Causes and course of the disease
Contributors to the occurrence of this disease are: often recurrent acute inflammation of the posterior wall of the pharynx (acute pharyngitis), diseases in the paranasal sinuses, chronic tonsillitis, acute tonsillitis (angina), and inflammatory diseases of the nasal cavity that last for a long time.
The development of chronic pharyngitis is also influenced by the following factors:
- Unfavorable ecological and climatic environmental conditions - dry air, elevated air temperature, dust, gas pollution and dustiness, exposure to harmful chemicals;
- Smoking and alcohol abuse;
- Disorders in the endocrine system, causing hormonal imbalance;
- Diseases affecting the gastrointestinal tract;
- Allergy;
- Dental caries;
- Too spicy food, etc.
Causes of the disease
A natural process for humans is nasal breathing.
The nasal passages are designed so that inhaled air enters with a slight delay. During these pauses, it warms up, is filtered and in this form is supplied to the body. When the nose is stuffy and breathing occurs through the mouth, the risk of pharyngitis increases - because the air does not pass through the “filters” and enters through the mouth with bacteria, viruses, dust, etc. The unnatural process causes the pharynx to dry out, it becomes a favorable environment for the development of pathogenic flora . The second common cause of pharyngitis is a runny nose due to ARVI. In this case, the source of inflammation is in the throat, developing gradually. Frequent treatment of the nasal passages with vasoconstrictor drops negatively affects the condition of the pharynx, which also causes the development of the disease.
Other reasons include:
- vitamin deficiency and malnutrition;
- bad habits;
- injuries;
- individual characteristics in the structure of the nasopharynx;
- long-term treatment with antibiotics;
- chemical fumes;
- ingress of allergens.
Often, pharyngitis is caused by previous diseases, for example, diabetes mellitus, dental caries, heart failure, kidney failure, sinusitis, sinusitis and others.
Classification of the disease
Chronic pharyngitis has three forms:
- catarrhal,
- hypertrophic (increase in the size of the mucous membrane of the posterior pharyngeal wall),
- atrophic (reduction in size and drying of the mucous membrane of the posterior pharyngeal wall).
The catarrhal form of chronic pharyngitis is characterized by fairly persistent diffuse venous hyperemia (plethora), pastiness (dough-likeness) of the mucous membrane, which occurs due to expansion and stasis (stagnation) in small-caliber veins.
In the hypertrophic form of chronic pharyngitis, thickening is observed in all layers of the mucous membrane, an increase in the number of layers of the epithelium, while the cylindrical ciliated epithelium is replaced by squamous epithelium. The altered epithelium tends to form growths, cystic expansions, thickenings and bays, which are very reminiscent of the lacunae of the palatine tonsils. There is an expansion of small vessels and capillaries. The submucosal layer of the posterior pharyngeal wall thickens and becomes saturated with cellular elements. In connection with the above changes, the mucous membrane becomes denser and thicker, lymphatic and blood vessels dilate, and lymphocytes accumulate in the perivascular space (cracks that exist in the outer membranes of the vessels of the spinal cord and brain).
Lymphatic formations, which look like very small granules scattered throughout the mucous membrane, expand and thicken. The mucous membrane is hyperemic, and hypersecretion is observed (increased secretion production). The hypertrophic process is usually localized on the posterior or lateral wall of the pharynx.
Atrophic chronic pharyngitis is characterized by dryness of the pharyngeal mucosa and its thinning. The cylindrical ciliated epithelium transforms into flat epithelium, which has several layers. At the same time, keratinization is observed in its surface layer. The number of glands decreases, and their canals become overgrown (obliteration process). The mucous membrane looks as if it was covered with varnish.
Quite often, chronic pharyngitis has a mixed form, when, against the background of atrophic changes in the mucous membrane, there are areas of its hypertrophy, which have a dull grayish color with infiltrates that have the form of granules and a rich red color. With a sufficiently pronounced inflammatory reaction, inhibition of factors that are responsible for the state of local immunity is noted.
Manifestations of pharyngitis
It all starts with discomfort in the throat, when a sore throat appears and it becomes difficult to swallow due to pain. The pain is less acute than with sore throat or acute tonsillitis, but is constant. Body temperature rarely rises or reaches subfebrile levels. If pharyngitis occurs as part of an acute respiratory viral infection, the condition is accompanied by symptoms of general intoxication. With chronic pharyngitis, bad breath may appear.
Manifestations in children and adults also include ear congestion because the lining of the eustachian tube swells. Almost always, inflammation is accompanied by enlargement of the lymph nodes - submandibular and occipital, which are easy to feel under the skin. A dry cough may be bothersome, which is caused by irritation of the larynx, and not inflammation of the bronchial tree.
