What is (and is) fat used for? Is fat always bad? Should you strive for a minimum body fat percentage?
Fat is much more than just passive energy storage. Although fat cells are surprisingly well adapted to this role, fat is also an active tissue that influences metabolism.
Fat cells are called adipocytes. Most of them are under the skin, this fat is called subcutaneous. There is also fat in the abdominal cavity around the organs, this fat is called visceral, and its excess threatens health problems (for example, the risk of cardiovascular diseases increases). There is very little fat in the muscles.
The human body can contain between XXX and YYY billions of fat cells, with a diameter ranging from 70 to 120 microns (a micron is one millionth of a meter).
80-95% of fat consists of triglycerides (a glycerol molecule linked to three chains of free fatty acids). The remainder of the cell is water, as well as various cellular “equipment” that produces enzymes and various other substances that cells need to function.
Fat is where energy is stored
The main role of fat cells is energy storage. And until 1994, it was believed that this was their only function - a passive storage room for excess energy coming from food. And in 1994, the hormone leptin was discovered, which plays a very important role in metabolism, which is discussed below.
When it comes to storing energy, fat cells are simply ideal. A kilogram of fat contains 7,000 calories of stored energy. Assuming you could use 100% fat as fuel (which doesn't happen in the real world), that would be enough energy for a 70kg person to walk 56km.
A slim man weighing 72 kg and with 15% body fat has 11 kg of fat, i.e. about 84,000 calories of stored energy. If his metabolic rate is 2400 calories/day, then even with complete fasting he will use up his fat reserves in 35 days. And the fat reserves of obese people will help them live without food for several months.
For comparison, another place where energy is stored is muscle and liver glycogen - this is only about 500 grams. Each gram provides 4 calories of energy, so that's a total of 2,000 calories. For some, this is not enough just to cover the body’s energy needs for one day. So fat is ideal for storing energy.
In addition, the fat cell can greatly increase in size and “deflate” when we lose weight. That is, it does not disappear and is always ready to fill up again.
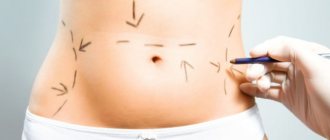
Rehabilitation after liposuction of the abdomen and sides
Rehabilitation after liposuction of the abdomen and sides averages approximately 3 weeks. For some, this period is a little less or a little longer due to the individual characteristics of the body. Bruising and swelling may occur after surgery. Do not be alarmed by them - this phenomenon is quite normal after this kind of intervention. The bruises go away pretty quickly.
Do not neglect wearing compression garments, which are specially created to avoid sagging of excess skin after liposuction and to form the correct body contour.
For some time you will have to exclude heavy loads, sports, tanning, visiting the sauna and swimming pool.
2 weeks before and 2 weeks after surgery you need to stop smoking and taking blood thinning medications.
The main thing is to follow all the doctor’s recommendations and advice during the rehabilitation period.
Comment by candidate of medical sciences, plastic surgeon Svetlana Nikolaevna Zharkova
I always tell my patients that successful surgery is only 50% of the work towards a perfect figure.
At this stage, my work is over and yours begins, where you need to properly care for yourself in order to ultimately get an ideal result that will delight you for many years. Do not neglect all the advice of the plastic surgeon and if you have any questions, you can seek advice after the operation. If complications arise or something bothers you, the main thing is to report it in a timely manner.
Fat and evolution
It often seems to a modern person that the body hates it: it is reluctant to give up fat, preferring to get rid of muscles, it adapts to any calorie restriction, reducing metabolism, to any of the best workouts, it tightly retains fat in problem areas.
Our body doesn't know that we live in the 21st century. Excess food and a sedentary lifestyle for 50 years is still nothing against tens of thousands of years of survival in difficult conditions.
And from a survival point of view, fat is an ideal energy store. It accumulates easily, its reserves can be replenished for a very, very long time, and if the cell swells to its limit, the body will create new cells (more on this below).
Fat, unlike muscles, requires almost no energy to exist. Therefore, those of our ancestors who were able to accumulate a lot of fat and survive cold and hunger survived and passed on their genes.
Thus, the ability to store huge amounts of energy in a very small space is an excellent evolutionary advantage that helped our ancestors survive during periods when food was not available. Most of us are programmed to have a lot of energy reserves and “extra” weight by modern standards (we are not talking about clinical obesity here).
How to get rid of visceral fat?
Harvard experts say diet and exercise can help reduce visceral fat. They may be even more effective than reducing subcutaneous fat. It often happens that obese people do not yet see the visual effect of changing diet and exercise, but the fat around their organs has begun to decrease.
People with excess visceral fat are advised to exercise for at least 30 minutes every day. It is advisable to include both cardio exercises and strength training.
You should also change your eating habits by eliminating processed foods that are high in sugar and fat and incorporating more lean sources of protein, vegetables, and complex carbohydrates into your diet. Instead of frying foods, they should be boiled or baked.
