Pain in the right hypochondrium, causes and possible diseases
Pain in the right hypochondrium is a sign of many diseases, so even an experienced and qualified specialist cannot make an accurate diagnosis based only on this symptom.
Pain syndrome can be caused by completely harmless reasons, such as overeating or excessive physical activity. But more often, discomfort in the area of the right hypochondrium provokes an inflammatory process, acute and chronic diseases of the digestive, genitourinary system, internal organs (liver, kidneys), and biliary tract.
Why does the right hypochondrium hurt, in which cases is this symptom not dangerous, and in which cases does it require immediate medical attention? You will find answers to all questions in our material.
Pain under the right hypochondrium in healthy people
Pain in the right hypochondrium can be caused by a variety of reasons. In some situations, discomfort also appears in completely healthy people: in this case, we are talking about a variant of the physiological norm. However, often the problem lies in the development of pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract and other organs.
Physiological reasons why it hurts in the right hypochondrium:
- Pregnancy. In pregnant women in the third trimester, the uterus is enormously stretched and puts pressure on all the organs it comes into contact with, displacing the intestines, pressing on the stump and gall bladder. Therefore, for healthy pregnant women, stabbing or pressing pain in the right hypochondrium is not uncommon. In addition, progesterone, which maintains pregnancy in the later stages, expands the bile ducts and stimulates bile stagnation. And if you give physical activity to such a belly, then some discomfort can be felt with a high probability.
- Pain on exercise. Surely many have noticed how after intense physical activity there is pain in the right side. This occurs due to excessive stretching of the liver tissue, which, in turn, is caused by a sharp flow of blood to the organ. This happens especially often after a heavy meal. This condition does not pose any danger.
- Pain in women. At the end of the menstrual cycle, some women experience a sharp imbalance between low progesterone and high estrogens, which leads to spasm of the biliary tract and can also cause colic in the right hypochondrium. Taking hormonal contraceptives can worsen the course of premenstrual syndrome and increase the frequency of stabbing pain due to disruption of the passage of bile.
When is a symptom not dangerous?
Yes, this happens. For example, with low mobility, physical activity increases blood circulation in the vena cava. And as a result of the release of adrenaline, heat occurs in the right hypochondrium. But stopping the load stops the burning sensation. Also, when the body bends, the tissues are compressed by the ribs, which causes an unpleasant symptom. It is temporary and does not continue to bother you after changing the position of the body.
In women during PMS, estrogen is released and a fever appears on the right side. Sometimes the pain is severe, causing nausea and a bitter taste. This is due to spasm of the bile ducts. Any discomfort that occurs in the body is evidence that a person may have health problems. A burning sensation in the ribs is a symptom that should not be ignored. It is imperative to identify the cause of the occurrence and take all measures to eliminate it.
Pathological causes of pain under the right rib
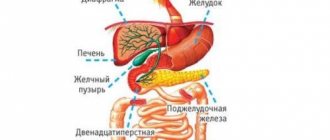
Anatomically, the upper right quadrant of the abdomen includes: liver, gall bladder, part of the diaphragm and small intestine, duodenum, right kidney, pancreas.
Diseases and injuries of these organs can intensify the occurrence of pain in the right side under the ribs:
- The most obvious cause of pain is liver disease. This includes hepatitis, hepatosis and cirrhosis of the liver, parasitic lesions.
- Impaired patency of the biliary tract (cholecystitis). A sharp, acute pain that suddenly began, especially at night, is formed when the patency of the biliary tract is impaired and in acute cholecystitis. If the tone of the gallbladder increases, its tendency to contract increases, and the frequency and strength of its contractions also increases. Such processes are accompanied by sharp and short-term pain and are often provoked by nervous tension and stress.
- Urolithiasis disease. The cause of pain in the right hypochondrium may be urolithiasis, in which pain from the right kidney is felt acutely, but not clearly and can be felt in the back of the lower back, lower abdomen, as well as under the left or right side of the lower ribs. Urolithiasis is manifested by the detection of stones in the kidneys, bladder and urinary tract. There is a sharp pain that intensifies with every movement.
