Make an appointment by phone: +7 (343) 355-56-57
+7
- About the disease
- How to cure
- Prices
- Sign up
- Specialists
- About the disease
- Prices
- Sign up
Spinal diseases affect 70% of the world's population. Pain reduces social activity and leads to temporary disability. The process can occur in different parts of the spine. Often the cause of ailments is destruction of the lower back, which characterizes lumbosacral radiculitis.
Causes
- degenerative changes: osteochondrosis (protrusion, disc herniation), spondyloarthrosis, vertebral displacement (spondylolisthesis, spondylolysis)
- vertebral compression fractures due to osteoporosis or trauma
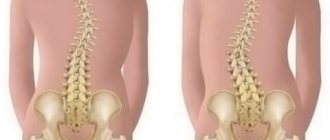
- problems with posture (scoliosis, kyphosis, lordosis);
- inflammatory process (spondylodiscitis, spondyloarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, abscess)
- tumors;
The process can be triggered by: physical activity, hypothermia, lifting (carrying) heavy objects, a sedentary lifestyle and excess weight, pregnancy.
How to treat radiculitis: technique
After a detailed diagnosis, the doctor prescribes therapy and determines how to treat radiculitis. In most cases, conservative methods are used. The treatment regimen includes:
- immobilization of the spine (the patient is prescribed strict bed rest until acute pain disappears);
- oral administration or intramuscular injections of analgesics;
- use of local irritants (for example, pepper patch);
- taking anti-inflammatory drugs;
- physical therapy;
- manual therapy courses;
- blockade of muscles in a state of spasm;
- vitamin B12 injections;
- acupuncture;
- traction of the spine, which allows you to increase the gaps between the vertebrae and release pinched nerve endings;
- radon and hydrogen sulfide baths;
- mud therapy.
Diet therapy plays a special role in the question of how to treat radiculitis. The patient is recommended to eat small portions up to 5 times a day. It is recommended to exclude the following foods from the diet:
- flour products;
- strong broths;
- sweets;
- fat meat;
- smoked meats;
- coffee and other drinks with high caffeine content;
- salty snacks;
- hot spices;
- alcohol;
- carbonated drinks.
The patient's menu should include a lot of vegetables and fruits, foods rich in fiber, lean fish, cereals and legumes. Cucumbers, radishes, tomatoes, persimmons, dried apricots, pomegranates, carrots, black elderberries, prunes and cabbage are especially useful for radiculitis.
It is not always advisable to treat radiculitis as prescribed by the conservative therapy regimen. If after 3-4 months of treatment the patient cannot completely get rid of the pain, then he is offered to undergo surgery (remove the herniated disc). The indisputable reason for surgical intervention is paralyzing sciatica (damage to the sciatic nerve roots).
Come to our clinic. With timely diagnosis and adequate treatment, the prognosis for radiculitis is favorable. We will help you achieve long-term remission or complete recovery!
Symptoms
The main place among the symptoms of lumbosacral radiculitis is pain. Classification by type of pain syndrome:
- 1. Lumbago. This is a reflex spasm of the paravertebral muscles. Characterized by acute pain in the lower back. Often occurs during (after) physical activity.
- 2. Lumboischialgia. This is a reflex spasm of the paravertebral muscles and piriformis muscle (usually on one side) irradiating to the gluteal region.
- 3. Lumbar radiculopathy: pain in the lumbar region with irradiation along the affected radicular nerve, sensory and motor disturbances in the area of nerve intervention. The upper segments 1-3 are the perineum, genitals, 4-5 and 1 cross are the lower limbs. In the chronic course of the disease, sensory and motor impairments may no longer recover, a chronic pain syndrome may form, the most dangerous complication is spinal canal stenosis with pressure on the spinal cord or spinal cord roots (cauda equina). Paresis of the lower extremities and pelvic dysfunction develop. This complication requires an emergency consultation with a neurosurgeon and a solution to the issue of surgical intervention and decompression of the spinal canal.
Radiculitis lumbosacral
11658 June 29
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Lumbosacral radiculitis: causes of occurrence, what diseases it occurs with, diagnosis and treatment methods.
Definition
Lumbosacral radiculitis, or radiculopathy, is a symptom complex that occurs as a result of pinching and inflammation of the spinal nerve roots in the lumbar and/or sacral spine.
Typically, this condition develops in people over 45, but in recent years, young people have also begun to complain of sciatica.
