Unpleasant sensations are caused in women by itching and burning in the vagina, and she experiences them more than once throughout her life. The nature of this ailment can be different: from a common cold to serious infectious diseases.
If you ignore the itching and pain, thinking that everything will go away on its own, then you can end up with extensive pustules appearing around scratches and wounds, the tissues will become inflamed, and you will have to contact a gynecologist for a much more serious problem.
In this situation, you should not rely on traditional methods, because self-medication can achieve the opposite effect. SM-Clinic uses modern treatment methods, thanks to which many women have completely gotten rid of vaginal itching.
Itching in the female genital area does not necessarily mean some kind of infectious disease of the genital organs, and can occur as a manifestation of serious disorders in the body. Only after undergoing a series of thorough studies at the SM-Clinic in Moscow can an accurate diagnosis be established.
Manifestations such as cheesy discharge, or yellowish-green discharge that has an unpleasant odor, constant pain in the lower abdomen, dry mucous membranes should alert a woman, because the cause of these symptoms may be thrush, an allergic reaction to a particular product, a sexually transmitted disease or a banal cold.
Symptoms of genital itching
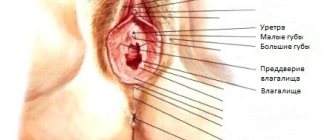
- Vaginal itching causes a strong desire to scratch the disturbing area. Sometimes the itching also spreads to the labia minora and labia majora, thereby causing even greater suffering.
- This unpleasant phenomenon is accompanied by redness and swelling of the external genitalia.
- Scratching leads to abrasions and scratches, into which a secondary bacterial infection penetrates, causing the formation of ulcers and cracks. There are cases when itching in the vagina extends to the anal area, and such itching is diagnosed as anogenital.
Features of examination in the presence of vaginal itching
What to do if there is itching in the vagina? First, determine its cause.
For this purpose, a comprehensive examination is used to identify not only infectious pathogens, but also other provoking factors.
The examination plan necessarily includes ELISA and PCR tests, which make it possible to accurately determine the pathogenic microorganism.
The standard diagnostic mechanism includes:
- blood and urine tests;
- advanced biochemistry to determine the activity of the inflammatory process and the involvement of other organs and systems;
- PCR for STDs;
- ELISA and PCR for herpes, other specific pathogens in agreement with the attending physician;
- scrapings from the anus or skin folds;
- urine culture for flora;
- standard genital tract smear, as well as PCR testing;
- Ultrasound of the pelvis.
When identifying microorganisms and diagnosing infectious inflammation of the vulva, control tests after treatment must be examined.
This ensures the prevention of relapses and guarantees the destruction of the pathogen.
If a woman has vaginal itching due to allergies, then a search for the irritating antigen is carried out using skin testing.
One test, even the best one, to identify the causes of vaginal itching will not help to accurately identify the problem.
A comprehensive examination is required.
Where to go for diagnostics?
You should choose a medical institution that has sufficient diagnostic potential and qualified personnel.
Since most often the problem is associated with sexually transmitted diseases, a dermatovenerological dispensary is best suited.
Here you can also learn how to prepare for specific tests.
If we talk about which doctor treats and examines patients, then it is preferable to choose a dermatovenerologist or gynecologist.
Why does this problem occur: causes of vaginal itching
External factors include:
- uncomfortable clothescausing excessive friction, underwear made of synthetic fabric that does not allow air to pass through and does not absorb secretions, personal hygiene products. Remember that to maintain normal flora and prevent vaginal itching, you need to wear cotton underwear or underwear with a gusset made from natural fabrics, change pads and tampons at least once every four to six hours, regardless of the amount of discharge.
