of the cerebral cortex. In this way, it will be possible to prevent the possibility of complications of the disease and begin treatment even before it fully manifests itself. A specialized department of acute stroke, as a rule, must have special equipment that will significantly improve treatment.
First aid for stroke.
The very first thing to do when you notice symptoms of this disease is to call an ambulance. During the manifestation of symptoms of this disease, a patient should in no case be disturbed without reason, therefore, immediately after the first signs it is necessary to isolate him.
At the next stage, all patients with stroke should lie in such a way that the upper body and head are raised, it is also necessary to rub the collar area of the body in order to make breathing easier for the patient. It is also necessary to provide fresh air access to the room where the patient is located (open the window, doors, and so on).
If the patient experiences vomiting, it is necessary to turn his head to the left side and clean the mouth with gauze or just a clean napkin. This is done to prevent the possibility of vomit entering the lungs when breathing, which can lead to additional problems.
One of the most common symptoms of stroke is an epileptic seizure - a person completely loses consciousness, after a few seconds a wave of convulsions sweeps through the body, which can last for several minutes. It is also worth noting that such attacks can be repeated several times.
How to prevent the occurrence of stroke diseases.
Based on the above statistics, it is clear that this disease manifests itself even in children. It is easy to guess that every year there are more and more people who suffer from this disease. All this is associated with poor diet, inactive lifestyle and high mental stress.
If a person does not lead an active lifestyle and constantly spends time at the computer, he has a high chance of contracting this disease. Obesity, as stated, is the main cause of this disease, which is why the issue of maintaining physical fitness is very relevant today for the younger generation.
Sudden loads also very often become a source of problems, since with an increase in blood pressure there is a risk of rupture of blood arteries and veins, which will also lead to stroke. Therefore, it is necessary to constantly exercise, lead an active lifestyle, and eat right - and the risk of stroke will significantly decrease.
The most deadly and terrible disease in our time is stroke. You already know what it is and what causes this disease, so you need to adhere to the above recommendations in order to prevent the disease in the future.-
Diagnosis of the disease
When the first signs of cerebrovascular accident appear, you must call an ambulance or go to the hospital yourself (if your condition allows). The doctor will perform an examination and collect anamnesis (description of the patient’s condition and related data). The doctor must be provided with the following information:
- main complaints (headache, disturbance in the functioning of the sensory organs, nausea, etc.);
- when the condition worsened;
- under what conditions;
- the presence of risk factors for stroke (smoking, alcoholism, chronic diseases, taking medications).
A simple test can detect the development of stroke or stroke (provided that the patient is conscious):
- It is necessary to ask the patient to smile (with stroke, the smile will be skewed);
- It is necessary to ask the patient to stretch his arms forward and then raise them up (with a stroke he will not be able to do this or will only raise one arm);
- Ask the patient to repeat any simple sentence (with stroke, this will cause difficulties);
- Ask the patient to stick out his tongue (with stroke, the tongue will be clearly displaced from the center).
The doctor assesses the general and local status of stroke. General status represents the general condition of the patient, clinical manifestations of cerebrovascular accident. Local status is described in the presence of head trauma. The collected data gives the doctor an idea of the patient’s condition, on the basis of which he prescribes examinations to obtain a complete picture of what is happening.
Diagnosis of stroke is carried out using visualization of nerve tissue using CT and MRI. These are the most informative diagnostic methods that allow you to identify the lesion. To provide timely assistance in case of acute stroke, the examination is carried out urgently. In some cases, the patient will need emergency surgery.
At the Yusupov Hospital you can undergo examinations of any complexity for acute stroke and stroke. The hospital is equipped with the latest technology, which allows for a quick and high-quality examination of the patient. High-precision technology will help establish an accurate diagnosis and the extent of brain damage.
Kinds
The main classification of strokes (according to ICD-10) takes into account the cause and mechanism of stroke.
- An ischemic stroke is characterized by a cessation of blood flow to the brain tissue. The reason is a violation of blood flow, blockage of an artery with a blood clot and/or narrowing by an atherosclerotic plaque (atherothrombotic), vasospasm, and a decrease in pressure. Most often develops at the age of 50-69 years. The incidence is 64-75% among all types of stroke.
- Hemorrhagic stroke is a hemorrhage into the substance of the brain or under the arachnoid membrane due to rupture of a vessel as a result of high blood pressure, atherosclerosis, vasculitis, aneurysms, coagulation disorders. Patients aged 50-69 years are at high risk. At 39-49 years old it is less common. The incidence is 15-20% among all types of stroke.
There are classifications that distinguish types of stroke taking into account other signs.
