Hypertrophy of the labia minora is their excessive protrusion beyond the labia majora. With lateral extension, their length exceeds 4-5 cm. This phenomenon is not pathological and does not pose a threat to women’s health, except perhaps psychologically. This is, rather, a cosmetic defect, and even then within the framework of individual criteria of beauty and sexuality. However, correction of the labia minora is one of the most common operations in the field of aesthetic surgery related to the genitals.
Why are the labia minora needed?
The labia minora (labia minora pudendi) is a pair of thin longitudinal mucocutaneous folds located in the genital cleft medially from the labia majora. The MPG surround the entrance to the vagina, connecting in front, forming the frenulum and clitoral hood, connecting at the back, forming the frenulum of the labia.
The labia minora are an erogenous zone; they cover the entrance to the vagina and the external opening of the urethra, protecting the vagina and urethra from infection, and direct the stream of urine away from the genitals.
Back to contents
Filling with lipofilling
With a deficiency of subcutaneous fat, the opposite picture is observed - the skin is flabby, inelastic, and lacking in volume. The injection of the patient’s own fat helps literally fill the genitals with life. First, fat is collected from donor areas (abdomen, thighs) and injected into the labia majora.
All labiaplasty operations are performed under local anesthesia (intravenous sedation is also possible)!
WE ALSO ADVISE YOU TO READ: Passion for sports and exercise equipment contributes to an increase in the number of intimate plastic surgeries
Variants of the structure of the labia minora
The labia are an intimate (hidden) part of the body. There are no generally accepted canons of beauty in this area, and yet, the sexual attractiveness of this area is of great importance to many women and their partners.
From an aesthetic point of view, it is generally accepted that in a standing position, the labia should be visible, slightly protruding beyond the edge of the labia majora. The normal length of the MPG (from base to edge) should be no more than 4 cm.
From a medical point of view, hypertrophy, elongation and asymmetry of the labia minora are distinguished.
MPG hypertrophy
With hypertrophy, there is thickening of the walls, increased folding and elongation. The labia minora are enlarged evenly and symmetrically throughout.
MPG elongation
Elongation is lengthening without thickening; more often there is a lengthening of the middle part of the labia minora. Elongation can be congenital or acquired.
Reasons for MPG elongation
- Heredity;
- Prematurity (the labia majora do not cover the labia minora);
- Masturbation;
- Age-related atrophic changes;
- Age-related atrophic changes;
- Traumatization (childbirth, horse riding, cycling, masturbation);
- Constitutional features (asthenic body type).
PGM asymmetry
Asymmetry of the labia minora can be congenital or acquired (trauma during childbirth, inflammatory changes, errors during plastic surgery). Asymmetry is considered to be both asymmetrical lengthening or shortening, as well as normal development of one labia and lengthening or underdevelopment of the opposite one. Asymmetry includes various types of post-traumatic deformities.
Traumatic deformation with the formation of a defect
Back to contents
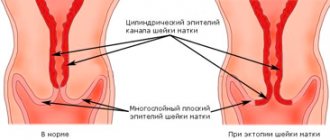
Disease concept
It is considered normal if the large lips completely cover the small lips. When the reverse structure is observed, hypertrophy of the labia minora is diagnosed.
In addition, with this disorder, asymmetry and differences in shape and color are often pronounced. This problem not only causes unpleasant physical sensations, but also causes emotional discomfort.
Classification
Plastic and aesthetic surgery has its own classification of pathology localized in the vulva, which is generally accepted and is used to determine the feasibility and method of correction through surgery.
Classification based on the degree of growth:
- The size of the labia minora practically does not differ from the norm, and the increase is no more than 2 cm. But it is important to take into account that with a normal anatomical structure, the major lips of the genitals should completely cover the minor lips.
- The growth ranges from 2 to 4 cm from the normal size. With such an anatomical disorder, certain difficulties already arise. A woman experiences discomfort when moving and performing hygiene procedures.
- Enlargement of the labia from 4 to 5 cm from normal. Such an anatomical defect is significant, as it causes a lot of discomfort and problems. This degree of hypertrophy of the labia is the basis for their correction by labiaplasty - surgical intervention.