- Renal colic. It occurs when kidney stones begin to move and their sharp edges touch internal organs. The pain becomes very severe when the person moves. The stones block the urinary tract, causing the pain to shift to the groin.
- Peptic ulcer disease. Characteristic pain in the right hypochondrium anteriorly accompanies gastric and duodenal ulcers. The nature of the pain and its intensity depends on many factors. Discomfort occurs after eating, on an empty stomach or after exercise. The pain syndrome is accompanied by heartburn, sour belching, vomiting, loss of strength, alternating diarrhea and constipation, and rapid heartbeat. Often, peptic ulcer disease occurs in a latent form; in advanced cases, there is a threat of internal bleeding and peritonitis, which poses a danger to the patient’s life and requires urgent surgical intervention.
- Biliary dyskinesia is a violation of the motor function of the organ. The main reasons for the development of the disease are stress, poor diet, and heavy physical activity. Usually, when examined for dyskinesia, the patient is diagnosed with diseases of the digestive system. The pathology occurs spontaneously, accompanied by heaviness, paroxysmal acute pain in the right side, nausea, stool upset (diarrhea or constipation), tachycardia, the appearance of a bitter taste in the mouth, and in rare cases, headache. Dyskinesia is accompanied by stagnation of bile in the gallbladder, which contributes to the formation of stones and the development of cholelithiasis.
- Pancreatitis. Throbbing pain indicates pancreatitis. The exact cause of inflammation of the pancreas has not been established. The pathology begins with throbbing, intense, girdling pain. If these symptoms occur, the patient requires immediate hospitalization and emergency surgical treatment. Pronounced pain in the right quadrant of the abdomen is observed during the transition of pancreatitis from the acute to the chronic stage and can be treated conservatively.
- Intercostal neuralgia. Pain in the hypochondrium is not always caused by pathology of the internal organs. Thus, pain in the rib area can occur due to skeletal diseases. Such a common disease as osteochondrosis occurs with degeneration of spinal cartilage. The altered cartilage puts pressure on the nerves, which leads to pain.
Diagnostics
The primary examination is carried out by a gastroenterologist or a highly specialized hepatologist. During the physical examination, bladder symptoms, liver size, signs of peritoneal irritation and local tension in the abdominal muscles are assessed. If necessary, a consultation with an infectious disease specialist, gynecologist, or oncologist surgeon is scheduled. The diagnostic plan includes:
- Ultrasound of the hepatobiliary zone.
An ultrasound examination visualizes the gallbladder, measures the thickness of its wall, and identifies stones in the cavity. To confirm the diagnosis of dyskinesia of the gallbladder, a test with a choleretic breakfast is performed. An examination of the liver is necessary to study the structure of the parenchyma and find individual hyperechoic foci. - ERCP.
The study is indicated to assess the condition of the bile and pancreatic ducts and duodenal mucosa. Cholangiopancreatography allows you to take samples of material from pathologically changed lesions to examine them under a microscope for signs of cellular atypia. - Duodenal sounding.
The method is used to determine the contractile function of the gallbladder. Then portions of bile are subjected to microscopic and bacteriological examination. Analysis of the biochemical composition of bile is necessary when diagnosing cholelithiasis. - X-ray methods.
CT scan of the abdominal cavity is a highly informative method that helps to detect benign and malignant tumors of the hepatobiliary zone and parasitic cysts. The structural and functional features of the liver can be studied by scintigraphy. - Additional methods.
To determine the degree of fibrosis, rapid and non-invasive elastography is performed. For unspecified forms of hepatitis and neoplasms, a biopsy of the liver tissue is performed, followed by histological analysis.
