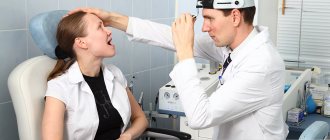
Hypertrophic pharyngitis is one of the varieties of the chronic form of the disease. It usually begins to appear 6-8 months after acute inflammation was diagnosed, which was not properly treated. The hypertrophic form of pathology affects not only the posterior wall of the pharynx, but also its lateral parts.
With pathology, the mucous membrane of the pharynx not only becomes thicker, but its density also increases. These changes are pathological, and as a result, it begins to function incorrectly and becomes inflamed. Also with this disease, the appearance of lymphoid granules is noted, which look like pink grains. The disease can appear in people of any age, but more often affects adults, since they often do not properly treat the acute form of the disease and suffer it on their feet. Gradually, disruption of the pharyngeal mucosa can also spread to the uvula. Hypertrophic pharyngitis symptoms increase as the damage to the mucous membrane progresses.
Causes
The disease develops against the background of the fact that negative factors cause excessive activity of the immune system, due to which it begins to provoke the development of a number of neoplasms on the mucous membrane, associated with the detection of even minor pathogens. As a result, inflammation develops and tissue changes occur. The main factors causing hypertrophic pharyngitis, in addition to its advanced acute form, are the following:
- living in areas with unfavorable environmental conditions;
- working in hazardous industries in violation of safety rules;
- long regular stay in a room in which the air is very dry and warm;
- smoking – not only active but also passive smoking has a negative effect on the mucous membrane and the body as a whole;
- abuse of alcoholic beverages - even not strong ones, they irritate and damage the tissues of the pharynx, making them more susceptible to pharyngitis;
- diseases of the cardiovascular system, in which blood circulation in the tissues of the pharyngeal mucosa is disrupted, as well as those that lead to congestion in the respiratory system;
- serious metabolic disorders, especially against the background of pathologies of the endocrine system;
- regular occurrence of allergies;
- disturbances in the structure of the pharynx;
- constant significant lack of vitamins.
Chronic pathologies of the nasopharynx, such as tonsillitis, sinusitis and rhinitis, can also cause the disease. Pathogenic bacteria will abundantly penetrate the mucous membrane and remain dormant in it until factors unfavorable for the immune system appear. When they develop an exacerbation of the disease.
What diseases cause the throat to turn red?
Pharyngitis, or inflammation of the pharynx, is one of the most common causes of redness of the throat. The disease can occur acutely or chronically1.
Acute pharyngitis
In 70% of cases, it accompanies ARVI and is more often associated with rhinovirus infection, which is especially common in the autumn2. In addition, influenza viruses, parainfluenza, adenoviruses, and respiratory syncytial virus can cause inflammation.
With viral pharyngitis, the throat looks red, “dry”, and the main complaints are soreness, dryness and pain in the throat, causing an obsessive superficial cough. The general condition depends on the nature of ARVI.
Viral inflammation often paves the way for bacterial infection2 caused by staphylococci, streptococci, neisseria, chlamydia, mycoplasma1. Bacterial pharyngitis is usually purulent and is characterized by an increase in temperature to 38°C or higher, and the appearance of purulent sputum.
Attention! Pharyngitis can be one of the first manifestations of “childhood” infections: measles, scarlet fever, rubella2. In adults, these infections are often severe and lead to complications2. Only a doctor can make the correct diagnosis.
In addition to viruses and bacteria, the cause of acute pharyngitis can be:
- allergic reactions1,2;
- diseases of the digestive system, in which the acidic contents of the stomach are thrown into the esophagus and pharynx (this includes cardial insufficiency and reflux esophagitis)1,2;
- tumor formations of the pharynx, including malignant1;
- specific infectious and inflammatory diseases (syphilis, tuberculosis, candidiasis)1.
