Damage to the skeletal muscles of inflammatory origin is called myositis. The body signals with local pain, indicating the location of the pathology. Painful sensations occur soon after injuries or infections, as a result of hypothermia or prolonged work in an uncomfortable position. If pain in muscle tissue increases, this indicates the progression of inflammation. How to treat myositis depending on the characteristics of its course, we will tell you in this article.
Types of myositis and causes
The appearance of muscle pain with compaction in the affected area, a feeling of spasms, swelling, general malaise, and increasing pain with movement indicate the development of myositis. The disease is classified according to its cause.
- Traumatic myositis. The occurrence is provoked by trauma. Muscle fibers are affected by excessive physical activity or injury. As a result, internal tissue ruptures, hemorrhage occurs, and local inflammation progresses. Pathology is indicated by redness, swelling, local pain, and muscle weakness.
- Parasitic. This form is caused by parasitic larvae. The disease is easily confused with other types of degenerative and inflammatory diseases. Muscles in any part of the body can be affected: diaphragm, tongue, eye muscles, buttocks, calves.
- Infectious. The impetus for development is a previous infection. The disease can develop against the background of acute respiratory viral infections, influenza, and other viral diseases. The pain affects one muscle group or several.
- Rheumatic. A disease of an infectious-allergic nature that develops against the background of infectious intoxication in the presence of immune disorders. The cause is often streptococcus.
- Ossifying. It means the gradual ossification of muscle tissue. This is a rare genetic disease.
- Dermatomyositis. A progressive disease of a systemic nature with an unknown etiology. Affects smooth, skeletal muscles and connective tissues. Causes damage to the skin. Accompanied by impaired motor functions.
- Polymyositis. Refers to a chronic type of muscle inflammation. The reasons lie in autoimmune disorders. May occur as a result of a viral infection.
The disease is also classified according to the nature of its course. The chronic form means that after treatment the disease subsides, but the problem is not completely eliminated. There is a sluggish manifestation of symptoms. As a result of an unfavorable combination of circumstances, for example, severe hypothermia, the disease worsens again. Traumatic and infectious myositis occurs in acute form. It is characterized by the sudden onset of pain, which is most often local in nature.
The main causes of myositis include:
- infectious diseases;
- soft tissue injuries;
- physical stress;
- hypothermia of the body;
- muscle infection by parasites;
- regularly performing work in an awkward position.
Classification
In clinical practice, several classifications of muscle myositis are used, which are based on the etiology, characteristics of symptoms and the course of the disease.
Depending on the origin, all myositis is divided into the following forms¹:
- Infectious purulent. Variants of myositis caused by pathogenic bacteria, in which the inflammatory process is accompanied by the formation of purulent-necrotic masses.
- Infectious non-purulent. Inflammation of striated muscles of infectious origin (most often viral), in which purulent masses do not form. They occur more easily than purulent forms.
- Parasitic. Muscle myositis, which is the result of toxic-allergic reactions and characteristic changes caused by infection with protozoa.
- Myositis ossificans. A characteristic difference is the deposition of calcium salts in the connective tissue. The shoulders, hips and buttocks are most often affected.
- Polymyositis. A variant of autoimmune myositis, in which a large number of muscles become inflamed at once. In children, such myositis can be combined with damage to the lungs, heart, blood vessels and skin, and in adults it is often associated with malignant tumors of internal organs.
- Dermatomyositis or Wagner's disease. An independent autoimmune pathology, in which, in addition to inflammation of the striated muscles, the skin, smooth muscles and internal organs are also affected.
Depending on the prevalence of the pathological process, the following are distinguished:
- Local myositis. More often they are of traumatic and infectious origin. Accompanied by inflammation of one or more adjacent muscles.
- Diffuse or generalized. Inflammation of skeletal muscles in different parts of the body differs. In most cases, they are associated with autoimmune pathologies.
Based on the activity and nature of inflammation, myositis is divided into the following options:
- Spicy. They are characterized by a debut with pronounced symptoms.
- Subacute. They often appear gradually, but progress relatively quickly.
- Chronic. They can be the result of acute myositis or develop independently, accompanied by moderate persistent symptoms.