Of the laboratory methods, a biochemical blood test with liver tests, which looks at the level of bilirubin, cytolysis enzymes, cholesterol and alkaline phosphatase, is of diagnostic value. To diagnose parasitic diseases, feces are analyzed for helminth eggs. To exclude the viral nature of pain in the right hypochondrium, serological tests are done for hepatitis A, B, C.
Ultrasound of the hepatobiliary zone
Other reasons
Other diseases and pathologies, the symptoms of which may include painful sensations of various types in the area of the lower ribs on the right side of the body, are the following:
- From the nervous system: compression of the nerve endings that are located in the intercostal space (intercostal neuralgia), herpes zoster, characterized by acute pain, the appearance of rashes, itching;
- From the digestive system: gastritis, peptic ulcer, various inflammatory processes, intestinal obstruction, colitis, pancreatitis, spasms and pain simulating gynecological diseases, peritonitis, etc.;
- From the urinary system: pyelonephritis affecting predominantly the right kidney (otherwise the pain is localized on the left side, and not in the area of the lower ribs on the right), renal colic, stones;
- From the respiratory system: pneumonia (pneumonia) or bronchitis in acute or chronic course - cough provokes spasms of the respiratory system, which are felt as painful sensations in the right hypochondrium;
- inflammation of the uterine appendages, osteochondrosis, appendicitis, etc.
- From the liver: liver dystrophy, cirrhosis, abscess, hepatitis, hepatitis C and others, heart failure accompanied by stagnation of blood in the liver, and other chronic diseases and acute inflammatory processes.
Treatment
First of all, you should understand that the doctor will prescribe treatment and therapy for you individually, having found out the cause of the pain. Here we will give examples of the main therapy used in medical practice. If there is no indication for surgical intervention, then first of all, therapy is aimed at relieving spasms and the inflammatory process, and then depending on the cause of the disease.
Drugs used in therapy:
- Antispasmodics: “No-shpa”, “Baralgin” (in injections), “Spazgan” (tablets).
- Anti-inflammatory drugs: Nimesulide, Aspirin, Ibuprofen.
- Broad-spectrum antibiotics: Levofloxacin, Amoxicillin.
- Hepatoprotectors: “Essentiale”, “Karsil”.
- Medicine to improve the flow of bile: Allohol.
- Heart medications: Nitroglycerin, beta-blockers (bisoprolol, metoprolol)
Effective medications for pain relief
You can use antispasmodics to relieve and relieve pain, but you should understand that in case of acute pain you need to wait for an ambulance and find out the cause. Ketorol and Baralgin are considered effective means of relieving pain and spasms , especially for back pain. For stomach pain, " No-shpu" is given as an injection . You can take “No-shpu” and “Spazmalgon” in .
Let me explain about pain therapy for pain in the right hypochondrium. If the cause is a stomach disease, then No-shpa or Spazmalgon is used, i.e. drugs with an antispasmodic effect. Why them and not analgesics? The stomach begins to worry when there is a defect in the mucous membrane, i.e. in the presence of an ulcer or gastritis. And any analgesic or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (analgin, meloxicam, xefocam, etc.) has an extremely negative effect even on the intact gastric mucosa, not to mention the inflamed one. Therefore, taking even one such tablet for an ulcer can aggravate the situation and provoke gastric bleeding - a life-threatening condition. Therefore, if acute surgical pathology (appendicitis, for example) is excluded, but you do not know whether the pain comes from the stomach or not, then it is safer to take an antispasmodic drug than any other.
Victoria Druzhikina
Neurologist, Therapist
To determine how serious your situation is, use an online consultation with a doctor on our website in a paid or free mode.
The doctor will make a preliminary diagnosis and give recommendations for first aid and advise on further actions. Under no circumstances should you self-medicate or get carried away with painkillers, as they do not eliminate the true cause of spasm and pain.
Be healthy!
Useful articles on the topic: What can you take for stomach pain: a review of medications. What can pain under the left rib in front indicate?
This article has been verified by a current qualified physician, Victoria Druzhikina, and can be considered a reliable source of information for site users.