Up to contents
Chronic pharyngitis
Its development can be caused by 3:
| Frequent colds | recurrent (repeating) acute respiratory diseases, which affect the upper respiratory tract and impair nasal breathing: rhinitis, sinusitis, adenoiditis |
| Gastropharyngeal reflux | periodic reflux of stomach contents into the esophagus and pharynx |
| General diseases | diabetes mellitus, renal and liver failure, immunodeficiency states3 |
Chronic pharyngitis can occur in three forms: catarrhal, hypertrophic and atrophic3.
With catarrhal inflammation, the throat is red, swollen, and there is discomfort: pain, soreness, tickling, sensation of a foreign body in the throat3.
Hypertrophic pharyngitis leads to thickening of the mucous membrane and proliferation of lymphoid formations. The walls of the pharynx become red, moist, and covered with a network of dilated blood vessels. Discomfort in the throat may be accompanied by a feeling of a foreign body in the throat and stuffy ears3.
Atrophic processes associated with tissue malnutrition are accompanied by thinning of the pharyngeal mucosa. Upon examination, it looks “dry”, “tight”, “granules” of lymphoid tissue rise above the general surface. The main complaints are dry throat and a dry, superficial cough that occurs at the slightest irritation of the respiratory tract3.
By the way, the development of atrophic pharyngitis is sometimes associated with frequent and prolonged instillation of vasoconstrictor drugs into the nose. Flowing into the nasopharynx, these drugs cause spasm of blood vessels, impair the nutrition of the mucous membrane and provoke its atrophy3.
Chronic pharyngitis is not common in children. Its development is facilitated by postnasal drip - the flow of mucus into the throat from the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses. In this case, wheezing, reminiscent of bronchial asthma, may appear. Special examination helps to exclude the disease2.
A chronic inflammatory process in the pharynx weakens its protective functions and predisposes to frequent acute respiratory viral infections. Exacerbation of pharyngitis is facilitated by hypothermia of the throat in winter, inhalation of hot steam and air during inhalation, in a bath or sauna, consumption of hard, hot and spicy, excessively sweet and salty foods, alcoholic beverages, etc.3.
Up to contents
Kinds
This form of the disease can have two types. Depending on which of them is diagnosed, the exact treatment method is determined. Granular hypertrophic pharyngitis affects only the back wall of the pharynx. With it, tissue swelling is not felt so much at the onset of the disease, which is why not all patients seek medical help in a timely manner.
Lateral hypertrophic pharyngitis is manifested by more acute pain and difficulty breathing. It is extremely difficult to ignore it for a long time, which is why treatment most often begins on time. The diagnosis is made after examining the patient's pharynx.
Symptoms of laryngeal cancer
There are no common signs for laryngeal cancer
, they are determined by the parameters of the tumor, its position, and growth rate. At the very beginning, it is sometimes difficult to notice a malignant formation.
Common symptoms of throat cancer
relate:
- pain in the throat, including when swallowing,
- sore throat,
- frequent bronchitis,
- hoarse voice,
- changes in the shape of the neck (swelling),
- a sharp decrease in body weight,
- discomfort in the ears.
Forecast
With timely, complete and systematic treatment of the disease, the prognosis for the patient is favorable. In this case, it is possible to stop pathological changes in the mucosal tissues. After quality therapy, exacerbations of the disease are extremely rare.
If treatment is started late, when the throat lesion is already quite serious, then the prognosis for the patient is relatively positive, since it will not be possible to ensure a long remission, but at the same time the risk of complications will be eliminated.
Diagnosis of laryngeal tumors
Methods for diagnosing throat cancer
:
- throat examination,
- palpation,
- fibrolaryngoscopy – a piece of tissue is taken with a special instrument, hard-to-reach areas of the throat are examined,
- a separate point should be the cytological and histological examination of samples taken from the throat,
- computed tomography is used to look at cartilage,
- MRI is necessary to study the folds, subglottic region and other parts,
- Ultrasound of the lymph nodes of the neck and liver is necessary if there is a danger of metastases spreading there.
