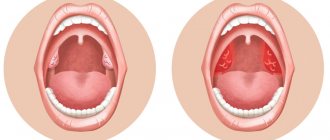
Rheumatoid arthritis
is a chronic inflammatory disease of connective tissue that most often manifests itself in the small joints of the hands and feet.
The danger of the disease lies in its systematic nature and high degree of disability. Being an autoimmune disease, rheumatoid arthritis can affect almost any joint in the body
, and also often leads to
polyarthritis
(affecting 4 or more joints). It can also manifest itself in the organs of the body - the heart, lungs, eyes, kidneys, blood vessels and others. As a result, up to 70% of patients partially or completely lose their ability to work and the ability to self-care, and in especially severe cases left without treatment, even death is possible.
Rheumatoid arthritis affects 1 to 5% of people over 45 years of age, with women getting sick on average 3-5 times more often than men due to their naturally high immunity. Therefore, it is important to be attentive to the slightest manifestations of the disease, diagnose it in time and choose good drugs for rheumatoid arthritis in accordance with the doctor’s prescriptions.
Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic inflammatory disease of connective tissue
Distinctive signs of rheumatoid arthritis
Symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis are usually complex and affect more than just the joints. But most often the onset of the disease is announced by:
- pain and discomfort in fingers or toes;
- stiffness, increasing difficulty in flexing and extending joints, especially after exercise, in the morning, after a long, immobile rest;
- swelling of the affected joints, severe edema;
- redness, heated skin and other symptoms of inflammation over the affected joints;
- decreased endurance, increased fatigue - both in the affected parts of the body and in general;
- increased body temperature (37-38°C);
- weakness, chronic fatigue;
- difficulty breathing, shortness of breath at the slightest physical exertion;
- anemia, pallor of mucous membranes.
These symptoms may include pain in the abdomen and/or chest, inflammation of the uvea (uveitis), and skin rashes.
The first symptoms of the disease usually appear after a shock to the body: physical or psycho-emotional stress, infection, allergies, hormonal changes or exposure to other unfavorable factors.
Side effects of cytostatics
Toxic reactions are caused by damage to normal tissues, which are usually very sensitive to cytostatics:
- blood cells, which is clinically manifested by changes in tests, most often leukopenia and neutropenia, thrombocytopenia and much less often - anemia;
- bone marrow gradually slows down the rate of restoration of hematopoietic sprouts, active tissue is replaced by connective and fatty tissue, and in blood tests the level of all formed elements decreases;
- mucous membranes react with necrosis with rejection, which is manifested by stomatitis, colitis, enteritis, pneumonitis and inflammation of the venous endothelium;
- the gonads respond by disrupting spermatogenesis and stopping menstruation;
- skin appendages - hair falls out, nails become coarser and change their structure.
The drug may have not only general, but also individual toxic manifestations, in which nerve cells or renal tubules, hepatocytes or muscle fibers of the heart selectively die. Sensitivity to drugs is very individual, and the spectrum and severity of adverse reactions also vary.
Release form of drugs for rheumatoid arthritis
Depending on the stage and specifics of the disease, as well as the patient’s convenience, drug therapy can be prescribed to him in the form of oral medications and injections.
Tablets and capsules
Drugs for rheumatoid arthritis in tablets and capsules are easily dosed and do not require manipulation by medical professionals
. Their disadvantage is the relatively low bioavailability of active substances (70-80%). Some groups of medications for the treatment of arthritis (for example, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, glucocorticoids) can affect the mucous membranes and are not used for patients with peptic ulcers, gastritis, duodenitis, dyspepsia and other diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Therefore, they also require the addition of gastroprotective drugs for the duration of the course; they are usually not suitable for permanent use. Medicines in tablets and capsules should usually be taken strictly after meals.
