What is rotavirus?
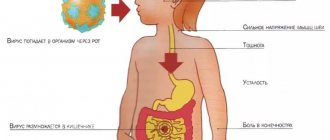
Rotavirus is a virus that infects the tissues of the oropharynx, stomach and intestines. It is also called stomach or intestinal flu. It is very viable and can survive in water and on the surface of vegetables and fruits for up to 8 weeks. Easily transmitted from person to person. This is the reason why rotavirus infections are in second place after classic acute respiratory viral infections.
There are many ways to become infected with rotavirus:
- From person to person, including from asymptomatic carriers;
- With water - while swimming in bodies of water of any size, or when drinking unsafe water;
- With food - most often the cause is poorly washed vegetables and fruits or foods prepared by an infected person;
- In case of contact with the surfaces of objects - if you traveled on public transport and then did not wash/disinfect your hands before eating.
- Immunity to rotavirus is very short-lived, so the likelihood of re-infection is high.
First aid for rotavirus infection
Regardless of whether this disease has developed in a child or an adult, care must be taken to provide timely first aid, which includes a set of such measures:
- The sick person should be in a horizontal position or in a sitting position.
- If the body temperature is more than 38 degrees, it is necessary to use antipyretics. Since rotavirus causes frequent and profuse vomiting, antipyretic drugs are best used in the form of rectal suppositories.
- To treat diarrhea, normalize water-salt balance and prevent dehydration, after each episode of vomiting or defecation, a sick person needs to drink at least 1 glass of Regidron solution.
- To combat concomitant digestive disorders and recover from rotavirus infection, it is necessary to take one of the sorbents (activated carbon, Polysorb or Enterosgel), Smecta or analogues of this drug. Also, taking enzymatic preparations (Mezim, Pancreatin) and prebiotics is indicated.
The diet after rotavirus infection excludes the consumption of dairy and fermented milk ingredients, as well as foods containing large amounts of carbohydrates.
Symptoms of rotavirus
The disease manifests itself 2–3 days after infection. Typical symptoms include:
- Pain in the stomach and intestines, rumbling in the abdomen
- Nausea and vomiting (especially common on the first day of illness and in severe cases of the disease)
- Diarrhea (it can last 3–5 days, and repeat every hour or a little less often up to 15 times a day)
- Constant urge to defecate
- Heaviness in the stomach and loss of appetite
- General weakness
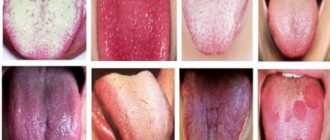
- White coating on the tongue and swelling of the larynx
- Increase in temperature to 37–37.5 * C (appear more often with severe manifestations of the disease)
- The infection may be accompanied by damage to the upper respiratory tract - rhinitis, inflammation of the nasopharynx and tonsils.
How to treat rotavirus
No specific medications have been developed for rotavirus infection, so there is no point in running to the pharmacy for a magic pill. The most important treatment methods:
- Drink plenty of fluids. It is important to drink a lot of water - pure and mineral (potassium-sodium) - throughout the day. You can use Regidron to reduce the risk of dehydration.
- A gentle diet. In the first couple of days, it is recommended to refuse food, then include in the diet boiled rice and rice “broth”, mashed potatoes with water, crackers and dryers, boiled soft white meat. During treatment, you should exclude all foods that cause fermentation from your diet - berries, vegetables, fruits, dairy products, sweets and baked goods.
- Adsorbent preparations - activated carbon, polysorb, enterosgel - and multienzyme preparations to improve the absorption of nutrients from food.
Under no circumstances should you take antibiotics! They do not have any effect on the virus, but at the same time they destroy the natural intestinal flora, which protects our immunity.
In most cases, a person recovers on his own without medical intervention if he follows the recommendations described above. But with a clear decrease in the body’s immune functions, complications are possible - bacterial damage to the intestines, damage to the nervous system, dehydration.
An increase in temperature to 38 * C or higher, uncontrollable vomiting and diarrhea, a serious loss of strength is a reason to urgently consult a doctor. If the condition does not improve on the third day after the onset of the disease, medical intervention is required. In some cases, the doctor may insist on hospitalization of the patient.
Rotavirus intestinal infection in adults: symptoms, treatment
Rotavirus infection is a disease of viral origin that affects the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract and causes inflammation. The danger of infection lies in the fact that in the absence of adequate medical care, severe dehydration of the body and the development of complications in all organs and systems are possible. Rotavirus infection in adults is not as severe as in young children, but it also poses a threat to health and life.
Causes and risk group
Rotovirus infection or viral gastroenteritis is a type of intestinal infection, the development of which is provoked by viruses of the Rotavirus genus from the Reovirus family of types A, B and C. In adults, rotavirus infection in most cases is caused by type A virus. There are several risk factors, the presence of which increases the risk get sick, these include:
- unfavorable social and living conditions;
- unbalanced diet, eating low quality foods;
- severe chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- immunodeficiency states;
- weak immunity due to constant colds, long-term treatment with antibiotics or chemotherapy drugs.
Routes of transmission
The main route of transmission of rotavirus infection is fecal-oral, that is, through dirty hands. The infection can also enter the body through the use of household items of a sick person or someone who has recently recovered from illness, or through the consumption of raw water or poor-quality food.