Symptoms of general intoxication are mild and include headache, some weakness, and weakness.
Symptoms of chronic pharyngitis
If chronic pharyngitis has a catarrhal or hypertrophic form, then patients complain of tickling, soreness and soreness in the throat. They feel awkward when swallowing and feel as if there is some kind of foreign body in their throat. The listed symptoms are more pronounced in the hypertrophic form, in which patients are bothered by mucopurulent discharge, which quite often flows down the back wall of the pharynx.
Make an appointment right now!
Call us by phone or use the feedback form
Sign up
When an atrophic form of pharyngitis occurs, patients complain of dryness, painful sensations when swallowing, and the inability to eat salty or spicy foods. Sleep disturbance may occur due to severe dryness in the throat, and in some cases, pain when breathing through the throat.
Friends! Timely and correct treatment will ensure you a speedy recovery!
Patients' complaints regarding the existing morphological picture in the mucous membrane are very variable, that is, they have many options. In some patients, complaints are more pronounced even with minor pathological changes than in patients with more severe inflammation.
Symptoms and signs of pharyngitis
More often, pharyngitis in adults occurs as an independent disease. The clinical picture always depends on the nature of the pathology. Signs of the disease appear after toxic exposure to irritating gases, dust, general overheating or hypothermia of the body. Patients complain about:
- sore throat, sore throat;
- general weakness, increased fatigue;
- paroxysmal occurrence of a dry, painful cough;
- increase in body temperature to 38°.
If inflammation of the pharynx occurs against the background of a primary cold or a specific infectious disease, the symptoms are complemented by manifestations of this pathology.
Diagnosis of the disease
Making a diagnosis is usually not difficult. The main diagnostic method is pharyngoscopy - direct examination of the pharynx. To identify the causative agent of the disease, the patient is sent by an ENT doctor to conduct a series of laboratory tests: a general, biochemical blood test, and a throat smear.
To identify the cause of chronic pharyngitis, additional tests may be needed to locate the site of primary infection. The patient may undergo:
- X-ray or CT scan of the paranasal sinuses;
- endoscopy of the nasopharynx;
- gastroscopy.
Our services in otorhinolaryngology
The administration of CELT JSC regularly updates the price list posted on the clinic’s website. However, in order to avoid possible misunderstandings, we ask you to clarify the cost of services by phone: +7
| Service name | Price in rubles |
| Appointment with a surgical doctor (primary, for complex programs) | 3 000 |
| Taking ENT smears | 600 |
| Rinsing tonsil lacunae (1 side) | 1 200 |
All services
Make an appointment through the application or by calling +7 +7 We work every day:
- Monday—Friday: 8.00—20.00
- Saturday: 8.00–18.00
- Sunday is a day off
The nearest metro and MCC stations to the clinic:
- Highway of Enthusiasts or Perovo
- Partisan
- Enthusiast Highway
Driving directions
Treatment of chronic pharyngitis
The goal of treatment on an outpatient basis is to relieve subjective discomfort in the pharynx and normalize the pharyngoscopy picture. It is necessary to carry out sanitation of foci of infection that have arisen in the upper respiratory tract. For all forms of chronic pharyngitis, a prerequisite is quitting smoking and compliance at work and at home with all measures to protect the respiratory tract from harmful factors.
Inhalation gives a good effect. In this case, aerosols from decoctions of chamomile, eucalyptus, sage, mineral alkaline water are used in combination with oil mixtures from sea buckthorn, rose hips, etc.
When treating the hypertrophic form of chronic pharyngitis, cauterization of granules and lateral ridges of the pharynx is used. It can be medicinal, using medicinal solutions (silver nitrate or triacetic acid) or physical, using physical factors (radio wave coagulation, ultrasonic coagulation, laser exposure, cryotherapy, cold and argon plasma, etc.).
In the treatment of chronic atrophic pharyngitis, the mucous membrane is lubricated with iodine-glycerin, and gargling with water-glycerin and alkaline solutions is prescribed.
Chronic pharyngitis often occurs as a consequence of a disease of the gastrointestinal tract. In this case, it is necessary to consult a gastroenterologist and, under his supervision, treat dysbiosis and examine the flora in the gastrointestinal tract.
If the cause of the development of chronic pharyngitis is diseases or disorders of the hormonal, endocrine and cardiovascular systems, it is necessary to undergo examination by a specialized specialist and continue treatment with his participation.