As a rule, drugs in tablets are somewhat cheaper than capsules or injection solutions, and sometimes contain a higher concentration of active ingredients. At the same time, the tablets begin to act more slowly, but provide a longer therapeutic effect. Due to oral administration, the active ingredients of the tablets are partially destroyed in the digestive tract and, alas, are not completely absorbed by the body in the stomach
. Capsules, on the contrary, are a fast-acting release form that has a protective shell against hydrochloric acid, are tasteless and odorless, but spoil much more easily (for example, when carried in a bag). If there are difficulties with finger mobility or during inflammatory diseases of the throat, removing tablets and capsules from the blister can present additional inconvenience.
Injections with drugs to treat rheumatoid arthritis
Injection treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with drugs can be carried out intra-articularly
,
intramuscularly
or
intravenously
.
Intra-articular injection of arthritis medications is considered a last resort
, since it causes additional microtrauma to the joint, it can cause an increased immune response and the risk of progression of secondary arthrosis. In addition, injections of drugs for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis have a fine-crystalline structure, and therefore can injure articular cartilage.
IM and IV infections bypass the stomach and therefore do not destroy the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract
. However, proper injection requires special skills. Also, injections of drugs for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis are not suitable for long-term use due to painful administration.
Sachet for rheumatoid arthritis
Sachet
- this is a single dose of medicinal powder in a bag.
Unlike drugs for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis in injections and tablets, sachets have virtually no disadvantages. They are easy to dose and easy to track the progress of the course. Sachets are taken with ½ glass of warm water, so they have a pleasant fruity drink taste. Taking the sachet does not require the participation of medical professionals and does not create difficulties when swallowing. Due to its excellent solubility, this release form is absorbed by at least 90% and has maximum bioavailability
.
Some drugs for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (for example, chondroprotectors) in sachet form can be used on an ongoing basis. Such medications for the treatment of arthritis include Artracam
, which is included in the list of the best chondroprotectors for rheumatoid arthritis.
Scope of application of cytostatics
Cytostatics are used for all malignant tumors, not excluding diseases of the blood and lymphatic tissue, tumors of the brain and gonads. Cyclophosphamide and antimetabolites in disproportionately lower doses than in oncology are used in rheumatology.
Each cytostatic drug has its own spectrum of antitumor activity, for example, doxorubicin and fluorouracil work great for breast cancer, but are ineffective for small cell lung cancer. Chemotherapy for intestinal carcinomas is not possible without fluorouracil, and doxorubicin is useless for them.
Pharmacological groups of drugs for rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis requires complex treatment aimed at relieving inflammation and pain, suppressing the immune response, healing erosions on the articular surfaces, restoring nutrition to the joint and periarticular tissues. Various pharmaceutical groups of medications for the treatment of arthritis serve this purpose.
Immunosuppressive drugs for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis
Immunosuppressants are used as the main group of drugs for rheumatoid arthritis.
- drugs that selectively suppress the activity of certain immune cells.
Since immunosuppressants have different profiles, for rheumatoid arthritis, only drugs designed to suppress autoimmunity are prescribed
. They help relieve inflammation and pain, stop the destruction of articular surfaces, and in some cases, even give the joints a “delay” to recover.
Immunomodulators are always combined with anti-inflammatory drugs and chondroprotectors.
As a rule, basic therapy is taken once a week.
Basic drugs for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis are used in courses or on an ongoing basis for life. Please note that in case of ARVI and other diseases, immunosuppressants should be stopped until complete recovery.
.
Immunosuppressants are available in tablets, capsules and injection solutions. The best effect is achieved by combining 2-3 basic drugs at the same time.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, they help reduce the activity of inflammatory mediators (prostaglandins, enzymes).
They relieve swelling and inflammation, relieve pain, normalize blood circulation and metabolism of tissues around the joint, and facilitate movement in the diseased joint. NSAIDs irritate the mucous membranes of the stomach and intestines, and therefore are used in short courses of 10-12 days to relieve exacerbations. This group of medications for the treatment of arthritis has only a symptomatic effect and does not help restore the joint or stop the progression of the disease
.
NSAIDs are available in the form of tablets, capsules, injection solutions, gels and suppositories.
Glucocorticoids
Glucocorticosteroids
(hormonal) drugs are used only in cases where the effect of NSAIDs is not enough to relieve pain.