Figure 1. Exercises for the neck: maximum turns of the head to the right and left (5 times), slow tilts of the head to the shoulders to the right and left (5 times in each direction). Dynamic resistance of the neck and palms to head tilts in different directions. Image: cteconsulting/Depositphotos
Symptoms of myositis
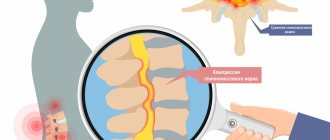
The main symptom of myositis is local pain. The pain increases with movement and pressure on the muscle. Tension and spasm are felt at the site of pain. The pain is often accompanied by redness and swelling. Manifestations of myositis also depend on the location of the lesion.
| Localization | Manifestations |
| Myositis of the chest muscles | Muscle spasms in the chest area, pain with deep breathing, coughing, changes in muscle tissue density |
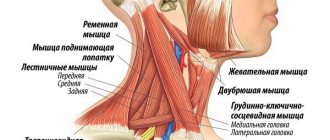
| Cervical region | Pain in the neck, difficulty turning the head, swelling of the muscles, presence of lumps in the tissues |
| Back and lower back | Aching pain intensifies while walking, there is general malaise, fever, and muscles gradually atrophy |
| Myositis of the upper extremities | The inflammatory process affects the elbows, forearms, shoulders, tension and pain are felt, joint mobility worsens, nodules form in the soft tissues |
| Myositis of the lower extremities | The disease often occurs due to injury to the knee, hip, or lower leg; swelling and redness are characteristic; it can become chronic. |
Diagnostics
A doctor may suspect myositis based on symptoms such as muscle weakness, pain, and other symptoms consistent with myositis. The following are used in the diagnosis of myositis:
Blood tests. Elevated levels of muscle tissue enzymes (eg, creatine kinase) may indicate muscle tissue damage. Autoantibody tests can identify autoimmune disease.
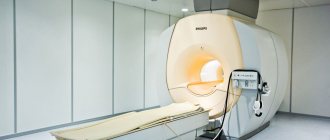
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). A scan using a powerful magnet and a computer produces images of the muscles. MRI analysis helps identify areas of muscle damage currently and over time.
Electromyography (EMG). By inserting needle electrodes into the muscles, the doctor can test how the muscles respond to electrical stimulators and nerve impulses. EMG allows you to identify muscles that are weak or damaged by myositis.
Muscle biopsy. This is the most accurate analysis for diagnosing myositis . The doctor identifies the weak muscle, makes a small incision, and removes a small piece of muscle tissue to examine the tissue under a microscope. A muscle biopsy provides a definitive diagnosis of myositis .
There are many causes of muscle weakness and muscle pain more common than myositis. And therefore, the diagnosis of myositis may not be made immediately, but after some time.
Treatment of myositis in the Solnechny sanatorium
Good treatment results are achieved through an integrated approach and a developed therapy program. All conditions for high-quality diagnosis and treatment of myositis have been created in the Solnechny sanatorium in the Republic of Belarus. This is a specialized medical institution specializing in diseases of the musculoskeletal system. A powerful therapeutic base includes a variety of techniques, including hydrotherapy, mud therapy, physiotherapy, physical therapy, ultrasound and laser effects on the body. A variety of treatment and rehabilitation programs are carried out using the latest equipment. Clients are offered a balanced diet. All this, coupled with a healing climate, gives excellent healing results.
Treatment of myositis
If the development of myositis is associated with an infectious component, then first of all it is recommended to pay attention to lifestyle. You should give up bad habits to avoid additional intoxication of the body and quickly stop the inflammatory process. Hypothermia must be avoided. If you are forced to work in an uncomfortable position, change your body position more often and take breaks. Exercise in moderation. Timely treatment of myositis under the supervision of doctors will avoid complications.
Drug treatment
Medicines are prescribed by the attending physician after receiving the diagnostic results. The purpose of taking them is to stop the inflammatory process, eliminate the causes of myositis, and alleviate symptoms. For the treatment of myositis, medications belonging to different pharmacological groups are prescribed:
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to relieve inflammation;
- analgesics for pain relief;
- combined means for external use (ointments) to eliminate spasms, distract, analgesic effects, for reflex expansion of capillaries.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed in tablets and injections. Injections are given for acute disease and unbearable pain. Intramuscular administration provides a rapid therapeutic effect. Medicines with snake and bee venom are often prescribed as antispasmodics.
Depending on the causative agent of the infectious disease, antibacterial and antiparasitic drugs may also be prescribed. When the body has an autoimmune reaction, immune suppressants are used.
To strengthen the body and normalize the conduction of nerve impulses in muscle tissue, the therapy program includes B vitamins, as well as vitamin and mineral complexes.
