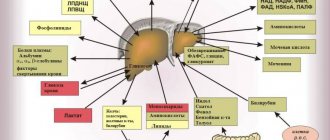
A hepatologist is a doctor whose professional activity is aimed at diagnosing and treating liver diseases. Hepatology is a branch of gastroenterology that focuses on problems of the liver, gallbladder and biliary tract. A separate field of medicine is pediatric hepatology, which takes into account the structure of the liver, its development and the characteristics of pathology in the child’s body.
Diseases treated by a hepatologist
Pathologies dealt with by a hepatologist:
- acute, chronic hepatitis;
- toxoplasmosis;
- cirrhosis (viral, alcoholic, medicinal, nutritional, stagnant, congenital);
- yellow fever;
- herpetic, enteroviral, autoimmune, toxic, reactive hepatitis;
- Legionnaires' disease;
- Gilbert's syndrome (bilirubin is not processed by the liver). Pathology is inherited;
- cholangitis;
- gall diseases (cholecystitis, tumors, cholangitis, cholelithiasis, ductal dyskinesia);
- mononucleosis;
- vascular diseases of the hepatobiliary system;
- hemochromatosis;
- alcoholic impairment.
The above list does not include all pathologies diagnosed and treated by a specialist.
In this video you will learn everything about hepatitis C:
to contents ^
We wish you good health!
And if you need liver examination and treatment, our specialists are always ready to help. We guarantee:
- high level of expertise in diseases of the hepatobiliary system
- extensive successful clinical experience in managing patients with liver diseases
- presence of a team of hepatologists
- work according to international standards of leading hepatological communities
- availability of highly specialized laboratory and instrumental equipment
- possibility of a comprehensive liver examination based on the “here and now” principle
- individual approach to each patient.
When to consult a hepatologist
In medicine, hepatology is classified as gastroenterology. This is a branch that examines pathologies not only of the liver, but of all organs of the digestive system and gastrointestinal tract.
Considering that therapy for liver diseases requires correction of the patient’s body weight and adherence to a certain diet, hepatologists join forces with gastroenterologists, offering the patient an integrated approach to treatment.
Diseases that require maximum attention are cirrhosis, hepatitis C and B. You should go to the doctor at the first manifestation of adverse symptoms. The following are signs of liver problems.
Common signs that indicate that there are malfunctions in the liver and related organs are the following:
- discomfort, heaviness, pain under the ribs on the right. Unpleasant sensations do not go away for a long time after they occur;
- bitter taste in the mouth, regardless of the type of food eaten;
- dyspepsia, digestive problems. The problem can be identified by flatulence, nausea (sometimes to the point of vomiting), and loss of appetite. Problems with stool (constipation, diarrhea) often occur;
- the sense of smell suddenly becomes acute, the smallest odors are felt, mostly unpleasant;
- itchy rashes covering the skin all over the body, age spots and other dermatological problems not related to existing diseases;
- decreased performance, increased fatigue, lack of strength for usual activities;
- urine and feces take on a different color (urine darkens and feces lighten);
- the sclera of the eyes and skin become yellow.
In addition to the general clinical picture, you need to know about the symptoms associated with the most common, dangerous diseases.
Liver cirrhosis can be suspected based on the following signs:
- bleeding gums;
- pain under the ribs on the right;
- drowsiness, fatigue, poor concentration, passive state;
- the stomach increases in volume;
- the skin turns yellow;
- in men, mammary glands enlarge;
- decreased libido;
- red palms;
- minor hemorrhages on the face.
The listed symptoms do not appear all at once; only a small part of them can be identified. This is especially true at the initial stage, when the disease is just beginning to develop.
The more signs, the more dangerous the stage of the disease. You should not postpone a visit to a specialist. The earlier treatment is started, the greater the chances of successful regeneration of organ cells and preventing consequences.
It is not always possible to suspect hepatitis C at first - the disease prefers to develop hidden. This is fraught with serious complications, since in the later stages of the pathology there is no hope for complete restoration of liver cells.