People with frequent stress can practice meditation, deep breathing and other stress management techniques. It is also recommended to get enough sleep regularly, quit smoking and limit alcohol consumption.
Fat in men and women
Men and women differ greatly in the distribution of body fat.
In men, fat is deposited mainly in the abdomen.
Women's problem areas are the hips. This fat should provide energy for breastfeeding. This is exactly that “stubborn” fat that often does not go away, even if the girl has lost weight all over her body. And during lactation, this fat becomes easier to mobilize.
The “male” type of fat deposition (on the abdomen and upper body) occurs when there is an excess of testosterone in the female body.
Additionally, many studies have clearly shown that men have a preference for a certain waist/hip ratio, which suggests fertility and health in women. A narrow waist and curvy hips are chosen many times more often than narrow hips and excess belly fat. And some of the causes that cause fat to accumulate around the belly and organs are associated with infertility, such as polycystic ovary syndrome (which is also associated with excess testosterone).
Where is visceral fat located?
Visceral fat is a type of fat that is found in the abdominal cavity. It does not accumulate under the skin, but around vital organs such as the liver, stomach, intestines and pancreas. It can also accumulate in the arteries.
All people have this tissue; normally it makes up about 10% of all adipose tissue in the body and covers the internal organs with a thin layer that provides their energy needs. With excess body weight, the volume of visceral fat is higher; it begins to compress the internal organs, disrupting their normal blood circulation and lymph flow.
Fat cell growth
Previously, it was believed that new fat cells do not grow in adults. That is, a person is born with a certain amount of them, and it can only increase during puberty or during pregnancy, and in other cases the cells are either filled with fat to a large size or blown away. Today we know that the adult body can create new fat cells throughout life.
When existing adipocytes reach their limiting size, their stretching stimulates the release of various signaling substances. They tell the body to make new fat cells from preadipocytes, i.e. "dormant" fat cells.
And if these new cells also become too large, the body will continue to make new ones. Unfortunately, the only way to get rid of newly created fat cells is through surgery.
By the way, a new class of diabetes drugs (TZDs) works exactly like this - by stimulating the production of new fat cells, which makes it possible to "move" glucose and fats out of the bloodstream to a safer place. This is extremely important for people with diabetes.
What else is visceral fat dangerous for?
According to research from Johns Hopkins Medical Institutions, visceral fat is metabolized by the liver, which converts it into cholesterol that circulates in the blood. “Bad” cholesterol (low-density lipoprotein, or LDL) accumulates in the arteries, where it forms plaques that narrow the blood vessels.
Visceral fat can increase insulin resistance (decreased responsiveness of insulin-sensitive tissues to the effects of insulin), which in turn can lead to glucose intolerance and type 2 diabetes. This effect is found even in people who have never had diabetes or prediabetes. It is due to the fact that visceral fat secretes retinol-binding protein, which increases insulin resistance, according to an article published in the medical library of the US National Center for Biotechnology Information.
Excess visceral fat increases the risk of developing several serious life-threatening conditions. These are heart attacks and heart disease, type 2 diabetes, stroke, breast cancer, colon cancer, Alzheimer's disease.
I have. Why extra pounds are especially dangerous for older people Read more
Belly of a young mother
In this case, there is loose skin on the abdomen, and on both sides of the navel there are two fat accumulations (pouches).
Reason: A not very toned stomach and loose skin are a natural side effect of pregnancy.
But if your belly continues to look like this months or years after having your baby, you may have diastasis recti. This is why the inner edges of these muscles along the abdomen (which separate when you are pregnant) do not reconnect.
What to do: Try not to do abdominal crunches. These exercises can aggravate any abdominal tear after childbirth. It's best to wait at least 6 weeks and then try special training programs designed to rebuild your muscles after childbirth.
Also try doing pelvic floor exercises:
- Lie on your back, bend your knees.
- Tighten your abs and lift your pelvis up to be in a glute bridge position.
- Pause at the top and then slowly lower down to the starting position.
Repeat 5-10 times.
What to eat: Rhiannon stresses: “Your baby has been growing inside you for 9 months - you won't get your belly back overnight. The postpartum period is a dangerous time to diet, as your body needs energy to breastfeed your baby and cope with sleepless nights. If it's been a year since your baby was born, a calorie deficit and a balanced diet are your best option."
see also
Tips for gaining weight despite exercise and diet
Possible complications after liposuction
Liposuction, like any other operation, is an intervention in the quiet “life” of the body. Although this procedure is considered low-traumatic, sometimes complications can arise. You need to know about this and carefully approach the choice of a plastic surgeon who has sufficient experience so that, after studying the patient’s situation, he can offer him exactly the method of removing fatty tissue that will reduce complications to a minimum and give a good result. final result.
