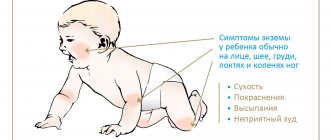
Symptoms and first signs of tuberculosis in children
First of all, tuberculosis in children is manifested by such clinical signs as:
- weakness;
- stopping weight gain;
- irritability;
- fatigue during school hours;
- absent-mindedness;
- lagging behind peers in studies;
- body temperature – up to 37.5°C;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- sweating;
- chills.Source: N.M. Koretskaya Tuberculosis in children and adolescents in modern conditions // Siberian Medical Review, 2010
Forms of tuberculosis and early signs
| Form | Symptoms |
| Tuberculosis of the bronchial glands | Cough, elevated body temperature for a long time, lethargy, fatigue, pallor, thinness. |
| Pulmonary form | Cough, shortness of breath, weakness after sleep, apathy, decreased performance, absent-mindedness, unhealthy blush, thinness, pale skin, sweating, chills, dry (and then “wet”) cough for more than 3 weeks, sputum with blood. |
| Lymph node involvement | An increase in the size of the lymph nodes, their softening, suppuration (the contents leak out), the formation of fistulas in places where pus comes out, scrofuloderma (skin lesions in the form of tumors with subsequent release of the contents). |
| Involvement of bones and joints in the process | Slow development, pain when moving, changes in gait, lameness. |
| Damage to the meninges (tuberculous meningitis) | Anxiety, lethargy, loss of appetite, bad mood, headaches, fever, vomiting, convulsions. |
| With damage to the gastrointestinal tract | Constipation or diarrhea, increased body temperature, blood in the stool, pain. Source: A.V. Mordyk, E.A. Tsygankova, L.V. Puzyreva, A.A. Turitsa Tuberculosis in children of the Russian Federation at the present stage // Pediatric pharmacology, 2014, v. 11, no. 3, pp. 27-30 |
Clinical manifestations by age of children
| Age | Symptoms |
| Infancy (up to one year) | Low mobility, apathy, weakness, attacks of suffocation or coughing, retraction of part of the chest, weight loss (including muscle mass), loss of appetite, cessation of crying, insomnia. Early detection and diagnosis are extremely important, because at this age this pathology is most dangerous. |
| 5-8 years | Decreased activity, weakness, lack of sleep and appetite, loss of body weight, cough, condensation of the chest. |
| 8-15 years | Rapid appearance of pain in the lungs against a background of apathy and weakness, active urge to cough, shortness of breath even at rest, thinning or discoloration of the skin, the appearance of cracks, wounds, hemoptysis, changes in lymph nodes in size and structure, intoxication of the lungs (at the last stage) . |
Manifestations of the chronic form:
- sleep disorders;
- liver enlargement;
- lagging behind peers in physiological development;
- dry and pale skin;
- mild euphoria.
Tuberculosis in children (questions and answers)
What is tuberculosis?
Tuberculosis is a dangerous infectious disease that, without timely and proper treatment, can lead to loss of ability to work, disability, and death. Tuberculosis most often affects the lungs (pulmonary tuberculosis), but can also develop in other organs (tuberculosis of the lymph nodes, skin, eyes, bones and joints, etc.).
What causes tuberculosis?
Tuberculosis is caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. This is an unusually viable microorganism that retains its properties during drying, freezing, and after treatment with alcohol, acid and alkali.
How does infection occur?
In most cases, tuberculosis is transmitted by airborne droplets from a patient with an infectious form of pulmonary tuberculosis, i.e. secreting Mycobacterium tuberculosis. The main source of infection is the patient’s sputum, tiny droplets of which, infected with Mycobacterium tuberculosis, enter the air when he coughs, sneezes, spits, or talks. They penetrate with air into the lungs of healthy people and lead to infection (infection) with tuberculosis.
Children, like adults, become infected with tuberculosis by inhaling air containing Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Infants and young children most often become infected within the family or from close friends and neighbors. School-age children can also become infected in public places through contact with a patient with pulmonary tuberculosis.
Why do some people get tuberculosis and others not?
Most people who are infected never get TB because their immune system suppresses the infection. 5-10% of those infected get sick. Usually this is facilitated by other serious illnesses, HIV infection, living in cramped, damp and cold rooms, poor nutrition, hard work in poor conditions, severe stress, that is, everything that leads to a weakened immune system.
At what age do children most often develop tuberculosis?
Young children (under 3 years of age), especially in the first year of life, are very susceptible to tuberculosis. At this age, the body’s defenses have not yet been developed, because when Mycobacterium tuberculosis enters it, the disease develops very quickly.
