Infectious disease specialist
Sinitsyn
Olga Valentinovna
33 years of experience
Highest qualification category of infectious disease doctor
Make an appointment
Rotavirus infection is a disease of viral origin that has an oral-fecal transmission mechanism. The peculiarity of the pathology is a combination of symptoms of damage to the digestive system with respiratory signs at the acute stage of the disease. The disease can be diagnosed in patients of any age, but more often in children under 2 years of age, in whom rotavirus accounts for up to 50% of all reported cases of intestinal infections.
What is rotavirus infection?
Translated from Latin, “rota” means “wheel”. Viruses received this name because they have a dense two-layer shell with a clear edge, which gives them the appearance of a wheel.
There are several types of rotaviruses that are similar in structure, so they are combined into one group.
Rotaviruses cause the development of acute intestinal infections. According to statistics, these viruses cause gastroenteritis (damage to the stomach and small intestine) in 25% of children under one year of age, in 60% - from 1 year to 3 years, in 40% - from 4 to 5-6 years.
Photo: www.pexels.com
The susceptibility of children under five to six years of age to rotaviruses is due to two factors:
- Reduced acidity of the stomach - a natural barrier to the penetration of bacteria, viruses and parasites into the gastrointestinal tract.
- Immaturity of the immune system in children of this age group.
Moreover, children under five or six years old often get this infection more than once. Moreover, the risk of a child getting sick is many times higher if he attends a kindergarten. Since there is contact with a larger number of children, among whom there may be a sick baby.
While older children and adults suffer from this disease much less frequently. Because a mature immune system gives a worthy rebuff to “strangers”. In addition, children who have been ill previously already have their own antibodies against certain types of rotaviruses, which protect them from infection.
Breastfed children are relatively protected from rotavirus infection. Because breast milk produces antibodies (immune system proteins) that prevent viruses from entering the body. However, babies are very inquisitive, and when getting acquainted with the world around them, they crawl and “test” objects. Therefore, their risk of encountering the virus is quite high.
Diagnostics
In order for a doctor to diagnose rotavirus infection, it is necessary to conduct a stool test for the presence of particles of the virus genome in it (this method is called “polymerase chain reaction”). In addition, various other tests are performed on blood, urine and stool. This allows you to detect infection earlier and prevent complications in the child.
Under domestic conditions, it is very difficult to diagnose this infection for an ill family member. Therefore, consultation with a doctor is necessary in any case, no matter how confident a person is in this diagnosis and methods of its treatment. There are a large number of infectious and non-infectious diseases that occur with symptoms similar to rotavirus infection.
For example, parents may mistake non-infectious diseases of the liver, stomach, intestines, and pancreas for a manifestation of rotavirus infection. With them, the sick child complains of nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain after certain (fatty, spicy, fried) foods, or indicates that all manifestations are disturbing only on one side of the body and began after severe emotional stress.
Similar signs of the disease can occur in case of poisoning with drugs or poisonous plants (more often it is children who suffer from this if they are left alone at home and can get to the home first aid kit, or walk unattended and can try different berries).
Read more about food poisoning in children in our article “Recommendations from a pediatrician for food poisoning in a child.”
Online consultation with pediatrician Olga Nikolaevna Tekutyeva
Registration online
During the consultation, you will be able to voice your problem, the doctor will clarify the situation, interpret the tests, answer your questions and give the necessary recommendations.
Rotavirus infection - “disease of dirty hands” or “intestinal flu”?
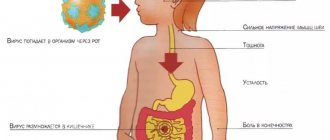
In fact, both names fully characterize the disease. Since viruses are mainly transmitted through unwashed children's hands, contaminated toys, food or water.
Once in the body, viruses rush into the small intestine, causing damage and rejection of its villi.
As a result, immature cells of the small intestine appear that do not produce enough digestive enzymes. Therefore, the digestion and absorption of nutrients is impaired. Thus, a cascade of complex processes is launched, leading to the release of water and salts into the intestinal lumen, which is manifested by loose stools and dehydration.
