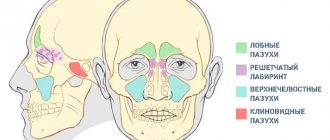
Why are colds dangerous during pregnancy?
Speaking about viral infections during this period, it is important to understand that in some cases consequences are possible for both the child and the expectant mother.
In the 1st trimester, the risk of negative effects on the fetus is highest. The placenta, as a natural barrier, has not yet been formed; viruses can enter the bloodstream and directly affect the embryo.
Among the most dangerous acute respiratory viral infections are influenza and coronavirus. Studies related to the effects of influenza during pregnancy suggest that the likelihood of developing deformities is influenced not only by the virions themselves, but also by the fever that occurs in response to their exposure.
In the case of ARVI in the 1st trimester, complications such as:
- development of severe defects in the fetus;
- termination of pregnancy in the early stages;
- the presence of a threat of miscarriage, which can persist for a long time.
In the 2nd trimester, the placenta is already performing its functions, and the baby’s main organ systems are already formed. At this time, infection can affect individual organ systems and prevents most viruses from harming the fetus. The exception is coronavirus. Studies conducted by French scientists confirm that it is able to penetrate the placenta and directly infect the fetus (vertical mode of infection).
In addition, coronavirus worsens the condition of the placenta: areas of inflammation, blood flow disturbances are found in it, and the size itself is smaller than normal.
When contracting ARVI in the 3rd trimester, the harm to the baby is associated with the initial state of health of the mother and the degree of damage to the placenta. If there are disturbances from the fetal site, negative consequences for the fetus are possible: the baby suffers from chronic hypoxia, and subsequently lags behind in physical development. Such a child may be born prematurely and have low weight.
And the pregnancy itself is under threat - in 3% of women with damage to the placenta due to ARVI, placental abruption with bleeding develops. This is a life-threatening condition that can cause the death of a mother or child. However, obstetricians-gynecologists are encouraging that chronic hypoxia and complications develop only when more than 50% of the placenta is affected; in other cases, the child does not suffer.
Is it possible for a pregnant woman to apply mustard plasters and pepper plaster?
Despite the fact that both mustard plasters and pepper plaster act externally and do not affect the development of the fetus, they are potentially dangerous for pregnancy. Heat treatments can increase uterine contractility, which is associated with an increased risk of miscarriage or premature birth. In addition, increased microcirculation, which occurs under the influence of mustard plasters or pepper patches, can change uteroplacental blood flow, which is also undesirable. The greatest danger is posed by thermal procedures in the first and last trimester of pregnancy - in the first they increase the risk of miscarriage, in the last - premature birth.
Signs of ARVI during pregnancy
The first symptoms of a viral infection in an expectant mother may appear simultaneously, or the deterioration of the condition may develop gradually. The speed of onset of symptoms and severity depend on the type of pathogen and the initial condition of the woman.
Signs of ARVI:
- runny nose, difficulty in nasal breathing;
- lack of smell;
- inability to taste food;
- general weakness;
- lacrimation;
- headache, dizziness;
- pain in muscles, joints;
- temperature increase;
- sore throat, cough, sore throat;
- nausea, vomiting, diarrhea.
Often the first, even minor manifestations of ARVI can be recognized at the very beginning of the disease. The task of the expectant mother is to observe her own well-being and not ignore the body’s signals. The slightest discomfort is a reason to rest and consult a doctor.
Dangerous complications of seasonal flu include:
- addition of a bacterial infection;
- sepsis;
- systemic inflammatory response syndrome
- acute respiratory failure
- multiple organ failure and death of a woman.
Vaccination of pregnant women against influenza
During the entire period of pregnancy, influenza is very dangerous for expectant mothers. To date, WHO is continuing research aimed at assessing the risks and benefits of vaccination against pandemic influenza in pregnant womenii. The European Center for Disease Control and Prevention states: “Influenza vaccination is the main strategy for preventing severe and complicated illness, even if the vaccine is less effective than expected.” Some time after the vaccine is administered, the woman and newborn develop specific immunity that protects in case of contact with sick people.
In the Russian Federation, the issue of influenza vaccine prevention arose urgently in connection with the 2009-2010 pandemic. During this period, domestic and foreign split vaccines were used for the first time, which largely made it possible to avoid the severe consequences of the influenza epidemic. Since 2014, pregnant women have been officially immunized for epidemiological reasons.
Vaccination can reduce the risk of infection after birth and also reduces the likelihood of a baby contracting the flu during the first months of life. Antibodies are transferred to the child from the mother, which helps the formation of passive immunity. It is advisable for all family members to be vaccinated against influenza, including older childreniii.
Prevention of ARVI
Prevention of viral infection during pregnancy is mostly nonspecific and is aimed at maintaining the woman’s physical health, limiting contact, especially with people who have signs of acute respiratory viral infection, and maintaining hygiene standards. Specific prevention is only possible to prevent infection with seasonal influenza.
Nonspecific prevention
Obstetricians-gynecologists do not advise taking immunostimulating, multivitamin medications unless absolutely necessary. Among the main recommendations:
- Avoid contact with people who have ARVI symptoms; if living together, organize isolation, wear a mask, frequently ventilate the room, and carry out wet cleaning with antiseptics.
- At home, maintain an air humidity level of 50% and irrigate the nasal mucosa with weak saline solutions.
- Limit visits to crowded places. During visits to a store, clinic, or other institutions, wear a medical mask and change it every 2 hours or until the material from which it is made becomes wet.