- The size exceeds the norm by 6 or more centimeters. This degree of anatomical change is extremely rare. With this pathology, intimate life is significantly complicated by psychological and physiological discomfort. Usually a woman is embarrassed about her body, avoids sexual contacts, and has many complexes. At this degree of impairment, surgical intervention is mandatory.
Often, the genitals not only grow, but their asymmetry also develops, which causes the woman even more aesthetic discomfort.
Types of deviations in the anatomical structure of the labia according to:
- the nature of the surface - folds, increased pigment formation, scars and scarring;
- size – enlarged, elongated, completely absent;
- shape - normal or asymmetrical.
Indications for labiaplasty
The operation is carried out for medical and aesthetic reasons (the woman’s desire).
Medical indications
Medical indications include situations when a woman complains of physical discomfort:
- Asymmetry of the labia;
- Congenital or acquired deformities of the labia;
- Discomfort when wearing underwear and playing sports;
- Pain and discomfort during sexual intercourse;
- Psychological complexes - “Locker room syndrome”.
Aesthetic indications
For aesthetic reasons, the operation is performed for asymmetry, elongation and deformation of the labia minora, as well as if a woman wishes to correct their shape and size.
Back to contents
Contraindications to intimate plastic surgery
- Pregnancy and lactation;
- Oncological diseases;
- Mental illnesses;
- Diabetes;
- Decompensated chronic diseases of internal organs;
- Acute infectious diseases;
- Bleeding disorders, treatment with anticoagulants;
- Acute inflammatory diseases of the female genital organs and exacerbations of chronic ones;
- Minor age.
Labiaplasty for aesthetic reasons is not recommended for women planning childbirth. During childbirth, there is a high probability of ruptures in the area of postoperative scars, and repeated plastic surgeries are complex and the expected effect is difficult to predict.
Absolute contraindications to labiaplasty for aesthetic reasons are conditions, diseases and genetic factors that prevent a positive result:
- Genetic predisposition to the formation of rough colloidal scars;
- Collagenoses are immunopathological processes characterized by systemic disorganization of connective tissue (Marfan syndrome, lupus erythematosus, scleroderma, rheumatism).
Keloid scar on the skin
Back to contents
Contouring of the labia minora
In addition to surgical methods, volume-forming methods are widely used - injection of dermal fillers (fillers), correcting the appearance (contour) of the labia, the so-called intimate contour plastic surgery. Fillers with hyaluronic acid, plasmagel, and own fat are used as fillers. The method is mainly used to increase volume.
Contour plastic surgery with hyaluronic acid (HA) fillers
The effect is achieved due to the hydrophilicity of hyaluronic acid. The HA molecule increases in volume 1000 times, binding up to 500 water molecules. HA is found in large quantities as a component of the extracellular matrix in connective tissue, skin, cartilage, fascia and ligaments.
In addition to cosmetic benefits, hyaluronic acid has an anti-inflammatory and moisturizing effect, which is used to improve tissue nutrition during atrophic processes. Since hyaluronic acid is actively degraded by enzymes, the effect of the procedure is temporary; re-introduction of fillers is required after 8-12 months.
Contour plastic surgery with plasmogel
Plasmogel is made from the patient’s blood plasma and is an autologous coagulated protein. The method is a continuation of the intimate plasma lifting method
Blood plasma contains growth factors, proteins, enzymes and platelets. Plasma causes pronounced stimulation of blood supply and regeneration of connective tissue (biorevitalization) at the injection site, which is used to treat atrophic and degenerative changes. The effect is also temporary, but unlike HA, it is cumulative.
Labia augmentation points
Lipofilling and liposuction
Lipofilling is a method of enlarging the labia majora and labia minora using your own fat. Unlike hyaluronic acid, the effect is longer lasting.
Liposuction is the removal of fatty tissue from the labia majora in order to reduce their size. Lipofilling and liposuction are usually performed by plastic surgeons because they have the appropriate tools and equipment in their arsenal.
Back to contents
Internal genital organs
The internal genital organs are located in the pelvic cavity and are fixed there by muscles, ligaments and connective tissue fascia.
1- vagina. 2- cervix. 3- uterus. Uterine appendages: 4- fallopian tubes. 5- ovaries.