Bibliography
1. https://vmede.org/sait/?page=7&id=Xirurgiya_gosp_sind_abdulaev_2013&menu=Xirurgiya_gosp_sind_abdulaev_2013
Rate how useful the article was
4.3 49 people voted, average rating 4.3
Did you like the article? Save it to your wall so you don’t lose it!
Pain in the right hypochondrium behind
If the patient complains that there is pain in the back under the right shoulder blade, the causes of this phenomenon may be associated with injuries to the lower ribs, damage to the intercostal nerves. Pain appears from behind under the right shoulder blade from the back and with lesions of the right kidney and adrenal gland. The causes of back pain may also be associated with diseases of the inferior vena cava.
- Urolithiasis disease. Diseases of the right kidney and, first of all, urolithiasis can cause intense pain. A stone or sand that begins its journey from the renal pelvis scratches it, and then the ureter, so pain with renal colic will be not only in the projection of the lower ribs, but also in the lower back and lateral abdomen. The pain is paroxysmal and severe. It radiates to the thigh and genitals. When you tap the edge of your palm on the lower back, the pain intensifies and can radiate to the groin. In this case, traces of blood may appear in the urine. In some patients, renal colic is accompanied by vomiting.
- Pyelonephritis. The development of acute infectious inflammation of the kidney is accompanied by pain in the kidney area, intoxication, and fever. It also hurts when urinating, periodic false urges are noted, and swelling appears on the face.
- Necrosis of the renal papillae. It can result from oxygen starvation of the kidney tissue due to blockage of the vessels that feed it (infectious agents or diabetes mellitus). In this case, the pain is constant, combined with blood in the urine. The patient may die from septic shock.
- Kidney cancer. This condition may not appear for a long time. Mild pain and bleeding appear already in the last stages of the disease. Sometimes the tumor interferes with the flow of urine, and then there is acute pain. Pain in the hypochondrium also occurs with tumors of the right adrenal gland, provided that the tumor is large.
- Acute upper paranephritis. This is an inflammation of the fatty tissue at the top of the kidney due to infection from the tonsils, carious teeth or other foci of inflammation. First, there is a temperature of up to 38, moderate pain in the lower back on the affected side. After 2-3 days, the pain moves to the right hypochondrium and intensifies with a deep breath. Lower back pain increases with sudden straightening of the body and when walking.
- Intercostal neuralgia. The reason that a person’s right side feels tight and numb in the hypochondrium area may be intercostal neuralgia. In this state, sometimes there is a pulling from the back, the ribs hurt on both sides in front. With neuralgia, there is a strong tingling sensation in different areas, even to the point of limited mobility. The pain becomes stronger when bending or turning. Also, the cause of a sudden tingling sensation in the pit of the stomach or twitching on both sides can be myositis, when a person’s muscles are inflamed.
- Osteochondrosis of the lumbar region. It produces pain of varying intensity, which is accompanied by limited mobility, muscle tightness and tension symptoms. The pain can range from aching to shooting of varying degrees of intensity.
- Shingles. In this case, herpetic eruptions appear along the nerve in the form of bubbles with cloudy liquid, and the skin turns red. Itching, burning, and pain develop at the site of the lesion. This means that you need to see a dermatologist.
- Thrombosis of the vena cava. A rare variant of thrombosis of the inferior vena cava (when a blood clot comes from the iliac veins and clogs the main trunk of the vein) causes pain in the lower back (right hypochondrium from the back) and a clinical picture similar to the late stage of kidney tumors. If the liver segment is thrombosed, then intense pain will occur in the right hypochondrium in front and will radiate under the right shoulder blade. This will cause fluid accumulation in the abdominal cavity and jaundice.
Nature of pain
In addition to the above classification of spasms in the hypochondrium, you need to remember some nuances associated with the type of discomfort that arises. This indicator is often decisive for making the correct diagnosis.
Pressure and heaviness in the side
A similar symptom often accompanies the late stages of pregnancy, when the grown-up baby is already too cramped in the stomach and any movement of the arm or leg, active upheavals cause the woman significant discomfort.
