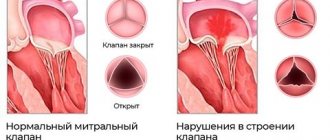
Medicines for ischemic heart disease
A cardiologist may recommend drug therapy if lifestyle changes seem insufficient. Medicines are prescribed only by the attending physician. Most often, drugs are prescribed that reduce the risk of thrombosis (aspirin, Plavix). Statins can be prescribed long-term to lower cholesterol levels. Heart failure should be treated with drugs that improve the function of the heart muscle (cardiac glycosides).
- Aspirin
In those with no history of heart disease, aspirin reduces the likelihood of a heart attack but does not change the overall risk of death. It is recommended only for adults who are at risk of developing blood clots, where increased risk is defined as “men over 60 years of age, postmenopausal women and young people with a background risk of coronary artery disease (hypertension, diabetes or smoking).
- Antiplatelet therapy
Clopidogrel plus aspirin (dual antiplatelet therapy, DAAT) reduces the risk of cardiovascular events more than aspirin alone. These drugs are contraindicated in patients with a history of gastrointestinal ulcers or gastric bleeding. Antiplatelet therapy should be carried out for life.
- β-blockers
Adrenergic blockers reduce heart rate and myocardial oxygen consumption. Studies confirm an increase in life expectancy when taking β-blockers and a decrease in the incidence of cardiovascular events, including recurrent ones. β-blockers are contraindicated in case of concomitant pulmonary pathology, bronchial asthma, COPD.
- β-blockers with proven properties of improving the prognosis of coronary artery disease:
- Carvedilol (Dilatrend, Acridilol, Talliton, Coriol).
- Metoprolol (Betalok Zok, Betalok, Egilok, Metocard, Vasocardin);
- bisoprolol (Concor, Niperten, Coronal, Bisogamma, Biprol, Cordinorm);
- Statins
Drugs in this group reduce cholesterol levels in the blood by reducing its synthesis in the liver, or inhibit the absorption of cholesterol from food, affecting the causes of atherosclerosis. Medicines are used to reduce the rate of development of existing atherosclerotic plaques in the walls of blood vessels and prevent the formation of new ones. There is a positive effect on the degree of progression and development of symptoms of coronary heart disease, on life expectancy, and these drugs also reduce the frequency and severity of cardiovascular events, possibly helping to restore the lumen of the vessel. The target cholesterol level in patients with coronary artery disease should be lower than in persons without coronary artery disease and equal to 4.5 mmol/l. In blood tests, the target LDL level in patients with coronary artery disease should be no more than 2.5 mmol/l. Lipid levels must be measured every month. Main drugs: lovastatin, simvastatin, atorvastatin, rosuvastatin.
- Fibrates
They belong to a class of drugs that increase the antiatherogenic fraction of lipoproteins - HDL, with a decrease in which mortality from coronary artery disease increases. Used to treat dyslipidemia IIa, IIb, III, IV, V. They differ from statins in that they reduce triglycerides and can increase the HDL fraction. Statins primarily reduce LDL and do not have a significant effect on VLDL and HDL. Therefore, the maximum effect occurs with a combination of statins and fibrates.
- Nitroglycerin preparations
Nitroglycerin is the main drug that relieves chest pain in the heart area. Nitrates predominantly act on the venous wall, reducing the preload on the myocardium (by dilating the vessels of the venous bed and deposition of blood). The unpleasant effect of nitrates is a decrease in blood pressure and headaches. Nitrates are not recommended for use if blood pressure is below 100/60 mmHg. Art. Modern studies have proven that taking nitrates does not improve the prognosis of patients with coronary heart disease, that is, it does not lead to an increase in survival, and therefore are used as a drug to relieve symptoms of coronary artery disease. Intravenous drip administration of nitroglycerin can effectively combat the symptoms of angina pectoris, mainly against the background of high blood pressure numbers. Every patient with coronary artery disease should know that if taking nitroglycerin at home does not relieve chest pain, then it is necessary to call an ambulance, as a heart attack may have developed.
Types of cardiac ischemia
- Angina (stable and unstable) is chest pain caused by a lack of oxygen supply to the myocardium.
- Myocardial infarction (primary, repeated) - partial or complete blockage of the artery through which blood flows to the heart.
- Post-infarction cardiosclerosis is the presence of parts of the heart that died during a heart attack and which were replaced by connective tissue.
- Heart failure is a violation of the pumping function of the heart, as a result of which the body does not receive sufficient oxygen supply.
- Sudden arrhythmic death is the death of a person within an hour after the onset of acute manifestations of the disease.