It is recommended to visit a hepatologist regularly if there are no complaints in his area. Chronization of hepatitis is a long process; the transition from acute to chronic form lasts two or more decades.
to contents ^
What is important to pay attention to when choosing a clinic and doctor?
What is the main profile of the medical institution where the hepatologist works?
If this is a specialized center specializing in the treatment of patients with liver diseases, this is the place for you. If not, additional information should be collected. The profile of the center is reflected in its services. It is important to evaluate:
- Does the clinic (medical center) have all the necessary laboratory and special examination methods so that you can be examined “here and now”?
- Is it possible to obtain an assessment of the stage of liver disease (fibrosis), including non-invasively - ultrasound with elastography?
Does the specialist have sufficient experience in managing patients with liver diseases?
Effective acquisition of such experience is possible only within specialized centers, where the doctor not only consults the patient, but treats and monitors his health and the health of his family members for a long time. Only in this case does the hepatologist have sufficient experience in managing patients with viral, non-viral diseases and their combinations.
How many hepatologists work in the center, do they have status and academic title?
The answer to this question will allow you to:
- be sure that in the event of vacation, illness or absence of your attending physician for any other reason, you will not be left without proper help and attention at the moment of a sudden exacerbation of the disease
- count on a consultation if there are hepatologists at the center, if your case is complex, as well as on the treatment and supervision of a professor at the stages of particularly complex treatment
- be confident in the high level of quality, the presence of principles of continuity and team support in both diagnosis and treatment in this center.
Does the medical center have a professional team of hepatologists?
Rate the level of professionalism and experience of the center’s specialists:
- Does the team include doctors, candidates of medical sciences?
- Is there a leader, a “senior colleague” who is responsible for the professional level of all employees of the clinic, which will allow them to confidently contact any doctor, since uniform diagnostic and therapeutic standards have been introduced into the team?
- What is the experience and academic titles of the “senior colleague”?
- Will he be able to provide insurance if you have a difficult case?
Clarify to what extent the clinic’s specialists are proficient in the most modern diagnostic and treatment methods, and to what extent their prescriptions comply with international standards:
- Are there any employees from departments of state medical educational institutions in this medical center?
- Are there training centers based at the clinic?
- Do the center’s staff participate and speak at conferences on hepatology and gastroenterology?
- are they working on scientific publications on hepatology?
- Are other doctors trained in hepatology?
Are there doctors of other specialties in the clinic?
Find out how holistically the hepatology department is represented in the medical center, that is, the opportunity to treat pathology of internal organs combined with the liver is provided. Since the treatment of liver diseases often affects other organs and systems, the complex approach of a hepatologist to problems in the patient’s body requires the participation of such specialists as:
- endocrinologist
- cardiologist
- psychotherapist.
Appointment with a hepatologist
If you identify these symptoms, you can consult a therapist or go to a hepatologist. The doctor will conduct a survey, clarify complaints, the timing of the onset of illness and related issues. It is necessary to take into account whether relatives have liver pathologies; the diseases are hereditary.
A detailed survey includes questions on lifestyle, gastronomic habits, and harmful hobbies. This information will help the doctor limit the range of causes that can negatively affect the liver and other organs. Based on the information received, the doctor assumes a diagnosis and, to confirm and clarify it, refers the patient to instrumental and laboratory diagnostics. Main types of measures for diseases:
- CBC (blood parameters are examined);
- biochemical blood test;
- LAM (laboratory testing of significant urine parameters).
In addition to the specified standard tests, the doctor will, if necessary, send for additional diagnostics if controversial issues arise. Ultrasound, x-ray, and stool analysis will help clarify the situation. A set of diagnostic procedures will allow you to create a complete picture of the patient’s health status, establish a diagnosis, identify the cause, and select adequate therapy.
to contents ^
When to contact
The following symptoms may be a reason to contact a hepatologist:
- constant weakness, increased fatigue and loss of performance;
- lack of appetite;
- sudden weight loss;
- temperature above 37.0°C for more than a week;
- periodic nausea and vomiting, especially associated with meals;
- abdominal pain radiating to the intestines;
- pain in the right hypochondrium;
- yellowness of the skin and eye sclera;
- increased turbidity of urine;
- whitish inclusions in stool;
- slight bruising of the skin;
- frequent bleeding from the gums and nose;
- the presence of blood in the stool;
- the appearance of a bulge in the abdominal area with general weight loss;
- "marbling" on the abdomen.