The causative agent of rotavirus infection is quite stable in the external environment; for example, in water it can remain viable for up to 2-3 weeks. The virus is highly contagious (infectious) and spreads quickly in confined spaces - this means that if one family member becomes ill, the infection is likely to be transmitted to everyone. As a rule, outbreaks of rotavirus infection occur in the autumn and winter periods, as a result of which it is also called intestinal flu.
What happens in the body when an infection occurs?
When pathogens enter the gastrointestinal tract, they penetrate the mucous membrane of the small intestine. By multiplying, rotavirus disrupts protein synthesis, the absorption capacity of cells and the evacuation function of digested food. As soon as all the vital resources of the intestinal cell are exhausted, the infected cell dies, releasing a huge amount of toxins that are absorbed into the blood and disrupt the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. All this is accompanied by the development of severe enzymatic deficiency and signs of gastroenteritis - an inflammatory process of all parts of the digestive tract.
Under the influence of toxic substances, the patient's process of water absorption in the intestines is disrupted, resulting in diarrhea. The accumulation of toxins in the blood provokes repeated vomiting, which significantly increases the risk of developing fluid and electrolyte imbalances and dehydration. If the patient is not provided with adequate medical care and rehydration is not started, then soon, due to diarrhea and vomiting, the volume of circulating fluid in the body decreases, signs of dehydration appear and hypovolemic shock develops.
Symptoms of rotavirus infection in adults
From the moment the virus enters the body until the first clinical signs of infection appear, 1 to 3 days pass. Rotovirus infection in adults, as a rule, occurs as food poisoning and is characterized by a number of symptoms:
- the appearance of pain in the epigastric region;
- nausea;
- excessive salivation;
- weakness, chills;
- dizziness;
- tachycardia;
- hand tremors;
- repeated vomiting, which brings relief only for a while;
- diarrhea up to 10 times a day;
- cutting pain in the abdomen.
Such signs may persist for 3-7 days. After vomiting and diarrhea stop, the patient will continue to experience weakness, lethargy, and poor appetite for several days (up to a week).
Rotovirus infection is insidious in that after the illness the patient does not develop immunity, that is, if he encounters the pathogen again, infection will occur again.
Possible complications
The main and life-threatening complication of rotovirus in adults is dehydration, which occurs as a result of the loss of large amounts of water and salts during vomiting and diarrhea and is characterized by the following symptoms:
- dry mouth, increased thirst;
- headache;
- dry skin and mucous membranes;
- reduction, and then complete absence of urination;
- tachycardia, shortness of breath;
- the appearance of acetone odor from the mouth, which is due to the accumulation of ketone bodies;
- drowsiness, weakness, lethargy;
- sunken eyes in severe cases.
Important! If the listed signs of dehydration appear, the patient should be taken to the hospital, where he will be given rehydration therapy with intravenous drips.
Treatment of rotavirus infection in adults
For a favorable outcome of the disease, the patient is prescribed symptomatic treatment, that is, aimed at combating the clinical signs of rotavirus and eliminating its consequences. The standard treatment regimen includes:
- oral rehydration;
- enterosorbents;
- diet.
In severe cases and when signs of dehydration appear, the patient is given IV drips, which help replenish fluid in the body and restore the balance of mineral salts in the blood.
Dietary nutrition for rotavirus infection in adults
For the first 2 days from the onset of the development of rapid clinical symptoms of rotavirus, the patient cannot eat anything, but, as a rule, he already has no appetite due to constant nausea and vomiting. Particular attention is paid to the drinking regime - saline solutions, compote of dried fruits, apples, uzvar, raisin decoction, sweet tea.
On the 3rd day, when vomiting and diarrhea stop, the patient can prepare boiled rice porridge without oil in water or vegetable soup with rice cereal. Portions should be small, it is better to eat often and very little, so as not to provoke vomiting again. As soon as the stool improves, the diet is gradually expanded, adding mashed potatoes in water without oil, boiled grated vegetables, fruit puree, biscuits, poultry meat without skin and fat. Jelly and berry decoctions, white bread crackers, bagels, and sweet crackers with raisins are allowed.
Exclude from the diet:
- milk and all dairy products (sour cream, cottage cheese, kefir, fermented baked milk, cream, cheese and others) - this rule should be followed for at least 1 month after rotavirus infection;
- pork, fatty meat, offal;
- fatty fish (mackerel, herring, salmon) and caviar;
- fresh vegetables and fruits;
- smoked meats;
- sausages;
- pasta;
- spices, vinegar;
- bakery products and pastries;
- candies, shortbread cookies, sweets.
All dishes are served to the patient boiled, stewed or baked without crust. This table should be followed for at least 1 month in order to minimize the load on the inflamed intestines.
If a strict diet is not followed or ignored, the patient develops enzymatic deficiency, and the symptoms of rotavirus resume - diarrhea, vomiting, total inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract.
Methods for preventing rotavirus infection
There is no specific prevention of rotavirus (vaccines), so absolutely everyone can get sick, especially those at risk. To reduce the risk of morbidity and prevent the development of rotavirus infection, follow simple rules:
- always wash your hands with soap after using the toilet and before eating;
- vegetables and fruits must be washed under running water before consumption;
- do not consume products of questionable quality;
- Do not drink raw water from unknown sources.
If someone in the family is sick with rotavirus infection, then the patient should have separate dishes, towels, bed linen and household items, which should be soaked daily in disinfectant solutions and thoroughly washed with hot water or boiled.