1. By severity:
- minor, including microstroke (transient ischemic attack) - a passing disturbance of cerebral circulation with complete disappearance of neurological symptoms within 1 day to 3 weeks;
- moderate severity;
- severe, extensive stroke of the brain - damage to a large area with pronounced neurological symptoms and severe condition, sometimes with falling into a deep coma.
2. By location
- left or right hemisphere. Each side is responsible for different functions, so the symptoms will be different. For example, if the left half is affected, the movements of the right side of the body suffer, speech and memory are impaired. The person loses the ability to read and write.
When the right hemisphere is damaged, the movement of the left side of the body, the perception of oneself, one’s body, and the surrounding space are impaired, and mental disorders develop.
3. By quantity
- primary stroke (first) and repeated strokes (second, third, fourth). Repeated strokes are more severe because the lesion area increases each time.
4. By age
- in children, starting from the prenatal period, young, elderly. The severity of clinical manifestations and prognosis depend on the patient’s age, the cause of concomitant pathology, and the timeliness of diagnosis. The most difficult prognosis is for delayed detection of a stroke, a large lesion, a weakened body due to concomitant diseases, bad habits, and vitamin deficiency.
5. By localization
:
- in the vertebrobasilar basin with damage to the occipital lobe of the brain, cerebellum and brainstem - visual disturbances develop, gait changes;
- frontal lobes - speech and swallowing suffer;
- temporal lobes - memory, writing, speech deteriorate;
- parietal lobe - speech and speech understanding suffer.
Treatment
Treatment of stroke will include first emergency care and subsequent therapy. Further therapy consists of a number of measures to normalize and support brain function. The doctor informs the patient about how to take nootropics for stroke and other medications, nutritional habits of patients with stroke, clinical recommendations for stroke. Treatment of acute cerebrovascular accidents includes basic and specific therapy. Basic therapy contains the following measures:
- Restoring and maintaining respiratory function.
- Maintaining optimal blood pressure and cardiovascular activity. The patient is given intravenous medications (labetalol, nicardipine, sodium nitroprusside) according to indications; anaprilin, enaprilin, captopril, esmolol are used to correct blood pressure. Antihypertensive therapy depends on the type of stroke - hemorrhagic or ischemic.
- Treatment of cerebral edema.
- Fighting seizures, intracranial hypertension, various neurological complications.
Specific therapy includes:
- Carrying out intravenous or intra-arterial thrombolysis depending on the time of onset of the first symptoms of the disease. Aspirin is prescribed, and anticoagulants are prescribed according to indications.
- Maintaining optimal blood pressure.
- In certain cases, surgery is performed to remove the brain hematoma, and the hemicraniectomy method is used to decompress the brain.
Treatment of stroke is carried out in a hospital setting. The faster the patient receives medical assistance, the higher the chance of recovery.
Procedure for providing medical care
The scope of medical care for stroke or stroke will depend on the severity of the patient’s condition. It is important to get to the hospital as soon as possible. If the cause of the stroke is a blood clot, then it is necessary to take an antithrombotic drug within 3 hours after the onset of cerebrovascular accident to reduce the consequences.
Treatment of stroke occurs in a hospital, its duration is from two weeks (for mild damage). The patient is prescribed infusion therapy, medications to stabilize blood pressure, and medications to normalize the functioning of nerve cells. In the future, the patient will need a rehabilitation course to restore lost skills or adapt to new living conditions. Rehabilitation is a very important part of treatment. It is rehabilitation measures, when performed regularly, that contribute to the restoration of working capacity.
At the Yusupov Hospital you can undergo a full course of treatment for acute stroke and stroke, including emergency care and rehabilitation. The hospital employs the best neurologists, cardiologists, surgeons in Moscow, doctors of science, and doctors of the highest category who have extensive experience in successfully treating these conditions. The hospital is equipped with everything necessary for a speedy and high-quality recovery of patients.
Artificial ventilation for acute stroke
When a patient is admitted with stroke or stroke, the doctor assesses the adequacy of spontaneous breathing and the level of oxygen in the blood. If the patient has a low level of consciousness, there is a risk of aspiration, high rates of intracranial hypertension, he requires artificial ventilation (ALV).
Ventilation is also performed for:
- Violation of central regulation of breathing;
- Obstruction of the tracheobronchial tree;
- Pulmonary embolism.
Treatment with a dropper (infusion therapy)
Infusion therapy begins from the moment a patient is admitted with stroke or stroke. A 0.9% sodium chloride solution is prescribed. With stroke, hypovolemia (decreased blood volume) quite often occurs, which can be eliminated by infusion therapy. Infusion is also necessary to control the water balance in the body. Infusion therapy is canceled gradually, after confirmation of normalization of the level of electrolytes and other elements in a blood test.