All these symptoms can appear simultaneously or in different combinations. Some of them may be more pronounced. The pain can also vary in intensity, sometimes reaching painful shock. All such manifestations should be a reason to contact a hepatologist.
What is the difference between an infectious disease hepatologist and a hepatologist?
If a patient is suspected of having liver disease, provoked by viruses, helminthic infestations, or the pathological course of chronic diseases in the body, it is necessary to be examined by an infectious disease specialist.
He deals with contagious diseases, prescribes treatment aimed at reducing side effects and the likelihood of complications. The competence of an infectious disease specialist is to vaccinate children and adults against hepatitis viruses. Vaccination is necessary for those who are at risk.
An infectious disease hepatologist can easily distinguish hepatitis A from hepatitis B, as well as diseases with similar clinical presentations. This doctor is consulted for parasitic diseases (ascariasis, amoebiasis, opisthorchiasis, toxoplasmosis, echinococcosis), infectious mononucleosis, the symptoms of which resemble ARVI.
Thanks to a specialist, you can stop the development of diseases and prevent them from becoming chronic.
to contents ^
Professional tasks
In order to work as a hepatologist, you need to obtain a diploma of higher medical education, after which you must complete an internship in the gastroenterology department under the guidance of a qualified experienced doctor. During training you need to perfectly master the following sections:
- anatomy and physiology of the hepatobiliary apparatus;
- pathological physiology of this system;
- age-related features of functioning in patients of different categories;
- specific diagnostic methods;
- therapy and prevention of liver and gallbladder diseases.
One of the most important areas remains preventive activity, which is necessary even after successful treatment and can save the patient from repeated serious dysfunctions. The hepatologist can adjust the daily routine and food intake in such a way that the need for therapy disappears or is postponed for a significant period.
In addition, this specialist, as a rule, is simultaneously engaged in scientific and research activities aimed at finding new and alternative methods for recognizing pathologies and neoplasms, as well as preventing their development.
Another area of activity of a hepatologist is the search for optimal and effective medications that can quickly and without side effects help patients with damage to the hepatobiliary system. In addition, this doctor can determine the need for consultation with related specialists, to whom he will refer the patient for consultation, if necessary.
Hepatologist's recommendations
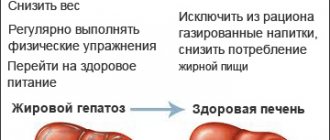
To protect yourself from liver and gall bladder diseases, follow preventive measures. Avoid excessive amounts of alcohol and fatty foods, they overload the liver. Paying attention to your health will help you avoid dangerous diseases.
The following recommendations will help against hepatitis infection:
- heat treatment of food, washing vegetables and fruits before consumption;
- exclude contact with blood and biological fluids of strangers;
- do not use other people’s personal hygiene items;
- sexual intercourse - only with protective equipment;
- Avoid sharing the same syringe or needle. You need to carefully go to tattoo parlors and hairdressers (piercing, manicure) - instruments must be processed in front of each new client;
- If a pregnant woman has hepatitis, measures must be taken to prevent the fetus from getting the disease from her.
The virus that causes hepatitis is a persistent pathogenic microorganism; the routes of infection are not fully understood. Therefore, doctors recommend vaccination as the best way to avoid the disease.
How to find your clinic and your doctor?
Option 1 - choose based on reviews.
Modern and smart. Many people do this. However, besides “I like everything, they helped me a lot, everything is very good” or “they didn’t help me, everything is bad, don’t go there,” is there anything specific in them? What was actually examined, how was it treated, with what regimens, what specific result did you get? In order to give correct feedback, you need to understand the problem. Everyone understands that situations are different, each patient is individual, so what is good for one may be unacceptable for another. Option 2 - listen to a friend, relative, acquaintance. Really a real option. If he, your friend, relative or acquaintance is directly related to medicine, then you are in luck, seek advice and draw conclusions. And if not? Then the advice is more like the feedback from the previous paragraph.