Vagina
The vagina is an easily extensible muscular organ, which is a tube 7–8 cm long. In the upper part, the vaginal walls are attached to the cervix. The vagina has anterior and posterior walls, which are bordered by the bladder, urethra and rectum.
Uterus
The uterus is a hollow, pear-shaped muscular organ consisting of two parts: the body and the cervix. The body of the uterus is “suspended” in the center of the pelvis. In front of it is the bladder, behind it is the rectum. The figure shows that in cross-section the uterine cavity is a triangle, with its apex facing downwards. There are two holes in the upper corners - left and right. These are the openings of the fallopian tubes. Through the orifice, the uterine cavity is connected to the fallopian tubes, and through them to the abdominal cavity.
The walls of the cavity are lined with a layer of mucous tissue - the endometrium. During the first half of the menstrual cycle, under the influence of sex hormones, the endometrium is prepared to receive a fertilized egg, but if fertilization does not occur, the uterine lining is rejected. This process is accompanied by bleeding - menstruation. The uterus is essentially a receptacle for fetuses. It is here that a fetus develops from a fertilized egg.
Pathological formations of the uterine cavity (polyps, fibroids, adhesions, etc.) disrupt the physiological processes of embryo implantation, leading to infertility and miscarriage. Pathological formations of the uterine cavity are removed by hysteroscopy.
Cervix
The cervix of the uterus (c.m.) has a cylindrical shape (for those who have not given birth, it is conical) and partially protrudes into the vagina (the vaginal part of the c.m.). In the center of the cervix there is a spindle-shaped canal - the cervical canal (cervical canal). The upper end of this canal opens into the uterine cavity - the internal os. The lower opening opens into the vagina - the external os. The cervical canal connects the vagina and the uterine cavity.
The mucous membrane of the cervical canal has glands that secrete viscous mucus, which is a mucus plug. Cervical mucus is a barrier to “biological debris” (the bodies of dead cells, bacteria, etc.) into the uterine cavity. During childbirth, the vagina, together with the cervical canal, forms the birth canal through which the fetus moves outward.
The cervix is fixed in the pelvic cavity due to the ligamentous apparatus: uterosacral and cardinal ligaments. The pubocervical and rectovaginal fascia are attached to it - supporting structures for the walls and vaults of the vagina, bladder and rectum. Damage to the ligamentous apparatus leads to prolapse of the pelvic organs - pelvic organ prolapse.
The fallopian tubes
Fallopian tubes (t.t.) are paired, hollow muscular formations, about 13 cm long. The end of the tubes adjacent to the ovary expands in the form of a funnel with fringed edges. The inner surface of the pipes is covered with mucous tissue having cilia. The cilia are in constant motion and, together with the peristaltic contractions of the tube itself, help the egg move from the ovary to the uterus. Thus, the main function of m.t. – transport.
Ovaries
The ovaries (there are two of them: left and right) are the gonads. The ovaries are located on the sides of the uterus and are in contact with the fimbriae of the fallopian tubes. The main function of this gland is the production of eggs and sex hormones. From birth, they contain a huge number of follicles - microscopic vesicles with eggs.
At the beginning of the menstrual cycle, in one of the ovaries (rarely in two), simultaneously 25-40 follicles begin to increase in size and fill with fluid - “ripen”. Only one of them will ripen, rarely two.
Under pressure from the enlarging follicle, the thinned wall of the ovary tears, the follicle bursts, and the egg exits to the fallopian tube. If circumstances are favorable, sperm are waiting for her here. The fusion of the egg with the sperm occurs - fertilization, and then it is transported through the tube into the uterine cavity. Read more about this here.
Unlike men, whose abdominal cavity is isolated from the external environment, in women, sperm can enter the abdominal cavity through the genitals.
Unfortunately, pathogenic microbes penetrate there in the same way, causing inflammatory processes not only in the genitals, but also in the abdominal cavity itself. As a result, complications can develop, ranging from infertility to organ loss.
The best prevention of such situations is the use of a condom (barrier method of contraception), a regular sexual partner and preventive examination of the married couple for sexually transmitted diseases (STDs).