The second period of reduced resistance to tuberculosis in children is the age from 10-11 to 14-16 years, when immunity decreases due to rapid growth and hormonal changes in the child’s body.
What contributes to the occurrence of tuberculosis in children:
- Intrafamily contact with a patient with a contagious form of tuberculosis.
- Past infections (measles, whooping cough, pneumonia, chicken pox).
- Smoking, drug use.
- Poor nutrition of the child (excess carbohydrates, lack of protein).
How to determine if a child is infected with tuberculosis?
This is done using immunodiagnostics of tuberculosis using the Mantoux test or recombinant tuberculosis allergen (Diaskintest).
How are children diagnosed with suspected tuberculosis?
Children are examined in the same way as adults: they are examined, while parents are asked about changes in the physical condition and behavior of the child, his complaints, a sputum test is done if the child produces it, a chest x-ray and other necessary studies.
Is there a vaccine against tuberculosis?
There is such a vaccine. This is the BCG-M vaccination. Although it does not completely eliminate the possibility of tuberculosis for a child, it must be done, as it protects children from fatal forms of the disease, such as tuberculin meningitis and miliary tuberculosis. All healthy newborns are vaccinated on the 3rd-5th day of life.
How to protect a child from tuberculosis?
Children get sick primarily through contact with adults with tuberculosis. Pay attention to your well-being and the health of those around you. A person who is coughing may be suffering from tuberculosis. Therefore, if your relative, co-worker or acquaintance who is in contact with your child coughs for a long time, insist that he see a doctor and limit his contacts with the child. Take an interest in the health of those people who will temporarily live in your family or often come to your home.
If there is a person with tuberculosis in the family, he should be isolated from children. Ventilate the room as often as possible and wet clean it 2-3 times a day. The patient should cover his nose and mouth with a handkerchief or napkin when coughing and sneezing; use a spittoon, which should be disinfected.
Take care to strengthen your child's immunity.
In order for a child to be able to resist any disease, he must eat regularly and nutritiously, follow a daily routine, be in the fresh air, and not overwork. Share on social media networks
Causes
Koch's bacillus has a shell that is resistant to acidic environments. It is able to survive freezing, drying, exposure to alkalis, and much more. etc. Characterized by the ability to form so-called L-forms with increased adaptability. The most pathogenic microbacteria for humans are:
- Mycobacterium tuberculosis humans;
- Mycobacterium bovis.
Microbacteria enter the body through contact, air, mixed and other routes. This is how the first inflammatory focus is formed. A child can also be infected during the mother's pregnancy - through the placenta or during childbirth, if it swallows amniotic fluid. Source: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24548085 Marais BJ Tuberculosis in children J Paediatr Child Health . 2014 Oct;50(10):759-67. doi: 10.1111/jpc.12503. Epub 2014 Feb 19
Children at risk include:
- not vaccinated with BCG;
- long-term treatment with antibiotics, hormonal or cytostatic agents;
- having HIV status;
- living in unfavorable conditions (social and/or sanitary);
- having diabetes mellitus;
- with weakened immunity;
- under 2 years of age;
- and etc.
CHEST PAIN WITH TUBERCULOSIS
Pain of varying intensity in the chest, under the ribs and behind the shoulder blades sometimes appears in the initial stages of the disease. As a rule, in the early stages there is discomfort or mild pain. As tuberculosis progresses, pain becomes more pronounced, especially when taking a deep breath.
Remember that you should consult a doctor at the first symptoms. This will save you valuable time and significantly increase your chance of a full recovery.
Types and forms of pathology
According to the period of occurrence in medicine, stages are distinguished:
- infiltration;
- decay;
- contamination;
- resorption;
- seals;
- the appearance of scars;
- calcification.
| Form | Peculiarities |
| Chronic and early | It occurs against a background of body temperature up to 40℃, cough, pain in the lungs, uneven breathing, wheezing, decreased appetite, and loss of strength. |
| Respiratory damage | Includes pathologies:
|
| Other localizations | There may be lesions:
|
TUBERCULOSIS: HOW THE DISEASE STARTS IN ADULTS
The first signs of tuberculosis appear individually.
It all depends on the localization of the pathological process, the age of the patient, the state of general health and a number of other features. If we talk about tuberculosis of the respiratory system (lungs), the first symptoms of the disease often resemble an acute respiratory infection or chronic fatigue. The patient experiences weakness, drowsiness, poor appetite and depressed mood. As a rule, there is restless sleep, and chills may occur in the evenings.