Normalization of blood pressure
The first three days are critical after stroke. During this period, repeated violations or the development of a major stroke are possible. Now it is necessary to stabilize the patient's condition and respond to any changes. Some important indicators are intracranial pressure and blood pressure. Pressure level indicators should not exceed the permissible norm or be below the norm. Therefore, pressure monitoring is carried out constantly. To normalize the indicators, special drugs are first administered intravenously, and then switched to tablet form of drugs.
Elimination of convulsive syndrome
With stroke, there is a high risk of seizures. However, there is no prevention for this condition. Anticonvulsants are prescribed immediately when a seizure occurs. The drugs are administered orally or intravenously.
Use of neuroprotectors and nootropics
An important direction in the treatment of stroke and stroke is the restoration of damaged nerve tissue and the protection of healthy tissue from the spread of “vascular catastrophe”. Treatment is performed with the help of neuroreparants and neuroprotectors.
Nutritional Features
If swallowing is impaired, the patient is prescribed feeding through a tube. At the beginning of treatment, food contains the necessary elements to maintain the functioning of the body, combined with infusion therapy. The calorie content of food increases gradually. In the future, the method of eating will depend on the severity of the brain damage. The course of rehabilitation of patients after acute stroke and strokes includes the restoration of self-care skills, so with the proper effort and capabilities of the patient, he can feed himself again. Food should be varied, contain all the necessary microelements and vitamins, that is, comply with the principles of rational nutrition.
Diagnostics of NMC
- Duplex ultrasound examination of blood vessels.
- Contrast venography, angiography.
- CT, MRI.
- Transcranial Doppler.
- Laboratory tests - clinical, biochemical blood tests with determination of lipid profile, hematocrit.
- Fundus examination.
- Detection of hearing loss, smell, taste, and pathology of the vestibular apparatus.
Providing emergency assistance
Acute cerebrovascular accident requires emergency care, since it will not be possible to normalize the patient’s condition on his own. The standard for emergency medical care for acute stroke and stroke states that the patient should be taken to the hospital within 3-5 hours after the onset of the attack. In this case, it is possible to stop the spread of the pathological condition and minimize the severity of the consequences. Help for a person with a stroke can only be provided in a hospital. At home you can do the following:
- Call an ambulance;
- Lay the person on a flat surface (floor, bed), placing a pillow, blanket or folded sweater under the head;
- Turn the person on their side if they feel sick;
- Open the windows to let in fresh air;
- Unfasten clothing that impedes blood flow and air flow (belt, collar, scarf, tight buttons);
- While waiting for doctors, collect documents and personal belongings.
In case of an emergency, it is necessary to provide assistance to the patient before the medical team arrives. If you lose consciousness, you should check your breathing and pulse, and place the person in a position that will not interfere with breathing. If there is no breathing or pulse, it is necessary to begin mouth-to-mouth artificial respiration and chest compressions. If convulsions occur, the patient should be protected from injury: remove nearby sharp and blunt hard objects. You should not try to restrain the patient or unclench his teeth. It is better to wait until the attack ends and check the airway.
If stroke develops, you can go to the Yusupov Hospital, whose emergency department is open 24 hours a day, seven days a week. The hospital has an ambulance, so the patient will receive all necessary medical care in a timely manner. In the intensive care unit of the Yusupov Hospital, the patient will be able to provide the required assistance to stabilize his condition.
The procedure for providing medical care to patients with stroke after admission to the hospital emergency department is as follows:
- Medical examination, ECG, blood tests;
- Examination by specialized specialists: neurologist, cardiologist, neurosurgeon, resuscitator;
- Performing a computed tomography scan of the brain;
- Evaluation of survey results;
- Start of therapy.
After the patient is admitted to the hospital and before the start of therapy, no more than an hour should pass. If necessary, the patient is sent to the intensive care unit immediately, after which the necessary examinations are performed.
Consequences
The consequences of stroke and stroke can be very severe, even death. Residual effects of stroke may be present throughout life, even after the end of the main therapy. Therefore, it is very important to undergo a rehabilitation course and, if necessary, repeat it over time. A person after a stroke needs willpower, as well as the support of loved ones to restore lost functions. Regular implementation of rehabilitation measures allows you to achieve good results in eliminating the consequences of stroke. Professionals at the Yusupov Hospital, using specialized techniques, will help you get the best effect in this difficult work.
The consequences of stroke will depend on the area of brain damage and the extent of the disorders. The degree of their severity can vary greatly: from imperceptible changes in behavior to complete paralysis. The consequences of stroke and stroke include:
- Complete or partial paralysis;
- Speech impairment;
- Impaired coordination of movements;
- Visual and hearing impairment;
- Impaired perception of space and time.