Synthetic materials create a “greenhouse effect”, which is an excellent environment for the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria.The same environment is provided by menstrual flow;
- failure to comply with intimate hygiene rules . It is necessary to wash the genitals daily, and you can use various gels and soaps no more than once or twice a day, since they dry out the delicate skin and mucous membranes. When treating vaginal itching, washing too frequently can make the itching worse. It is not recommended to use deodorants for the vagina, as they disrupt the natural microflora and their effect is short-lived. On long trips and hikes, use special wipes for intimate hygiene. Don't forget to change your linen daily;
- allergic reactions . Slight vaginal itching may occur due to mechanical effects (for example, friction with underwear), due to chemical effects (lubricant, intimate hygiene gel, lubricant). Many women are allergic to contraceptives - creams, pills, suppositories, latex, spermicidal lubricant of condoms.
Among the internal factors, the most common ones include:
- venereal diseases such as trichomoniasis, gardnerellosis, genital herpes, candidiasis, saprophytic vaginosis. Intestinal dysbiosis sometimes leads to such diseases;
- weakening of general or local immunity . Due to the disruption of the natural composition of the vaginal microflora, pathogenic fungi and bacteria multiply. In this case, the itching in the vagina is accompanied by discharge with an unpleasant odor and a burning sensation during urination. In such situations, treatment of itching is mainly aimed at boosting immunity and restoring microflora. However, taking any medications on your own is not recommended;
- Often itching of the genitals occurs due to stress or excessive emotional disturbances , mental and physical stress. Psychogenic factors and women's reactions to them are individual and sometimes unpredictable;
- itching can be a reaction to serious diseases such as blood diseases, hepatitis, ovarian dysfunction, renal failure, diabetes mellitus, atrophy of the vaginal walls, hyperprolactinemia.
To determine the exact cause of itching, it is necessary to undergo an examination and undergo appropriate tests.
Expert opinion
Hormonally-related causes of vaginal itching deserve special attention. This condition is a common companion for pregnant and lactating women, as well as women during premenopause and menopause. In addition, vaginal itching and dryness may be present if the patient has diseases of the endocrine system that are not directly related to the genitals (for example, diabetes and thyroid diseases).
Obstetrician-gynecologist of the highest category Oksana Anatolyevna Gartleb
Itching in the vagina - how to cure?
Infection with a sexually transmitted infection
If a patient experiences itching and discomfort in the vagina, there is a high probability of contracting a sexually transmitted infection (STI). These diseases are primarily transmitted through unprotected sex. For a long time, STIs occur without significant symptoms.
The genitals may itch when infected with the following STIs:
- Chlamydia.
The disease is caused by chlamydia. The disease does not cause pronounced symptoms, but sometimes itching appears in the vaginal area. The danger of chlamydia lies in chronic inflammation of the genital organs. This can lead to reproductive dysfunction, complete infertility, and spontaneous miscarriage during pregnancy. - Mycoplasmosis.
The disease is caused by mycoplasma. Characteristic signs of mycoplasmosis are vaginal itching, redness of the genitals, and copious clear discharge. Patients also experience pain during sexual intercourse and urination. Mycoplasmosis is very dangerous during pregnancy, as it can cause polyhydramnios, fetal abnormalities, and spontaneous miscarriage. - Trichomoniasis.
The cause of the disease is infection with Trichomonas vaginalis. The disease is manifested by itching, unpleasant odor from the vagina and foamy discharge. Trichomoniasis affects a woman's reproductive function. - Genital herpes.
This is an incurable infection that, once it enters the human body, may not manifest itself for a long time. The main symptom of genital herpes is a small blistering rash on the surface of the mucous membranes. In this case, one of the symptoms is itching and burning in the vagina and other areas of the rash. Sometimes the temperature rises, headaches and muscle pain occur. Neglected conditions can lead to damage to the central nervous system. - Gonorrhea.
The causative agents of this disease are gonococci (Neisseria gonorrhoeae). Women have a several times higher risk of contracting this infection than men. The first signs of the disease are vaginal itching and profuse purulent discharge. Other symptoms of gonorrhea include pain in the lower abdomen, difficulty urinating, discomfort and burning in the urethra. - Syphilis.
This is a very dangerous disease, sexually transmitted through infection with Treponema pallidum. With the development of primary syphilis, chancres - hard ulcerations - form on the mucous membranes. They do not hurt or itch, which often leads to the patient not taking them seriously. This can lead to advanced syphilis, which at the next stage causes repeated lesions of the genital organs with itchy ulcers. Severe forms of the disease affect the nervous system, hearing, vision, and circulatory system.