The source of rotavirus infection is a sick or clinically healthy carrier (without signs of disease). Isolation of the virus in feces begins on the second day of illness and then continues for two months even after all symptoms of the disease have disappeared.
What is rotavirus?
Rotavirus is a virus that infects the tissues of the oropharynx, stomach and intestines. It is also called stomach or intestinal flu. It is very viable and can survive in water and on the surface of vegetables and fruits for up to 8 weeks. Easily transmitted from person to person. This is the reason why rotavirus infections are in second place after classic acute respiratory viral infections.
There are many ways to become infected with rotavirus:
- From person to person, including from asymptomatic carriers;
- With water - while swimming in bodies of water of any size, or when drinking unsafe water;
- With food - most often the cause is poorly washed vegetables and fruits or foods prepared by an infected person;
- In case of contact with the surfaces of objects - if you traveled on public transport and then did not wash/disinfect your hands before eating.
- Immunity to rotavirus is very short-lived, so the likelihood of re-infection is high.
What is the danger of rotavirus infection for children?
In a short time, intoxication and rapid dehydration of the child’s body develop, which leads to a rather severe course of the disease. Therefore, the baby runs the risk of receiving not entirely pleasant procedures in the form of injections and intravenous drips.
The maximum incidence of rotaviruses occurs in winter and spring. However, it also occurs during the rest of the year, when it would seem that the “season” has come for other intestinal infections - for example, salmonellosis or dysentery.
Moreover, it is important to distinguish a bacterial infectious disease from a rotavirus infection. Because antibiotics must be used to fight bacteria. Whereas their use for viral infections is not only inappropriate, but also harmful, weakening the functioning of the baby’s already immature immune system.
Photo: www.pexels.com
Possible complications8
Rotavirus infection poses the greatest danger to young children from the first days of life to 3-5 years and pregnant women:
- At an early age, intestinal flu is a deadly disease - severe dehydration of the body can lead to death.
- Dehydration caused by rotavirus gastroenteritis during pregnancy leads to the risk of miscarriage.
Possible complications of rotavirus infection:
- Pancreatitis, gastritis, enlarged pancreas.
- Intestinal inflammation.
- Hemorrhagic gastroenteritis.
- Acute renal failure.
- Circulatory disorders.
- Gasser syndrome.
- Necrotizing enterocolitis.
To minimize the risk of the disease and prevent the development of complications, it is important to promptly diagnose rotavirus infection and begin adequate treatment.
How to recognize rotavirus infection?
- The incubation period for this disease is from one to two days - the time from the moment of infection until the appearance of the first signs of the disease.
- Sometimes the disease begins gradually with the development of the prodrome period - when the disease does not manifest itself with typical symptoms, but the baby has signs of slight malaise.
“At the same time, infants become capricious, refuse to eat, and develop a slight runny nose and cough. Older children complain of fatigue, poor appetite, rumbling and discomfort in the stomach, headache, chills, nasal congestion, sore throat, and slight cough. Only after 12-72 hours do typical signs of rotavirus infection develop.
Epidemiology
Rotavirus infection is a typical seasonal disease. According to statistics, in almost 93% of cases the disease develops in the winter months.
The infection often spreads in epidemic outbreaks - especially in kindergartens, hospitals, nursing homes and other institutions where children or adults with weakened immune systems are in close contact.
Children are most susceptible to infection. The share of rotavirus infection is 39.4% of all episodes of diarrhea under the age of 5 years.
The most common course of rotavirus infection in children
The disease begins acutely with a steady increase in body temperature to 38-39°C. Moreover, it is difficult to respond to antipyretic drugs. However, sometimes older children may experience severe chills at normal or subfebrile body temperature (37-38°C).
In addition, the baby develops symptoms of intoxication: severe weakness and lethargy, dizziness. In severe cases, fainting may occur. The child also has nasal congestion, runny nose and dry cough, headache, sore throat and stomach pain.