People whose work involves heavy physical labor or prolonged stay in one position, professional athletes are susceptible to the development of radiculopathy; patients with autoimmune diseases; those who are overweight and/or have metabolic diseases.
Radiculitis is characterized by lower back pain combined with shooting or pulling pain along the side or back of the leg (sometimes down to the foot), numbness and paresthesia, muscle weakness, increased pain when raising a straight leg.
Varieties of radiculitis
Radiculopathy can result from mechanical damage or an infectious process. Damage can develop both in the intervertebral discs and directly in the vertebral body or its processes.
Pain with radiculitis can be sharp (lumbago), shooting or stabbing (sciatica), burning or aching (lumboischialgia).
- Lumbago is an acute pain that appears suddenly as a result of sudden lifting of weights, sneezing, coughing, due to hypothermia of the lower back (for example, under air conditioning) or spasms of the lower back muscles, or intervertebral hernias.
- Sciatica is a shooting or stabbing pain that radiates to the buttocks, thighs, and calf muscles, as a result of which the patient may complain of muscle weakness (“legs can’t hold up”) and even numbness of the limbs.
- Lumboischialgia is a burning or aching pain that is localized in the gluteal muscles and thighs. It is characterized by a gradual increase.
Possible causes of sciatica
- Hernia or protrusion (bulging) of the intervertebral disc.
- Spondylosis is a chronic degenerative lesion of the spine that develops as a result of aging, overload or injury.
- Spinal stenosis.
- Osteophytes are growths of bone tissue that resemble hooks or spines in shape.
- Sacralization or lumbarization of the sacrum.
- Spondyloarthrosis is a chronic disease of the intervertebral joints, manifested by degenerative changes in cartilaginous tissues and leading to a decrease in the height of the intervertebral discs, tightening of the ligaments, and deformation of the intervertebral joints.
- Ankylosing spondylitis (Bechterew's disease).
- Vertebral fractures (including compression fractures due to osteoporosis).
- Hormonal changes that reduce the strength of cartilage and bone tissue.
Which doctors should you contact if you have lower back pain
? If you have signs of radiculitis, you should consult a doctor for examination and clarification of the diagnosis. In the future, he is engaged in the treatment of radiculitis.
Diagnostics and examinations for radiculitis
Before prescribing instrumental examinations, the doctor collects anamnesis and conducts physiological tests to identify symptoms of “tension” - specific signs of pathology of the nerve roots.
To diagnose spinal diseases the following is prescribed:
- X-ray of the lumbosacral spine with functional tests;
Radiculitis during pregnancy
During pregnancy, a woman's body is subjected to double stress. To ensure the normal development and functioning of a growing embryo, a large amount of nutrients is needed, the volume of blood circulating in the body increases, and weight increases. Untrained back muscles cannot cope with the increasing loads on the spine, because a woman needs to maintain balance. This leads to the need to bend forward and entails curvature of the spine. Reducing the space between the spinal discs can lead to pinched nerve endings and the development of radiculitis. It is important to lead an active lifestyle long before pregnancy to protect yourself from possible complications. Attacks of radiculitis during pregnancy can increase the tone of the uterus and lead to miscarriage or premature birth. No wonder they say that pregnant women should not be upset. Muscle spasms due to stress can also serve as a signal for the development of radiculitis.
Folk remedies for radiculitis
Rubbing
- Mix 5-7 drops of lavender oil with 10 drops of any vegetable oil, heat the mixture slightly and rub into the inflamed area.
- Dissolve 25 grams of salt in 100 ml of alcohol, add a pod of hot pepper and 40 grams of pork fat. Keep all components in a water bath until the fat is completely melted.
- Burdock roots infused with alcohol. This tincture is sold ready-made in pharmacies and is inexpensive, but it has proven itself to be an excellent remedy for radiculitis.
Diagnostics
For the diagnosis of radiculopathy, the presence of tension symptoms is important. For example, Lasegue's symptom is typical - when you try to raise a straight leg while lying on your back, pain in the lower back increases.
An MRI or CT scan of the lumbosacral spine is important for making a correct diagnosis, because only these studies will allow the attending physician to identify the presence of diseases such as intervertebral hernias or other diseases of the spine (spondylitis, compression fractures, neoplasms).
First aid
An acute attack of radiculitis limits the patient's ability to move, so the person needs outside help. The algorithm of actions is as follows:
1. Give the patient a painkiller in the form of a tablet or give an analgesic injection. Neuropathic pain cannot be tolerated.