A relatively new method of treating myositis is pharmacopuncture. Medicinal substances are injected subcutaneously into biologically active points on the human body. Such injections with homeopathic compounds, vitamins, and biostimulants combine the advantages of reflexology, homeopathy and traditional medicine. The undeniable advantages of this method include:
- therapeutic effect directly on sore muscles and ligaments;
- minimizing the risk of allergic reactions;
- almost instant effect from the procedure;
- the minimum dose of the drug eliminates the risk of side effects;
- injections are given only 1-3 times a week.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic methods are used in the complex treatment of myositis. They give excellent results at any stage of the disease. In mild cases, sometimes only physiotherapeutic treatment is sufficient, without the use of medications.
The following physiotherapy procedures are prescribed:
- electrophoresis;
- magnetic therapy;
- laser therapy;
- amplipulse therapy.
During electrophoresis, soft tissue is exposed to a constant electric current. Thanks to this, pain is reduced, the intensity of the inflammatory process is reduced, increased muscle tone is eliminated, and the body’s defenses are activated. The medicine is first applied to the pad, but in a smaller volume compared to internal use. Active substances penetrate the skin and intercellular spaces and act locally on the problem area. The therapeutic effect occurs faster.
During magnetic therapy, the body is exposed to a static or alternating magnetic field. As a result, the physicochemical properties of the water systems present in the body change. Muscle weakness, swelling, inflammation are eliminated. Pain is reduced. Blood circulation in tissues improves, metabolism stabilizes.
Laser therapy provides good therapeutic results. The light flux, consisting of rays of a fixed length, affects muscle tissue. As a result, the patient receives an anti-inflammatory, immunocorrective, analgesic, and restorative effect.
Amplipulse therapy involves influencing the body with low-power currents. The earlier the stage of myositis, the more effective the treatment is. The technique is allowed to be used even in childhood. In the tissues involved in the pathology, spasms are eliminated, blood circulation is improved, drainage of fluids is enhanced, and the occurrence of edema is prevented.
Exercise therapy
Therapeutic exercise refers to rehabilitation therapy. A set of physical exercises, performed under the supervision of an instructor, stimulates the restoration of functions, improves joint mobility, and prevents the development of complications. After exercise therapy, swelling decreases, blood supply to tissues is activated, and the sensation of pain decreases. Exercise therapy is beneficial for a person’s physiological and psychological health.
MYASTHENIAS
A disease of the autoimmune system that causes muscle weakness due to interruptions in neuromuscular transmission is called myasthenia gravis. The activity of the ocular, facial and masticatory muscles is usually impaired; the muscles of the respiratory organs are less commonly affected. Characteristic manifestations: drooping of the lower eyelid, disturbances in vocal function (nasal sound, hoarseness, hoarseness or weakness), disturbances in swallowing and chewing.
The word "myasthenia" means impotence, muscle weakness. This is a pathological process, which is based on the self-destruction of body cells. The normal immune response changes direction and begins to destroy its own cells instead of foreign ones, which leads to the destruction of organs and tissues of the body.
Possible reasons:
- genetic predisposition;
- benign or malignant tumors;
- systemic diseases;
- damage to the nervous system;
- hyperthyroidism, sleeping sickness.
Treatment depending on location
Myositis affects any muscle group. The set of therapeutic measures depends on the location of the pathology.
Pain concentrated in the cervical spine indicates myositis of the neck. A sample list of assignments would look like this:
- anti-inflammatory drugs for internal use;
- local application of creams and ointments with a warming, antispasmodic, analgesic effect;
- massage to eliminate spasms, restore blood circulation, improve neck mobility;
- physiotherapeutic procedures to speed up recovery.
The inflammatory process in the muscles of the back and lumbar region most often occurs as a result of a cold, hypothermia, or after high physical activity. Myositis is differentiated from kidney diseases, spinal osteochondrosis, and then treatment is prescribed. The therapy program stipulates bed rest and restriction of movements for the duration of acute pain. Analgesics are prescribed in the form of injection blockades and for internal use, NSAIDs, hardware muscle traction, and reflexology.
Myositis of the chest is often accompanied by an increase in body temperature. Under these conditions, the patient is prescribed bed rest. The main task is to stop the cause of inflammation. To alleviate the condition, painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed. If there is a bacterial component, antibiotic treatment is carried out. For autoimmune pathology, the treatment program includes immunosuppressants and glucocorticosteroids. Electrophoresis of the thoracic region is prescribed as maintenance therapy during recovery. Acupuncture and hirudotherapy have a good effect.