- Do not touch your face with dirty hands after any contact (for example, handrails, door handles, bills or goods in a store) - wash your hands first or treat them with antiseptics.
- Try to maintain a sleep-wake schedule and eat a balanced diet. Take regular walks in the fresh air.
Specific prevention
Flu vaccination during pregnancy is allowed for women in the 2nd and 3rd trimesters. Its safety has been confirmed by clinical trials. The vaccine is usually well tolerated and provides immunity from the virus within 4 weeks. WHO experts recommend the use of drugs with an antigen dosage of 15 mcg; they assess other vaccines as insufficiently effective.
So the expectant mother can choose a vaccination from the following list:
- "Ultrix";
- "Vaxigrip";
- "Influvac";
- "Flu-M".
Vaccination is contraindicated in patients with individual intolerance to vaccine components, systemic diseases, acute conditions or decompensation of severe chronic pathologies. If a woman has had an acute respiratory viral infection during pregnancy without any complications, she can maintain an interval of about 2-3 weeks and get a flu shot.
What is not recommended to do
It is important to understand that therapy for pregnant women is very different from usual. You should absolutely not take medications without consulting your doctor. Many drugs are contraindicated during pregnancy, others are prescribed only if the potential benefit outweighs the harm.
A cold without fever requires symptomatic care. Her treatment excludes drugs that include alcohol, antibiotics, and sulfonamides. Their appointment must be supervised by a doctor.
Rinsing and drinking plenty of fluids are good if the first signs of a cold are observed. Complications are always treated by a specialist. Help is needed urgently if:
- high temperature (above 39 degrees) or it does not go down;
- there is constant vomiting;
- uterine tone or contractions are observed;
- there is bloody discharge from the vagina;
- on the fifth day there is no improvement, the general condition worsens;
- there are rashes.
Treatment of viral infections in pregnant women
If a cold during pregnancy cannot be avoided, it is important to approach treatment as competently and carefully as possible. What do you need to know? There is no specific and safe treatment that can destroy all viruses that cause ARVI. Neither homeopathy nor interferons will become that “magic wand” that will help a woman quickly “come to her senses.” On an outpatient basis, a therapist and obstetrician-gynecologist have the right to observe pregnant women with a mild course of the disease. Treatment mostly consists of eliminating unpleasant symptoms.
Treatment of ARVI and influenza at home
An increase in temperature during infection is not an annoying fact. This is a sign that the immune system is beginning to cope with the disease on its own. Interferon synthesis occurs at body temperature from 37 degrees. Attempts to get rid of fever lead to the recovery process being delayed over time. Temperature should be reduced during pregnancy only when it rises to 38.0 - 38.5 degrees. Hyperthermia is dangerous - it can lead to fetal deformities. It is permissible to use drugs based on paracetamol and ibuprofen as antipyretics.
Sore throat, cough, runny nose, and a feeling of nasal congestion directly worsen the quality of life. During an acute respiratory viral infection, the expectant mother is at a “disadvantage” - swelling of the nasal mucosa, difficulty in nasal breathing, a feeling of dryness and increased sensitivity to environmental humidity are characteristic of a normal pregnancy. Against the background of infection, these symptoms worsen, bringing with them headaches, inability to sleep due to a stuffy nose, and in some cases, a greater risk of sinusitis (for example, sinusitis). To eliminate dryness and cleanse the mucous membranes of infectious agents, it is recommended to irrigate the nasal passages with sterile saline solutions. For swelling and difficulty breathing, drops with a vasoconstrictor and softening effect are used for a course of up to 3-5 days.
For sore throat, it is recommended to gargle with chamomile decoction or a weak solution of soda and salt. These products cleanse the nasopharynx and have a mild anti-inflammatory effect.
To alleviate the condition, you need to provide bed rest and create a favorable microclimate in the room (air temperature no higher than 22 degrees, humidity from 50%). If there are no health restrictions, the expectant mother should drink enough fluids and eat food often and in small portions.
Formally, this is all that can be done at home if a pregnant woman has a cold or flu and tolerates the infection quite easily. It is not advisable to start taking antiviral drugs, interferon drugs, sore throat lozenges, or iodine solution on your own. If disturbing symptoms appear, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Moderate and severe acute respiratory viral infection, according to clinical recommendations, requires hospitalization in a hospital. Here are the main indications for translation:
- fever from 38 °C in the presence of chronic somatic diseases;
- fever from 37.6 °C against the background of influenza with moderate and severe severity of the disease;
- pneumonia;
- severe intoxication in a woman, regardless of the severity of the disease.
Scheme for using suppositories VIFERON 500,000: how to treat ARVI during pregnancy
Suppositories VIFERON 500 thousand units. included in the complex therapy of ARVI and influenza. Used for children over 7 years of age and adults, including pregnant women from the 14th week of gestation. VIFERON 500,000 IU is prescribed 1 suppository 2 times a day every 12 hours every day for 5 days. According to clinical indications, therapy can be continued. In Order of the Ministry of Health of Russia No. 572 [1], the main regulatory document on obstetrics and gynecology, interferon preparations are recommended as one of the means for the treatment of respiratory diseases, including bronchitis and pneumonia, in pregnant women.
The inclusion of the drug VIFERON® in the complex therapy of ARVI and influenza in pregnant women helps reduce the risk of premature termination of pregnancy by 3.54 times [2], and also helps to significantly reduce the duration of intoxication symptoms.