It would seem that such manifestations are characteristic of ARVI or a cold. However, along with symptoms indicating damage to the respiratory tract, the baby experiences vomiting and diarrhea . Moreover, loose stool with rotavirus infection has its own characteristics: it is copious, watery and foamy, yellow or yellow-green in color, and does not contain impurities (mucus, streaks of blood). In mild cases of the disease, the stool is mushy.
The child’s appetite also decreases, loud rumbling and pain appear in the upper abdomen, or the pain spreads throughout the entire abdomen.
Due to vomiting and loose stools, the child develops dehydration, the symptoms of which depend on the degree of fluid loss from the body:
- With moderate dehydration, the child develops thirst, dry mouth, and pale skin.
- With severe dehydration, the baby's condition is serious. These symptoms include hoarseness, the skin becomes dry, the amount of urine produced decreases, and convulsions may occur.
However, not all children develop a severe disease. In many ways, the severity of symptoms depends on the number of rotaviruses that have entered the body.
When to see a doctor?
So, you have noticed your child has a runny nose, cough and loose stools. What to do? Perhaps there is no need to tempt fate by believing that this is just a mild intestinal upset due to the fact that the baby ate a little more fruit the day before or had a slight cold.
Therefore, if the child’s condition allows, go to see a doctor. Whereas if your baby has a high body temperature, frequent diarrhea and vomiting, call an ambulance immediately.
Principles of treatment of rotavirus infection
1. Lost fluid is replenished
In case of moderate dehydration, the child is “hydrated” using solutions used orally.
In case of severe dehydration, fluid is administered intravenously in a hospital setting. Also, if the child is able to drink and is conscious, then he is simultaneously continued to be given oral solutions.
How to “desolder”?
It is better to use ready-made pharmaceutical preparations (for example, Regidron, Reosolan or Gidrovit) in powders for dissolution. Because they have an optimal ratio of salts and dextrose.
You can also make a sugar-salt solution at home. To do this, add one teaspoon of salt, half a teaspoon of soda and 8 teaspoons of granulated sugar to one liter of boiled warm water. Then mix everything thoroughly, cool to room temperature and “drink” the baby.
It is necessary to give the baby 1-2 teaspoons of liquid every 5-10 minutes. If you exceed the volume and frequency, you can provoke vomiting, which will lead to even greater loss of fluid from the body.
Moreover, the earlier “wetting” is started, the more favorable the outcome of the disease. Therefore, as soon as the first signs of the disease appear, offer your baby something to drink before going to the doctor.
2. Enzyme preparations are prescribed because the production and activity of digestive enzymes is impaired: Pancreatin, Creon and others.
3. It is advisable to adhere to a diet so as not to increase the fermentation processes in the intestines. To do this, it is recommended to refrain from feeding the child milk and fermented milk products, exclude fruits, and also limit foods rich in easily digestible carbohydrates (sweets, pasta made from first-grade flour, and others).
4 . Due to the fact that rotavirus infection disrupts the intestinal microflora, it is advisable to use bacterial biological preparations containing lactobacilli: Lactobacterin, Acylact and others.
5. An immunoglobulin complex preparation (ICP) for oral use , containing antibodies (proteins) against rotaviruses, salmonella, Escherichia and some other pathogens of intestinal infections, has proven itself well Moreover, its use significantly reduces the duration of diarrhea, and also reduces the signs of intoxication. Therefore, recovery occurs many times faster.
6. To accelerate the removal of viruses and toxins from the body, enterosorbents are used: Lactofiltrum, Enterosgel and others.
7. Body temperature is lowered using medications containing paracetamol or ibuprofen. They are used in the form of suppositories (if stool allows, this manipulation may cause it to become more frequent) or syrup (if vomiting is rare). In case of excessive vomiting and diarrhea, an antipyretic mixture is injected intramuscularly.
Methods for treating rotovirus
To treat rotavirus pathology, symptomatic and etiological therapy is prescribed. Patients are also prescribed a diet and auxiliary methods.
The main goal of treatment is to prevent dehydration. For this purpose, rehydration drugs are used for parenteral and oral administration. Such drugs prevent large fluid loss, improve well-being and relieve intoxication syndrome. Representatives are: Regidron, Acesol, Kvartasol, Refortan.