For myositis of the extremities, muscle rest is provided at the initial stage of treatment. It is necessary to exclude any stress on muscles and joints. Injections and external agents are used for pain relief. To relieve the inflammatory process, NSAIDs are prescribed. Thermal procedures are indicated in the absence of swelling and redness. After stopping the acute process, massage procedures, exercise therapy, and reflexology are allowed.
Shoulder myositis is also treated comprehensively: anti-inflammatory therapy, anesthetics, and physiotherapy are used. Additionally, kinesiotherapy can be prescribed - a rehabilitation technique, a type of physical therapy, the purpose of which is to reduce muscle tension, reduce inflammation, and increase mobility. Kinesiotherapy also includes various types of therapeutic massage. The technique is effective for severe pain and functional disorders of the limbs and spine. If the shoulder joint is affected at the same time as the muscle tissue, chondroprotectors and massage products are used for external use.
Possible complications
Lack of timely treatment leads to the risk of developing atrophic processes. Tissue death is possible.
The danger of the disease lies in the fact that prolonged restriction of the work of the articular joint leads to a malfunction in its functionality. After treatment of myositis in an advanced stage, the joint may not regain its previous mobility.
The disease affects the most important life processes. If there is no treatment for cervical myositis, the inflammation spreads to the larynx, which can lead to breathing problems. Untreated costal or lumbar myositis can cause shortness of breath and respiratory failure. You have Examinations for myositis
If symptoms are detected, you should contact a therapist, neurologist or surgeon. The set of diagnostic procedures includes:
- examination, questioning of complaints, collection of anamnesis;
- taking a general blood test, urine test, blood biochemistry test to identify infections, intoxication, parasitic infestation;
- radiograph;
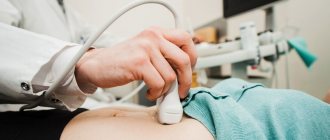
- ultrasonography;
- CT and MRI;
- tests to identify rheumatic diseases;
- biopsy according to indications.
Already during the examination, the doctor can identify the disease; further examinations are necessary to confirm the diagnosis and prescribe the necessary medications.
Treatment of infectious myositis
According to its clinical course, infectious myositis is classified as acute. The main symptoms are severe discomfort and pain in the area of the affected tissues, high temperature, muscle tightness, and general weakness of the patient. This is a dangerous type of disease that can only be treated under the supervision of doctors.
The drug therapy program includes antibiotics, anesthetics, and antipyretics. In the purulent form, surgical intervention is often required. The surgeon opens the abscesses, excises necrotic tissue, and installs drainage. Enzyme therapy is performed to cleanse dead cells and stimulate the production of collagen fibers.
Antibiotic drugs are prescribed depending on the infectious pathogen. Antibiotic agents can be combined with bactericidal agents. In severe cases of infectious myositis, steroids are prescribed.
When the acute infectious process can be stopped, the recovery stage begins. At this stage, exercise therapy, balneological procedures, massage, and physiotherapy are recommended.
Rhabdomyolysis
With muscle injuries (more common in athletes), gradual destruction of tissue occurs, this condition is called rhabdomyolysis. This process ultimately ends with the death (necrosis) of cells and the release of toxins into the circulatory system. This disease can cause serious complications and lead to kidney failure. If qualified assistance is not provided, it can result in death.
Possible reasons:
1. Bodily injuries (injuries, beatings, accidents, accidents).
2. Stage 3 and 4 burns.
3. Long surgical operations (more than 8–10 hours).
4. Long-term compression of tissues with impaired blood supply.
5. Electric shocks.
The development can be provoked by: increased loads during training, epileptic seizures, severe muscle spasms, delirium tremens.
It is very difficult to recognize the disease; the manifestations are similar to the symptoms of many diseases; sometimes rhabdomyolysis occurs secretly. Often the correct diagnosis can only be made based on the results of a blood test. In an advanced form, the patient may fall into a coma and die.
Treatment of chronic myositis
The acute form of myositis that is not completely cured becomes chronic. Chronic muscle inflammation is also characteristic of spinal diseases such as osteochondrosis, arthrosis, and vertebral hernia. Therapeutic measures are usually carried out at the time of exacerbations. The medications used are the same as for acute myositis. The main emphasis is on means that eliminate the cause of the development of pathology. These are mainly drugs to combat inflammation and autoimmune disorders.
For chronic forms of the disease, it is recommended to keep a set of medicinal plasters in stock. The patches are effective for pain and inflammatory processes in the tissues of the musculoskeletal system. They release biologically active substances to the body within 12 hours, providing a warming, analgesic effect, increasing blood circulation, and preventing the further development of inflammation.