Pressure under the ribs from the side may also occur due to the following conditions:
- Thoracic osteochondrosis, in which it is painful to move, breathe and move your arms.
- Pathologies of the liver, gall bladder, urinary system. Diseases can be suspected by the addition of vomiting and nausea to the pain. Patients with such diseases tend to lie down more, since any movement, including walking and just a strong sigh, provokes an increase in spasm.
Stitching pain
{banner_banstat5}
People often complain about it after a long run. To exclude the cause in the form of stretching of the liver capsule against the background of dysfunction of the diaphragm and low blood outflow, it is important for both women and men to plan the load only after a preliminary warm-up.
The following tips will help you avoid tingling:
- Inhalation is always done through the nose. It is important that it be deep.
- Exhale through the mouth and only smoothly.
- While running, breathe exclusively from the stomach.
Stitching in the side above the center of the peritoneum can also occur with right-sided pneumonia. Lung damage is accompanied by shortness of breath, dyspepsia, increased temperature and blue discoloration of the tissues that form the nasolabial triangle.
Video: What can sting in the right side under the ribs
Blunt pain
Smoothed but persistent unpleasant sensations are characteristic of a number of chronic pathologies:
- Cholecystitis. Increased spasm occurs after eating fatty foods. Additional signs are vomiting, bloating. As the disease progresses, ulcers form on the thickened walls of the gallbladder, which scar over time.
- Pancreatitis. As a result of the replacement of the correct anatomical structure with connective tissue, the production of enzymes and the hormone insulin is disrupted. A dull pain may be present on both the right and left under the ribs. It is complemented by signs of dyspepsia: belching, bloating, diarrhea, nausea, heartburn, vomiting.
- Pyelonephritis. With inflammation in the pyelocaliceal system, the spasm may spread to the opposite side and intensify during physical activity. Additional signs: unreasonable increase in temperature and chills, increased urine flow, increased blood pressure, migraines, chronic fatigue.
- Hepatitis. The causes of discomfort that does not go away over time are improper treatment and lack of healing effect. The disease is accompanied by decreased appetite, regular nausea, flatulence, intolerance to fatty foods and alcohol. When palpating the hypochondrium and pressing on the liver, a characteristic aching spasm occurs.
- Duodenitis. The pain on the right side is accompanied by heartburn, poor appetite, regular diarrhea, and vomiting with bile.
If there is pain in the right hypochondrium in front
Tingling or sharp pain in the right side occurs due to diseases of the organs that are adjacent to this area. Some conditions are accompanied by pain from the back, sometimes it radiates to the leg, shoulder blade, kidney, etc. There may also be pain in the lungs when taking a deep breath. With some diagnoses, pain may be periodic, appearing when walking or coughing. With others, unpleasant sensations bother you constantly.
- Hepatitis. Viral, alcoholic or toxic hepatitis gives a picture of intoxication (weakness, lethargy, loss of ability to work) and dyspepsia (nausea, loss of appetite, vomiting). At the height of the disease, jaundice occurs with a lemon tint to the skin and whites of the eyes. During the same period, urine becomes the color of beer, and feces - the color of clay due to disturbances in the exchange of bile pigments.
- Cirrhosis of the liver. In patients with cirrhosis, liver cell death and changes in its structure are observed. People with this diagnosis have pain in the right side at the waist level, sometimes the pain is felt in the back. With cirrhosis, a person may notice pain in the right side below the ribs, already at the very beginning of the disease. At the same time, the burning sensation in the right side is persistent. In the later stages of cirrhosis, the liver becomes smaller, its performance decreases, the patient develops hepatic coma, and death is likely.