To remove pathogenic pathogens from the body, sorbents are prescribed. They accelerate the restoration of the mucous membrane, suppress pain and flatulence. Activated carbon, Polysorb, Enterosgel, Karbolen are prescribed.
Antiviral drugs based on interferon are indicated as etiotropic treatment.
To improve the normal intestinal microflora, probiotics are prescribed - Acipol, Linnex, Enterol, Bifiform.
Additionally, patients with rotavirus pathology are prescribed painkillers, antiemetics and antipyretics.
Prevention is everything!
There is a misconception that if rotaviruses are transmitted through contaminated objects, then it is enough to observe the rules of personal hygiene to defeat them. This is partly true, but in the case of young children the rule does not work. Because the virus is highly contagious, it is also less affected by common hand sanitizers and soaps. Only solutions of alcohol, iodine and chlorine are effective against rotaviruses.
It is also generally accepted that it is enough to get sick once to acquire immunity for life. This idea is not entirely correct, since there are several types of rotaviruses. Therefore, there is a risk that each time the body encounters a different type of virus from the same group.
Today, a vaccine against rotaviruses has been developed - the live Rotatek vaccine for oral administration. It protects against the five most common types of rotaviruses in Russia. Immunity after vaccination lasts about five years.
What is the danger of infection and how to prevent it
The symptoms of rotavirus infection are difficult to tolerate even by adults. If an intestinal infection has settled in the baby’s body, parents should be prepared that the child may have to be admitted to a hospital. Indications for calling emergency medical help are the following:
- increased dehydration, despite the measures taken;
- lack of urination for 3 - 4 hours;
- persistent diarrhea;
- exhausted state of the child.
One of the ways to protect your baby from the dangerous effects of rotaviruses on the body is the use of the live preventive vaccine RotaTek. Vaccination consists of three oral doses of the drug. The child should receive the first dose between 6 and 12 months of age. The recommended interval between drug administration is at least a month.
Parents' attentive attitude towards their baby will help prevent dangerous symptoms of a disease called “intestinal flu”. Mom and dad should carefully choose the foods that the child eats, protect him from communicating with sick peers and teach him to maintain personal hygiene.
Rotavirus and other intestinal infections: how to distinguish?
Children are often susceptible to infection with salmonella and dysentery bacillus.
For dysentery
The disease begins acutely with an increase in body temperature. Then liquid, mushy stool appears. Its frequency is about 10 times a day, but may be more often depending on the severity of the disease.
However, soon its volume decreases, it becomes scanty, a large amount of mucus appears in it, followed by streaks of blood. It is noteworthy that during the act of defecation (passing stool), nagging pain (tenesmus) occurs in the rectal area, sometimes quite pronounced.
Forms of the disease
Doctors divided the disease into 3 forms according to severity:
- light;
- moderate severity;
- heavy.
The mild form is characterized by a slight deterioration in general condition, diarrhea up to 5 times a day. On the fourth or fifth day of the disease, the person recovers.
Next comes a moderate rotavirus infection. How many days does the body fight viruses? Over the course of a week, frequent bowel movements (up to 16 times a day), vomiting, weakness, fever, decreased blood pressure, and low pulse have been a concern.
A severe form of the disease occurs with severe intoxication, the patient suffers from repeated vomiting, defecation up to 20 times a day, with a large number of watery stools. Due to dehydration, kidney and heart failure develop. How long does rotavirus infection last with this variant of the disease? Due to the addition of bacterial flora, the disease has to be treated a little longer - up to 10 days.
If therapy is started in a timely manner, the prognosis is favorable. The body’s defenses actively fight against rotavirus infection, and in most cases this fight ends in the defeat of the “strangers”.
Recovery of the body after rotavirus infection is accompanied by weakness, indigestion, fatigue and takes 1-2 weeks.
Be vigilant - past rotavirus infection does not exclude the possibility of re-infection. Only partial immunity to the virus remains!
This is interesting
Sick animals do not pose a danger to humans, but the “king of nature” may well cause illness in his pet.