2. Additionally, give a sedative to drink. Preference should be given to natural remedies (valerian, peony, motherwort). This will partially relieve the pain.
3. Place the patient on a chair in a position comfortable for him if it is impossible to ensure bed rest, otherwise, put him to bed.
4. Immobilize the painful part of your back with a tight belt (you can use a sheet, bath towel or corset).
5. Apply ointment or gel from the NSAID group to the sore area to relieve inflammation.
6. Hold the patient if necessary.
After the ambulance arrives, provide the patient with peace, and then help him visit a neurologist for further treatment.
Development of radiculitis in childhood
Children are at risk of developing sciatica due to constant use of computers and reduced time for physical activity. The modern rhythm of life and the stress of studying lead to the inability to fully move during the day, which leads to weakening of the back muscles. In children, cervical and thoracic forms of radiculitis are diagnosed due to the development of scoliosis. It is necessary to instill in your child a love of sports and monitor posture from an early age. At the first signs of spinal curvature, you should contact a pediatric orthopedist, who will prescribe the necessary set of therapeutic measures. Due to their age, children manage to overcome the disease forever.
Treatment
Treatment of radiculitis involves the need to limit the patient's physical activity. Refusal of any physical activity and a sleep regime are indicated during the acute course of the disease in the first few days. In this case, you need to ensure that the surface on which the patient lies does not bend under the person. The ideal solution would be an orthopedic mattress; if it is not available, plywood or any other solid base is placed under a regular mattress. The damaged part of the spine is fixed with an orthopedic belt or corset.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (ibuprofen, diclofenac) are widely used to reduce pain. Intramuscular administration of painkillers is used for severe pain; in mild cases, it is enough to limit yourself to taking tablets and using ointments. If the pain is unbearable, then treatment of radiculitis cannot be done without blockade injections. After relief of the painful syndrome, further treatment and physical therapy are prescribed.
Long-term use of painkillers has a detrimental effect on the condition of internal organs. The mucous membrane of the stomach, liver and kidneys are severely affected. Therefore, it is important to treat the disease rather than stop the symptoms.
Modern methods of treating radiculitis:
1. Drug treatment.
2. Physiotherapy.
3. Medicines based on snake venom.
4. Therapeutic plasters and ointments.
Manual therapy has shown greater effectiveness in eliminating radicular syndrome. Massage and stretching of the spine allows you to release pinched roots, which leads to the elimination of the cause of the disease. It should be remembered that all actions with the spine must be done carefully, avoiding excessive pressure on the affected tissues. Stretching the spine by hanging on a horizontal bar is strictly prohibited. This can lead to complications.
Lumbar radiculitis is the most common form of the disease, which has bothered people since ancient times. Therefore, there are a huge number of folk recipes that can cope with the disease and chronic attacks. Non-traditional remedies should be used on the recommendation of your attending physician, who will be able to select the necessary prescriptions for your case.
Treatment at the Solnechny sanatorium
Diseases associated with the musculoskeletal system directly affect the quality of life. Often people turn to doctors when the disease is already in an advanced state, ignoring pain symptoms for a long time. Like any other disease, radiculitis at the initial stage is treated faster and easier. It is important to maintain spinal health at any age and respond in a timely manner to pain signals sent by the body.
The Solnechny sanatorium employs highly qualified specialists with extensive experience in the treatment of radiculitis. The use of modern methods and the latest equipment results in patients returning the ability to move easily and helps them forget about pain. Wellness holidays in Polesie also include manual therapy, hydrotherapy, diet therapy and climatotherapy. In addition to the treatment of radiculitis, the sanatorium provides services for the restoration of the spine after injuries.
Prevention
Preventive measures to prevent radiculitis are simple:
- competent organization of sleeping space. A comfortable bed is an elastic mattress of medium hardness and a small pillow of medium thickness. The ideal choice is orthopedic bedding;
- a complete and balanced diet will not only provide the body with healthy vitamins and minerals, but will also help maintain normal weight;
- adequate physical activity. Hard work is bad for your back, so if possible, you should reduce the load. Physical inactivity also threatens with negative consequences for the spine, and you should exercise at least once a week.
Doctors at our center have been working with patients suffering from radiculitis for many years. With timely treatment, the prognosis is always favorable. With us you will receive complete treatment, starting from examination and diagnosis, and ending with advice on lifestyle correction.