Mammary gland
Mammary glands (m.g.), paired skin formations on the anterior surface of the chest. In the center of the gland there is a nipple around which there is a circle of pigmented skin - a halo. The gland consists of lobules of glandular tissue with milk ducts (canals) and adipose tissue. The channels, connecting with each other, form excretory ducts that open on the nipple of the mammary gland. The growth of the mammary glands and their secretory function are activated by hormones of the ovary and pituitary gland.
The final development of m.f. occurs only after feeding a newborn. Breastfeeding is a powerful prevention of breast cancer, and the period of breastfeeding should last at least 8 months. At this age, the child begins to be given his first complementary foods.
Examination and preparation before labiaplasty
At the first visit to the doctor, it is clarified whether there are indications for plastic surgery, whether there are associated problems in this area and contraindications to the operation. The patient's complaints and especially the wishes regarding the size and shape of the labia are clarified in detail.
A woman is advised to formulate her desires in advance, since most people find it difficult to explain what worries them and how they imagine the final result of the correction.
In order to evaluate the results of treatment, before and after surgery, photographs of the labia are taken in standing and supine positions.
After getting acquainted with the problem, an examination is performed on a gynecological chair, during which the method of correction is determined, an informed consent for surgical intervention is signed, and a preoperative examination is prescribed. Based on the results of the examination, a second consultation is held, at which the date of the operation is set.
Examination before intimate plastic surgery and expiration dates of tests
Valid for 6 months:
- Fluorography.
Valid for 3 months:
- Blood test for HIV (AIDS);
- Blood test for RW (syphilis);
- Blood test for hepatitis B and C viruses;
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs;
- Cervical smear for oncocytology.
Valid for 1 month:
- Blood group and Rh factor.
- Clinical blood tests;
- General urine analysis;
- Biochemical blood tests (sugar);
- ECG with consultation with a therapist.
Valid for 10 days:
- A smear to determine the degree of vaginal cleanliness (if infections and inflammation are detected, treatment is indicated).
Based on the results of the preoperative examination, a second consultation is carried out, the date of the operation and preoperative preparation are set.
Preparation for labiaplasty
- Stop sexual intercourse two days before surgery.
- The day before the procedure, cut or shave the pubic hair, labia and perineum short.
- On the eve of the intervention, go to bed no later than 22:00. You can take a sedative: tinctures of motherwort, peony, valerian, etc., according to the instructions included with the medications.
- In the morning, on the day of surgery, empty your bowels, take a shower and thoroughly clean the external genitalia, and put on clean knitted underwear.
- Hunger – last meal three hours before surgery.
- Immediately before the procedure, empty your bladder.
- HAVE WITH YOU:
- Referral for surgery, examination results (ultrasound and tests).
- A clean shirt (robe) and socks, sanitary pads, slippers. Leave jewelry (earrings, rings, etc.) at home.
Back to contents
Rehabilitation process
How effective the surgical intervention will be directly depends on whether the entire range of additional procedures is carried out during the recovery period. In most cases, rehabilitation after labiaplasty includes the following therapeutic and restorative measures:
- daily douching with antiseptic drugs;
- applying wound healing preparations to the sutures that are specially designed for the care of postoperative sutures;
- a ten-day course of antibiotics prescribed by your doctor.
- In addition, to avoid damage to the operated epithelium and possible bleeding, the girl should take care to:
- For 2 - 3 weeks, sit less and avoid wearing tight-fitting underwear;
- Avoid any damage to the external genitalia,
- Avoid hot water treatments and sunbathing for 2 or 3 weeks;
- Avoid swimming in public pools and natural bodies of water for a month;
- Avoid intimacy and masturbation for a month;
- Postpone sports activities for 3 weeks.
Experience shows that if all the listed tips and recommendations are followed, healing in the operated area occurs quickly and without complications.
Complications of labiaplasty
The anatomical norm and physiological function require that the labia minora cover the entrance to the vagina and the external opening of the urethra. Excessive resection of the lips leads to disruption of the barrier function, which in turn leads to negative consequences - chronic inflammation of the vaginal opening, chronic urethritis and cystitis. As a result, a woman experiences pain during intimacy, which is why she is forced to avoid sexual intercourse.
Changing the natural appearance of the external genitalia causes psycho-emotional discomfort in the woman and her partner. It is extremely difficult to correct this situation, since there is no supply of tissue for plastic surgery. To form the MPG, skin has to be cut out from the labia majora, and the final result is difficult to predict.