Drug therapy is supplemented with physiotherapeutic procedures, physical exercises, and massage. Patients are prescribed a special diet. For effective rehabilitation and prevention of relapses, sanatorium treatment is encouraged.
Features of myalgia
Pain emanating from the muscles is usually deep6. Acute myalgia is protective in nature because it causes reactions aimed at eliminating the damaging factor11. Such reactions include, for example, muscle spasms4. But despite its protective nature, there is almost always a risk that the pain will become chronic11. There are 2 main causes of chronicity:
- Increased sensitivity. In response to irritation, the muscle releases substances that support inflammation. They further irritate pain receptors in the muscles. In response to frequent signals, the central nervous system lowers the pain threshold, so we can feel soreness in the muscle even when it is not strongly irritated11.
- Spasm. If pain and spasm persist, a “vicious circle” is formed: pain causes spasm, and spasm maintains pain1,5, 11.
Features of therapy in pregnant women
Myositis develops during pregnancy for two reasons: against the background of an infectious disease and due to increased load on the back muscles as a result of weight gain.
The difficulty of treatment is the fact that a limited list of medications can be used during pregnancy. Most analgesics and anti-inflammatory drugs have a wide range of side effects and contraindications. The active substances from their composition can penetrate the placenta to the fetus and cause harm and have a negative impact on development. The doctor must take into account the duration of pregnancy, the peculiarities of its course in the patient, and correlate the risks of taking medications with the effect of treatment.
To relieve inflammation and reduce fever, medications containing paracetamol are mainly prescribed. Creams and ointments based on herbal ingredients are suitable for local anesthesia and relief of muscle spasms. It is prohibited to use ointments containing animal and insect poisons.
To relieve pain, dry heat and light massage procedures are suitable. For preventive purposes, it is recommended to avoid sudden weight gain, use a bandage in the third trimester, and perform special exercises for pregnant women.
Injuries
Severe pain can occur when muscle fibers and tendons are torn. This usually happens if the load is excessive and the muscles are not prepared for it1. But they can also be damaged by sudden movements3. Unlike “ache” due to muscle overwork, pain due to injury occurs immediately, at the peak of the load3.
It should be remembered that even a small, but untreated injury can cause an even more severe sprain3. Therefore, if you experience pain during physical activity, be sure to consult a doctor to rule out a serious injury.
to come back to the beginning
Nutrition for myositis
The diet should consist of nutritious but easily digestible dishes. Foods high in vitamins A, B, C, D, E, PP help fight inflammation. The daily menu should include:
- fresh vegetables and herbs;
- sweet and sour fruits - oranges, apples, plums, kiwi;
- foods rich in salicylates - honey, vegetable oils, legumes, nuts, black and green tea, peppers;
- boiled and stewed beets, carrots, potatoes;
- decoctions of beneficial herbs;
- sea fish.
In addition to clean water, it is recommended to consume more vitamin drinks: juices, fruit drinks, homemade compotes. The total volume of liquid should reach 2 liters.
For spasmodic pain, it is recommended to include foods rich in calcium, magnesium, and zinc in the diet. These elements are found in cereals, dairy products, green crops, liver, pumpkin, and chicken eggs.
Prevention of myositis
You can exclude recurrent manifestations of myositis if you pay attention to prevention:
- harden the body, often walk in the fresh air, regularly ventilate the room, conduct contrasting douches with cool and warm water;
- sunbathing, swimming in natural reservoirs in the warm season;
- avoid drafts, protect the body from hypothermia, dress according to the weather;
- exercise in moderation, avoid unnecessary stress on the muscles, start with warm-up exercises;
- when working in an uncomfortable position, take short breaks, perform warm-up exercises for stiff and tired muscles;
- Regularly use the services of a massage room, do a general preventive massage for all muscle groups, massage the back or collar area.
The myositis treatment program includes drug treatment, exercise therapy, physiotherapy, and dietary nutrition. Following the doctor’s recommendations and giving up bad habits speeds up recovery and serves as a preventive measure against relapses.
Causes of the disease
Common ways you can develop inflammation are working in drafty areas, or having a viral disease in someone you are in close contact with. But being constantly surrounded by people and visiting public transport cannot guarantee your safety from myositis of the back muscles. Symptoms that do not appear immediately play a cruel joke on us. The process of treating a disease directly depends on its cause. It could be:
- infection that is transmitted by airborne droplets;
- heavy physical activity on any part of the body;
- sudden change in body temperature;
- frequent injuries at work and at home.