Prevention
Up to 90% of cardiovascular diseases can be prevented by avoiding established risk factors. Prevention includes adequate exercise, reducing obesity, treating high blood pressure, eating a healthy diet, lowering cholesterol levels and stopping smoking. Medicines and exercise are about equally effective. High levels of physical activity reduce the risk of coronary heart disease by approximately 25%. In diabetes, tight blood sugar control reduces heart risk and other problems such as kidney failure and blindness. The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends "low to moderate alcohol consumption" to reduce the likelihood of developing coronary heart disease, while excessive consumption is very dangerous for the heart.
Causes
IHD occurs as a result of atherosclerosis of large (epicardial) coronary (heart) arteries of varying degrees: from a slight narrowing of the lumen in the vessel to its complete blockage by atheroma (cholesterol, fat) masses or a blood clot that has developed at the site of a “vulnerable” (damaged) atherosclerotic plaque (ASP) . Other causes of IHD are spasm of the coronary arteries and damage to the microvasculature in the myocardium. In most cases, they also develop against the background of existing atherosclerosis.
It is possible to identify the population groups most susceptible to the development of coronary artery disease: people suffering from high blood pressure, those addicted to smoking, those suffering from high cholesterol levels, diabetes mellitus, and chronic kidney diseases. . Male gender and old age are also powerful risk factors for the development of coronary artery disease.
Diagnosis of coronary heart disease
Usually, complaints and symptoms characteristic of coronary heart disease help to suspect the disease.
To confirm myocardial ischemia, instrumental and laboratory diagnostic methods are used. Tests for coronary heart disease may include:
- Leukocytosis and decreased hemoglobin in a general blood test.
- Increased cholesterol and glucose, changes in the lipid profile according to biochemical blood tests.
- An increase in specific enzymes formed during the destruction of cardiomyocytes - creatine phosphokinase (its special fraction - MB) during the first 3-4 hours of a heart attack (lasts 48-72 hours), troponin-I, troponin-T (their level increases 6 hours after a heart attack and remains elevated for 7-14 days), aspartate aminotransferase (AST) (exceeds the normal level 8-12 hours after the onset of pain, normalizes within 3-4 days), lactate dehydrogenase (begins to exceed the normal level 14-48 hours after the onset of symptoms, returns to normal on days 7-14), myoglobin (increases 2 hours after the onset of symptoms and normalizes within 24 hours) in the blood.
- Elevated C-reactive protein and homocysteine levels are a risk for sudden cardiovascular events.
- Increased blood clotting according to the results of a coagulogram may also increase the risk of developing certain forms of coronary artery disease.
Instrumental research methods can be invasive or non-invasive. In the latter case, the following is used to diagnose coronary heart disease:
- electrocardiography;
- ultrasound examination of the heart - Echo-CG;
- Holter ECG monitoring;
- stress ECG tests: treadmill and bicycle ergometry;
- PET/CT of the heart.
Functional load tests are widely used.
They are used, among other things, to detect the early stages of coronary artery disease or a painless form of the pathology, when the disorders cannot be determined at rest. Walking, climbing stairs, exercises on exercise machines (an exercise bike, a treadmill), accompanied by ECG recording of current indicators, are used as stress tests for suspected coronary heart disease. The standard and most accurate method for this is diagnostics using a treadmill (treadmill) and an exercise bike (bicycle ergometry). Positron emission tomography (PET) is used to diagnose viable cardiac muscle cells. Radiopharmaceuticals are used, the accumulation of which in heart cells reveals viable and necrotic areas.
Among the invasive techniques, coronary angiography is used - x-ray examination of blood vessels using a contrast agent.
Symptoms
The main symptom of coronary heart disease is pressing pain behind the chest or in the heart area. It can radiate to the lower jaw, left shoulder, hand, back and neck. During the acute form, a heart attack or pre-infarction condition develops. In chronic ischemic heart disease, pain is felt during physical activity, and pain tolerance decreases over time.
Main features:
- burning, suffocating pain in the heart area;
- heaviness in the chest;
- feeling of uneven heart rate, heart palpitations;
- dyspnea;
- weakness, dizziness, fainting;
- sweating;
- nausea;
- soreness after physical activity;
- duration from 30 seconds to 15 minutes;
- high efficiency of nitroglycerin.
Fatigue sometimes goes away completely after stopping physical activity. If the patient has unstable angina or myocardial infarction, then there may be no complaints about the heart after exercise. On the contrary, they appear during rest and last a long time - up to several hours. Depending on the form of the pathology, a certain discomfort prevails.
If the described signs of coronary heart disease are detected, you must make an appointment with a cardiologist. If acute pain does not go away for more than 10 minutes, you should call an ambulance.
In this case, progressive ischemic heart disease can develop over several years. In some patients, there are no signs or symptoms are vague. To avoid severe complications and not to trigger the disease, it is necessary to undergo a comprehensive examination regularly, especially in adulthood.