The main types of complications include:
- Formation of hematomas and edema. These are rather the consequences of the intervention, which pass quickly enough if all the doctor’s instructions are followed.
- The disproportionality of the removed fat may result in a bumpy relief of the liposuction area.
- Flabbiness and sagging skin. If you have excess skin on your abdomen, shoulders or thighs, then after liposuction the skin itself may not tighten (especially in older patients) and, as a rule, the doctor warns in advance that abdominoplasty or brachioplasty may be required in the future to achieve an optimal effect.
- Skin pigmentation, which takes quite a long time (it all depends on the characteristics of the body). In this case, it is necessary to protect problem areas from the sun and use whitening creams.
- Suppuration is extremely rare and can be eliminated with a course of antibiotics. Occurs as a result of violation of the rules of asepsis and antisepsis by a doctor or patient in the postoperative period.
- Seroma is an accumulation of fluid that looks scary, but poses no real danger. It can be eliminated by puncturing the contents and wearing compression garments. Sometimes your doctor may prescribe antibiotics.
Fortunately, in modern medicine, the occurrence of any complications after liposuction occurs in very rare cases. It is very important to follow all the doctor’s instructions and not neglect his advice, then the result will definitely please you.
Beer belly
In this case, your belly is shaped like the belly of an early pregnant woman.
Reason: Alcohol. Alcoholic drinks are full of calories, ranging from 180 to 500 per drink. And if you mix it with sugar-containing soda, it often leads to the accumulation of gas in the stomach. As a result, we get that same “beer belly.”
What to do: Any physical activity will help, but we recommend focusing on regular cardio training. Boxing is a great option that targets the entire body. You can burn up to 800 calories per hour (that's four large glasses of wine) depending on the intensity of your workout.
Try boxing classes online, buy a punching bag and sign up for classes at a fitness club when it opens its doors again in your city.
And also try to drink no more than 14 servings of alcohol per week - this is 2.5 liters of beer or 6 medium glasses of wine.
According to the nutritionist, there is a direct link between alcohol and weight gain. “If you want to lose weight, learn to limit yourself to one or two drinks.
Drinking alcohol late at night can affect your sleep and hormones and, in turn, cause sleep apnea, snoring and other problems that won't benefit your waistline, says Rhiannon Lambert.
see also
17 real weight loss tips from people who have lost more than 20 kg
"Lifebuoy"
This is the name for excess weight that is concentrated around the hips. In this situation, your stomach really looks like a life preserver.
Reason: Your body is storing excess fat - most likely, you have been leading a sedentary lifestyle and eating unbalanced foods. In short, you consumed more calories than you burned.
What to do: Any physical activity will help. The most important thing is regularity of training. The UK's National Health Service recommends that all adults get at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week. Let this be your goal.
For the more advanced and experienced, high-intensity interval training (HIIT) is suitable, which is very effective in reducing fat percentage. Research shows that 20 minutes of HIIT exercise three times a week is as effective for weight loss as 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise daily.
Start by running. Run as fast as you can for 40 seconds, then rest for half a minute. Repeat for 20 minutes.
What to eat: To lose weight, you need to eat fewer calories than you burn. Lambert states: “Reducing your intake of saturated fat can be a good start.
Too much of them in your diet can lead to the accumulation of visceral fat around your organs. A Mediterranean diet with plenty of fatty fish, olive oil, grains and legumes has been shown to increase levels of good fat (HDL) and reduce levels of bad fat (LDL).”
Bloated belly
As a rule, when bloating occurs, the lower abdomen protrudes.
Reason: While increased lower belly fat is associated with weight gain, bloating is often associated with hormonal changes during the menstrual cycle. Most women suffer from this. And even celebrities! For example, Lucy Mecklenburgh recently posted a photo of her bloated belly.
About a week before your period, progesterone levels drop, causing the uterus to shed its lining. During this period, the body retains more water, causing the belly to become larger and heavier.
What to do: Yoga will be very helpful in this matter, as it improves blood circulation and stretches muscles. Look for classes on YouTube or sign up for a yoga studio once the danger of the pandemic has passed.
Be sure to try the following exercise to relieve discomfort:
- Lying face down on the floor, place your palms under your shoulders and then straighten your arms until your hips lift off the floor.
- Pushing your chest forward and slowly lowering your head back, stretch your entire body. Feel the stretch in your abdominal area.
What to eat: While eating won't help with your period, you can reduce your chances of bloating. Reduce your intake of salty, processed foods to minimize water retention in the body.
Focus on foods rich in potassium, such as bananas and spinach, to help combat bloating. And watch how you eat. Rhiannon emphasizes: “Chewing your food properly can minimize bloating.
And limit your intake of foods that promote gas, such as legumes, Brussels sprouts and cauliflower. And also try not to chew sugarless gum.”
see also
The real story of losing 50 kilograms: how the lost weight completely changed a girl’s life