Option 3 - search on the Internet - on the websites of various clinics offering hepatologist services. But how to choose when they write everywhere that they have the most wonderful doctors and the latest equipment?
Is there another option - how to make an informed decision, based not only on emotions, external signs of success and positive reviews? Let's talk about this.
Indications for consultation
What does a hepatologist treat? Patients with a variety of chronic pathologies of the hepatobiliary system, acquired or genetically inherited, come to him. The list includes diseases such as:
- Hepatitis (inflammation of liver tissue). Hepatitis is classified primarily by etiology. Viral hepatitis comes in first place in terms of prevalence, followed by toxic (provoked by household and industrial poisons, drugs, alcohol) and autoimmune (caused by aggression of the immune system against the tissues of one’s own body). Acute viral hepatitis is treated by an infectious disease specialist. The prerogative of the hepatologist is to confirm the diagnosis and stage of chronic hepatitis, search for the cause, choose a method of therapy, correct it during treatment and evaluate the effectiveness of the result, as well as prevent complications.
- Cirrhosis (excessive production of fibrous tissue and its replacement of functioning hepatocytes - liver cells). The cirrhotic process starts as a result of damage and necrosis of hepatocytes and has a chronic course. It occurs as a result of hepatitis, severe hypoxia (oxygen starvation) and shock.
- Alcoholic liver disease. This is a combined pathology that includes chronic hepatitis and liver cirrhosis.
- Storage diseases affecting the liver. These are lipidosis and dyslipoproteinemia, mucopolysaccharidosis, glycogenosis, as a result of which an excess amount of a substance is deposited in the liver.
- Hereditary pathologies. These include Gilbert's syndrome, or familial non-hemolytic jaundice, Wilson-Konovalov disease, or hepatocerebral dystrophy.
- Diseases of the gallbladder and bile ducts. Among them are cholecystitis and cholangitis of various etiologies, including primary sclerosing cholangitis.
The benefits of early diagnosis and timely treatment
A characteristic feature of many ailments in this industry is a long asymptomatic course. That is, for a long time the disease may not manifest itself in any way, systematically destroying the cells of the organ. The liver, as we know, does not have nerve endings, so obvious symptoms of the disease begin to appear when the pathological process affects nearby organs. Late or incorrectly selected treatment in most cases is fraught with dire consequences.
The accumulation of fats in liver cells accelerates degenerative processes, tissue fibrosis occurs, and the organ ceases to function normally. And this is just the most “harmless” complication. Much more dangerous is cirrhosis, accompanied by stagnation of blood flow in the portal vein. Against the background of venous insufficiency, varicose veins of the stomach and esophagus develop, which in 30% of cases causes death.
Ascites is a serious threat to life - a complication of liver cirrhosis, accompanied by an acute inflammatory process and accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity. As a rule, the pathology is rapid in nature and in its advanced form causes coma.
That is why we recommend that patients do not neglect the possibilities of early diagnosis. The optimal combination of modern technologies and knowledge accumulated over the years allows our hepatologist to identify liver diseases in the initial stages.
Another unique characteristic of the organ is its ability to recover quickly. Even serious illnesses can be completely cured and liver functions can be restored. However, this is only possible if adequate therapy is started in a timely manner. In Kaliningrad, you can get diagnosed, confirm or rule out a hepatological disease in our medical office.
Treatment prescribed by a hepatologist
The principles on which therapy is based are as follows:
- Prescription of antiviral therapy. The goal of such treatment is to eliminate the pathogen (in this case, a virus) from the body. This requires an integrated approach.
- Identification of concomitant chronic diseases of other organ systems in the patient. If they are detected, it is necessary to carry out additional measures, the task of which is to achieve stable remission.
- Prescribing dietary nutrition to the patient. Most often, people with liver problems are recommended diet table number five. However, it can be changed depending on the individual characteristics of the disease in a particular patient.