Even slight vaginal itching cannot be ignored, as this may be the first symptom of an STI. Late diagnosis and untimely treatment of these diseases can cause severe inflammation, infertility and even tumor formation. STIs are treated by a venereologist or gynecologist.
Treatment for vaginal itching
Correct treatment of the genital organs can only be prescribed by a gynecologist after an examination, so taking any medications on your own is highly not recommended. Incorrectly selected medications can only worsen the situation.
But before you see your doctor, you can relieve the itching by doing the following:
- following a hypoallergenic diet: cereals, fruits, vegetables, dairy products. Try to exclude spicy, pickled and spicy foods;
- Wash your genitals as often as possible, but without using detergents. You can add furatsilin to the water, but not potassium permanganate, which can dry out the mucous membrane. Talc and baby powders also help;
- Avoid long stays in stuffy rooms and in the heat, serious physical activity is contraindicated, and sexual activity is undesirable.
Washing gels for intimate hygiene "Ginocomfort" are recommended for daily use, including during menstruation, during pregnancy and after childbirth. These products were developed by specialists from the pharmaceutical company VERTEX from ingredients that are safe for health and have a full list of necessary documents and certificates. Gels provide a feeling of cleanliness and comfort throughout the day.
If the itching does not go away within three days, you should immediately consult a specialist.
Allergy
A hypersensitivity reaction to external factors is one of the most common causes of itchy skin. Sometimes a woman’s genitals can also itch due to allergies.
Allergic irritation of the genital organs can be caused by the following substances:
- hygiene products – soap, shower gels, intimate hygiene products;
- underwear washing products;
- synthetic clothing fabrics;
- tampons, pads, condoms;
- intimate lubricants, sexual accessories;
- medications (in particular antibiotics);
- some food ingredients;
- house dust, dirt.
When treating allergies, the doctor’s main task is to identify the allergen and eliminate the body’s contact with it. Antiallergic drugs are also prescribed.
Itching in intimate areas, video
is not responsible for the accuracy of the information presented in this video clip.
Source - KVD - dermatovenerological dispensary Sources:
- FROM THE EXPERIENCE OF TREATING BACTERIAL VAGINOSIS. Gabdullina L. R., Vorobyova E. P. // Bulletin of modern clinical medicine. – 2012. – No. 1. – P. 40-42.
- COMPREHENSIVE TREATMENT AND PREVENTION OF ESTROGEN-DEPENDENT UROGENITAL DISORDERS: CLINICAL ASPECTS AND PHARMACOECONOMIC ANALYSIS. Ledina A.V., Kulikov A.Yu. // Pharmacoeconomics. Modern pharmacoeconomics and pharmacoepidemiology. – 2009. – No. 1. – P. 13-18.
- Bacterial vaginosis: clinical features, diagnosis and treatment / A.S. Ankirskaya, V.N. Prilepskaya, G.R. Bayramova, V.V. Muravyova // Russian Medical Journal. - 1998. - T. 6, No. 5. - P.276-282.
- Disturbance of vaginal microbiocenosis, ways of its correction. V.N. Prilepskaya, G.R. Bayramova // Gynecology. - 2007. - T. 9, No. 4. - P.25-27.
- Bacterial vaginosis: what's new? I.A. Apolikhina, S.Z. Muslimova // Gynecology. - 2008. - T. 10, No. 6. - P.36-37.
Treatment is prescribed only after a complete diagnosis of the cause of the disease
Treatment in each case will depend on the type of pathogen detected and its sensitivity to antibiotics. When sexually transmitted infections are detected, the doctor prescribes antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs, and both sexual partners must undergo treatment, since it is often quite difficult to identify an infectious pathogen in a man, since it is concentrated in the secretion of the prostate gland. For vaginal dysbiosis, local treatments and drugs that stimulate the immune system are used. In addition, it is recommended to wear cotton underwear instead of “synthetics”. Changes will also affect the power supply system. You should introduce more fermented milk products into your diet and significantly reduce your consumption of sweet foods. If allergic reactions occur, contact with allergens, in particular chemical contraceptives, should be limited. In case of allergic reactions, contact with allergens (condoms, chemical contraceptives) should be avoided.