- Echinococcosis. These are cysts with liquid contents, which are caused by the worm Echinococcus. Cysts are most often located in the right lobe of the liver and, as they grow, they compress the capillaries and intrahepatic bile ducts, causing severe heaviness in the hypochondrium and uneven enlargement of the liver. If the cyst festeres, a cavity filled with pus develops - a liver abscess. In this case, the pain intensifies, the body temperature rises and inflammation of the peritoneum or even blood poisoning may develop.
- Congestive heart failure. Why discomfort in the right hypochondrium in this case is bothersome is explained by the patient’s condition. Initially, his blood circulation deteriorates, as a result, the liver enlarges, and fluid accumulates in the abdominal cavity. A nagging pain appears in the right side, a feeling of heaviness. A nagging pain is disturbing as the disease progresses. With abdominal myocardial infarction, the patient experiences severe, burning pain in the lower right hypochondrium. Sometimes the patient complains that there is pressure in the side. But in some cases, the onset of pain is sometimes very sharp, similar to the blow of a knife; the pain appears in the shoulder blade and sternum. As a rule, this happens with the development of infarctions of the posterior wall of the heart muscle. Sometimes it seems to the patient that this painful sensation manifests itself in waves: periodically it decreases and intensifies. In this case, pallor, heart rate disturbances, and a drop in pressure may be noted.
- Gallbladder diseases. They give the greatest percentage of intense and sharp (cutting or stabbing pains), which are characteristic of acute inflammation. In this case, a displaced stone that closes the lumen of the bladder neck or bile duct or bacterial flora may be to blame for the inflammation. Pain during acute inflammation occurs at the point between the rectus abdominis muscle on the right and the costal arch. They are cramping, strong, and radiate to the right shoulder or left hypochondrium. There may be a bitter taste in the mouth, belching of air, nausea and vomiting of bile. Sometimes the body temperature rises. For calculous cholecystitis, the development of obstructive jaundice with a yellow-green tint to the skin and mucous membranes is typical.
What happens in the hypochondrium during breathing?
Everything inside the human body is interconnected. The breathing process involves not only the lungs, but also other organs . At the upper border of the hypochondrium is the diaphragm, which takes an active part in breathing. Thanks to it, negative pressure is created inside the pleural cavity, due to which the lung tissue is greatly stretched and air enters it during inhalation.
How does a person breathe?
The muscles located between the ribs are also involved in the act of breathing. When they contract, the ribs move upward and the chest increases in volume. At this moment, the diaphragm descends towards the peritoneum and becomes flat.
Muscles of inhalation and muscles of exhalation
On a note! There are two types of breathing - chest and abdominal. The first is typical for women and occurs due to the muscles between the ribs; abdominal breathing is more often observed in men and its main participant is the diaphragm.
During movement, the diaphragm pulls along with it the internal organs located in the abdominal cavity. For example, the liver is connected to it by a special ligament. In turn, the gallbladder is attached to the liver. The intestinal organs are also involved in movement.
Respiratory system
Pain after eating
Eating accelerates the secretion and movement of bile, increases blood flow to the liver and stimulates intestinal peristalsis. Therefore, food provokes pain in pathologies of the liver, gall bladder, and intestines.
In this case, the nature of the pain can be different: nausea and dull pain are characteristic of cholecystitis, sharp pain of a spastic nature accompanies colitis and intestinal dysbiosis, stabbing pain accompanies biliary dyskinesia or cholelithiasis.
1.General information
From the school course of human anatomy and physiology, we remember how important the pain mechanism, formed and fine-tuned during evolution, is for humans. Pain is an alarming electrochemical signal to the brain; it is a neuronal lightning telegram about dysfunction or damage to an organ. If humanity didn’t have this alarm system, our species would have died out a long time ago, and in most cases without knowing what kind of blockages, inflammations, perforations and injuries.
However, a person in pain has no time for theory and, by and large, no time for evolution; The main thing for him is that he stops getting sick. It is also obvious that pain is different, and in some cases this “panic button” simply needs to be turned off artificially - with analgesics, anesthetics, or even life-saving general anesthesia. However, we cannot brush off pain in any case, especially if it hurts “somewhere inside” and we don’t really know why. Areas of particular importance, the pain in which is never trivial or unimportant, include the so-called. hypochondrium - areas above the border between the abdominal cavity and the ribs, which serve as a natural shield for life-sustaining internal organs.
