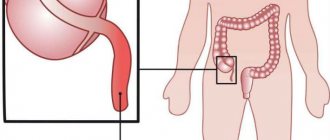
Prevention
A healthy lifestyle is the best prevention
Preventive recommendations are very banal. They mean:
- compliance with the norms of rational nutrition and physical activity;
- rejection of bad habits;
- timely treatment of chronic diseases.
If the pathology has already developed, following the doctor’s recommendations for treatment and diet, avoiding heavy physical activity and psycho-emotional stress will help maintain it in a state of remission.
Kinds
There are several options for classifying pathology, depending on the type of development it is:
- temporary - functional;
- constant - persistent, fixed bends.
The permanent form of kinks of the gallbladder is more common. The main classification, which allows diagnosing pathology and selecting treatment, is associated with the location of the inflection. Pathology can affect:
- bending of the body;
- necks;
- bottom;
- duct between the bladder and the liver.
An inflection in the body and bottom of the gallbladder is less common; damage to the neck of the organ is more often diagnosed. At the same time, the size of the cervix changes, so the pathology is easy to diagnose by ultrasound. A gallbladder with a bend in the body quickly loses its functionality, the outflow of bile is disrupted, so this type of pathology is considered the most dangerous.
Depending on the shape of the bend of the gallbladder, the degree of development of the pathology is determined. The organ can be bent into the shape of an arc, an hourglass, or a hook. There is also an S-shaped or double bend, which results in double torsion of the organ. Usually one bend is diagnosed, less often two; more is extremely rare.
Fact. An S-shaped bend is often found among the congenital form of the pathology.
Pathogenesis
Several factors play a role in the development of congenital anomalies:
- Genetic.
- Infectious in the antenatal and postnatal period.
Most often, constrictions and kinks are congenital in nature and this is associated with a violation of ontogenesis. The formation of the duodenum, ducts and bladder, and liver occurs in the fifth week of pregnancy. The influence of various unfavorable factors, many of which are unknown, disrupts the formation processes and causes the development of birth defects. A distinctive feature of congenital bladder defects is their uniformity in different patients. At the same time, constitutional features in patients are also revealed - signs of connective tissue dysplasia , which include: asthenic constitution, deformities of the spine and chest, mitral valve prolapse .
Acquired gallbladder deformities are most often associated with pericholecystitis . This is an inflammatory process of the outer serous membrane of the gallbladder. With this disease, neighboring organs are involved in the inflammatory process, adhesions and adhesions are formed, which deform the gallbladder and fix it to neighboring organs. The same adhesions that deform the bladder are formed after operations in the abdominal cavity. Acquired deformities have a varied and bizarre shape. The contours of the bubble become uneven, it moves poorly due to fixing adhesions and constrictions.
Diet
All patients diagnosed with “S-shaped gallbladder” are shown a special menu and drinking regimen. The diet for this pathology limits consumption:
- fried and fatty foods;
- smoked meats;
- hot and spicy sauces;
- rich broths;
- pickles;
- baking;
- sour cream;
- coffee;
- whole milk.
It is because of such dishes that patients experience bile stagnation, and the disease progresses faster. To maintain normal well-being, you need to eat small meals, but often.
At the same time, the diet should be complete, rich in beneficial microelements and vitamins. In addition, it is very important to drink more. It is advisable to create a menu based on the following dishes:
- Porridge cooked in water.
- Fish and seafood.
- Boiled or baked vegetables in the form of puree.
- Green teas.
- Meat and vegetable broths.
- Boiled and steamed lean meat.
- Sour compotes.
- Decoctions of herbs and berries.
- Fruits and vegetables (exceptions are garlic and onions).
List of sources
- Vakhrushev, Ya.M. Functional state of the liver and biliary tract in patients with gallbladder deformation // Hepatology. – 2003. – No. 3. – P. 4–6.
- Kuznetsov I.S., Slobozhanin M.I., Kiryanov N.A., Chernov A.I., Sapegin A.V. Anomalies of the biliary tract as hidden risk factors in biliary surgery // Clinical surgery. -1990.-No.9.-P.62.
- Baranskaya E. K., Yuryeva E. Yu., Lemina T. L., Ivashkin V. T. Diagnosis and possibilities of correction of functional pathology of the biliary tract // Clinical perspectives of gastroenterology, hepatology. 2007; 2:5–8.
- Ilchenko A. A. Diseases of the gallbladder and biliary tract. A guide for doctors. M.: MIA, 2011.
- Vishnevskaya V.V., Loranskaya I.D. Study of the motor function of the biliary system and gastroduodenal zone in pathology of the biliary tract // Rus. honey. magazine 2005; vol. 1–7.
Treatment
The doctor decides how to treat the patient based on the diagnostic results. The basis of therapy is medications, the action of which is aimed at normalizing the outflow of bile and eliminating inflammatory processes. In addition to this, physiotherapy is prescribed. Compliance with diet and other recommendations of the attending physician plays an important role.
Traditional medicine for deformation of the gallbladder is powerless; they cannot in any way affect its position. They can only be used in addition to drug treatment as a general tonic.
Medication
Medications are selected based on the degree of development of the pathology, the general condition of the patient and the individual characteristics of his body. Among choleretic drugs, the following are often prescribed:
- Gepabene. Normalizes the flow of bile, has an antispasmodic effect, eliminating pain due to inflammation. And Gepabene also helps normalize liver function.
- Allohol. The advantages of the drug are its low cost. Allochol is often prescribed for diseases of the gallbladder. The composition of the drug is unique, which includes bile of horned animals, extracts of nettle and garlic.
- Flamin. It has a natural base and is effective due to the presence of flavonoids and glycosides. The drug normalizes bile synthesis and has antispasmodic and analgesic effects.
- Hofitol. A popular choleretic drug, which includes artichoke extract. It has a hepaprotective effect, eliminates discomfort and pain, reducing the inflammatory process.
Doctors often prescribe herbal remedies in addition to medications, which usually require long-term use.
And Odeston, Ursofalk, Tanacechol, Nicodin and other drugs belonging to the choleretic group can also be prescribed.
Tests and diagnostics
- Ultrasound diagnostics is the main and informative method of research for this disease. The deformity of the bladder may disappear when changing body position or protruding the abdomen. To study the function of the gallbladder, ultrasound is often performed in two stages - on an empty stomach and after a choleretic breakfast.
- If necessary, hepatobiliscintigraphy is performed. Hepatobiliscintigraphy is an X-ray radiological method for studying liver function (bile production and bile secretion) with the introduction of a radiopharmaceutical (isotope). The study is carried out in a gamma camera, where images are taken every 2-5 minutes. The study determines the level of deformation and evaluates the condition of the biliary tract.
- CT scan.
- General clinical tests and biochemical (liver tests).
Photo
The photo below shows different types of pathology, in which the bladder is twisted in different places. And it is also shown, using the example of torsion in the cervical area, what a healthy and changed organ looks like.