It is difficult for a person to move around, do the same job, or take care of himself. In severe cases, a person remains bedridden after a stroke. After a moderate stroke, the patient's speech is impaired; he cannot speak clearly or control the timbre and volume of his voice. Communication usually occurs through gestures and facial expressions. Memory impairment and the development of dementia are often noted. Another serious consequence of a stroke is depression. This condition should be taken seriously as a positive mental attitude is important for a person's continued recovery.
After a stroke, it is very important to undergo rehabilitation. With its help, you can recover after a stroke, albeit not completely, but significantly. The brain also needs training, like the rest of our body. A damaged brain requires special training under the supervision of professionals. The sooner rehabilitation measures are started, the greater the chances of maximum recovery after a stroke.
Symptoms of a stroke
Stroke leads to various brain injuries, depending on the location of the lesion and the pathological type of cerebrovascular accident:
- disturbances of movement in the limbs: from restrictions (paresis) to complete paralysis. When the lesion is localized on the right, the left limbs suffer; with a left-sided lesion, right hemiparesis is formed; in some cases, movements in all limbs may stop (tetraparesis or double hemiparesis);
- sensory disturbances on one or both sides;
- speech disorders (dysarthria - poor articulation; aphasia - inability to pronounce and understand words, write and read);
- ataxia (impaired coordination of movements, “overshooting”, unsteadiness, imbalance, tremor);
- visual impairment: from blindness to double vision and gaze paresis;
- hearing impairment and dizziness;
- violation of mental functions (consciousness, thinking, attention, memory, will, behavior);
- paresis of the soft palate and pharynx, swallowing disorders;
- disorders of urination and defecation;
- depression of respiration and vascular tone;
- increased intracranial pressure;
- patients complain of headaches, vomiting, hiccups, yawning, shoulder pain;
- consciousness is gradually depressed to the point of coma [1, 3].
Causes of death may include cerebral edema, pneumonia, heart failure, and recurrent stroke. In severe cases, “locked-in syndrome” may develop: the patient is conscious, but cannot move, swallow or speak [3].
Rehabilitation after stroke
In rehabilitation after stroke, the Yusupov Hospital uses an integrated approach to ensure the best recovery for patients. Physiotherapists, speech therapists, massage therapists, exercise therapy instructors, and occupational therapists work with the patient. Physiotherapy and exercise therapy can help restore motor functions. The massage therapist eliminates muscle spasms and normalizes their tone. The speech therapist's task is to restore speech and swallowing. An ergotherapist helps to adapt to new living conditions and teaches everyday skills.
The human brain has a unique property - neuroplasticity - the ability to regenerate. New connections between neurons are formed in the brain, due to which lost functions are restored. Neuroplasticity can be stimulated, which is what happens during the rehabilitation process. Regular exercises, which are selected individually depending on what function is to be restored, must be performed constantly, every day until the desired effect is obtained. Regularity is a key factor in achieving your goal; without it, it is impossible to achieve any results.
During the rehabilitation process, various elements of breathing exercises and intellectual exercises are used. All this helps the brain work better and better. Also in rehabilitation, various simulators can be used to help learn how to walk again or perform any action (for example, alternately bending and straightening fingers), provoking its implementation.
An important part of rehabilitation is moral and psychological support. The development of post-stroke depression significantly worsens the patient's condition. This condition can be caused by social isolation, lack of desired results in treatment, and certain medications.
Prevention of stroke
Prevention of pre-stroke and stroke conditions are measures to improve overall health and reduce the negative impact on the circulatory system. First of all, you need to quit smoking. Statistics for smokers are not favorable, and smoking negatively affects not only blood vessels, but also the condition of the lungs, heart muscle, liver, and skin.
You need to reconsider your diet. Eat more fruits and vegetables, foods with fiber (oatmeal, bran, beans, lentils). Reduce the amount of salt and salty foods you consume (salted fish, pickles, ready-made frozen meals, instant foods). Limit consumption of fatty foods (fatty meats, poultry skin, rendered pork and lamb fat, heavy cream and butter).
An effective way to prevent cerebrovascular accidents is moderate physical activity. Physical education should be done for at least 30 minutes three times a week. The intensity of exercise should correspond to the level of physical fitness and increase gradually, without overdoing it.
At the clinic you can get advice on individual methods of preventing strokes and strokes. Here they not only perform treatment, but also talk about measures to prevent pathology. You can make an appointment with a neurologist, cardiologist, or rehabilitation specialist by calling the Yusupov Hospital.