On the right side, as we know from the same school textbooks, we have the liver, gall bladder, one of the kidneys with the adrenal gland and one lung, half of the diaphragm, as well as some of the intestinal loops. And all this can hurt, and in completely different ways and under the influence of a huge variety of possible reasons.
A must read! Help with treatment and hospitalization!
After load
Unpleasant sensations in the form of nagging or stabbing pain occur after physical exertion in people with hepatitis, cirrhosis, or congestive liver. After shaking or physical exertion, an attack of calculous cholecystitis may occur. Also, periodic pain during exercise appears in patients with myositis, intercostal neuralgia, osteochondrosis, rib fractures, and vena cava thrombosis.
Pain in acute appendicitis
The appendix is a lymphoid organ that takes part in the immune defense of the digestive system. It is located in the area of the right ilium, but its position is quite variable. This causes difficulties in diagnosing inflammation of the appendix. Appendicitis has its own distinct stages of development, which only a surgeon can diagnose.
Signs of appendicitis are:
- Diffuse pain in the navel and stomach;
- The pain is localized in the right half of the abdomen for three hours;
- Reducing pain when lying on the right side;
- Increased pain when walking and lying on the left side;
- Against the background of pain, general health worsens, body temperature rises, vomiting and diarrhea occur.
In such cases, emergency surgical treatment is performed in a surgical hospital.
Which doctor should I contact?
It is impossible to independently determine the cause of pain in the right hypochondrium. You should definitely visit a therapist. After the examination, the doctor will prescribe initial tests and examinations, after which he will decide which specialist the patient should be referred to.
When visiting a doctor, you will need to answer the doctor’s questions and indicate the location of the pain. In this case, you should mark a specific point or focus on the fact that the area of pain is blurred. It is advisable to remember when pain first appeared in the right hypochondrium. It is also important to report whether the onset of pain was sudden or gradual. An important role in the diagnosis of diseases is also played by whether the pain stops periodically or whether it is constantly present. You will also need to describe the nature of the pain. You will also need to discuss other important points with the doctor, namely:
- How much has your appetite worsened?
- Has there been a change in weight?
- Do you have constipation or diarrhea?
- Has the color of your urine changed?
You will need to talk about your lifestyle. As a rule, doctors will be interested in such issues as smoking and drinking alcohol, as well as uncontrolled use of medications. A general blood test is mandatory to make an initial diagnosis. Certain indicators in it may indicate the presence of an inflammatory process. A urine test is also performed, which excludes or confirms a urinary tract infection, in particular the development of pyelonephritis.
Pain differentiation
Depending on the pain felt by the patient who consults a doctor with this problem, it is possible to identify which organ disease is associated with certain painful sensations.
So, pain in the right hypochondrium, what could it be:
- Burning pain in the right hypochondrium is often the cause of acute cholecystitis.
- Acute pain in the right hypochondrium is most likely associated with diseases of the gallbladder.
- Severe pain in the right hypochondrium is usually felt by patients suffering from hepatitis.
- Dull pain may be a consequence of inflammatory processes in the gallbladder.
- Aching or pressing pain can be classified as symptoms that occur with biliary dyskinesia.
- Nagging pain is characteristic of chronic hepatitis.
- The bursting type of pain can be caused by chronic diseases of the pancreas.
- Throbbing pain is typical for patients diagnosed with pancreatitis.
- Stitching pain is observed in patients with problems with the right kidney.
Also, pain in the right hypochondrium can only occur in the evening or at night. As medical practice shows, constant night pain in this area is often the first sign of a duodenal ulcer.