Physiotherapy is often prescribed to treat chronic pharyngitis. You can use electrophoresis in the submandibular areas using a 0.5% solution of nicotinic acid, exposure to a low-energy therapeutic laser or alternating magnetic field, ultrasonic medicinal irrigation of the posterior pharyngeal wall, ultraviolet irradiation and vibroacoustic therapy sessions.
Provoking factors for the development of pharyngitis
In addition to the causes of the disease (which are infectious agents), the development of pharyngitis is significantly influenced by some environmental factors and bad habits:
- polluted atmospheric air;
- exposure to extreme conditions – hypothermia;
- aggressive chemical particles in the inhaled air;
- habit of eating very hot or very cold food, drinking ice-cold drinks;
- smoking (tobacco, hookah);
- background allergy and its seasonal exacerbation;
- excessively dry air.
Poor nutrition weakens all types of immunity, when the body “overloads” calories and does not receive the substances that are needed for complete cell repair: animal protein, vitamins and microelements.
A risk factor is pregnancy, when the mother's body wastes many resources, and hormonal changes change the reactivity of tissues. Treatment of pregnant women is a difficult task when the leading role is given to local drugs that cannot be absorbed into the blood and harm the fetus.
The situation is worsened by chronic diseases of the internal organs, when the metabolism is perverted and the body cannot quickly and effectively respond to the invasion of infection. Dental problems (especially teeth that have been in an untreated condition for a long time) often provoke inflammation in the oral cavity and pharynx.
Complication
Possible complications of chronic pharyngitis are:
- Peritonsillar abscess is a purulent inflammation that develops due to bacterial pharyngitis caused by streptococcal infection.
- A retropharyngeal abscess is a purulent inflammation of the tissue located in the retropharyngeal space.
- Laryngitis is an inflammatory process affecting the mucous membrane of the larynx.
- Chronic bronchitis develops when the infection descends lower into the bronchi and causes inflammation in them.
- Systemic inflammatory diseases (glomerulonephritis, myocarditis, rheumatism) - chronic inflammation of the pharynx can cause complications on the kidneys, heart and joints.
- Atrophic processes of the pharyngeal mucosa. The most dangerous consequence of this condition is the development of oncological processes in the pharynx.
Why does pharyngitis occur?
An inflammatory reaction on the pharyngeal mucosa can be caused by:
- exposure to too cold or hot air;
- contact with aggressive chemicals;
- too dusty and polluted atmosphere;
- smoking as a special case of inhalation of toxins;
- traumatic damage to the mucous membrane as a result of surgical interventions or removal of foreign objects from the pharynx.
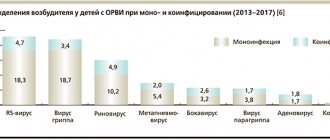
Very often the cause is infection. Inflammation can be caused by both bacteria (mainly streptococci and staphylococci), viruses and even fungi (for example, the genus Candida). Infectious agents can immediately affect the mucous membrane of the pharynx or spread to it from the teeth and sinuses. Therefore, to get rid of pharyngitis, it is necessary to first destroy third-party infectious foci.
In addition to direct causes, inflammation can be caused by:
- decreased immunity;
- vitamin deficiency;
- pathologies of the digestive tract and liver;
- cardiovascular, renal and pulmonary failure;
- difficulty breathing through the nose;
- allergic disorders;
- endocrine system disorders.
Prevention of chronic pharyngitis
Prevention of chronic pharyngitis includes significant adjustments to habits and lifestyle - this is the only way you will reduce the risks of developing the disease.
Preventive measures to prevent the development of chronic pharyngitis include:
- timely treatment of acute pharyngitis and other inflammatory ENT diseases;
- reducing cases of contact with irritating harmful substances at work and allergens;
- cessation of smoking and drinking alcoholic beverages;
- treatment of gastrointestinal diseases;
- limiting the consumption of spicy and sour foods;
- strengthening the immune system;
- avoiding crowded places during ARVI epidemics;
- maintaining the required level of humidity and temperature in the room.
Complications of the disease
It is necessary to treat pharyngitis in a timely manner and in compliance with all instructions. A seemingly harmless disease can cause serious consequences for the body.
Depending on the nature of the pathogen, pharyngitis causes different complications. These include:
- Decreased immunity and, as a result, increased sensitivity to viral diseases.
- Inflammation of the lymph nodes and salivary glands.
- Inflammatory processes of the middle ear and auditory tube lead to hearing loss.
- Tracheitis and chronic bronchitis.
If pharyngitis is not treated, there is always a chance that it will become chronic.