Gaping of the vaginal opening as a result of excessive resection
Back to contents
Surgical treatment
Treatment can only mean surgical correction of overgrown tissues of the external female intimate organs. This is explained by the fact that any other treatment methods are simply unable to bring any obvious and lasting results. The reasons for prescribing surgical intervention are considered to be:
- Unaesthetic appearance of the external intimate organs, associated with the growth of the labia minora by more than 5 centimeters.
- The third and fourth stages of development of the disease bring the patient significant physical discomfort, which has a negative impact on her quality of life, physiological and emotional state.
In the presence of advanced stages of the disease, the risk of damage to the external genital organs during active physical exercise, sexual activity, or during childbirth increases significantly. To avoid all the problems listed above, the attending gynecologist can refer a patient with an overgrowth of the lower intimate lips for surgical treatment.
Plastic surgery of the labia, aimed at correcting their size, will relieve the girl of all problems associated with the growth of external intimate organs. Surgical intervention is performed by excision of the overgrown area of the labia, which is performed using a laser or scalpel.
These manipulations are performed under local anesthesia or sedation. The patient may be offered anesthesia in the form of injection or application of a special anesthetic cream to the site of surgical adjustment. After removing the overgrown labia, sutures made of easily absorbable modern medical threads will be placed on the surface of the external intimate organ. Typically, the operation time ranges from 30 minutes to one hour.
Where to go, to whom to surrender?
This is truly a fateful question; I’ll take this opportunity to put in a word for my fellow gynecologists. In Krasnoyarsk, surgeries on the labia are performed by plastic surgeons, operating gynecologists, urologists, dentists, I even know one ophthalmologist, and there are probably representatives of other specialties. To be honest, everything is decided by experience, “golden hands” and trusting relationships.
Experience is the amount of things seen, studied, done. Regarding what we have seen and studied, practicing gynecologists are unrivaled. Regarding what has been done, we can say that each surgeon had his first patient, successes and failures.
Whoever you choose as a surgeon, to exclude diseases of the genital organs, clarify medical indications and contraindications, consult a gynecologist before the operation!
Back to contents
They have become larger: what to do?
When changing sizes, you should not immediately rush to plastic surgeons. And also you shouldn't panic. First, try to figure out the reasons for such changes yourself. Women's labia can become larger for various reasons. First of all, the following is recommended.
- If a girl experiences discomfort when putting on panties, then it is worth purchasing more comfortable or high-quality underwear. It is advisable to choose underwear made from natural materials, such as cotton.
- If a girl very often satisfies herself by stimulating the clitoris with her hand, then it is worth temporarily stopping such practices. You can, for example, replace finger stimulation with a dildo or dildo.
- You also need to comply with all intimate hygiene requirements.
- Swelling of the lips is not normal, so it is worth visiting a gynecologist for an examination for gynecological problems. As well as cancer and skin diseases. In this case, you can do an analysis of hormone levels.
What determines the price of intimate plastic surgery?
The operation involves an operating team, and collective labor cannot be cheap. If we omit this component, the price of labiaplasty will be influenced by the following factors:
- Type and method of intimate plastic surgery;
- The degree of technical complexity of this clinical case;
- Cost of consumables (suture material, fillers, surgical instruments), the better they are, the more expensive they are;
- Type of anesthesia (anesthesia or local anesthesia);
- Surgeon's qualifications;
- Pricing policy of the clinic.
Back to contents
Postoperative period and recommendations
To prevent early complications, immediately after surgery, bed rest is prescribed for 3–6 hours. After 3-6 hours, after examining the stitches, the doctor sends the patient home with the following instructions:
- Take prescribed medications;
- Appear for examination 7-10 days after surgery;
- Avoid sexual intercourse, baths, saunas, and physical activity for 6-8 weeks;
- Perform hygienic toileting twice a day;
- If you have any complaints, consult a doctor immediately.
The result of the operation is assessed after four weeks. By this time, the swelling of the tissues subsides, the labia are leveled and acquire the expected shape and size.
The final healing of the labia minora is completed in 8-10 weeks, by which time restrictions are lifted, including exercise and sexual activity.
Make an appointment