Since such medications have serious contraindications and complications, rheumatologists recommend using them in short courses no more than 1-3 times a year
. In severe cases, it is possible to use prednisolone for up to 6-12 months. Their more frequent and prolonged use is justified only in case of a sharply unfavorable course of the disease, its rapid progression, or severe complications from basic therapy.
Glucocorticoids can only be taken as prescribed by a doctor and in strict accordance with the dosage, otherwise the condition of the joints may even worsen.
There are many types of drugs for rheumatoid arthritis
Chondroprotective drugs for rheumatoid arthritis
Chondroprotectors
is a group of drugs for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis that contain glucosamine and/or chondroitin sulfate. They are helping:
- Enrich synovial fluid, the quality of which suffers during the inflammatory process. The composition of synovial fluid, the natural lubrication of the joint, is directly related to its health. If the viscosity is insufficient, the lubricant does not ensure sliding of the articular surfaces and normal shock absorption of the joint. Its depletion leads to the fact that the cartilage tissue does not receive enough nutrients, loses its elasticity, dries out and cracks. At the same time, normal cartilage regeneration is also inhibited, because new cells grow unstable and are quickly destroyed.
- Strengthen cartilage cells, making them more resistant to adverse factors. This helps to grow new cartilage tissue and even completely restore small areas of erosion on the cartilaginous lining of the joint. Thanks to chondroprotectors, the progression of the disease slows down. Maintaining and preserving cartilage helps delay the disability of rheumatoid arthritis for many years!
- Avoid switching to heavier medications or delaying their use.
To achieve a lasting effect, chondroprotectors are taken in long courses of 3-6 months, 1-2 times a year. Since they have virtually no contraindications and cannot cause complications, this group of drugs remains one of the preferred ones in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis.
Chondroprotectors are produced in the form of tablets and capsules, injections, sachets and gels. Artracam is considered one of the best chondroprotectors
.
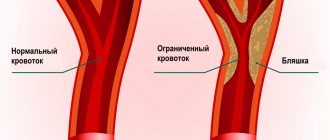
Angioprotectors and microcirculation correctors
Microcirculation correctors
used as auxiliary drugs to prevent complications. On the quality of blood circulation, incl. in small capillaries, the nutrition of the joint depends. In severe cases, disruptions in the circulatory system and subchondral sclerosis of the articular surfaces can lead to death (necrosis) of the bone heads that form the joint.
Swelling and inflammation can cause compression of the articular walls
;
Vasculitis
(inflammation of blood vessels) is also common in rheumatoid arthritis
Antispasmodics and muscle relaxants
The inflammatory process in the joint also affects the soft periarticular tissues. Muscles and ligaments are no exception. Constant muscle tension accelerates muscle atrophy in rheumatoid arthritis due to their destruction and increases the feeling of fatigue. Spasms can also cause serious discomfort: intensify or cause pain (cramping pain), interfere with normal sleep, the patient’s movement and performance of household chores, and cause disturbances in fine motor skills.
New generation drugs for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis
New generation drugs in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis mean genetically engineered biological drugs that control the course of the disease. T.N. targeted therapy with synthetic drugs
lasts about 3-6 months from the moment RA symptoms are identified.
The use of new generation products is due to the fact that in rheumatoid arthritis, the cartilage is “self-damaged” by enzymes from the affected cells. Increased production of cytokines triggers a cascade reaction in cells, provoking chronic inflammation and, as a consequence, disability of the patient.
Modern biologics help slow down this process by blocking cytokines (messenger molecules that are responsible for the body's immune responses) or producing antibodies to them, inactivating T-lymphocytes, or otherwise preventing the transmission of signals to attacking immune cells.
In some cases, according to rheumatologists, it is possible to get by with new generation drugs for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis.
What are cytostatics?
Chemotherapy is exclusively the use of cytostatics. In addition to chemotherapy, antitumor treatment includes endocrine effects using hormonal drugs, targeted therapy that “turns off” a certain biochemical reaction, and the use of biological - immuno-oncological agents, which themselves do not act on the malignant cell, but activate immune defenders.