At the initial stage of tuberculosis, body temperature, as a rule, rises to subfebrile levels (37-37.5). A dry cough appears, which worries the patient most in the early morning and at night.
It is noteworthy that the onset of tuberculosis may be accompanied by one of the above symptoms or several signs at once.
How does the disease progress?
The mechanism of development of such an infection includes several stages:
- entry of the pathogen into the upper respiratory tract (on the mucous membranes), from where, with a weak immune response, they enter the lungs;
- penetration into the alveoli of the lungs and further through their walls (without specific changes);
- entry into the lymph nodes and lymphatic pathways with further reproduction (here the infection can take a latent form and persist without external phenomena);
- circulation of microbacteria through the bloodstream without reproduction (about 2 weeks);
- spread of infection through tissues and organs, manifestation of a primary disease or latent infection;
- formation of immunity - formation of granulomas around microbacteria;
- infection (if the process does not progress, the granuloma becomes covered with connective tissue or resolves, the microbacterium inside it turns into the L-form);
- disease – transition of L-forms into rods.
HEMOPTYSIS IS A DANGEROUS SYMPTOM OF TUBERCULOSIS
If hemoptysis occurs during tuberculosis, this usually indicates that the disease is acquiring an infiltrative form. At the same time, the doctor should correctly differentiate tuberculosis from tumors, since hemoptysis is one of the symptoms of malignant lung tumors. In addition, hemoptysis may also indicate acute heart failure. As a rule, with tuberculosis, blood is released in small quantities during an attack of wet cough. If a cavity ruptures, then blood is released in large quantities (sometimes even gushes out). In such cases, the patient needs urgent surgery.
Treatment
Chemotherapy, antibiotics
Bactericidal and bacteriostatic drugs are used to achieve complete recovery. In this case, the correct combination of drugs is important, taking into account the resistance of some bacteria to this type of therapy. First, treatment is aimed at suppressing the growth of bacteria and eliminating their resistance to medications. Residual infection in the cells is then eliminated. Duration of therapy is 6-12 months.
Surgery
Pulmonary resection is practiced as a radical technique. The operation is performed for bronchial stenosis, fibrous-cavernous lesions, pleural empyema, abscesses in the lungs, tuberculomas prone to progression, etc. In addition, decortication is used, that is, removal of fibrous layers, and cavernotomy - cleansing of the opened cavity.
DOTS
A treatment system consisting of several levels: bacterioscopic examination, chemotherapy, anti-tuberculosis treatment.
Sources:
- N.M. Koretskaya. Tuberculosis in children and adolescents in modern conditions // Siberian Medical Review, 2010.
- A.V. Mordyk, E.A. Tsygankova, L.V. Puzyreva, A.A. Turitsa. Tuberculosis in children of the Russian Federation at the present stage // Pediatric pharmacology, 2014, v. 11, no. 3, pp. 27-30.
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24548085 Marais BJ. Tuberculosis in children // J Paediatr Child Health. 2014 Oct;50(10):759-67. doi: 10.1111/jpc.12503. Epub 2014 Feb 19.
- V.N. Krivohizh. Modern methods of early detection of tuberculosis among children and adolescents // Health is the basis of human potential: problems and solutions, 2013, pp. 570-585.
The information in this article is provided for reference purposes and does not replace advice from a qualified professional. Don't self-medicate! At the first signs of illness, you should consult a doctor.
DRY AND WET COUGH IN TUBERCULOSIS
This is a typical symptom characteristic of pulmonary tuberculosis. As mentioned above, in the initial stages there is a dry paroxysmal cough. However, with the progression of the disease, when the granulomas increase to cavities, exudate accumulates in the lungs. Sputum production begins, and the cough turns from dry to wet. As a rule, after coughing up sputum, the patient feels a little better. It should be remembered that if a person has been bothered by a cough for more than three weeks, the causes of which are not related to a cold or flu, then he should consult a TB doctor as soon as possible. Perhaps this is a symptom of tuberculosis.
Prices
| Name of service (price list incomplete) | Price |
| Appointment (examination, consultation) with a pulmonologist, primary, therapeutic and diagnostic, outpatient | 1750 rub. |
| Consultation with a candidate of medical sciences | 2500 rub. |
| Professor consultation | 4300 rub. |
| Consultation (interpretation) with analyzes from third parties | 2250 rub. |
| Prescription of treatment regimen (for up to 1 month) | 1800 rub. |
| Study of external respiratory function (RPF) with drug tests | 1800 rub. |
| X-ray of the chest organs (survey) | 1900 rub. |
| X-ray of the chest organs in 2 projections | 2900 rub. |