What not to do
During the treatment period there are certain restrictions, by violating which the patient risks significantly aggravating his condition. The doctor will not be able to guarantee the patient a positive result of therapy if the following actions are allowed:
- smoking during treatment;
- use of alcohol preparations for gargling;
- eating spicy food;
- staying in a dusty room;
- violation of medical instructions regarding treatment.
If there are no violations in the course of therapy, then it is possible to stop the disease at the beginning of its development without the use of surgical methods of therapy. Treatment of hypertrophic pharyngitis in adults and children is the same.
Treatment of laryngeal cancer
There are two treatment options for throat cancer
– surgery and conservative treatment. A specific method is selected based on a combination of factors, primarily the location and size of the formation. Radiation and chemotherapy are often used initially. In most cases, in the first stages, conservative treatment gives positive results, and the larynx continues to function fully.
throat cancer treatment
Sometimes surgery may be necessary; now, for small tumors, only a small part of the larynx is cut out; in case of serious damage, the entire organ must be removed. Then you will need to restore your voice; exercises will have to be done for at least 2 months.
After recovery, it is necessary to be under the supervision of a doctor for several more years, as there is a possibility of relapse and all kinds of complications. During treatment, you should eat food rich in vitamins and microelements. You should avoid sweets, spices, spicy, fried, salty foods, because such foods affect the larynx.
Diagnostics
Only an external examination of the pharynx is not enough to identify not only the disease itself, but also the causes of its occurrence, as well as the condition of the body. Because of this, the doctor, having identified pharyngitis by eye during the initial examination, necessarily prescribes further tests to the patient, which help to obtain a complete picture of the health condition and select the most effective treatment.
1. A swab from the pharynx followed by inoculation on a nutrient medium. It is necessary to determine the composition of pathogenic microflora and its sensitivity to certain antibiotics.
2. Biochemical blood test. It requires venous blood. The study reveals the presence of antibodies to certain inflammatory agents, hormonal parameters and the presence or absence of malignant cells.
3. Clinical blood test. Blood from a finger is used. Shows the percentage of the ratio of its main components. Deviation of one or another up or down makes it possible to detect a number of pathologies.
4. General urine analysis. The study of the material allows you to accurately assess the severity of inflammation in the body, as well as whether there are any disturbances in the functioning of the kidneys against its background.
5. Biopsy of tissue of the pharyngeal mucosa. Not always prescribed. The procedure is necessary if there is a suspicion of the development of a cancer process. When examining a tissue sample, the presence or absence of malignant (cancerous) cells in the mucosa is determined.
If necessary, an electrocardiogram and x-ray of the sinus area may also be prescribed. These procedures are rarely required. They are usually carried out if complications of the disease begin to develop. In young children, an X-ray of the lungs may also be necessary, since quite often, against the background of inflammation of the larynx, pneumonia or bronchopneumonia appears quickly enough.
Types of laryngeal tumors
How to tell if you have throat cancer
? Tumors of the larynx can be divided depending on their location in certain parts of the larynx.
types of laryngeal tumor
Vestibular cancer
One of the most aggressive types of cancer, it develops very quickly, metastases occupy nearby organs and enter the lymph nodes. This type of laryngeal cancer is very common, you need to pay attention to the discomfort when swallowing, it seems that there is a foreign body inside. Sore throat with enlarged tumor becomes severe over time. In the future, pain is felt in the ears, pain is felt while eating.
Midsection cancer
This is one of the easiest types of throat tumors
, it does not cause much pain, since there are few lymphatic vessels here, metastases rarely occur. A clear symptom of such cancer is a hoarse voice, because the vocal folds do not close tightly due to the tumor. Subsequently, the folds may become completely immobilized, and the voice will disappear completely. Breathing problems may also occur. When enlarged, the tumor can penetrate into neighboring areas.
Subglottic cancer
This type of laryngeal cancer is quite rare, accounting for about 2% of all cases. Such a tumor is characterized by an endophytic form of development; it is formed in the vocal fold, so soon the voice becomes hoarse, and sometimes it becomes difficult to breathe. The tumor affects the first rings of the trachea.
Often, patients are diagnosed with a combination of lesions in several parts of the larynx.