Cytostatics damage all rapidly dividing cells - any malignant and normal cells in the blood, bone marrow and gonads. Over time, cell clones develop resistance to cytostatics, reducing the effectiveness of chemotherapy.
Drugs for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis at different stages
The specifics of treatment depend on how far the changes in the cartilage and bone tissue of the joint have gone
. Since many medications for rheumatoid arthritis, when taken for a long time, have a negative effect on the condition of internal organs, doctors are trying to move from safe drugs to potent ones.
Stage 1 of the disease
After stopping the first inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis, taking chondroprotectors
and
immunosuppressants
. This supportive therapy gives the body the opportunity to recover on its own.
NSAIDs
are used only in the acute phase of the disease.
Also, in the early stages of RA, long-term remission is possible, which is maintained not by the use of heavy drugs, but by following a diet. It is important to dress according to the weather, alternate periods of exercise and periods of rest, be less nervous, take vitamin courses 2 times a year
.
At stage 1 of the disease, glucocorticoids are never used
- they are indicated only in case of a destructive process with the formation of bone erosions. Antispasmodics, painkillers and microcirculation correctors, as a rule, are not required.
In the early stages of arthritis, it is important to maintain a moderate lifestyle and daily routine.
Stage 2 of the disease
At the second stage of the disease, rheumatologists usually add anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), angioprotectors, decongestants to chondroprotectors and immunosuppressants, and, in the presence of spasms, muscle relaxants. In addition to external agents (gels, ointments, creams, balms), systemic therapy drugs are added. If the course is unfavorable, new generation drugs for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis are usually prescribed.
Stage 3 of the disease
Stage 3 rheumatoid arthritis is characterized by severe destruction of the joints, therefore basic therapy, drugs for the treatment of new generation rheumatoid arthritis, NSAIDs and glucocorticoids come first, and chondroprotectors are taken exclusively as an auxiliary supportive agent. Patients may also be prescribed additional medications to mitigate the side effects of the main therapy.
How do cytostatics work?
Ultimately, all methods of cytostatic effects lead to the same thing - cell apoptosis. Apoptosis is a natural stage of cellular life, in contrast to death due to inflammation, infection, and necrosis. This is programmed death, each cell comes to it in its own time, and cytostatics lead to it outside the program. Every day in the human body, 100 billion cells undergo apoptosis; we can assume that every two years the cellular composition of the body is completely renewed. In a simplified form, apoptosis is represented as follows:
- formation of a biochemical signal to trigger death, a kind of cellular awareness of the need to die;
- production of intracellular enzymes that burn cellular “insides”;
- absorption of the dead body by neighboring cells and macrophages;
- decomposition by intracellular lysosomes of what is eaten into microelements for further use.
The process proceeds according to the principle “there was and there is no”, which is why during chemotherapy there is no inflammation or scars at the site of the tumor, but almost normal tissue, as if there was no disease.
Mechanism of action of cytostatics
Two driving mechanisms:
- changes in the structure of DNA, including abnormal twisting that prevents the strands from diverging during division, as well as repair disorders - restoring the continuity of the strand when damaged;
- cell division disorder is a disorder in the formation of the cell spindle, which separates chromosomes into daughter cells, typical of herbal preparations.
Not only each group, but also each cytostatic has its own mechanism of antitumor action, or rather, several mechanisms of damage, most of which are unknown.
What cytostatics are most often prescribed?
Only those that actively treat this malignant nosology and are optimal in a specific clinical case are prescribed. The widest range of activity is found in the antibiotic doxorubicin, alkylating platinum derivatives and cyclophosphamide, plant taxanes and the antimetabolites fluorouracil and methotrexate.
Clinical guidelines suggest using the most effective combinations of drugs with an optimal balance of effectiveness and toxicity. In our clinic, we select cytostatic therapy individually, depending on the sensitivity of the cancer tumor. We do not guarantee the absence of toxicity, but we can minimize its manifestations and accelerate the restoration of normal tissues.
Book a consultation 24 hours a day
+7+7+78