Conditions for pain
The causes of pain in the right hypochondrium consist of the structure of the walls of the internal organs and the characteristics of their innervation. For the diseased organ, the following conditions must be met:
- in dense parenchymal organs - swelling, increase in size and stretching or destruction of the capsule that has pain receptors;
- for the intestine and gallbladder - spasm or stretching of the muscle layer, inflammation in the submucosa (the mucosa itself has no pain points), violation of the integrity of the wall.
An equally important feature of the abdominal viscera is the general innervation from some parts of the spinal cord, so pain under the right lower ribs may reflect local pathology in the stomach, pancreas, duodenum, and inferior vena cava.
How to relieve pain?
In order to relieve pain, you can drink no-spa, but you should not abuse the painkiller - this will not make it possible to correctly determine the cause of the discomfort.
It is necessary to immediately call an ambulance if the patient exhibits the following symptoms:
- incessant vomiting;
- fainting and presyncope;
- delay or complete inability to urinate;
- the pain is acute, unbearable, lasts more than a few minutes (not attacks - spasms, characterized by cramping pain, but constant significant discomfort);
- uterine bleeding;
- blood in vomit, feces, urine;
- significant increase in body temperature (above 38.5°C);
- diarrhea or constipation lasting several days.
If there is pain in the right hypochondrium and the causes have been clarified, the question remains of what to do. The main thing that the patient should know is that under no circumstances should you self-medicate. Taking antispasmodics, analgesics and similar drugs significantly blurs the picture and complicates the doctor’s work.
First aid recipes widely circulated on the Internet are also ineffective, but also dangerous. Under no circumstances should you take alcohol tinctures, place heating pads on your stomach, etc.: for unknown reasons, this can cause death. The main thing the patient should do is consult a doctor. In this case, it is not necessary to go to the local police officer. In case of intense pain, you should contact an ambulance.
Treatment is almost always medicinal and includes taking analgesics, antispasmodics, diuretics, choleretic drugs, etc. These medications are prescribed exclusively by a doctor. Surgical assistance is required in extreme, urgent cases, such as intestinal obstruction, perforated ulcers, etc. In all other cases, conservative therapy is indicated.
Features of diseases of internal organs
Pain, the source of which is diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, liver and other organs that ensure the digestion process, can be differentiated by several associated characteristics:
- Dyspeptic disorders
. Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and pancreas are accompanied by nausea, vomiting with bile, increased gas formation, constipation and diarrhea. - Bleeding organs
. Bleeding may occur in the affected areas, which is expressed by rectal or oral discharge of blood clots, as well as traces of blood in vomit or bowel movements. - Allergic reactions
. Due to the accumulation of toxins or lack of nutrients absorbed in the stomach or intestines, rashes (dermatitis) form on the skin.
As accompanying symptoms, severe weakness, dizziness, drop in blood pressure, fatigue, rapid heartbeat, and elevated temperature are observed.
Prevention
Preventive measures to prevent pain in the right hypochondrium boil down to following the following recommendations:
- taking medications only as prescribed by a doctor;
- avoidance of stressful situations;
- compliance with personal hygiene rules;
- healthy and active lifestyle;
- rejection of bad habits;
- proper and nutritious nutrition;
- use of barrier contraceptives during sexual intercourse, refusal of casual relationships.
Regular medical examination (once a year) will allow you to prevent or promptly detect any health problems and receive the necessary treatment.
Associated symptoms
Pain in the right hypochondrium is rarely the only symptom of a health disorder. As a rule, there are others, which, together, form the clinical picture of the pathology. These include:
- digestive disorders (nausea, vomiting and loose stools);
- signs of intoxication (hyperthermia, hyperhidrosis, decreased general tone and other manifestations);
- drowsiness and dizziness;
- changes in blood pressure;
- clouding of consciousness and fainting;
- pain and discomfort in the heart area, as well as changes in pulse;
- swelling and bleeding of mucous membranes;
- yellowing of the skin and sclera;
- painful urination;
- body hyperemia and rashes;
- copious discharge from the external genitalia;
- respiratory failure, cough and other symptoms.