To ensure the effectiveness of dietary therapy for patients with coronary artery disease, an energy balanced diet is necessary. Patients with normal body weight or some deficiency are prescribed a diet with a calorie content of 2900 kcal. If you are overweight, the calorie content of your diet should be reduced by limiting animal fats and carbohydrates, mainly refined ones, and bread. It is advisable to prescribe various contrast (fasting) days against the background of treatment with a diet that is appropriate in calorie content. The rhythm of nutrition is essential. Infrequent meals increase hyperlipidemia, impair carbohydrate tolerance and promote weight gain. The distribution of the diet throughout the day should be uniform, the number of meals should be 5 times a day.
Characteristics of the anti-atherosclerotic diet and its application
Indications for use. IHD, atherosclerosis of coronary, cerebral, peripheral vessels, hypertension stage II-III.
Special purpose. Help improve metabolic processes, blood circulation, restore metabolism of the vascular wall and heart muscle, reduce hemocoagulation of the blood, normalize nervous processes that regulate various functions of the body.
General characteristics. A diet limiting table salt and animal fat, replacing a significant amount of the latter with vegetable fat and including foods rich in cell membranes, lipotropic substances, ascorbic acid, vitamins P, group B (especially B6), potassium and magnesium salts. The diet includes seafood (marine invertebrates, seaweed), which have high biological value due to the rich content of organic compounds of iodine, manganese, zinc, as well as methionine and B vitamins.
Two diet options are recommended: the first is for people with excess body weight, the second is for people with normal or low body weight.
Culinary processing. All dishes are prepared without salt; meat and fish - boiled or baked.
Calorie content and chemical composition. The first diet option (table of an approximate one-day menu for people with excess body weight): proteins 90 g, fats 70 g (animal 35%), carbohydrates 300 g. Calorie content 2100-2200 kcal. The second diet option (table of an approximate one-day menu for people with normal or low body weight): proteins 100 g, fats 80 g, carbohydrates 350 g. Calorie content 2600-2900 kcal.
Mineral composition: table salt 3-5 g; calcium 0.5-0.8 g, phosphorus 1-1.6 g, magnesium 1 g. Content of vitamins C - 100 mg, B1 - 4 mg, B2 - 3 mg, PP - 15-30 mg, B6 - 3 mg .
The total weight of the diet is about 2 kg, free liquid is about 1 liter, the food temperature is normal. Number of meals - 6 times a day.
List of recommended products and dishes. Bread and bakery products. Bread without salt, yesterday's baking, coarsely ground rye and wheat, crackers, dry unsweetened cookies, crispbread. Bran bread with phosphatides.
Soups. Vegetarian, fruit, dairy, cereal. Prepared without salt.
Meat and poultry dishes. Lean meats, poultry (excludes internal organs of animals) boiled or baked (in pieces or chopped).
Fish dishes. Low-fat varieties boiled or baked.
Vegetable dishes and side dishes. All kinds, with the exception of vegetables with coarse fiber (radish, radish), spinach, sorrel. Raw vegetables in chopped form.
Fruits, berries, sweet dishes, sweets. Any ripe fruits, berries. Any juices (except grape). Sweets (sugar, jam) are limited to 50 g. Raw fruits with coarse fiber in crushed form.
Dishes and side dishes made from cereals, flour, pasta.
Flour and pasta products in limited quantities.
Various crumbly cereals, puddings, casseroles.
Eggs and dishes made from them. Soft-boiled eggs (2-3 per week), steamed egg white omelet.
Milk, dairy products and dishes made from them. Milk in its natural form and in dishes, kefir, yogurt, acidophilus. Fresh cottage cheese in its natural form and in dishes.
Fats. Vegetable oils for cooking and ready-made dishes (vinaigrettes, salads). Butter for cooking.
Beverages. Rosehip decoction, tea, tea with milk, weak coffee, fruit, berry, vegetable juices, kvass. Carbonated drinks are limited.
Snacks. Low-fat ham, doctor's sausage, unsalted and mild cheeses, vinaigrettes, salads with the addition of seaweed. Lightly salted herring (once a week).
Sauces. Dairy, vegetable broth, fruit and berry sauces.
It is recommended to include belip (a mixture of unleavened cottage cheese and raw crushed cod) in combination with bread, cereals and vegetable products in the anti-atherosclerotic diet. Shown are dishes from seaweed, squid, scallop, mussels, etc. d.
Prohibited: fatty meats, fish, strong meat broths, beef, lamb, pork fat, internal organs of animals, brains, caviar, lard, cream, baked goods, cream cakes, spicy, salty, fatty snacks, cocoa, chocolate, ice cream , alcoholic drinks.
For patients with coronary artery disease who are overweight and on a diet, it is recommended to prescribe fasting days once every 3-7-10 days: milk days (100 g of warmed milk 8 times a day), kefir days (a glass of kefir 5-6 times a day) and curd days (100 g of cottage cheese or cheesecakes, or cottage cheese casserole 4-5 times a day; in this case, add 100 g of kefir or milk to each serving of cottage cheese).