Popular questions
I am concerned about itching and unpleasant smell.
Hello! The appearance of odor and itching in the genital tract may indicate an inflammatory process, dysbacteriosis, or a more serious disease. Therefore, you need to see a specialist and undergo an examination: a smear for flora, examinations to identify specific and nonspecific microflora (for example, vaginal culture or femoflora analysis). This will allow you to prescribe etiotropic therapy. At this stage, before receiving the results of the examinations, you can use Gynocomfort gel with tea tree oil to prevent the spread of inflammation. The composition will help eliminate itching and odor, relieve swelling and restore the condition of the mucous membranes. The gel is used in 1 dose 1 time per day for 7-10 days. It is introduced into the genital tract using an applicator.
Both my partner and I began to itch. Before this we took antibiotics. Will Gynocomfort gel help?
Hello! Most often, after taking antibiotics, dysbiosis develops associated with a yeast fungus of the genus Candida. To clarify the nature of the itching, you still need to contact an obstetrician-gynecologist and urologist, respectively, and conduct an examination - a smear on the flora. Until you get the result, you can use Gynocomfort gel with tea tree oil. This will relieve itching and accelerate the anti-inflammatory effect. The gel is administered 1 dose 1 time per day for 10 days using an applicator.
Hello, I have a burning and itching of the genitals, please tell me what can be done?
Hello! At this stage, you can use Gynocomfort gel with tea tree oil, which will have an anti-inflammatory effect and eliminate swelling and burning. And then you need to contact an obstetrician-gynecologist for an examination to identify the cause of the disease.
After sexual intercourse, itching and burning began and it is very itchy, sometimes there is pain, it hurts to walk small to the toilet, sometimes but not often there is a white discharge, and menstruation should begin soon. I apply clotrimazole 2 times a day, the itching subsides during the day and appears in the morning.
Hello!
Such manifestations indicate an inflammatory process in the genital tract and a possible ascending infection in the urinary system. See a doctor as soon as possible, conduct an examination to identify the inflammatory factor and carry out treatment to the required extent. For an accurate diagnosis, contact a specialist
Diagnostics
The examination of women complaining of a burning sensation in the intimate area begins with a standard gynecological examination. The doctor assesses the condition of the external genitalia, performs vaginal examination in speculums, and bimanual palpation. To understand the causes of the pathological condition, the information obtained during a physical examination is usually not enough, so instrumental and laboratory methods are used:
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs.
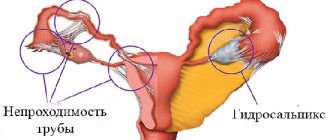
Sonography of the genital and urinary organs in women is carried out if complaints of burning are accompanied by pain in the lower abdominal cavity, dysuric disorders or fever. On ultrasound, the obstetrician-gynecologist finds signs of inflammation, neoplasms, and foreign bodies. - Colposcopy.
A targeted examination of the cervix is indicated if precancerous processes are suspected. With leukoplakia, white or yellowish lesions with an unexpressed vascular pattern are detected. To confirm the diagnosis, a Schiller test is performed, with the help of which areas of altered epithelium are visualized. Additionally, vulvoscopy is performed. - Analysis of secretions
. Microscopic examination of a smear in women reveals a large number of epithelium and leukocytes, an increase in secretion pH of more than 6.5, and the presence of pathogenic bacterial flora. To identify possible causative agents of inflammation, the secretions are inoculated onto nutrient media, where specific colonies of bacteria or fungi are found. - Blood tests.
Serological tests are required for the main pathogens of STDs (gonococci, chlamydia, Treponema pallidum). To exclude allergic causes of burning, a hemogram is performed to determine the level of eosinophilia, an extended immunogram to measure IgE.
Colposcopy